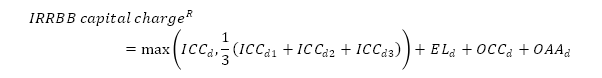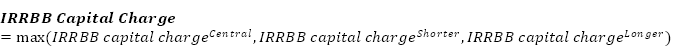Financial Sector (Collection of Data) (reporting standard) determination No. 16 of 2025
Reporting Standard ARS 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book
Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001
I, Andrew Robertson, delegate of APRA, under paragraph 13(1)(a) of the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001 (the Act) and subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901:
- revoke Financial Sector (Collection of Data) (reporting standard) determination No. 30 of 2019, including Reporting Standard ARS 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book (IRRBB) made under that Determination; and
- determine Reporting Standard ARS 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book, in the form set out in the Schedule, which applies to the financial sector entities to the extent provided in paragraphs 3 and 4 of that reporting standard.
Under section 15 of the Act, I declare that Reporting Standard ARS 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book shall begin to apply to those financial sector entities on the day after this instrument is registered on the Federal Register of Legislation.
This instrument commences at the start of the day after it is registered on the Federal Register of Legislation.
Dated: 3 June 2025
Andrew Robertson
General Manager - Chief Data Officer
Technology and Data Division
Interpretation
In this Determination:
APRA means the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority.
Federal Register of Legislation means the register established under section 15A of the Legislation Act 2003.
financial sector entity means financial sector entities of a kind referred to in paragraphs 5(2)(a) to (d) of the Act.
Schedule
Reporting Standard ARS 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book comprises the document commencing on the following page.

Reporting Standard ARS 117.1
Authority
- This Reporting Standard is made under section 13 of the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001.
Purpose
- Information collected in Reporting Form ARF 117.1 Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book (ARF 117.1) is used by APRA for the purpose of prudential supervision including assessing compliance with capital adequacy standards. It may also be used by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS).
Application
- This Reporting Standard applies to an authorised deposit-taking institution (ADI) that has APRA’s approval or is seeking APRA’s approval to use an internal model approach for the calculation of the ADI’s interest rate risk in the banking book regulatory capital.
- This Reporting Standard may also apply to the immediate parent non-operating holding company (NOHC) of an ADI (refer to paragraph 7).
- This Reporting Standard applies for reporting periods ending on or after 1 October 2025.
Information required
- An ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies must provide APRA with the information required by this Reporting Standard designated for an ADI at Level 1 for each reporting period.
- If an ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies is part of a Level 2 group, the ADI must also provide APRA with the information required by this Reporting Standard designated for an ADI at Level 2 for each reporting period, unless the ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC. If the ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC, the ADI’s immediate parent NOHC must provide APRA with the information required by that form for each reporting period. In doing so, the immediate parent NOHC must comply with this Reporting Standard (other than paragraphs 6 and 13) as if it were the relevant ADI.
Method of submission
- The information required by this Reporting Standard must be given to APRA:
- in electronic format using an electronic method available on APRA’s website; or
- by a method notified by APRA prior to submission.
Reporting periods and due dates
- Subject to paragraph 10, an ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies must provide the information required by this Reporting Standard in respect of each quarter based on the financial year (within the meaning of the Corporations Act 2001) of the ADI.
- APRA may, by notice in writing, vary the reporting periods, or specified reporting periods, for a particular ADI, to require it to provide the information required by this Reporting Standard more frequently, or less frequently, having regard to:
- the particular circumstances of the ADI;
- the extent to which the information is required for the purposes of the prudential supervision of the ADI; and
- the requirements of the RBA or the ABS.
- The information required by this Reporting Standard must be provided to APRA within 35 calendar days after the end of the reporting period to which this information relates.
- APRA may, by notice in writing, extend the due date by which an ADI must provide the information required by this Reporting Standard, in which case the new due date will be the date specified in the notice of extension.
Note: For the avoidance of doubt, if the due date for a particular reporting period falls on a day other than a usual business day, APRA’s expectation is that an ADI will submit the information required no later than the due date.
Quality control
- All information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard (except for the information required under paragraph 7) must be the product of systems, processes and controls that have been reviewed and tested by the external auditor of the ADI as set out in Prudential Standard APS 310 Audit and Related Matters. Relevant standards and guidance statements issued by the Auditing and Assurance Standards Board provide information on the scope and nature of the review and testing required from external auditors. This review and testing must be done on an annual basis or more frequently if required by the external auditor to enable the external auditor to form an opinion on the accuracy and reliability of the information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard.
