Schedule 1 Amendment of Occupational Health and Safety (Commonwealth Employment) (National Standards) Regulations 1994
(regulation 3)
[1] Part 10
renumber as Part 20
[2] Regulation 10.01
renumber as regulation 20.01
Schedule 2 Further amendment of Occupational Health and Safety (Commonwealth Employment) (National Standards) Regulations 1994
(regulation 4)
[1] Regulation 4.29, note 1
omit
subregulation 10.01 (1).
insert
subregulation 20.01 (1).
[2] Part 9
substitute
Part 9 Major hazard facilities
Division 9.1 Preliminary
9.01 Object of Part 9
The object of this Part is to prevent the occurrence of major accidents at a facility that is a major hazard facility or a potential major hazard facility and, if a major accident occurs, to minimise its effect:
(a) by requiring an employer in control of a potential major hazard facility to notify the facility to the Commission in accordance with regulation 9.06; and
(b) by requiring an employer in control of a major hazard facility to:
(i) hold a licence to operate the major hazard facility, or a certificate of compliance in relation to the major hazard facility, in accordance with Division 9.3; and
(ii) identify, assess and control all hazards at the major hazard facility; and
(iii) implement measures to reduce the likelihood and effects of a major accident; and
(iv) give information to the Commission, a relevant person, and an at‑risk community; and
(v) investigate all major accidents at the facility, and report them to the Commission in accordance with Subdivision A of Division 9.4; and
(vi) record the analysis of, and the lessons learnt from, the occurrence of a major accident, and to discuss that analysis and those lessons with employees, contractors and health and safety representatives.
9.02 Application of Part 9
This Part applies to a major hazard facility, or a potential major hazard facility, of which an employer is in control.
9.03 Definitions for Part 9
In this Part:
aggregate threshold quantity, in relation to 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9, is the sum of the threshold quantity for each material.
approved assessor means a person, an organisation, or a statutory authority approved by the Commission under Division 9.6 to assess the safety report of a major hazard facility.
AS/NZS 2243.3:2002 means Australian Standard AS/NZS 2243.3:2002: Safety in Laboratories: Microbiological aspects and containment facilities, published on 9 January 2002, as amended by AS/NZS 2243.3:2002/Amdt 1:2003 (published on 29 April 2003).
at‑risk community means a community that is at risk of being directly affected by a major accident at a major hazard facility or a potential major hazard facility.
bridging licence means a licence that is taken to have been issued under regulation 9.30.
certificate of compliance means a certificate issued under paragraph 9.25 (5) (a).
dangerous goods has the same meaning as in subregulation 8.04 (3).
health and safety representative has the same meaning as in section 25 of the Act.
identified major hazard facility means a facility:
(a) that is licensed, before the commencement of this Part, under an identified State or Territory law; and
(b) the classification of which has not been revoked, by the Commission, under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i).
identified State or Territory law means the Occupational Health and Safety (Major Hazard Facilities) Regulations 2000 of Victoria.
in control, in relation to an employer and a facility, means having responsibility for the day to day operations of the facility.
major accident, in relation to a major hazard facility or a potential major hazard facility, means a sudden occurrence at the facility causing serious danger or harm to:
(a) a relevant person; or
(b) an at‑risk community; or
(c) property; or
(d) the environment;
whether the danger or harm occurs immediately or at a later time.
Examples
1 A major emission of dangerous goods or hazardous substances from the facility.
2 A loss of containment of dangerous goods or a hazardous substance.
3 A fire or explosion.
4 A release of energy.
major hazard facility means:
(a) a facility classified as a major hazard facility by the Commission under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i); or
(b) an identified major hazard facility.
modification, in relation to a facility, means any of the following changes to the facility that significantly alters the risks associated with the facility:
(a) a change to plant, a process, or a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9;
(b) the introduction of new plant, a new process, new material or a new operating procedure;
(c) a change to the safety management system for the facility, in particular, a change in the organisation of the facility.
national security information means information the disclosure of which is likely to prejudice Australia’s national security.
nuclear installation has the meaning given by section 13 of the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Act 1998.
occupational health and safety competency standards means the standards included in a training program developed for a major hazard facility under regulation 9.51.
potential major hazard facility means a proposed or existing facility, other than an identified major hazard facility:
(a) that is or will be:
(i) a nuclear installation; or
(ii) a prescribed radiation facility; or
(iii) a laboratory that deals with a biological agent that requires Physical Containment 3 or 4, within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002; or
(iv) a facility at which an activity undertaken involves, or is likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of:
(A) a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds 10% of the threshold quantity for that material; or
(B) a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds 10% of the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials; or
(b) in relation to which a notification has been issued by the Commission under regulation 9.05.
prescribed radiation facility means a facility or installation prescribed by regulation 6 of the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Regulations 1999.
threshold quantity means, in relation to a material specified in an item in Part 2 of Schedule 9, the threshold quantity specified in column 4 of that item.
9.04 Interpretation – quantity equalling or exceeding aggregate threshold quantity
In this Part, a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 equals or exceeds the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials if the result of the application of the aggregation formula in Part 4 of Schedule 9 in relation to those materials exceeds 1.
Division 9.2 Notification and classification of a potential major hazard facility
Subdivision A Notifications of potential major hazard facilities
9.05 Identification of potential major hazard facility — notification by Commission
(1) If the Commission believes, on reasonable grounds, that an activity undertaken at an existing facility could cause a major accident, the Commission must give written notice of that belief to the employer in control of the facility.
(2) If the Commission believes, on reasonable grounds, that an activity that is likely to be undertaken at a proposed facility once it is in operation could cause a major accident, the Commission must give written notice of that belief to the person that intends to be the employer in control of the facility.
9.06 Notification of potential major hazard facility
(1) An employer in control of, or an employer that intends to be in control of, a potential major hazard facility must notify the Commission about the facility, in a form approved by the Commission.
(2) Subject to subregulation (4), a notification given to the Commission under this regulation in relation to a facility that is an existing facility must include the following information:
(a) the name of the employer in control of the facility;
(b) the address or location of the facility;
(c) the name, title and contact details of a contact person for the facility;
(d) a description of the nature of the facility, including:
(i) whether the facility is:
(A) a nuclear installation; or
(B) a prescribed radiation facility; or
(C) a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 3 or 4 within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002; and
(ii) a description of general site activities;
(e) whether an activity that is undertaken at the facility involves, or is likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of:
(i) a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the threshold quantity for that material; or
(ii) a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials;
(f) whether, in the opinion of the employer, an activity that is undertaken at the facility could cause a major accident;
(g) the likely consequences of a major accident at the facility;
(h) for each material present at the facility — the quantity in which the material is present;
(i) if a material specified in an item in Part 2 of Schedule 9 is, or is likely to be, present at the facility in a quantity that is more than 2% of the threshold quantity for that material — sufficient information to identify the material, including, if applicable:
(i) the name of the material; and
(ii) the chemical name of the material; and
(iii) the Chemical Abstract Service (CAS) number for the material; and
(iv) any other name by which the material is known; and
(v) the molecular formula for the material; and
(vi) the maximum quantity in which the material is, or is likely to be, present at the facility; and
(vii) the maximum rate of production of the material undertaken at the facility.
(3) Subject to subregulation (4), a notification given to the Commission under this regulation in relation to a facility that is a proposed facility must include the following information:
(a) the name of the employer that intends to be in control of the facility;
(b) the proposed address or location of the facility;
(c) if possible, the name, title and contact details of a contact person for the facility once it is in operation;
(d) a description of the proposed nature of the facility, including:
(i) whether the facility will be, or is likely to be:
(A) a nuclear installation; or
(B) a prescribed radiation facility; or
(C) a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 3 or 4 within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002; and
(ii) a description of planned general site activities;
(e) whether an activity that will be, or that is likely to be, undertaken at the facility once it is in operation involves, or is likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of:
(i) a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that will, or that is likely to, equal or exceed the threshold quantity for that material; or
(ii) a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that will, or that is likely to, equal or exceed the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials;
(f) whether, in the opinion of the employer, an activity that will be, or that is likely to be, undertaken at the facility once it is in operation could cause a major accident;
(g) the likely consequences of a major accident at the facility once it is in operation;
(h) for each material that will be, or that is likely to be, present at the facility once it is in operation — the quantity in which the material will be, or is likely to be, present;
(i) if a material specified in an item in Part 2 of Schedule 9 will be, or is likely to be, present at the facility once it is in operation in a quantity that is more than 2% of the threshold quantity for that material — sufficient information to identify the material, including, if applicable:
(i) the name of the material; and
(ii) the chemical name of the material; and
(iii) the Chemical Abstract Service (CAS) number for the material; and
(iv) any other name by which the material is known; and
(v) the molecular formula for the material; and
(vi) the maximum quantity in which the material will be, or is likely to be, present at the facility; and
(vii) the maximum rate of production of the material that will be, or that is likely to be, undertaken at the facility.
(4) For subregulations (2) and (3), if information to be included in a notification is national security information, the employer may comply with the relevant subregulation by giving the Commission a summary, in a form approved by the Commission, of that information.
(5) A notification must be given to the Commission:
(a) for a proposed potential major hazard facility — at least 3 months before operations begin at the facility; and
(b) for a potential major hazard facility that:
(i) is in existence before the commencement of this Part; and
(ii) is not a facility in relation to which a notification has been given by the Commission under regulation 9.05;
within 3 months after the commencement of this Part; and
(c) for a facility:
(i) that is not a proposed potential major hazard facility; and
(ii) in relation to which a notification has been given by the Commission under regulation 9.05;
within 3 months after the notification is given; and
(d) for a facility that:
(i) is not a proposed potential major hazard facility; and
(ii) will become a potential major hazard facility because of a modification to the facility;
at least 3 months before the modification becomes operative.
9.07 Consideration of notification
(1) On receiving notification of a potential major hazard facility under regulation 9.06, the Commission must:
(a) consider the information provided by the employer; and
(b) either:
(i) decide whether or not to classify the facility as a major hazard facility; or
(ii) ask the employer, by written notice, to give the Commission additional information necessary to assist it to decide whether or not to classify the facility as a major hazard facility.
(2) If the Commission asks the employer to give it additional information:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to classify the facility as a major hazard facility until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(3) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to classify the facility as a major hazard facility on the basis of the information about the facility that is available to the Commission.
Subdivision B Classification of potential major hazard facility
9.08 Classification as major hazard facility
(1) In making a decision under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), the Commission must classify a potential major hazard facility that is an existing facility as a major hazard facility if:
(a) an activity that is undertaken at the facility involves, or is likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of:
(i) a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the threshold quantity for that material; or
(ii) a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials; or
(b) the facility is a nuclear installation; or
(c) the facility is a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 4, within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002.
