
Reporting Standard ARS 113.3
Internal Ratings-based (IRB) Approach to Credit Risk – Retail
This Reporting Standard is made under section 13 of the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001.
This Reporting Standard outlines the overall requirements for the provision of information to APRA in relation to an authorised deposit-taking institution’s retail exposures under the internal ratings-based approach to credit risk. It should be read in conjunction with:
- the versions of Reporting Form ARF 113.3A IRB Retail – Residential Mortgages, Reporting Form ARF 113.3B IRB Retail – Qualifying Revolving, Reporting Form ARF 113.3C IRB Retail – Other and Reporting Form ARF 113.3D IRB Retail – SME designated for an authorised deposit-taking institution reporting at Level 1 and Level 2, and the associated instructions (all of which are attached and form part of this Reporting Standard); and
- Prudential Standard APS 113 Capital Adequacy: Internal Ratings-based Approach to Credit Risk.
Authority
- This Reporting Standard is made under section 13 of the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001.
Purpose
2. Data collected in Reporting Form ARF 113.3A IRB Retail – Residential Mortgages (ARF 113.3A), Reporting Form ARF 113.3B IRB Retail – Qualifying Revolving (ARF 113.3B), Reporting Form ARF 113.3C, IRB Retail - Other (ARF 113.3C) and Reporting Form ARF 113.3D IRB Retail – SME (ARF 113.3D) is used by APRA for the purpose of prudential supervision, including assessing compliance with Prudential Standard APS 113 Capital Adequacy: Internal Ratings-based Approach to Credit Risk (APS 113). It may also be used by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS).
Application and commencement
3. This Reporting Standard applies to an authorised deposit-taking institution (ADI) that has APRA’s approval or is seeking APRA’s approval to use the internal ratings-based approach to credit risk for capital adequacy purposes.
This Reporting Standard may also apply to the non-operating holding company (NOHC) of an ADI (refer to paragraph 6).
4. This Reporting Standard commences on 1 April 2018.
Information required
5. An ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies must provide APRA with the information required by the versions of ARF 113.3A, ARF 113.3B, ARF 113.3C and ARF 113.3D designated for an ADI at Level 1 for each reporting period.
6. If an ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies is part of a Level 2 group, the ADI must also provide APRA with the information required by the versions of ARF 113.3A, ARF 113.3B, ARF 113.3C and ARF 113.3D designated for an ADI at Level 2 for each reporting period, unless the ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC. If the ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC, the ADI’s immediate parent NOHC must provide APRA with the information required by that form for each reporting period. In doing so, the immediate parent NOHC must comply with this Reporting Standard (other than paragraphs 5 and 12) as if it were the relevant ADI.
Forms and method of submission
7. The information required by this Reporting Standard must be given to APRA in electronic format, using the ‘Direct to APRA’ application or by a method notified by APRA, in writing, prior to submission.
Note: the Direct to APRA application software (also known as D2A) may be obtained from APRA.
Reporting periods and due dates
8. Subject to paragraph 9, an ADI to which this Reporting Standard applies must provide the information required by this Reporting Standard for each quarter based on the financial year (within the meaning of the Corporations Act 2001) of the ADI.
9. APRA may, by notice in writing, change the reporting periods, or specified reporting periods, for a particular ADI, to require it to provide the information required by this Reporting Standard more frequently, or less frequently, having regard to:
(a) the particular circumstances of the ADI;
(b) the extent to which the information is required for the purposes of the prudential supervision of the ADI; and
(c) the requirements of the Reserve Bank of Australia or the Australian Bureau of Statistics.
10. The information required by this Reporting Standard must be provided to APRA within 30 business days after the end of the reporting period to which the information relates.
11. APRA may grant an ADI an extension of a due date in writing, in which case the new due date for the provision of the information will be the date on the notice of extension.
Quality control
12. All information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard (except for the information required under paragraph 6) must be the product of systems, processes and controls that have been reviewed and tested by the external auditor of the ADI as set out in Prudential Standards APS 310 Audit and Related Matters. Relevant standards and guidance statements issued by the Auditing and Assurance Standards Board provide information on the scope and nature of the review and testing required from external auditors. This review and testing must be done on an annual basis or more frequently if necessary to enable the external auditor to form an opinion on the accuracy and reliability of the information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard.