- All information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard must be subject to processes and controls developed by the ADI for the internal review and authorisation of that information. These systems, processes and controls are to assure the completeness and reliability of the information provided.
Authorisation
- When an officer of an ADI submits information under this Reporting Standard using a method notified by APRA, it will be necessary for the officer to digitally sign the relevant information using a digital certificate acceptable to APRA.
Variations
- APRA may, by written notice to the ADI, vary the reporting requirements of this Reporting Standard in relation to that ADI.
- APRA may determine, in writing, that an individual ADI of one class of ADI is to be treated, for the purposes of this Reporting Standard, as though it was an ADI of another class of ADI.
Transition
- An ADI must report under the old reporting standard in respect of a transitional reporting period. For these purposes:
old reporting standard means the reporting standard revoked by the determination that makes this Reporting Standard (being the reporting standard that this Reporting Standard replaces); and
transitional reporting period means a reporting period under the old reporting standard:
- that ended before 1 October 2025; and
- in relation to which the ADI was required, under the old reporting standard, to report by a date on or after the date of revocation of the old reporting standard.
Note: For the avoidance of doubt, if an ADI was required to report under an old reporting standard, and the reporting documents were due before the date of revocation of the old reporting standard, the ADI is still required to provide any overdue reporting documents in accordance with the old reporting standard.
Interpretation
- In this Reporting Standard:
AASB has the meaning in section 9 of the Corporations Act 2001.
ADI means an authorised deposit-taking institution within the meaning of the Banking Act 1959.
APRA means the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority established under the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Act 1998.
APS 001 means Prudential Standard APS 001 Definitions.
authorised NOHC has the meaning given in the Banking Act 1959.
business days means ordinary business days, exclusive of Saturdays, Sundays and public holidays.
due date means the relevant due date under paragraph 11 or, if applicable, the date on a notice of extension given under paragraph 12.
immediate parent NOHC means an authorised NOHC, or a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC, that is an immediate parent NOHC.
Level 1 has the meaning given in APS 001.
Level 2 has the meaning given in APS 001.
reporting period means a period mentioned in paragraph 9 or, if applicable, paragraph 10.
subsidiary has the meaning given in the Corporations Act 2001.
- Unless the contrary intention appears, a reference to an Act, Regulation, Prudential Standard, Reporting Standard, Australian Accounting Standard or Auditing Standard is a reference to the instrument as in force or existing from time to time.
Reporting Form ARF 117.1
Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book
Instruction Guide
This instruction guide is designed to assist in the completion of the Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book form (ARF 117.1). This form captures the calculation of the IRRBB Capital Charge and contains a breakdown of IRRBB capital across banking book items. In completing this form, authorised deposit-taking institutions (ADIs) should refer to Prudential Standard APS 117 Capital Adequacy: Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book (APS 117).
Terms highlighted in bold italics are defined in paragraph 19 of this Reporting Standard, Prudential Standard APS 117 or the Definitions in this Instruction Guide.
General directions and notes
Reporting basis
This form is to be completed at Level 1 and Level 2 by each ADI that has APRA’s approval or is seeking APRA’s approval to use an internal model approach for the calculation of the ADI’s IRRBB capital charge, in accordance with APS 117.
If an ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC, the report at Level 2 is to be provided by the ADI’s immediate parent NOHC.
Data is to be reported as at the end of the reporting period.
Securitisation deconsolidation principle
Except as otherwise specified in these instructions, the following applies:
- Where an ADI (or a member of its Level 2 consolidated group) participates in a securitisation that meets APRA’s operational requirements for regulatory capital relief under Prudential Standard APS 120 Securitisation (APS 120):
- special purpose vehicles (SPVs) holding securitised assets may be treated as non-consolidated independent third parties for regulatory reporting purposes, irrespective of whether the SPVs (or their assets) are consolidated for accounting purposes;
- the assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses of the relevant SPVs may be excluded from the ADI’s reported amounts in APRA’s regulatory reporting returns; and
- the underlying exposures (i.e. the pool) under such a securitisation may be excluded from the calculation of regulatory capital (refer to APS 120). However, the ADI must still hold regulatory capital for any securitisation exposure that it retains or acquires and such exposures are to be reported in Reporting Form ARF 120.1 Securitisation – Regulatory Capital. The risk-weighted assets (RWA) relating to such securitisation exposures must also be reported in ARS 110.0.