(2) In making a decision under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), the Commission may classify a potential major hazard facility that is an existing facility as a major hazard facility if, having regard to the information provided by the employer under regulations 9.06 and 9.07 (if any), the Commission is satisfied that an activity undertaken at the facility could cause a major accident.
Examples
Potential major hazard facilities that could be classified as a major hazard facility include the following:
- a prescribed radiation facility;
- a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 3 (within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243:3:2002);
- a facility at which a material specified in an item in Part 2 of Schedule 9 is present, or is likely to be present, in a quantity that is more than 10% of the threshold quantity for that material;
- a facility at which 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 are present, or are likely to be present, in a quantity that is more than 10% of the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials;
- a facility at which large quantities of a dangerous good specified in Schedule 8 are present.
9.09 Notification of decision under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i)
(1) The Commission must give an employer in control of, or an employer that intends to be in control of, a potential major hazard facility written notice of a decision to classify or to not classify the facility as a major hazard facility.
(2) The notice must:
(a) subject to subregulation (3), be given to the employer within 6 months after the date when the employer gave the Commission notification under regulation 9.06; and
(b) state:
(i) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(ii) if the decision is to classify the facility as a major hazard facility — the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
(3) If the Commission is likely to take more than 6 months to make a decision about whether to classify a potential major hazard facility as a major hazard facility, the Commission must tell the employer, by written notice, before the end of the 6 months, when the decision is likely to be made.
(4) If the Commission gives an employer written notice under subsection (3), the Commission must decide whether or not to classify the potential major hazard facility as a major hazard facility by the date specified in the notice.
Subdivision C Revocation of classification of major hazard facility
Note For this Subdivision, an identified major hazard facility is taken to have been classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) — see regulation 9.14.
9.10 Application for revocation of classification of major hazard facility
(1) An employer in control of a facility that has been classified as a major hazard facility by the Commission under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) may apply to the Commission to have the classification revoked in any of the following circumstances:
(a) if, at the time the facility was classified, an activity at the facility involved, or was likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of a quantity mentioned in subparagraph 9.08 (1) (a) (i) or (ii) — any such activity has ceased, or will cease, to be undertaken at the facility;
(b) if, at the time the facility was classified, it was a nuclear installation — the facility has ceased, or will cease, to be a nuclear installation;
(c) if, at the time the facility was classified, it was a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 4, within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002 — the facility has ceased, or will cease, to be such a laboratory;
(d) in any other case — if the employer is of the opinion that no activity undertaken at the facility could cause a major accident.
(2) An application under this regulation must be made:
(a) in a form approved by the Commission; and
(b) not later than 6 months before the date on which the employer wishes the revocation to take effect.
9.11 Consideration of application for revocation of classification
(1) On receiving an application under regulation 9.10, the Commission must:
(a) consider the information provided by the employer; and
(b) either:
(i) decide whether or not to revoke the classification of the facility as a major hazard facility; or
(ii) ask the employer, by written notice, to give the Commission additional information necessary to assist it to decide whether or not to revoke the classification.
(2) If the Commission asks the employer to give it additional information:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to revoke the classification of the facility as a major hazard facility until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(3) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to revoke the classification of the facility as a major hazard facility on the basis of the information about the facility that is available to the Commission.
9.12 Revocation of classification as major hazard facility
In making a decision under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i), the Commission may revoke the classification of a facility as a major hazard facility if:
(a) no activity undertaken at the facility involves, or is likely to involve, temporarily or permanently, the processing, production, disposal, handling, use or storage of:
(i) a quantity of a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the threshold quantity for that material; or
(ii) a quantity of 2 or more materials specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9 that equals or exceeds the aggregate threshold quantity for those materials; and
(b) the facility is not a nuclear installation; and
(c) the facility is not a laboratory dealing with biological agents requiring Physical Containment 4, within the meaning of AS/NZS 2243.3:2002; and
(d) the Commission is satisfied that no activity undertaken at the facility could cause a major accident.
9.13 Notification of decision under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i)
(1) The Commission must give an employer that has made an application under regulation 9.10 written notice of a decision to revoke or to not revoke the classification of a facility as a major hazard facility.
(2) The notice must:
(a) be given to the employer within 6 months after the date when the employer made the application under regulation 9.10; and
(b) state:
(i) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(ii) if the decision is to refuse to revoke the classification of the facility as a major hazard facility — the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
Subdivision D Classification of identified major hazard facility
9.14 Identified major hazard facility taken to be classified under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i)
For Subdivision C of Division 9.2, an identified major hazard facility is taken to have been classified under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i).
Division 9.3 Licence to operate a major hazard facility
Subdivision A Licensing scheme for employers in control of major hazard facilities
9.15 Definition for Subdivision A
In this Subdivision:
safety report means:
(a) for:
(i) a facility classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), other than a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force; or
(ii) an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a licence issued under this Subdivision is in force;
a report prepared in accordance with regulation 9.47; and
(b) for a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force — a report that deals with the kinds of matters specified in Schedule 9A and that is prepared in accordance with a condition of the certificate of compliance; and
(c) for an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a bridging licence is in force — a report that deals with the kinds of matters specified in Schedule 9A and that is prepared in accordance with a condition of the bridging licence.
9.16 Licence to operate a major hazard facility
An employer in control of a major hazard facility must hold a licence, issued under regulation 9.20, to operate the facility, unless:
(a) a bridging licence, or a certificate of compliance, is in force in relation to the employer and the facility; or
(b) the employer is exempt from this requirement under regulation 9.17.
9.17 Exemptions from licensing requirement
Period for making an application for a licence has not expired
(1) Regulation 9.16 does not apply to an employer in control of a major hazard facility if:
(a) the employer has not made an application to the Commission for a licence in accordance with regulation 9.18; and
(b) the period within which the application must be made, worked out under regulation 9.19, has not expired.
Application for licence, certificate of compliance or transfer of licence or certificate of compliance made to Commission and not determined
(2) Regulation 9.16 does not apply to an employer in control of a major hazard facility if:
(a) the employer has made an application to the Commission for:
(i) a licence, in accordance with regulation 9.18; or
(ii) a certificate of compliance, in accordance with regulation 9.25; or
(iii) the transfer of a licence (including a bridging licence) or a certificate of compliance, in accordance with regulation 9.34; and
(b) the Commission has not notified the employer whether the application has been granted or refused.
9.18 Application for licence
(1) Subject to regulation 9.17, an employer in control of, or an employer that intends to be in control of, a major hazard facility must apply to the Commission for a licence to operate the facility.
Note A licence issued under this Division will be in force for a specified period — see regulation 9.21. If an employer that holds a licence issued under this Division intends to continue to be in control of a major hazard facility after the expiration of the licence period, the employer must apply for a new licence — see subregulation 9.19 (1) for the timeframe for making an application for a new licence.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in writing, in a form approved by the Commission; and
(b) be accompanied by an executive summary, prepared in accordance with subregulation (3), of the assessment of the current safety report for the major hazard facility; and
(c) be made within the period worked out under regulation 9.19.
(3) The executive summary of an assessment of the safety report must:
(a) be prepared by an approved assessor; and
(b) include a brief description of how the major hazard facility complies with these Regulations and with the conditions of any licence (including a bridging licence) or certificate of compliance issued under this Division that is in force in relation to the employer and the facility; and
(c) for:
(i) a facility classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), other than a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force; or
(ii) an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a licence issued under regulation 9.20 is in force;
include a statement about whether the approved assessor is satisfied that the safety report complies with the requirements of regulation 9.47; and
(d) for a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force — include a statement about whether the approved assessor is satisfied that the safety report complies with the requirements (if any) for the safety report included in the certificate; and
(e) for an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a bridging licence is in force — include a statement about whether the approved assessor is satisfied that the safety report complies with the requirements (if any) for the safety report included in the bridging licence; and
(f) address the following matters:
(i) hazard identification for major hazards at the facility;
(ii) risk assessment for major hazards at the facility;
(iii) risk control for major hazards at the facility;
(iv) whether the employer has implemented an adequate safety management system;
(v) the development of the safety report; and
(g) include an assessment of the employer’s ability to operate the major hazard facility in a safe manner; and
(h) include a statement about whether, in the approved assessor’s opinion, the employer should be granted a licence and what conditions (if any) the grant of the licence should be subject to.
(4) The employer must ensure that a copy of the safety report, and a copy of the assessment of the safety report, is available for inspection on request by an investigator.
9.19 Period for making an application for a licence
(1) If an application for a licence is made under regulation 9.18 by an employer that holds a licence (including a bridging licence) or a certificate of compliance, issued or taken to be issued under this Division, in relation to the facility, the application must be made at least 6 months before the date on which the licence or certificate will cease to be in force.
(2) If an application for a licence is made under regulation 9.18 by an employer whose application for the transfer of a licence issued under this Division (including a bridging licence) or a certificate of compliance has been refused under paragraph 9.35 (1) (b), the application under regulation 9.18 must be made by the end of 6 months after the date when the refusal decision was notified to the employer under subregulation 9.35 (5).
(3) If subregulation (2) does not apply and an application for a licence is made under regulation 9.18 in relation to a facility that has been classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) and by an employer (the second employer) that has, or that will, take control of the facility from another employer (the first employer), the application must be made, subject to subregulation (2), either:
(a) by the later of:
(i) the end of 21 months after the date when the facility was classified as a major hazard facility; and
(ii) the end of 6 months after the second employer takes control of the facility; or
(b) if the second employer has applied, under subregulation 9.47 (5), for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared — within the period approved by the Commission under subregulation 9.47 (7).
Note 1 See also regulation 9.72 for requirements in relation to a major hazard facility that an employer will take control of from another employer.
Note 2 If the employer applies for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared, the Commission may ask the employer to submit a timetable for the preparation of the safety report to the Commission — see subregulation 9.47 (8).
(4) If an application for a licence is made under regulation 9.18 in relation to an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a bridging licence is in force and by an employer (the second employer) that has, or that will, take control of the facility from another employer (the first employer), the application must, subject to subregulation (2), be made by the end of 6 months after the second employer takes control of the facility.
Note See also regulation 9.72 for requirements in relation to a major hazard facility that an employer will take control of from another employer.
(5) If an application for a licence is made under regulation 9.18 in relation to an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a licence issued under regulation 9.20 is in force and by an employer (the second employer) that has, or that will, take control of the facility from another employer (the first employer), the application must be made, subject to subregulation (2), either:
(a) by the end of 6 months after the second employer takes control of the facility; or
(b) if the second employer has applied, under subregulation 9.47 (5), for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared — within the period approved by the Commission under subregulation 9.47 (7).
Note 1 See also regulation 9.72 for requirements in relation to a major hazard facility that an employer will take control of from another employer.