13. All information provided by an ADI under this Reporting Standard must be subject to processes and controls developed by the ADI for the internal review and authorisation of that information. These systems, processes and controls are to assure the completeness and reliability of the information provided.
Authorisation
14. When an officer of an ADI submits information under this Reporting Standard using the D2A application, or other method notified by APRA, it will be necessary for the officer to digitally sign the relevant information using a digital certificate acceptable to APRA.
Minor alterations to forms and instructions
15. APRA may make minor variations to:
(a) a form that is part of this Reporting Standard, and the instructions to such a form, to correct technical, programming or logical errors, inconsistencies or anomalies; or
(b) the instructions to a form, to clarify their application to the form
without changing any substantive requirement in the form or instructions.
16. If APRA makes such a variation it must notify in writing each ADI that is required to report under this Reporting Standard.
Interpretation
17. In this Reporting Standard:
AASB has the meaning in section 9 of the Corporations Act 2001.
ADI means an authorised deposit-taking institution within the meaning of the Banking Act 1959.
APRA means the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority established under the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Act 1998.
authorised NOHC has the meaning given in the Banking Act 1959.
business days means ordinary business days, exclusive of Saturdays, Sundays and public holidays.
immediate parent NOHC means an authorised NOHC, or a subsidiary of an authorised NOHC, that is an immediate parent NOHC within the meaning of paragraph 21(b) of Prudential Standard APS 110 Capital Adequacy (APS 110).
Level 1 has the meaning in APS 001.
Level 2 has the meaning in APS 001.
reporting period means a period mentioned in paragraph 8 or, if applicable, paragraph 9.
subsidiary has the meaning in section 9 of the Corporations Act 2001.
18. Unless the contrary intention appears, a reference to an Act, Prudential Standard, Reporting Standard, Australian Accounting or Auditing Standard is a reference to the instrument as in force from time to time.
Reporting Forms ARF 113.3A, ARF 113.3B, ARF 113.3C and ARF 113.3D
IRB Retail – Residential Mortgages, Qualifying Revolving, Other and SME
Instruction Guide
This instruction guide is designed to assist in the completion of the IRB Retail suite of forms. This suite of forms consists of the following:
(a) Reporting Form ARF 113.3A IRB Retail – Residential Mortgages (ARF 113.3A);
(b) Reporting Form ARF 113.3B IRB Retail – Qualifying Revolving (ARF 113.3B);
(c) Reporting Form ARF 113.3C IRB Retail – Other (ARF 113.3C); and
(d) Reporting Form ARF 113.3D IRB Retail – SME (ARF 113.3D).
These forms capture the credit risk-weighted assets (RWA) and risk components of retail exposures under the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach to credit risk. In completing these forms, authorised deposit-taking institutions (ADIs) should refer to Prudential Standard APS 113 Capital Adequacy: Internal Ratings-based Approach to Credit Risk (APS 113).
General directions and notes
Reporting entity
These forms are to be completed at Level 1 and Level 2 by each ADI that has APRA’s approval or is seeking APRA’s approval to use the IRB approach to credit risk for capital adequacy purposes, in accordance with APS 113.
If an ADI is a subsidiary of an authorised non-operating holding company (NOHC), the report at Level 2 is to be provided by the ADI’s immediate parent NOHC.
Securitisation deconsolidation principle
Except as otherwise specified in these instructions, the following applies:
- Where an ADI (or a member of its Level 2 consolidated group) participates in a securitisation that meets APRA’s operational requirements for regulatory capital relief under Prudential Standard APS 120 Securitisation (APS 120):
(a) special purpose vehicles (SPVs) holding securitised assets may be treated as non-consolidated independent third parties for regulatory reporting purposes, irrespective of whether the SPVs (or their assets) are consolidated for accounting purposes;
(b) the assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses of the relevant SPVs may be excluded from the ADI’s reported amounts in APRA’s regulatory reporting returns; and
(c) the underlying exposures (i.e. the pool) under such a securitisation may be excluded from the calculation of the ADI’s regulatory capital (refer to APS 120). However, the ADI must still hold regulatory capital for the securitisation exposures that it retains or acquires, and such exposures are to be reported in Reporting Form ARF 120.1 Securitisation – Regulatory Capital. The RWA relating to such securitisation exposures must also be reported in Reporting Form ARF 110.0.1 Capital Adequacy (Level 1) and Reporting Form ARF 110.0.2 Capital Adequacy (Level 2).