- Where an ADI (or a member of its Level 2 consolidated group) participates in a securitisation that does not meet APRA’s operational requirements for regulatory capital relief under APS 120, or the ADI undertakes a funding-only securitisation or synthetic securitisation, such assets are to be reported as on-balance sheet in APRA’s regulatory reporting returns.
Units of measurement
Unless otherwise specified, report all values in whole Australian dollars (AUD), with no decimal place.
Amounts denominated in foreign currency are to be converted to AUD in accordance with AASB 121 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates (AASB 121).
Scope
An ADI is to report in ARF 117.1 the values calculated with reference to all items in the augmented banking book, as defined in APS 117.
Definitions
Augmented banking book | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Australian State Government or Territory Central Borrowing Authorities Securities | Has the meaning given in Reporting Standard ARS 117.0 Repricing Analysis. |
Australian Government Securities (AGS) | Has the meaning given in Reporting Standard ARS 117.0 Repricing Analysis. |
Book value | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Core Deposits | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Derivatives that are hedging AGS and semis | These are derivatives that are hedging AGS and Australian State Government or Territory Central Borrowing Authorities Securities. |
Earnings Offset | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Economic value (EV) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Embedded loss (ELd) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
IRRBB capital charge | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Optionality capital charge (OCCd) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Other Amount (OAAd) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Other market-related derivatives | Market-related derivatives that are not Derivatives that are hedging AGS and semis |
Other market-related items | Market-related items that are not AGS, Australian State Government or Territory Central Borrowing Authorities Securities, Derivatives that are hedging AGS and semis or Other market-related derivatives |
Other principal and interest (P&I) items | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Net interest income (NII) | Is the difference between interest revenues and interest expenses. Interest revenues are payments received from interest-bearing assets and interest expenses are the cost of servicing interest payments. |
Non-market-related Derivatives | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Non-maturity deposits | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Non-principal and interest (P&I) items | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Prepayment-exposed loans | A loan that has prepayments made in advance of an official due date. Prepayment is the early repayment of a loan by a borrower (in part or in full). |
Post-shock EV | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Pre-shock EV | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Prospective IRRBB capital charge | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Prospective IRRBB capital charge – month end 1 (ICCd1) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Prospective IRRBB capital charge – month end 1 (ICCd2) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Prospective IRRBB capital charge – month end 1 (ICCd3) | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Rate locks | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer | Has the meaning given in APS 117. |
Specific instructions
Interest rate shock scenarios
The six prescribed interest rate shocks scenarios are defined in Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) (2016) Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book. These include:
- Parallel shock up;
- Parallel shock down;
- Steepener shock (short rates down and long rates up);
- Flattener shock (short rates up and long rates down);
- Short rate shock up; and
- Short rate shock down.
ADIs are to provide the ΔEVE and value of NII

| ARS | AUD | BRL | CAD | CHF | CNY | EUR | GBP | HKD |
Parallel | 400 | 300 | 400 | 200 | 100 | 250 | 200 | 250 | 200 |
Short | 500 | 450 | 500 | 300 | 150 | 300 | 250 | 300 | 250 |
Long | 300 | 200 | 300 | 150 | 100 | 150 | 100 | 150 | 100 |
| IDR | INR | JPY | KRW | MXN | RUB | SAR | SEK | SGD |
Parallel | 400 | 400 | 100 | 300 | 400 | 400 | 200 | 200 | 150 |
Short | 500 | 500 | 100 | 400 | 500 | 500 | 300 | 300 | 200 |
Long | 350 | 300 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 150 | 150 | 100 |
| TRY | USD | ZAR |
Parallel | 400 | 200 | 400 |
Short | 500 | 300 | 500 |
Long | 300 | 150 | 300 |
For New-Zealand dollar exposures (NZD), ADIs are to use the same calibration as AUD.
For each currency, the following parameterisations of the six interest rate shock scenarios are to be applied:
- Parallel shock for currency
 : a constant parallel shock up or down across all time buckets.
: a constant parallel shock up or down across all time buckets.
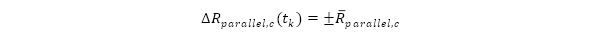
- Short rate shock for currency
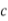 : shock up or down that is greatest at the shortest tenor midpoint. That shock, through the shaping scalar
: shock up or down that is greatest at the shortest tenor midpoint. That shock, through the shaping scalar 
, where 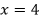 , diminishes towards zero at the tenor of the longest point in the term structure.
, diminishes towards zero at the tenor of the longest point in the term structure.