Note 2 If the employer applies for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared, the Commission may ask the employer to submit a timetable for the preparation of the safety report to the Commission — see subregulation 9.47 (8).
(6) If subregulations (1) to (5) do not apply, an application for a licence made under regulation 9.18 must be made either:
(a) within 21 months after the date when the facility was classified as a major hazard facility; or
(b) if the employer has applied, under subregulation 9.47 (5), for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared — within the period approved by the Commission under subregulation 9.47 (7).
Note If the employer applies for an extension of the period within which a safety report must be prepared, the Commission may ask the employer to submit a timetable for the preparation of the safety report to the Commission — see subregulation 9.47 (8).
9.20 Issue of licence
(1) On receiving an application from an employer for a licence under subregulation 9.18 (1), the Commission must:
(a) issue a licence to the employer; or
(b) refuse to issue a licence to the employer; or
(c) ask the employer, by written notice, to give the Commission additional information necessary to assist it to decide whether to issue a licence to the employer.
(2) If the Commission asks an employer to give the Commission additional information in relation to an application:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to issue a licence until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(3) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to issue a licence on the basis of the information about the facility and the employer that is available to the Commission.
(4) The Commission may issue a licence if it is satisfied that:
(a) the current safety report for the major hazard facility has been prepared in accordance with:
(i) regulation 9.47; or
(ii) the conditions of any bridging licence or certificate of compliance that is in force in relation to the employer and the facility; and
(b) the assessment of the safety report has been undertaken by an approved assessor; and
(c) the employer has implemented an adequate safety management system; and
(d) the employer has the ability to operate the major hazard facility in a safe manner.
(5) If the Commission refuses to issue the licence, the Commission must give the employer a written notice setting out:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
(6) A notice under subregulation (5) must be given within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the licence.
(7) If the Commission decides to issue a licence to the employer, the licence must, subject to subregulations (8) and (9), be issued within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the licence.
(8) The Commission must give the employer written notice if a licence will be issued later than 6 months after receiving the employer’s application for the licence.
(9) If the Commission gives an employer written notice under subregulation (8), the licence must be issued within the period specified in the notice.
Note An application may be made under regulation 9.34 for the transfer of a licence issued under this regulation.
9.21 Period for which licence is in force
(1) A licence issued under regulation 9.20 must specify:
(a) the date on which it takes effect; and
(b) the period for which it is to be in force.
(2) The period for which the licence is to be in force must not be longer than 5 years from the date on which the licence takes effect.
9.22 Conditions of licence
(1) A licence issued under regulation 9.20 is subject to the following conditions:
(a) the employer to whom the licence is issued must ensure that a copy of the licence is kept at the major hazard facility operated under the licence;
(b) the employer must ensure that the licence is available for inspection on request by an investigator, an employee, a contractor, a health and safety representative or a representative of emergency services;
(c) the employer must allow the Commission access to the facility for the purpose of assessing the employer’s compliance with the conditions of the licence;
(d) any other condition specified by the Commission in the licence.
(2) The Commission may, by notice in writing given to the employer to whom the licence is issued:
(a) add a condition to the licence; or
(b) vary a condition specified in the licence; or
(c) revoke a condition specified in the licence.
(3) An employer must comply with the conditions to which a licence is subject, including a condition that has been added or varied.
(4) A notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
9.23 Suspension or cancellation of licence
(1) The Commission may suspend or cancel a licence issued under regulation 9.20 if:
(a) the classification of the major hazard facility in relation to which the licence was issued is revoked under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i); or
(b) the Commission is satisfied that:
(i) the safety management system no longer provides a comprehensive and integrated management system for the prevention of major accidents at the major hazard facility; or
(ii) the employer has failed to comply with a condition of the licence; or
(iii) the employer no longer has the ability to operate the major hazard facility in a safe manner; or
(iv) the licence was issued on the basis of:
(A) the provision of false or misleading information; or
(B) a failure to disclose particular information;
in the employer’s application for the licence or under regulation 9.20.
(2) If the Commission decides to suspend or cancel an employer’s licence under subregulation (1), the Commission must give the employer written notice of that decision.
(3) A notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the date from which the licence is suspended or cancelled; and
(b) if the decision is to suspend the licence — the period for which the licence is suspended; and
(c) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(d) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
Subdivision B Certificate of compliance scheme for employers in control of major hazard facilities
9.24 Definition for Subdivision B
In this Subdivision:
existing Commonwealth scheme means a law of the Commonwealth that has a direct effect or an indirect effect on occupational health and safety.
9.25 Application for certificate of compliance
(1) An employer in control of, or an employer that intends to be in control of, a major hazard facility may apply for a certificate of compliance in relation to the facility if, at the time the application is made, operations at the facility are regulated by an existing Commonwealth scheme.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in writing, in a form approved by the Commission; and
(b) be accompanied by:
(i) sufficient information to identify the existing Commonwealth scheme under which the major hazard facility is regulated; and
(ii) a copy of any licence, certificate or other instrument made or issued under the existing Commonwealth scheme that imposes conditions on the operation of the facility; and
(iii) a copy of any report (however described) that:
(A) relates to an incident at the facility that would, if this Part had applied in relation to the facility at the time of the incident, have been a major accident within the meaning of this Part; and
(B) was prepared under the existing Commonwealth scheme.
(3) If the Commission asks an employer to give the Commission additional information in relation to an application:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to issue a certificate of compliance until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(4) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to issue a certificate of compliance on the basis of the information about the facility and the employer that is available to the Commission.
(5) On receiving the application, the Commission must:
(a) issue a certificate of compliance in accordance with regulation 9.26; or
(b) refuse to issue the certificate; or
(c) ask the employer, by written notice, to give the Commission further information necessary to assist it to decide whether or not to issue a certificate of compliance.
(6) If the Commission refuses to issue a certificate of compliance, the Commission must give the employer a written notice setting out:
(a) the reasons for refusing to issue the certificate; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
(7) A notice under subregulation (6) must be given within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the certificate of compliance.
(8) If the Commission decides to issue a certificate of compliance, the certificate must, subject to subregulations (9) and (10), be issued within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the certificate.
(9) If the Commission is likely to take more than 6 months to issue a certificate of compliance, the Commission must tell the employer, by written notice, before the end of the 6 months, when the certificate is likely to be issued.
(10) If the Commission gives an employer written notice under subregulation (9), the certificate of compliance must be issued by the date specified in the notice.
9.26 Issue of certificate of compliance
(1) The Commission may issue a certificate of compliance to an employer in relation to a major hazard facility if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) the existing Commonwealth scheme under which the facility is regulated is comparable to the scheme set out in this Part; and
(b) the employer has been complying with the existing Commonwealth scheme; and
(c) the employer’s continued compliance with the existing Commonwealth scheme would satisfy the requirements of Subdivision B of Division 9.4.
Note An application may be made under regulation 9.34 for the transfer of a certificate issued under this regulation.
(2) For subregulation (1), in determining whether the existing Commonwealth scheme is comparable to the scheme set out in this Part, the Commission must have regard to the requirements imposed in relation to the facility by or under the existing Commonwealth scheme, including, in particular, whether the employer in control of the facility is required to undertake, prepare or provide any of the following:
(a) hazard identification;
(b) risk assessment;
(c) risk control by implementation of a safety management system;
(d) a safety report (however described);
(e) community information;
(f) training and education;
(g) emergency planning;
(h) security planning.
9.27 Period for which certificate of compliance is in force
If the Commission issues a certificate of compliance under paragraph 9.25 (5) (a), the certificate of compliance must specify:
(a) the date on which the certificate takes effect; and
(b) the period for which the certificate is to be in force.
9.28 Conditions of certificate of compliance
(1) A certificate of compliance is subject to the following conditions:
(a) if operations at the facility cease to be regulated by the existing Commonwealth scheme that applied in relation to the facility at the time the certificate was issued, the employer must, as soon as practicable after the existing Commonwealth scheme ceases to apply, give the Commission written notice of that fact;
(b) the employer to whom the certificate is issued must ensure that a copy of the certificate is kept at the major hazard facility operated under the certificate;
(c) the employer must ensure that the certificate is available for inspection on request by an investigator, an employee, a contractor, a health and safety representative or a representative of emergency services;
(d) the employer must allow the Commission access to the facility for the purpose of assessing the employer’s compliance with the conditions of the certificate;
(e) any other condition specified by the Commission in the certificate of compliance.
(2) The Commission may, by notice in writing given to the employer to whom the certificate of compliance is issued:
(a) add a condition to the certificate of compliance; or
(b) vary a condition specified in the certificate of compliance; or
(c) revoke a condition specified in the certificate of compliance.
(3) An employer must comply with the conditions to which a certificate of compliance is subject, including a condition that has been added or varied.
(4) A notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
9.29 Suspension or cancellation of certificate of compliance
(1) The Commission may suspend or cancel a certificate of compliance if:
(a) operations at the major hazard facility to which the certificate relates ceases to be regulated by the existing Commonwealth scheme that applied in relation to the facility at the time the certificate was issued; or
(b) the employer has failed to comply with a condition of the certificate of compliance; or
(c) the Commission is satisfied that the existing Commonwealth scheme that applied in relation to the facility at the time the certificate was issued is no longer comparable to the scheme set out in this Part; or
(d) the certificate was issued on the basis of:
(i) the provision of false or misleading information; or
(ii) a failure to disclose particular information;
in the employer’s application for the licence or under regulation 9.25; or
(e) the classification of the major hazard facility in relation to which the certificate was issued is revoked under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i).
(2) If the Commission decides to suspend or cancel a certificate of compliance under subregulation (1), the Commission must give the employer written notice of that decision.
(3) A notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the date from which the certificate of compliance is suspended or cancelled; and
(b) if the decision is to suspend the certificate of compliance — the period for which the certificate is suspended; and
(c) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(d) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
Subdivision C Bridging licence scheme for employers in control of identified major hazard facilities
9.30 Bridging licence taken to be issued to employer in control of identified major hazard facility
An employer in control of a facility that is an identified major hazard facility is taken to have been issued with a bridging licence under this regulation.
Note An application may be made under regulation 9.34 for the transfer of a bridging licence that is taken to have been issued under this regulation.
9.31 Period for which bridging licence is in force
A bridging licence that is taken to have been issued under regulation 9.30:
(a) takes effect on the day on which the definition of identified major hazard facility first applied to the facility; and
(b) ends:
(i) at the end of 18 months after that day; or
(ii) if the Commission has determined, in writing, a longer period in relation to the licence — at the end of the period determined by the Commission.