2. Where an ADI (or a member of its Level 2 consolidated group) participates in a securitisation that does not meet APRA’s operational requirements for regulatory capital relief under APS 120, or the ADI undertakes a funding-only securitisation or synthetic securitisation, such exposures are to be reported as on-balance sheet assets in APRA’s regulatory reporting returns. In addition, these exposures must also be reported as a part of the ADI’s total securitised assets within Reporting Form ARF 120.2 Securitisation – Supplementary Items.
Reporting period and timeframe for lodgement
These forms are to be completed as at the last day of the stated reporting period (i.e. the relevant quarter) and submitted to APRA within 30 business days after the end of the relevant reporting period.
Requirements applying to certain ADIs reporting under the forms
The following particular requirements apply to certain ADIs:
Description of ADI | Reporting requirement | Timeframe for lodgement |
ADI is operating under Prudential Standard APS 112 Capital Adequacy: Standardised Approach to Credit Risk (APS 112) standardised approach, but has applied to adopt (or APRA has indicated that it proposes to approve it for) the IRB approach for most or all of its operations | Report under ARF 113.3A, ARF 113.3B, ARF 113.3C and ARF 113.3D (the forms) in respect of relevant operations to be covered by the IRB approach (for purposes of assessing prospective credit risk component of regulatory capital calculation after IRB approval (i.e. “parallel run” of data)) | Within 30 business days of end of reporting period |
ADI has IRB approval, but some operations remain under the standardised approach set out in APS 112 | Report under the forms in respect of relevant operations that are covered by the IRB approach (for purposes of calculating credit risk component of regulatory capital) | Within 30 business days of end of reporting period |
These ADIs will also have certain reporting obligations under Reporting Form ARF 112.1A Standardised Credit Risk – On-balance Sheet Assets and Reporting Form ARF 112.2A Standardised Credit Risk – Off-balance Sheet Exposures.
Unit of measurement
These forms are to be completed in millions of Australian dollars (AUD) rounded to one decimal place, unless otherwise specified in this instruction guide.
Amounts denominated in foreign currency are to be converted to AUD in accordance with AASB 121 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates.
Scope
An ADI is to report in ARF 113.3A, ARF 113.3B, ARF 113.3C and ARF 113.3D:
- all on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet retail exposures in its banking book that are subject to the IRB approach, including those that expose the ADI to counterparty credit risk, except the following specifically excluded items (refer to APS 113):
(a) those assets or investments that are required to be deducted from Tier 1 or Tier 2 capital under Prudential Standard APS 111 Capital Adequacy: Measurement of Capital; and
(b) securitisation exposures, which are subject to the requirements of APS 120; and
2. all retail exposures in its trading book that expose the ADI to counterparty credit risk (refer to APS 113).
Definitions
In this instruction guide and its corresponding reporting forms (ARF 113.3A, 113.3B, 113.3C and 113.3D), the following expressions have the defined meanings as set out below:
Retail exposures
Refer to APS 113 for definitions of the retail IRB asset class and its associated sub-asset classes.
SME retail exposures
A small- and medium-sized enterprise (SME) retail exposure is a small business exposure, which can be treated as a retail exposure in accordance with APS 113.
Specific instructions
The following instructions are applicable at Level 1 and (where relevant) Level 2.
These forms do not calculate the RWA and expected loss (EL) amounts. An ADI completing these forms is required to disclose these data items based on its own regulatory capital calculations.
Section A: On-balance sheet risk-weighted assets and expected loss amount
Column 1. PD by band
For the purposes of reporting on the IRB retail asset class, probability of default (PD) bands have been pre-defined within the forms. Pools of exposures are to be allocated to the pre-defined PD bands in the forms, based on an ADI’s own internal estimates of PD for each pool of retail exposures.
Column 1 includes a row with a 100 per cent PD to be used for all defaulted exposures.
Column 2. Exposures before CRM
Exposure at default (EAD) estimates are to be calculated in accordance with Attachment C to APS 113.
Report exposures before credit risk mitigation (CRM) in the relevant row.
Column 3. Exposures after CRM
Derived field that totals the exposures after CRM by LGD bands for a PD band.
Columns 4.1 to 4.9 (or 4.13/4.14) Exposures after CRM by LGD bands
Refer to Attachment C to APS 113 for details of the recognition of CRM for the IRB retail asset class.