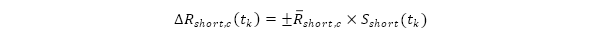
- Long rate shock for currency
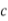 : the shock is greatest at the longest tenor midpoint and has shaping scalar
: the shock is greatest at the longest tenor midpoint and has shaping scalar 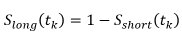
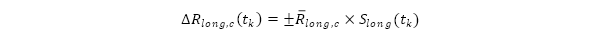
- Rotational shocks for currency
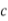 : rotational shocks to the term structure (i.e. steepener and flattener shocks) of the interest rates whereby both the long and short rates are shocked and the shift in interest rates at each tenor midpoint is obtained by:
: rotational shocks to the term structure (i.e. steepener and flattener shocks) of the interest rates whereby both the long and short rates are shocked and the shift in interest rates at each tenor midpoint is obtained by:

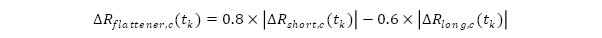
Reporting tables
Table 1.1: Immaterial currencies
Table 1.1 captures the material currency code(s), reported in Table 1.2, into which any immaterial currencies have been combined.
Table 1.2: Interest rate shock scenarios on economic value of the banking book and net interest income
Table 1.2 captures the impact of six interest rate shock scenarios on an ADI’s economic value of equity (EVE) and net interest income (NII) across reported currencies. ADIs are required to report values separately when ‘including’ and ‘excluding’ the earnings offset.
Data fields required to be reported are listed below. They are shown sequentially in the column order that they will appear in the reported data set. Each row of the table must be a unique combination of Currency, Interest Rate shock scenario, and Earnings Offset (columns 1-3). Constraints on the data that can be reported for each field have also been provided.
| Name | Valid values | Description |
1 | Currency | Applicable three-letter currency code | Report the currency to which the exposure relates. Currency codes are the three-letter currency code as assigned by the ISO 4217 Maintenance Agency to a currency defined under the International Organization for Standardization’s International Standard ISO 4217:2015. Where an ADI has exposures in currencies that do not meet the definition of a material currency (i.e. immaterial currencies), these exposures may be combined into one or more groups of currencies, based on the interest rate characteristics of the group of currencies. ADI’s are to indicate into which material currency the group of immaterial currencies have been combined in Table 1.1. A material currency is a currency for which the total book value of an ADI’s banking book items in that currency is more than five per cent of the total book value of all of its banking book items. In determining whether a currency is material, the effect of currency hedges that reduce foreign currency exposure may be taken into account, provided these hedges are in a hedge effective relationship. |
2 | Interest rate shock scenario | - Baseline
- Parallel shock up
- Parallel shock down
- Steepener shock
- Flattener shock
- Short rate shock up
- Short rate shock down
| Report the six interest rate shock scenarios as specified by BCBS IRRBB standards in 2016. The Baseline is the base case scenario, which does not have any interest rate shock applied. |
3 | Earnings Offset | | Report whether the values are ‘including’ or ‘excluding’ the earnings offset. |
4 | Impact on EVE | Whole dollars | Report the impact of the six interest rate shock scenarios on EVE. ADIs are not required to report the Baseline EVE. The impact of interest rate shock scenarios on EVE is calculated by comparing EVE for a baseline interest rate scenario with the outcome for a scenario where interest rates are shocked. |
5 | Value of NII | Whole dollars | Report the value of NII across each of the interest rate shock scenarios. |
Table 2 captures an ADI’s IRRBB capital charge calculation. ADIs are to report a breakdown of the IRRBB capital charge across IRRBB components and repricing assumptions, as detailed within APS 117.
When determining the IRRBB capital charge, an ADI must calculate its prospective IRRBB capital charge at the calculation date and the latest three months.
For example, when calculating the IRRBB capital charge for the June quarter, the calculation date 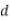 is June-end, and the latest three-month ends would correspond to April-end (d1), May-end (d2) and June-end (d3). For this purpose, the prospective IRRBB capital charge at the calculation date, ICCd, corresponds to and must be equal to the prospective IRRBB capital charge at the latest month-end, ICCd3, where d and d3 correspond to the same date.
is June-end, and the latest three-month ends would correspond to April-end (d1), May-end (d2) and June-end (d3). For this purpose, the prospective IRRBB capital charge at the calculation date, ICCd, corresponds to and must be equal to the prospective IRRBB capital charge at the latest month-end, ICCd3, where d and d3 correspond to the same date.