9.32 Conditions of bridging licence
(1) A bridging licence that is taken to have been issued under regulation 9.30 in relation to an identified major hazard facility is subject to the following conditions:
(a) the employer to whom the licence is taken to have been issued must comply, subject to subregulation (2), with any condition, duty or function that was imposed, in relation to the employer or the facility, by or under the identified State or Territory law to which the facility was subject immediately before the day on which this Part first applied to the employer in control of the facility;
(b) any other condition specified by the Commission in relation to the licence.
(2) The Commission may, by notice in writing given to the employer:
(a) add a condition to the bridging licence; or
(b) vary a condition specified in relation to the bridging licence; or
(c) revoke a condition specified in relation to the bridging licence; or
(d) specify that the employer to whom the licence is taken to have been issued is not required to comply with a specified condition, duty or function mentioned in paragraph (1) (a); or
(e) specify the manner in which the employer to whom the licence is taken to have been issued is required to comply with a specified condition, duty or function mentioned in paragraph (1) (a).
(3) An employer must comply with:
(a) the conditions to which a bridging licence is subject, including a condition that has been added or varied; and
(b) a notice given under subregulation (2).
(4) A notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
9.33 Powers, duties and functions under identified State or Territory laws
(1) This regulation applies if:
(a) an identified State or Territory law confers a power, duty or function:
(i) on a State or Territory authority; and
(ii) in relation to a person or facility; and
(b) the power, duty or function does not relate to the conferral of judicial power; and
(c) the power, duty or function could have been exercised or performed by the State or Territory authority in relation to an employer in control of a facility that is an identified major hazard facility if the employer was not taken to have been issued with a bridging licence under regulation 9.30.
(2) If the power, duty or function relates to the review of a decision:
(a) application may be made to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for the exercise or performance of the power, duty or function in relation to the employer; and
(b) the Administrative Appeals Tribunal may exercise or perform the power, duty or function in relation to the employer in the same way, and on the same conditions, as the power, duty or function could have been exercised or performed by the State or Territory authority.
(3) If the power, duty or function does not relate to the review of a decision:
(a) application may be made to the Commission for the exercise or performance of the power, duty or function in relation to the employer; and
(b) the Commission may exercise or perform the power, duty or function in relation to the employer in the same way, and on the same conditions, as the power, duty or function could have been exercised or performed by the State or Territory authority.
Subdivision D Transfer of licence or certificate of compliance between employers
9.34 Application for transfer of licence or certificate of compliance
(1) If:
(a) a licence issued under regulation 9.20, a bridging licence or a certificate of compliance is in force in relation to an employer (the first employer) and a major hazard facility; and
(b) the licence or certificate will be in force for at least 12 months; and
(c) another employer (the second employer) has taken, or will take, control of the major hazard facility from the first employer;
the second employer may apply to the Commission for the licence or certificate (as applicable) to be transferred to the second employer.
Note See also regulation 9.72 for requirements in relation to a major hazard facility that an employer will take control of from another employer.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in writing, in a form approved by the Commission; and
(b) be accompanied by a written assurance from the second employer that it will:
(i) comply with:
(A) this Part (to the extent to which it is applicable); and
(B) the conditions to which the licence or certificate of compliance is subject; and
(ii) take any other steps that are necessary to ensure the safe operation of the facility.
(3) The application must be made by the end of 6 months after the second employer takes control of the facility.
Note The application may be made before the second employer takes control of the facility.
9.35 Transfer of licence or certificate of compliance between employers
(1) On receiving an application from an employer for the transfer of a licence or a certificate of compliance under subregulation 9.34, the Commission must:
(a) transfer the licence or certificate to the employer, including transferring the licence or certificate subject to a condition; or
(b) refuse to transfer the licence or certificate to the employer; or
(c) ask the employer, by written notice, to give the Commission additional information necessary to assist it to decide whether to transfer the licence or certificate to the employer.
(2) If the Commission asks an employer to give the Commission additional information in relation to an application for a transfer:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to transfer the licence or certificate of compliance until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(3) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to transfer the licence or certificate of compliance (as applicable) on the basis of the information about the facility and the applicant that is available to the Commission.
(4) The Commission may transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance if it is satisfied that the employer to whom the licence will be transferred has the ability to:
(a) comply with the conditions of the licence or certificate (as applicable); and
(b) operate the major hazard facility in a safe manner.
(5) If the Commission refuses to transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance, the Commission must give the employer a written notice setting out:
(a) the reasons for refusing to transfer the licence or certificate; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
(6) A notice under subregulation (5) must be given within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the transfer.
(7) If the Commission decides to transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance to an employer, the licence or certificate must, subject to subregulations (8) and (9), be transferred within 6 months of receiving the employer’s application for the transfer.
(8) If the Commission is likely to take more than 6 months to transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance, the Commission must tell the employer, by written notice, before the end of the 6 months, when the transfer is likely to be made.
(9) If the Commission gives an employer written notice under subregulation (8), the Commission must transfer the licence or certificate of compliance by the date specified in the notice.
9.36 Effect of transfer of licence or certificate of compliance
(1) If the Commission decides to transfer a licence that was issued under regulation 9.20 to an employer under regulation 9.35, the transfer has effect as if:
(a) the licence had been issued to the employer under regulation 9.20; and
(b) if the transfer was made subject to a condition — the condition was imposed in relation to the licence under paragraph 9.22 (1) (d).
(2) If the Commission decides to transfer a certificate of compliance to an employer under regulation 9.35, the transfer has effect as if:
(a) the certificate of compliance was issued to the employer under paragraph 9.25 (5) (a); and
(b) if the transfer was made subject to a condition — the condition was imposed in relation to the certificate under paragraph 9.28 (1) (e).
(3) If the Commission decides to transfer a bridging licence to an employer under regulation 9.35, the transfer has effect as if:
(a) the licence was taken to have been issued to the employer under regulation 9.30; and
(b) if the transfer was made subject to a condition — the condition was imposed in relation to the licence under paragraph 9.32 (1) (b).
Division 9.4 Duties of an employer
Subdivision A Duties applying to all employers
9.37 Application of Subdivision A
This Subdivision applies to an employer in control of a major hazard facility.
9.38 Reporting requirements in relation to major accidents at major hazard facilities
If a major accident occurs at a major hazard facility, the employer must give a report to the Commission:
(a) within 6 weeks of the employer becoming aware of the major accident; or
(b) if the Commission has determined a longer period within which a report in relation to a major accident must be provided — within that longer period.
Note The employer may also be required to notify the Commission of the major accident — see Part 5 of the Occupational Health and Safety (Safety Arrangements) Regulations 1991 (formerly the Occupational Health and Safety (Commonwealth Employment) Regulations 1991).
9.39 Form of reports about major accidents
A report about a major accident that is given under regulation 9.38 must include the following information, as far as reasonably practicable:
(a) the name and business address of the employer;
(b) the address of the major hazard facility;
(c) the time and date of the accident;
(d) a statement about whether:
(i) a licence (including a bridging licence) issued or taken to have been issued under Division 9.3, or a certificate of compliance, was in force in relation to the major hazard facility and the employer at the time of the major accident; and
(ii) if a licence or a certificate of compliance was not in force in relation to the major hazard facility or the employer at the time of the major accident — the employer has made an application under Division 9.3 for a licence or a certificate of compliance;
(e) a description of the part of the major hazard facility where the major accident happened;
(f) the nature of the major accident;
(g) sufficient information to identify each material involved in the major accident;
(h) the quantity of each material involved in the major accident;
(i) the cause of the major accident;
(j) the effects of the major accident, if any, on:
(i) persons; and
(ii) property; and
(iii) the built and natural environment;
(k) the methods used to clean up or otherwise remedy the effects of the major accident;
(l) the effectiveness of any emergency plans and emergency procedures that were in place for the major hazard facility;
(m) action that the employer has taken, or proposes to take, to prevent recurrence of a major accident of the same kind.
Note Comcare may publish a form to facilitate the preparation of a report under regulation 9.39.
9.40 Service of reports
A report that is to be given to the Commission under regulation 9.38 may:
(a) be delivered in business hours to a Comcare office; or
(b) be given by a message transmitted to a computer system known to be in use by the Commission, being a message that is:
(i) in a form compatible with the computer system; and
(ii) capable of being recorded by the computer system.
9.41 Records of major accidents
For section 69 of the Act (‘records of accidents and dangerous occurrences’), an employer must retain a record of a report under regulation 9.38 for a period of 30 years.
Subdivision B Duties applying to an employer in control of certain major hazard facilities
9.42 Application of Subdivision B
(1) This Subdivision applies to an employer in control of a facility classified as a major hazard facility by the Commission under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), unless a certificate of compliance is in force in relation to the employer and the facility.
(2) This Subdivision also applies to an employer in control of an identified major hazard facility if a licence issued under regulation 9.20 is in force in relation to the employer and the facility.
9.43 Hazard identification
The employer must identify, in consultation with employees, contractors (as far as is practicable) and health and safety representatives:
(a) all reasonably foreseeable hazards at the major hazard facility that may cause a major accident; and
(b) the kinds of major accidents that may occur at the major hazard facility, the likelihood of a major accident occurring and the likely consequences of a major accident.
9.44 Risk assessment
(1) If a hazard or kind of major accident at the major hazard facility is identified under regulation 9.43, the employer must ensure that any risks associated with the hazard or major accident are assessed, in consultation with employees, contractors (as far as is practicable) and health and safety representatives.
(2) The employer must ensure that the risk assessment is reviewed:
(a) within 5 years after the assessment is carried out, and afterwards at intervals of not more than 5 years; and
(b) before a modification is made to the major hazard facility that may significantly change a risk identified under regulation 9.43; and
(c) when developments in technical knowledge or the assessment of hazards and risks may affect the method at the major hazard facility for assessing hazards and risks; and
(d) if a major accident occurs at the major hazard facility.
9.45 Risk control
(1) The employer must, in consultation with employees, contractors (as far as is practicable) and health and safety representatives, ensure that any risk associated with a hazard at the major hazard facility is:
(a) eliminated; or
(b) if it is not practicable to eliminate the risk — reduced as far as practicable.
(2) The employer must:
(a) implement measures at the major hazard facility to minimise the likelihood of a major accident occurring; and
(b) implement measures to limit the consequences of a major accident if it occurs; and
(c) protect relevant persons, an at‑risk community, and the built and natural environment surrounding the major hazard facility, by establishing an emergency plan and procedures in accordance with regulation 9.53.
9.46 Safety management system
(1) The employer must prepare and implement a comprehensive and integrated system (a safety management system) for managing safety and preventing the occurrence of major accidents at the major hazard facility.
(2) The safety management system must:
(a) be documented in writing; and
(b) provide for the following:
(i) the objectives of the safety management system;
(ii) the procedures that must be followed to achieve those objectives;
(iii) the performance standards that must be met by the safety management system;
(iv) the means of ensuring that relevant persons at the major hazard facility comply with the performance standards.