For reporting purposes, loss given default (LGD) bands have been pre-defined within the forms. An ADI’s LGD estimates are to be grouped into these specified LGD bands. LGD estimates are to be calculated in accordance with APS 113.
For ARF 113.3A, the LGD bands that have been provided begin below the minimum LGD required by APS 113 for exposures in the residential mortgage sub-asset class. This is relevant for reporting purposes only. For details on calculation of the RWA, refer to Column 7. RWA below.
Report exposures after CRM in:
(a) Columns 4.1 to 4.9 in ARF 113.3A;
(b) Columns 4.1 to 4.13 in ARF 113.3B and ARF 113.3C; and
(c) Columns 4.1 to 4.14 in ARF 113.3D.
Pools of exposures are to be allocated to the column for the appropriate LGD band and the row for the relevant PD band, based on an ADI’s own internal estimates of LGD and PD for each pool of retail exposures.
Column 5. Weighted average LGD
Report the exposure-weighted average LGD, as a percentage rounded to two decimal places, for exposures allocated to each PD band.
Exposure-weighted average LGD = 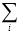 LGDi x EAD i /
LGDi x EAD i /  EAD i
EAD i
Total
Column 6. Weighted average PD
Report the exposure-weighted average PD, as a percentage rounded to two decimal places, for exposures allocated to each PD band.
Exposure-weighted average PD = 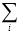 PDi x EAD i /
PDi x EAD i /  EAD i
EAD i
Total
Column 7. RWA
RWA are to be calculated in accordance with the requirements of APS 113, including the application of either the minimum LGD required under APS 113, or an alternative higher minimum LGD required by APRA, for exposures in the residential mortgage sub-asset class (refer to Attachment C to APS 113).
Report the sum of RWA for exposures allocated to each PD band in the relevant rows.
Column 8. EL amount
EL amount is to be calculated in accordance with APS 113. Report the sum of the EL amounts for exposures allocated to each PD band in the relevant rows.
Row – Weighted average LGD
Report the exposure-weighted average LGD, as a percentage rounded to two decimal places, for exposures allocated to each LGD band.
Weighted average LGD = 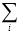 LGDi x EAD i /
LGDi x EAD i /  EAD i
EAD i
Section B: Off-balance sheet risk-weighted assets and expected loss amount
Off-balance sheet exposures include both non-market-related (including undrawn lines) and market-related off-balance sheet transactions.
For the following columns in the off-balance sheet schedule, refer to the instructions in section A of this instruction guide:
(a) Column 1. PD by band;
(b) Column 2. Exposures before CRM;
(c) Column 3. Exposures after CRM;
(d) Columns 4.1 to 4.9 (or 4.13/4.14). Exposures after CRM by LGD bands;
(e) Column 5. Weighted average LGD;
(f) Column 6. Weighted average PD;
(g) Column 7. RWA; and
(h) Column 8. EL amount.
Also, refer to the instructions in section A of this instruction guide for reporting weighted average LGD for each LGD band.
Refer to Attachment C to APS 113 for further details on the calculation of EAD for off-balance sheet retail exposures.
Memorandum items: breakdown of non-market-related off-balance sheet exposures
Report the breakdown of non-market-related off-balance sheet retail exposures (refer to Attachment C to APS 113).
Column 1. Nature of transaction
Report the nature of the non-market-related off-balance sheet transactions (e.g. commitments, direct credit substitutes, performance-related contingencies (refer to Attachment C to APS 113 for further details)). This field is limited to 80 characters.
Column 2. Notional amount
Report the notional amount (or the undrawn amount in the case of undrawn commitments) of off-balance sheet exposures after CRM in the relevant row for each transaction type listed in column 1.
Column 3. Credit equivalent amount
The credit equivalent amount is calculated by multiplying the notional amount/undrawn amount of off-balance sheet exposures for a transaction type by the appropriate credit conversion factors (refer to Attachment C to APS 113). Report the credit equivalent amounts in the relevant row for each transaction type.
Section C: Memorandum items: purchased receivables
Report the breakdown of RWA and EL amount for default risk and dilution risk for all pools of purchased receivables, which are included in the calculation of RWA and EL amount for retail exposures in sections A and B of the forms.
