Data fields required to be reported are listed below.
Report values as whole dollars.
Column 1 | Shorter | The Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer are defined as per APS 117. |
Column 2 | Central |
Column 3 | Longer |
Item 1 | Report the Prospective IRRBB capital charge - month end 1 (ICCd1) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. |
Item 2 | Report the Prospective IRRBB capital charge - month end 2 (ICCd2) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. |
Item 3 | Report the Prospective IRRBB capital charge – month end 3 (ICCd3) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. |
Item 4 | Report the Embedded Loss (ELd) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. Report the embedded loss as a positive amount and embedded gain as a negative amount. Report the same Embedded Loss (ELd) value for Columns 1, 2 and 3. |
Item 5 | Report the Optionality capital charge (OCCd) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. |
Item 6 | Report the Other Amount (OAAd) for each of the Repricing Assumptions – Central, Shorter and Longer. |
Item 7 | The IRRBB capital charge across each Repricing Assumption is a derived field in this table and is calculated using values entered in Items 1 – 6 of this table. For a given repricing assumption (R), the IRRBB capital charge is the maximum of zero and: 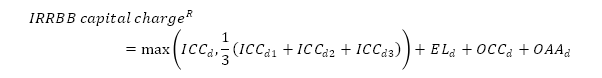
Where 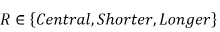 The central, shorter and longer repricing assumptions are defined as per APS 117. |
Item 8 | The Total IRRBB Capital charge is a derived item in this table and is calculated as: 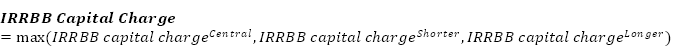
|
Table 3: Augmented Banking Book - Pre-Shock EV and Embedded loss
Table 3 captures the pre-shock economic value, book value and embedded loss of an ADI’s banking book items in the augmented banking book.
Column 1 | Pre-Shock EV | Report the pre-shock economic value of each listed Banking Book item. Pre-Shock EV is to be calculated as per the methodology in APS 117, consistent with a one-year holding period. |
Column 2 | Book Value | Report the Book Value of each listed Banking Book item. |
Column 3 | Embedded Loss | This is a derived field in this table and will be automatically calculated as: 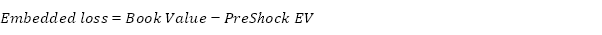
|
Banking Book Items
Items 1-13 | Report the values in columns 1 and 2 for the banking book items as below: - Earnings Offset
- Australian Government Securities
- Australian State Government or Territory Central Borrowing Authorities Securities
- Derivatives that are hedging AGS and semis
- Other market-related Derivatives
- Other market-related items
- Non-principal and interest (P&I) items
- Non-maturity deposits
- Non-market-related Derivatives
- Other P&I items
- Rate locks
- Prepayment-exposed loans
- Core Deposits
|
Table 4: Augmented Banking Book shock scenarios - daily observation dates
Table 4 captures daily post-shock economic values across banking book items within the eight-year observation period defined in APS 117.
For each of the observations within the eight-year observation period, ADIs are required to report the observation period start and end dates and post-shock economic values across a breakdown of items within the augmented banking book and across different repricing assumptions.
Data fields required to be reported are listed below. They are shown sequentially in the column order that they will appear in the reported data set. Each row of the table must be a unique combination of Start Date, End Date, Repricing Assumptions, and Banking Book item (columns 1-4). Constraints on the data that can be reported for each field have also been provided.
| Name | Valid values | Description |
1 | Start date | Date values (dd/mm/yyyy) | Report the first observation date in the respective ten-business day holding period shock within the eight-year observation period, as defined in APS 117. Observation dates are to be entered using DD/MM/YYYY format. |
2 | End date | Date values (dd/mm/yyyy) | Report the last observation date in the respective ten-business day holding period shock within the eight-year observation period, as defined in APS 117. Observation dates are to be entered using DD/MM/YYYY format. |
3 | Repricing Assumptions | | Report the repricing assumption used. The central, shorter and longer repricing assumptions are defined as per APS 117. |
4 | Banking Book item | - Earnings Offset
- Australian Government Securities
- Australian State Government or Territory Central Borrowing Authorities Securities
- Derivatives that are hedging AGS and semis
- Other market-related Derivatives
- Other market-related items
- Non-principal and interest (P&I) items
- Non-maturity deposits
- Non-market-related Derivatives
- Other P&I items
- Rate locks
- Prepayment-exposed loans
- Core Deposits
| Report the banking book item to which the post-shock economic value relates. |
5 | Post-Shock EV | Whole dollars | Report the post-shock economic value of each listed Banking Book item. The Post-Shock EV is to be calculated as per the methodology in APS 117. The ten-business day shock scenarios are to be scaled up to one-year holding period equivalents, consistent with APS 117. |
Table 5: Breakdown of the IRRBB component – Other Amount (OAAd), Capital Overlays
Table 5 captures a breakdown of the Other Amount (OAAd) IRRBB capital component, which includes a split across an ADI’s APRA-imposed and bank-applied overlays within the reporting period.