9.47 Safety report
(1) The employer must prepare a safety report for the major hazard facility in accordance with subregulation (3):
(a) either:
(i) if the facility was classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) — within 15 months after the date on which the facility was classified; or
(ii) if the facility is an identified major hazard facility — within the period determined by the Commission in relation to the facility; or
(b) if the Commission has approved another period under subregulation (7) — within the period approved by the Commission.
Note 1 If the safety report is prepared by a person who is an approved assessor, the assessment of the safety report must be carried out by a different approved assessor, in accordance with subregulations 9.49 (4) and (5).
Note 2 If the Commission approves another period under subregulation (7), the Commission may ask the employer to submit a timetable for the preparation of the safety report — see subregulation (8).
(2) An employer in control of a facility that is classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) must give the Commission an outline of the safety report within 6 months after the date on which the facility was classified.
(3) The outline of the safety report must include:
(a) a written statement describing the process the employer will follow to develop the safety report; and
(b) a written program containing details and timeframes for the preparation of the safety report; and
(c) details of the consultation that will be undertaken during the preparation of the safety report; and
(d) a draft of the emergency plan that the employer proposes to include in the safety report.
(4) The safety report must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be prepared, and revised (if necessary), in consultation with employees, contractors, and health and safety representatives at the major hazard facility; and
(c) contain the information specified in Schedule 9A.
(5) If an employer is unable to prepare the safety report within the period mentioned in paragraph (1) (a) or (b) (as applicable), the employer may apply to the Commission for an extension of the period within which the report must be prepared.
(6) An application under subregulation (5) must be made as soon as practicable but, in any event, not later than 3 months before the expiration of the period mentioned in paragraph (1) (a) or (b) (as applicable).
(7) If an application is made to the Commission under subregulation (5), the Commission may approve a period within which the employer must prepare the safety report.
(8) If the Commission approves a period under subregulation (7), the Commission may ask the employer to submit a timetable for the preparation of the report.
9.48 Review of safety report by employer
(1) The employer must review and, if necessary, revise the safety report for the major hazard facility:
(a) if a proposed modification to the major hazard facility will alter the risks associated with the facility — before the modification is made; and
(b) when developments in technical knowledge or the assessment of hazards and risks may affect the method at the major hazard facility for assessing hazards and risks; and
(c) at least once every 5 years after the safety report is first prepared; and
(d) if the Commission requests a review of the safety report; and
(e) if a major accident occurs at the major hazard facility.
(2) In reviewing the safety report, the employer must take into account any changes at the major hazard facility in relation to the following matters:
(a) hazards and risks;
(b) the safety management system;
(c) technology;
(d) training programs;
(e) work procedures;
(f) use of land near the major hazard facility.
9.49 Assessment of safety report by approved assessor
(1) If the employer applies, or intends to apply, under Division 9.3, for a licence to operate the major hazard facility in relation to the facility, the employer must arrange for the safety report for the facility to be assessed in accordance with this regulation.
Note The employer’s application for a licence must be accompanied by an executive summary of the assessment of the current safety report for the major hazard facility — see paragraph 9.18 (2) (b).
(2) Subject to subregulations (3), (4) and (5), the assessment of the safety report must be carried out by an approved assessor.
(3) The assessment of the safety report must not be carried out by:
(a) an approved assessor who is an employee of, or a contractor of, the employer; or
(b) an individual who is employed, engaged or contracted by an approved assessor who is an employee of, or a contractor of, the employer.
(4) If the safety report was prepared by an approved assessor, the assessment of the safety report must not be carried out by:
(a) that approved assessor; or
(b) any individual who is employed, engaged or contracted by the approved assessor.
(5) If the safety report was prepared by an individual (the first individual) who is employed, engaged or contracted by an approved assessor, the assessment of the safety report must not be carried out by:
(a) the approved assessor; or
(b) the first individual; or
(c) any individual who is employed, engaged or contracted by:
(i) the approved assessor; or
(ii) the first individual.
9.50 Provision of information to community
(1) The employer must ensure that adequate information is given to an at‑risk community on the procedures to be followed if a major accident occurs at the major hazard facility.
(2) The information given under subregulation (1) must include the following details:
(a) the name and location of the major hazard facility;
(b) the name, title and telephone number of a person at the major hazard facility who can be contacted for information about a major accident;
(c) general information about the nature of the hazards related to the facility, including potential effects on people, property and the built and natural environment;
(d) the system to be used for warning people likely to be affected by a major accident at the major hazard facility and for keeping those people informed about an accident at the facility;
(e) the actions people should take if a major accident occurs;
(f) relevant information about the off‑site emergency procedures formulated under subparagraph 9.53 (2) (b) (ii).
9.51 Training program
(1) The employer must develop a training program at the major hazard facility:
(a) for the purpose of assisting a relevant person at the major hazard facility to achieve a reasonable standard of knowledge and practice in occupational health and safety that is appropriate to the person’s role and responsibilities at the major hazard facility; and
(b) that addresses the hazards and risks identified under regulation 9.43.
(2) The training program must include the following standards:
(a) practices and procedures that must be followed by relevant persons at the major hazard facility to prevent a major accident;
(b) emergency procedures that must be followed if a major accident occurs;
(c) a standard that sets out the responsibilities of employees and contractors under the safety management system.
(3) The employer must ensure that the training program is monitored, reviewed, modified, recorded and undertaken in consultation with the employees, contractors (as far as is practicable) and health and safety representatives.
9.52 Ongoing training and education
The employer must ensure that each relevant person at the major hazard facility:
(a) takes part in the training program developed under regulation 9.51 before the person first starts work at, or visits, the major hazard facility; and
(b) receives further education and training:
(i) as often as necessary; and
(ii) to maintain the occupational health and safety competency standards; and
(iii) before implementing any modifications of the major hazard facility; and
(iv) before introducing new plant, processes, operating procedures or materials to the major hazard facility; and
(v) before any change is made to the safety management system for the major hazard facility.
9.53 Emergency plan
(1) The employer must, in consultation with employees, contractors (as far as is practicable), health and safety representatives and emergency services, prepare an emergency plan for the major hazard facility for the purposes of:
(a) containing and controlling a major accident at the major hazard facility, so as to minimise the effect of the accident on people, property and the built and natural environment; and
(b) implementing measures to protect people, property and the built and natural environment if a major accident occurs.
(2) The employer must:
(a) ensure that the emergency plan addresses the consequences of a major accident at the facility, in relation to the facility and the area surrounding the facility; and
(b) in consultation with the emergency services, establish, maintain and agree to include in the emergency plan:
(i) procedures (on‑site emergency procedures) setting out the action to be taken inside the major hazard facility in relation to a major accident at the facility; and
(ii) procedures (off‑site emergency procedures) setting out action to be taken outside the major hazard facility in relation to a major accident at the facility; and
(c) ensure that the on‑site emergency procedures and the off‑site emergency procedures complement each other.
(3) The emergency plan, the on‑site emergency procedures and the off‑site emergency procedures must be prepared:
(a) if the facility was classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) — within 3 months after the date on which the facility was classified; and
(b) if the facility is an identified major hazard facility — within 3 months after the date on which a licence was first issued under regulation 9.20 in relation to the facility.
(4) The employer must:
(a) ensure that the emergency plan is kept in a place that is readily accessible by employees, contractors, health and safety representatives and emergency services; and
(b) regularly test, evaluate and review and, if necessary, revise (in accordance with regulation 9.54) the emergency plan to ensure its effectiveness; and
(c) ensure that all relevant persons at the major hazard facility are appropriately trained in the implementation of the on‑site and off‑site emergency procedures; and
(d) give information to an at‑risk community about the off‑site emergency procedures, in accordance with regulation 9.50.
9.54 Review of emergency plan
(1) The employer must, in consultation with employees, contractors (as far as is practicable), health and safety representatives and emergency services, review and, if necessary, revise the emergency plan prepared under regulation 9.53 for the major hazard facility:
(a) when the safety report for the major hazard facility is reviewed under regulation 9.48; or
(b) after a major accident at the major hazard facility; or
(c) when, because of the result of a test undertaken under paragraph 9.53 (4) (b), it is necessary to do so; or
(d) when requested in writing to do so by the Commission.
(2) The review of the emergency plan must:
(a) take into account all relevant modifications of the major hazard facility; and
(b) take into account, in the off‑site emergency procedures, any changes to the use of the land surrounding the major hazard facility.
9.55 Securing the major hazard facility
(1) The employer must establish a system for securing the major hazard facility that:
(a) controls entry to the major hazard facility by all persons at all times; and
(b) applies to all elements of the major hazard facility affecting its safe operation, including documents, computer hardware and software, and the boundaries of the facility.
(2) The employer must take all reasonably practicable steps to protect the major hazard facility from any action against the facility by any person who is not authorised to have access to the facility.
Subdivision C Additional duty applying to employer in control of identified major hazard facility
9.56 Provision of licence issued under identified State or Territory law
(1) An employer in control of an identified major hazard facility must give the Commission a copy of the licence (if any) (the former licence) that was issued or otherwise given to the employer, or in respect of the identified major hazard facility of which the employer is in control, under the identified State or Territory law to which the facility was subject immediately before the day on which this Part first applied to the employer.
(2) The employer must give the Commission a copy of the former licence within 30 days of the day on which the bridging licence that is taken to have been issued under regulation 9.30 in relation to the identified major hazard facility takes effect.
Note Paragraph 9.31 (a) explains when a bridging licence that is taken to have been issued under regulation 9.30 takes effect.
Division 9.5 Duties of an employee and a contractor
9.57 Duties of an employee and a contractor
(1) This regulation applies to a person who is an employee or a contractor of an employer in control of a major hazard facility.
(2) The person must, at all times while at work, comply with all practices and procedures relating to the prevention and control of major accidents at the major hazard facility.
Example
The person must participate, as required, in the training program developed by the employer under regulation 9.51 and in any further education and training provided pursuant to regulation 9.52.
(3) The person must, in the event of a major accident, comply with the major hazard facility’s emergency plan prepared under regulation 9.53.
(4) The person must report to the employer, as soon as practicable, any matter of which the person is aware that may affect the employer’s compliance with the provisions of this Part.
(5) If the person reasonably believes, based on his or her training and experience at work, that a major accident may occur, the person must, within the limits of his or her responsibilities at work and without risk to his, her or any other person’s health:
(a) take appropriate action to prevent the major accident, including, if necessary, interrupting the operation of the major hazard facility; and
(b) before, or as soon as possible after, taking such action:
(i) inform the person’s supervisor about the possibility of a major accident occurring; or
(ii) raise the alarm, in the most appropriate manner, about the possibility of a major accident occurring.
(6) If the person considers that a hazard exists at the major hazard facility that may cause a major accident, the person:
(a) must notify the employer about his or her concerns; and
(b) may notify the Commission about the hazard.