Data fields required to be reported are listed below. They are shown sequentially in the column order that they will appear in the reported data set. Constraints on the data that can be reported for each field have also been provided.
| Name | Valid values | Description |
1 | Type | | Report the type of capital overlay. ‘APRA-imposed’ capital overlay means an overlay that APRA has imposed to an ADI’s internal model. This can occur, although is not limited to, when APRA considers the ADI is not appropriately capitalising, measuring, monitoring or controlling its level of IRRBB risk, in addition to gaps in an ADI’s model governance framework. ‘Bank-applied’ capital overlay means an overlay that an ADI has imposed proactively through its own internal monitoring. These overlays are not subject to APRA approval. |
2 | Start date | Date values (dd/mm/yyyy) | Report the start date when the capital overlay was implemented by the ADI, for the purposes of the IRRBB capital calculation. Dates of implementation are to be entered using DD/MM/YYYY format. |
3 | Style | | Report the style of capital overlay. ‘Fixed’ capital overlay means that the capital overlay is a fixed amount that does not change in size quarter-to-quarter. ‘Variable’ capital overlay means that the capital overlay does change in size quarter-to-quarter. |
4 | Name | Free text | Report the name of the capital overlay. Maximum character length string is 100 characters. |
5 | Description | Free text | Report the description of the capital overlay. Maximum character length string is 400 characters. |
6 | Value | Whole dollars | Report the value of the capital overlay. The value of the capital overlay is to be undiversified with the other components within the IRRBB calculation, including the Prospective IRRBB capital charge - month end 1 (ICCd1), Prospective IRRBB capital charge - month end 2 (ICCd2), Prospective IRRBB capital charge - month end 3 (ICCd3), Embedded loss (ELd) and Optionality capital charge (OCCd) components. |
7 | Status | | Report the status of the capital overlay. A ‘New’ status means that the capital overlay was imposed within the reporting period. An ‘Active’ status means that the capital overlay was in effect during the reporting period although did not come into effect within the reporting period. A ‘Revoked’ status means that the capital overlay is no-longer in effect and has been ceased within the IRRBB capital calculation. If a capital overlay has a ‘New’ status within a given reporting period and is in effect in the subsequent reporting period, then the overlay would be reported as ‘Active’ in the subsequent reporting period. |
8 | Date revoked | Date values (dd/mm/yyyy) | Report the date the capital overlay was revoked by the ADI, for the purposes of the IRRBB capital calculation. This date must be within the reporting period. This field is only required to be completed if the status is ‘Revoked’. ADI’s are to leave this field blank for ‘New’ and ‘Active’ overlays. If the capital overlay has been revoked within a given reporting period, the ADI is not required to report the capital overlay in subsequent reporting periods. Dates of revocation are to be entered using DD/MM/YYYY format. |
Table 6: IRRBB model changes
Table 6 captures an ADI’s list of model changes within a given reporting period. This encompasses all model changes that were implemented by the ADI within a given reporting period and is not limited to model changes that required APRA-approval.
Data fields required to be reported are listed below. They are shown sequentially in the column order that they will appear in the reported data set. Constraints on the data that can be reported for each field have also been provided.
| Name | Valid values | Description |
1 | Start date | Date values (dd/mm/yyyy) | Report the start date when the model change was implemented by the ADI and incorporated in the IRRBB capital calculation. Dates of change are to be entered using DD/MM/YYYY format. |
2 | Description | Free text | Report the description of the model change. Maximum character length string is 400 characters. |
3 | Value | Whole dollars | Report the value of the model change capital impact. |
4 | Quantitatively material | | Report whether the model change is quantitatively material, based on the ADI’s assessment of materiality. |
5 | Qualitatively material | | Report whether the model change is qualitatively material, based on the ADI’s assessment of materiality. |
6 | APRA approval | | Report whether the model change was approved by APRA prior to being implemented by the ADI. |