Division 9.6 Approval scheme for assessors
Subdivision A Definition
9.58 Definition for Division 9.6
In this Division:
safety report means:
(a) for:
(i) a facility classified as a major hazard facility under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i), other than a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force; or
(ii) an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a licence issued under this Subdivision is in force;
a report prepared in accordance with regulation 9.47; and
(b) for a major hazard facility in relation to which a certificate of compliance is in force — a report that deals with the kinds of matters specified in Schedule 9A and that is prepared in accordance with a condition of the certificate of compliance; and
(c) for an identified major hazard facility in relation to which a bridging licence is in force — a report that deals with the kinds of matters specified in Schedule 9A and that is prepared in accordance with a condition of the bridging licence.
Subdivision B Requirements for application for approval
9.59 Who may apply for approval?
A person, an organisation or a statutory authority of a State or Territory may apply to the Commission for approval as an assessor under this approval scheme.
Note There is no fee for making an application for approval under this approval scheme.
9.60 Form of application
An application must be made:
(a) in writing; and
(b) in a form approved by the Commission.
9.61 Information to be included in application
The following information must be included in an application made under this Subdivision:
(a) information about the applicant, including:
(i) the qualifications held by the applicant; and
(ii) a description of the applicant’s professional experience in relevant disciplines; and
(iii) the details of any security clearance held by the applicant;
(b) if the applicant is not an individual — information about the persons who, at the time the application is made, are:
(i) principals of the applicant; or
(ii) employees of the applicant who will, or who are likely to, participate in the assessment of safety reports;
(c) information about any actual or potential conflict of interest between the applicant’s business or other interests and the role and function of an approved assessor under this Part;
(d) any other information determined, by legislative instrument, by the Commission.
Subdivision C Decision on application
9.62 Commission to decide application
(1) On receiving an application under regulation 9.59, the Commission must:
(a) approve the applicant as an assessor; or
(b) refuse to approve the applicant as an assessor; or
(c) ask the applicant, by written notice, to give the Commission additional information necessary to assist it to decide whether to approve the applicant as an assessor.
(2) If the Commission asks an applicant to give the Commission additional information in relation to an application for approval:
(a) the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice; and
(b) the Commission must not decide whether or not to approve the applicant until the earlier of:
(i) the expiration of the period; and
(ii) the date the information is given to the Commission.
(3) If the additional information is not provided within the period specified in the notice, the Commission may decide whether or not to approve the applicant on the basis of the information about the applicant that is available to the Commission.
(4) The Commission may approve a person, an organisation or a statutory authority of a State or Territory (the applicant) as an assessor under this regulation if the Commission is satisfied that the applicant has the necessary skills, training, knowledge and abilities to perform the functions of an approved assessor under this Part.
(5) If the Commission refuses to approve an applicant, the Commission must give the applicant a written notice setting out:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the applicant’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
(6) A notice under subregulation (5) must be given within 6 months of receiving the application for approval.
(7) If the Commission decides to approve an applicant as an assessor, the Commission must notify the applicant within 6 months of receiving the application for approval.
9.63 Period for which approval is in force
(1) An approval must specify:
(a) the date on which it takes effect; and
(b) the period for which it is to be in force.
(2) The period for which the approval is to be in force must not be longer than 5 years from the date on which the approval takes effect.
Note If an approved assessor wishes to continue as an approved assessor after the period of approval expires, they must apply for a new approval.
Subdivision D Conditions of approval
9.64 Conditions of approval
(1) The approval of an assessor under regulation 9.62 is subject to the conditions specified by the Commission in the approval.
(2) The Commission may, by notice in writing given to an approved assessor:
(a) add a condition to the approval; or
(b) vary a condition specified in the approval; or
(c) revoke a condition specified in the approval.
(3) An approved assessor must comply with the conditions to which an approval is subject, including a condition that has been added or varied.
Subdivision E Revocation of approval
9.65 Revocation of approval
(1) The Commission may revoke an approval given under regulation 9.62 if it is satisfied that:
(a) the approved assessor has failed to comply with a condition of the approval; or
(b) the approval was given on the basis of false or misleading information, or a failure to disclose particular information, in the application for approval.
(2) If the Commission is of the opinion that an approval given under regulation 9.62 may be revoked, the Commission must:
(a) tell the approved assessor, in writing, of its opinion and the reasons for that opinion; and
(b) ask the approved assessor to show cause, in writing, within a specified period of at least 21 days, why the approval should not be revoked.
(3) If the approved assessor does not show adequate cause within the specified period, the Commission may revoke the approval.
(4) If the Commission decides to revoke the approval of an assessor under subregulation (3), the Commission must give the assessor written notice of that decision.
(5) A notice given under subregulation (4) must state:
(a) the date from which the approval is revoked; and
(b) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(c) the assessor’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
Subdivision F Register of approved assessors
9.66 Commission to maintain register of approved assessors
(1) The Commission must establish and maintain a register of approved assessors that sets out the following:
(a) the name of each approved assessor;
(b) if the approved assessor is an individual who carries on business under a name other than his or her own name — that other name;
(c) the business address of each approved assessor.
(2) If the Commission becomes aware that any particulars entered on the register in relation to an approved assessor are incorrect, the Commission must make such alterations to the register as are appropriate.
(3) The Commission must make the register available in electronic form.
Division 9.7 Miscellaneous
9.67 Review of decisions
An application may be made to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for the review of the following decisions:
(a) a decision under subregulation 9.05 (1) to notify an employer in control of an existing facility that an activity undertaken at the facility could cause a major accident;
(b) a decision under subregulation 9.05 (2) to notify a person that intends to be the employer in control of a facility that an activity that is likely to be undertaken at the facility once it is in operation could cause a major accident;
(c) a decision under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) to classify a potential major hazard facility as a major hazard facility;
(d) a decision under subparagraph 9.11 (1) (b) (i) to refuse to revoke the classification of a facility as a major hazard facility;
(e) a decision under paragraph 9.20 (1) (b) to refuse to issue a licence;
(f) a decision under paragraph 9.22 (1) (d) to specify a condition for a licence;
(g) a decision under subregulation 9.22 (2) to:
(i) add a condition to a licence; or
(ii) vary a condition specified in a licence; or
(iii) revoke a condition specified in a licence;
(h) a decision under subregulation 9.23 (1) to suspend or cancel a licence;
(i) a decision under paragraph 9.25 (5) (b) to refuse to issue a certificate of compliance;
(j) a decision under paragraph 9.28 (1) (e) to specify a condition for a certificate of compliance;
(k) a decision under subregulation 9.28 (2) to:
(i) add a condition to a certificate of compliance; or
(ii) vary a condition specified in a certificate of compliance; or
(iii) revoke a condition specified in a certificate of compliance;
(l) a decision under subregulation 9.29 (1) to suspend or cancel a certificate of compliance;
(m) a decision under paragraph 9.32 (1) (b) to specify a condition for a bridging licence;
(n) a decision under subregulation 9.32 (2) to:
(i) add a condition to a bridging licence; or
(ii) vary a condition specified in relation to a bridging licence; or
(iii) revoke a condition specified in relation to a bridging licence; or
(iv) specify the manner in which the employer to whom the licence is taken to have been issued is required to comply with a specified condition, duty or function mentioned in paragraph 9.32 (1) (a);
(o) a decision under paragraph 9.35 (1) (a) to transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance to an employer subject to a condition;
(p) a decision under paragraph 9.35 (1) (b) to refuse to transfer a licence or a certificate of compliance to an employer;
(q) a decision under paragraph 9.47 (1) (b) to determine a period within which a safety report must be prepared in relation to an identified major hazard facility;
(r) a decision under paragraph 9.62 (1) (b) to refuse to approve an applicant as an assessor;
(s) a decision under subregulation 9.64 (1) to specify a condition in relation to the approval of an applicant as an assessor;
(t) a decision under subregulation 9.64 (2) to:
(i) add a condition to the approval of an assessor; or
(ii) vary a condition specified in the approval of an assessor; or
(iii) revoke a condition specified in the approval of an assessor;
(u) a decision under subregulation 9.65 (3) to revoke the approval of an assessor;
(v) a decision under regulation 9.71 to give a direction to an employer in control of a major hazard facility or a potential major hazard facility.
Note Under section 27A of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975, the decision‑maker must give to any person whose interests are affected by the decision notice, in writing or otherwise, of the making of the decision and of the person’s right to have the decision reviewed. In giving the notice, the decision‑maker must have regard to the Code of Practice determined under section 27B of that Act (Gazette No. S 432, 7 December 1994).
9.68 Confidentiality of information
The Commission must protect the confidentiality of information given to it by an employer in control of a major hazard facility if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) protecting the confidentiality of the information will not compromise the safety of any person, property or the built or natural environment; or
(b) the information is national security information.
9.69 Annual report of the Commission
For paragraph 75 (e) of the Act, the annual report of the Commission must include an analysis of the operation of these Regulations in relation to the following facilities:
(a) a major hazard facility classified by the Commission under subparagraph 9.07 (1) (b) (i) in the financial year to which the annual report of the Commission relates;
(b) an identified major hazard facility that was taken to have been issued with a bridging licence in the financial year to which the annual report of the Commission relates.
9.70 Report to Minister on major accident
(1) If a report of an investigation of a major accident at a major hazard facility is provided to the Commission under section 53 of the Act, the Commission must, as soon as practicable after the report is provided to the Commission, prepare a summary of the report.
(2) The Commission must, as soon as practicable after the summary is prepared, provide to the Minister:
(a) a copy of the summary; and
(b) a statement about the following matters:
(i) whether the employer in control of the major hazard facility at the time that the major accident occurred had made an application, in accordance with Division 9.3, for a licence to operate the facility or for a certificate of compliance in relation to the facility;
(ii) whether a licence (including a bridging licence) or a certificate of compliance was issued, or taken to have been issued, under Division 9.3, to the employer in relation to the facility;
(iii) if a licence or certificate of compliance was issued or taken to have been issued — whether that licence or certificate of compliance was in force at the time that the major accident occurred;
(iv) if no licence or certificate of compliance was issued or taken to have been issued — the reason for this; and
(c) if the major hazard facility continues to operate after the major accident:
(i) a statement about whether the major hazard facility is operated at a level of safety that satisfies the requirements of:
(A) a licence or certificate issued, or taken to have been issued, under Division 9.3 that is in force in relation to the facility (if any); and
(B) this Part, to the extent that it is applicable to the employer; and
(ii) such information as the Commission considers is reasonably necessary to support the statement.
9.71 Directions to employer
(1) This regulation applies to an employer that is:
(a) an employer in control of a major hazard facility; or
(b) an employer in control of a potential major hazard facility.
(2) The Commission may give a direction, by written notice, to an employer mentioned in subregulation (1), with respect to the performance of the employer’s duties under these Regulations, for the purpose of ensuring the safety of:
(a) a person inside or outside of the facility; and
(b) property near the facility; and
(c) the built or natural environment.
(3) The employer must comply with a direction given under subsection (2).
(4) A written notice given under subregulation (2) must state:
(a) the reasons for the Commission’s decision; and
(b) the employer’s review rights under regulation 9.67.
9.72 Notification of transfer of control of major hazard facility
(1) If:
(a) a licence issued under regulation 9.20, a bridging licence or a certificate of compliance is in force in relation to an employer (the first operator) and a major hazard facility; and
(b) another person (the second operator) proposes to take control of the major hazard facility from the first employer;
the first operator must notify the Commission of this fact.
(2) The Commission may, by written notice, ask the first or second operator to give the Commission information about the proposal.
(3) If the Commission asks the first or second operator to give it information under subregulation (2), the information must be given to the Commission within the period specified in the notice.
Note 1 Providing advice and information to the Commission under this regulation will allow Comcare to advise operators on the application of this Part to the transfer of control.
Note 2 If a licence issued under regulation 9.20, a bridging licence or a certificate of compliance is in force in relation to the first employer, and that licence or certificate will be in force for less than 12 months, the licence or certificate cannot be transferred to the second operator — see regulation 9.34.
Part 10 Electricity
Division 10.1 Introduction
10.01 Object of Part 10
The object of this Part is to control the risks to the health or safety of persons from hazards arising from the use of electricity in a workplace by:
(a) ensuring that persons at a workplace are, as far as reasonably practicable, safe from the risk of injury or death caused by the use of electricity; and
(b) minimising the risk of injury or death because of electrical installations at a workplace; and
(c) ensuring that electrical installation work is carried out safely; and
(d) ensuring that electrical work is undertaken only by a person who is a competent person in relation to that work.
10.02 Definitions for Part 10
In this Part:
competent person, in relation to a specified task, means a person who:
(a) has, through a combination of training, education and experience, acquired knowledge and skills that enable the person to perform correctly that task; and
(b) meets any specific requirements imposed by a State or Territory law in relation to undertaking that task (including, for example, a State or Territory law that requires a person to be licensed to undertake the task).
Note Paragraph (a) of this definition reflects the definition of competent person in regulation 10.01.
electrical connection work means connecting electrical equipment to, or disconnecting electrical equipment from, a supply of electricity.
electrical equipment work means the repair, alteration or maintenance of electrical equipment.
electrical installation work means the repair, alteration or maintenance of an electrical installation.
electrical work means any of the following:
(a) electrical connection work;
(b) electrical equipment work;
(c) electrical installation work.
employer, in relation to a workplace, employee, equipment, thing or activity, means an employer who has management or control of the workplace, employee, equipment, thing or activity.
Division 10.2 Duties of employers
10.03 Duty to identify risks
(1) An employer must identify any risk of injury from:
(a) the existence or use of electricity at a workplace; and
(b) the existence, operation or use of electrical installations at the workplace.
(2) The employer must make a record of each risk that has been identified.
10.04 Duty to assess and control risks
(1) If a risk is identified under subregulation 10.03 (1), the employer must:
(a) arrange for an assessment of the risk; and
(b) either:
(i) take measures to eliminate the risk; or
(ii) if it is not reasonably practicable to eliminate the risk — take measures to minimise the risk as far as reasonably practicable.
(2) The employer must make a record of:
(a) each risk that has been assessed; and
(b) each measure taken to eliminate or minimise the risk.
10.05 Duty to ensure that electrical work is carried out by a competent person
An employer must take all reasonably practicable steps to ensure that electrical work is carried out at a workplace:
(a) only by a competent person; and
(b) only in accordance with Australian/New Zealand Standard Wiring Rules (AS/NZS 3000:2000).
Note Electrical work includes the maintenance of electrical equipment or an electrical installation at a workplace.
10.06 Duty to inspect and test electrical equipment
(1) This regulation applies to electrical equipment that is:
(a) supplied with electricity through an electrical outlet socket; and
(b) either:
(i) used in construction work; or
(ii) located at a workplace at which the safe operation of the electrical equipment could be affected by a hostile operating environment.
(2) An employer must ensure that the electrical equipment is regularly inspected by a competent person.
(3) An employer must ensure that the electrical equipment is regularly tested by a competent person.
(4) In subparagraph (1) (b) (ii):
hostile operating environment means an operating environment where electrical equipment in its normal use is subject to operating conditions that are likely to result in:
(a) damage to the equipment; or
(b) the compromising of insulation or of other protective measures.
Examples
1 Conditions that might cause mechanical damage to the equipment.
2 Conditions that might expose the equipment to moisture, heat, vibration, corrosive substances or dust that is likely to result in damage to the equipment.
10.07 Duty to inspect and test electrical installations
An employer must ensure that each electrical installation at a workplace is inspected and tested by a competent person during the period:
(a) starting when it is installed; and
(b) ending before it is first energised for the purpose of normal use.
Note Further duties relating to electrical installation work are set out in Division 10.4.
10.08 Duty to disconnect unsafe electrical equipment and installations
(1) If electrical equipment or an electrical installation at a workplace is unsafe, or is reasonably believed to be unsafe, the employer must, as soon as practicable, arrange for the installation or equipment to be:
(a) disconnected from the electricity supply; and
(b) repaired, removed from use, or replaced.
(2) The employer must also:
(a) place at least one warning label or sign on the equipment in a prominent place; and
(b) take measures to avoid inadvertent reconnection while the equipment is disconnected.
10.09 Underground electrical cables
An employer at a workplace at which excavation work is to be carried out must:
(a) obtain information about the location of all underground electrical cables at or near the workplace; and
(b) give the information to all persons who are undertaking, or intending to undertake, excavation work at the workplace.
10.10 Overhead electrical lines
(1) Subject to subregulation (2), an employer must ensure that none of the following comes within close proximity of overhead electrical lines at a workplace:
(a) employees at the workplace;
(b) plant;
(c) tools;
(d) equipment other than tools;
(e) material used in or arising from the work.
(2) Subregulation (1) does not apply to work that is done in accordance with:
(a) a written risk assessment; and
(b) a safe work method statement; and
(c) the requirements of the electricity supply authority in relation to the workplace.
10.11 Cords, cables and fittings
(1) An employer must ensure that an electrical cord or electrical cable:
(a) is located where it is not likely to be damaged; and
(b) is protected from damage; and
(c) is not laid across a passageway unless the cord or cable is suitably protected.
(2) An employer must ensure that a fitting for an electrical cord or electrical cable:
(a) is located where the fitting and the cord or cable are not likely to be damaged; and
(b) is protected from damage; and
(c) for a fitting that can be laid — is not laid across a passageway unless the fitting and the cord or cable are suitably protected.
10.12 Hazard warning signs
(1) An employer must ensure, as far as reasonably practicable, that signs are displayed at or near an area of the workplace at which there is a risk of exposure to hazards arising from electricity.
(2) The employer must ensure that each sign:
(a) warns of the hazards; and
(b) if necessary — restricts access of employees, contractors and other persons at the workplace to the area.
Division 10.3 Duty to keep records
10.13 Record‑keeping
(1) In addition to keeping the records required under Division 10.2, an employer must keep a record of:
(a) all maintenance carried out on electrical equipment and electrical installations; and
(b) all inspections and tests carried out under regulations 10.06 and 10.07.
(2) The records must include the following information:
(a) the name of the person who carried out the maintenance, inspection or test;
(b) the date or dates on which the maintenance, inspection or test was carried out;
(c) the result of the maintenance, inspection or test;
(d) the date on which the next inspection or test is to be carried out.
(3) The employer must keep the record for at least 5 years.
Division 10.4 Electrical installations
10.14 Electrical installations not energised
(1) Subject to subregulation (2), an employer must ensure that electrical installation work at a workplace is not carried out at any time at which a circuit or apparatus of the installation on which the work will be carried out is energised.
(2) Subregulation (1) does not apply to electrical installation work if all of the following circumstances exist:
(a) it is necessary, to minimise the risk of injury, to carry out the work while the circuits and apparatus are energised;
(b) a written risk assessment for the work has been completed in consultation with the person proposing to do the work;
(c) the work is to be carried out in accordance with a safe work method statement for the work;
(d) the work has been authorised by the person in control of the workplace;
(e) each employee who is to do the work is appropriately qualified, trained and instructed in safe work practices for the particular task, including the proper use of equipment, tools, accessories and personal protective equipment;
(f) appropriate test equipment, tools and accessories are:
(i) provided to the persons doing the work; and
(ii) properly used; and
(iii) well maintained;
(g) appropriate clothing and personal protective equipment are:
(i) provided to the persons doing the work; and
(ii) properly worn and used;
(h) the isolation point of the electricity supply:
(i) has been clearly identified; and
(ii) is able to be reached and operated quickly without any need to remove or negotiate obstacles;
(i) the work area is clear of obstructions to safe entry and exit;
(j) unauthorised persons are prevented from entering the work area by signage or barriers;
(k) the work is carried out in the presence of a safety observer who is:
(i) competent to perform the task to be carried out; and
(ii) competent in electrical rescue and cardio‑pulmonary resuscitation.
10.15 Electrical installation work — safe system of work
(1) If subregulation 10.14 (1) applies to an employer, the employer must ensure that a safe system of work exists to ensure that:
(a) electrical installation work at the workplace is not carried out at any time at which a circuit or apparatus of the installation on which the work will be carried out is energised; and
(b) each circuit or apparatus of the installation on which the electrical installation work will be carried out:
(i) is not energised when the work commences; and
(ii) does not become energised until the work is completed.
(2) If subregulation 10.14 (2) applies to an employer, the employer must ensure that electrical installation work at a workplace is carried out using a safe system of work that includes procedures to ensure that the circuits and apparatus of the installation on which the work will be carried out are energised to the minimum extent practicable.
(3) For subregulations (1) and (2), the employer must also ensure that the safe system of work includes procedures to eliminate or minimise the risk that the employee carrying out the work may inadvertently contact:
(a) a part of the installation that remains energised; or
(b) another electrical installation; or
(c) electrical equipment.
Division 10.5 Duties of employees
10.16 Duty to undertake electrical work
An employee must not undertake electrical work at a workplace unless the employee is a competent person in relation to that work.
Division 10.6 Duties of contractors
10.17 Duty to undertake electrical work
A contractor must not undertake electrical work at a workplace unless the contractor is a competent person in relation to that work.
Part 11 Driver fatigue
Division 11.1 Introduction
11.01 Object of Part 11
The objective of this Part is to control driver fatigue, and to ensure the safety of drivers and other people:
(a) by the implementation of suitable plans to manage the fatigue of drivers of heavy trucks, buses and commercial buses; and
(b) by requiring employees and contractors to comply with driver fatigue management plans; and
(c) by requiring consignors, consignees and other people not to act in a way that imposes unreasonable timeframes on drivers.
11.02 Application of Part 11
(1) This Part applies to an employer who is in control of:
(a) a heavy truck; or
(b) a bus; or
(c) a commercial bus;
because the employer uses the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus on a regular basis to transport people or goods.
(2) Divisions 11.1 and 11.4 of this Part also apply to an employer who is a consignor or consignee.
11.03 Definitions for Part 11
In this Part:
bus means a motor vehicle that:
(a) is built principally for the purpose of carrying people; and
(b) is capable of carrying 12 or more seated adults (including the driver); and
(c) is not operated to carry people or goods for reward, or as part of a commercial business.
commercial bus means a motor vehicle that:
(a) is built principally for the purpose of carrying people; and
(b) is capable of carrying 12 or more seated adults (including the driver); and
(c) is operated to carry people or goods for reward, or as part of a commercial business.
consignee means an employer who engages or proposes to engage a person who is not an employee, directly or through an agent or other intermediary, for the purpose of:
(a) transporting goods to the employer by road; or
(b) transporting people to the employer by road.
consignor means an employer who engages or proposes to engage a person who is not an employee, directly or through an agent or other intermediary, for the purpose of:
(a) transporting goods from the employer by road; or
(b) transporting people from a workplace by road; or
(c) transporting people by road from another place for the purposes of the employer.
driver means a person who drives a heavy truck, a bus or a commercial bus for the purposes of an employer, whether the driver is an employee or not.
driver fatigue management plan means a plan that:
(a) sets out details of an employer’s processes to manage the risks imposed by driver fatigue; and
(b) is prepared in accordance with regulation 11.07.
driving means the driving of a heavy truck, bus or commercial bus, including:
(a) being in the driver’s seat of a stationary heavy truck, bus or commercial bus while the engine is running; and
(b) being in a heavy truck, bus or commercial bus for the purpose of:
(i) instructing another person to drive it; or
(ii) supervising another person’s driving of the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus.
driving time, for a driver, is the time that the driver spends driving on:
(a) a road within the meaning of the National Transport Commission (Road Transport Legislation — Driving Hours Regulations) Regulations 2006; or
(b) a road‑related area within the meaning of those Regulations.
heavy truck means:
(a) a motor vehicle that:
(i) is not a bus or tram; and
(ii) has a Gross Vehicle Mass (GVM) of over 12 tonnes; and
(b) a motor vehicle that:
(i) is not a bus or tram; and
(ii) forms part of a combination vehicle in relation to which the total of the GVMs of the vehicles in the combination is more than 12 tonnes.
rest time, for a driver, is a continuous period of at least 15 minutes that is not the driver’s work time.
work time, for a driver, is the total of:
(a) the driver’s driving time; and
(b) any time that the driver spends:
(i) loading or unloading a heavy truck, bus or commercial bus to which this Part relates; or
(ii) inspecting, servicing or repairing the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus; or
(iii) inspecting or attending to the load on the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus; or
(iv) attending to the passengers of the bus or commercial bus; or
(v) cleaning or refuelling the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus; or
(vi) performing marketing tasks in relation to the operation of the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus; or
(vii) helping with, or supervising, an activity mentioned in paragraph (a) or subparagraphs (i) to (vi); or
(viii) recording information, or completing a document, in accordance with these Regulations in relation to the operation of the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus; or
(ix) recording information, or completing a document, in accordance with another obligation in relation to the operation of the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus.
Division 11.2 Duties of employers
11.04 Duty to assess and manage fatigue of drivers
(1) An employer must identify:
(a) any significant risk of serious injury; or
(b) any risk of death;
arising from the fatigue of a driver.
(2) The employer must make a record of each risk that has been identified.
11.05 Duty to assess risks
(1) If a risk is identified under subregulation 11.04 (1), the employer must:
(a) arrange for an assessment of the risk; and
(b) either:
(i) take measures to eliminate the risk; or
(ii) if it is not reasonably practicable to eliminate the risk — take measures to minimise the risk as far as reasonably practicable.
(2) The employer must make a record of:
(a) each risk that has been assessed; and
(b) each measure taken to eliminate or minimise the risk.
11.06 Duty to ensure that driver does not risk fatigue
An employer must not allow a driver to transport people or goods in a heavy truck, a bus or a commercial bus for the purposes of the employer unless the employer has complied with regulations 11.04 and 11.05.
11.07 Duty to develop and implement driver fatigue management plan
(1) An employer must develop and implement a management plan (a driver fatigue management plan) for the control of the risks of serious injury or death arising from the fatigue of a driver who is:
(a) an employee; or
(b) a contractor.
(2) The employer must ensure that the management plan:
(a) deals with all drivers who are employees or contractors; and
(b) is prepared in consultation with those employees; and
(c) is prepared, as far as practicable, in consultation with those contractors.
(3) The management plan must include arrangements for the following matters:
(a) the preparation of rosters for drivers that take into account:
(i) timeframes for carrying out the transport safely; and
(ii) times actually taken to perform tasks; and
(iii) the rest periods required to recover from the fatigue effects of work; and
(iv) the cumulative effects of fatigue over more than one day; and
(v) the management of the cumulative effects of driving during the day and during the night;
(b) identifying the driver’s fitness for the work, including ensuring that the driver will undertake a medical examination at least once in each period of 3 years to determine his or her fitness to continue as a driver;
(c) training and education of drivers about fatigue management, including:
(i) ensuring the driver’s fitness for duty before commencing work; and
(ii) planning the driver’s non‑work time to ensure that the driver rests adequately; and
(iii) ways of recognising and dealing with fatigue;
(d) procedures and processes for managing incidents relating to fatigue, including recording the details of the procedures and processes;
(e) establishing and maintaining safe conditions at a workplace, as far as reasonably practicable.
(4) The management plan must also include arrangements for the scheduling and conduct of transport in a way that controls the risk of serious injury or death arising from a driver’s fatigue, including:
(a) arrangements for the way in which, and the time in which, the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus is to be loaded and unloaded; and
(b) arrangements for time spent waiting for the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus to be loaded or unloaded; and
(c) arrangements for determining timeframes for carrying out the transport safely; and
(d) arrangements for rest periods required to recover from fatigue; and
(e) arrangements for the management of the cumulative effects of fatigue; and
(f) arrangements for the management of the cumulative effects of driving during the day and during the night.
(5) The management plan must also include arrangements for the management of work time and rest times, including arrangements to ensure that:
(a) as far as reasonably practicable, the driver’s driving time, work time and rest time are consistent with the regulated hours specified in Part 2 of Schedule 1 to the National Transport Commission (Road Transport Legislation — Driving Hours Regulations) Regulations 2006; and
(b) if an employer decides to require or allow driving time, work time or rest time that is not consistent with those regulated hours:
(i) the employer records the reason for requiring or allowing the different time; and
(ii) the employer records the hours that are required or allowed; and
(iii) the employer records the measures to be taken to control the risk of serious injury or death arising from fatigue.
(6) The management plan must also contain:
(a) a timetable for the implementation of the plan; and
(b) an explanation of the responsibilities of people involved with the implementation of the management plan.
(7) The employer must:
(a) keep its management plan current; and
(b) review its management plan at least once in each period of 3 years; and
(c) keep accurate records relating to the implementation, operation and review of its management plan; and
(d) make a copy of the plan available to each driver; and
(e) make a copy of the plan available on request to a person who may be at risk of serious injury or death arising from a driver’s fatigue.
Division 11.3 Additional duty of employer to keep records
11.08 Record‑keeping
(1) In addition to keeping the records required under Division 11.2, an employer must keep a record of:
(a) all driving time, work time and rest time taken on a day by a driver who is an employee; and
(b) the final destination, on a day, of each driver who:
(i) is an employee; and
(ii) is required to drive a heavy truck, bus or commercial bus that forms the whole or part of a workplace.
(2) The employer must also keep a record of the odometer reading, at the end of each period of work time, for each heavy truck, bus and commercial bus that forms the whole or part of a workplace.
(3) The employer must keep records required under Division 11.2 or this Division:
(a) in a clear and systematic manner; and
(b) for at least 5 years from the date on which the record is made.
Division 11.4 Duty of employer in the capacity of consignee or consignor
11.09 Consignee or consignor
(1) A consignor or consignee must not enter into a contract with another person for the transport of the people or goods unless the employer is satisfied, on reasonable grounds, that the proposed timetable (if any) for the transport is reasonable, having regard to:
(a) the risk of serious injury or death arising from a driver’s fatigue; and
(b) the time that is likely to be reasonable for carrying out the transport, including:
(i) time in which the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus is to be loaded and unloaded; and
(ii) time that is likely to be spent waiting for the heavy truck, bus or commercial bus to be loaded or unloaded; and
(iii) the rest periods required to recover from the fatigue effects of work.
(2) The consignor or consignee must also keep a record of the reasons why the consignor or consignee considers the proposed timetable (if any) to be reasonable.
Division 11.5 Duty of drivers who are employees
11.10 Cooperation with driver fatigue management plan
(1) A driver who is an employee must perform his or her work as a driver in accordance with the applicable driver fatigue management plan.
(2) A driver who is an employee must cooperate with his or her employer to the extent necessary to ensure that the employer’s driver fatigue management plan complies with regulation 11.07.
(3) A driver who is an employee must attend a medical examination arranged by the employer in compliance with paragraph 11.07 (3) (b).
Division 11.6 Duty of drivers who are contractors
11.11 Cooperation with driver fatigue management plan
(1) A driver who is a contractor must perform his or her work as a driver in accordance with the applicable driver fatigue management plan.
(2) A driver who is a contractor must cooperate with an employer to the extent necessary to ensure that the employer’s driver fatigue management plan complies with regulation 11.07.
[3] Regulation 20.01, definition of electrical installation
substitute
electrical equipment means an appliance, wire, fitting, cable, conduit, meter, insulator, apparatus, material or other electrical article that generates, uses, conveys or controls electricity.
electrical installation means electrical equipment that is fixed, or intended to be fixed, in, on, under or over land.
[4] Subregulation 20.01 (1), paragraph (b) of definition of relevant person
substitute
(b) a contractor in respect of whom an employer has obligations in accordance with subsection 16 (4) of the Act;
[5] After Schedule 8
insert
Schedule 9 Materials at major hazard facilities and potential major hazard facilities — threshold quantities
(regulations 9.03, 9.06 and 9.08)
Part 1 Classification of explosive materials
1 Determining Subclass of explosive materials stored with other explosive materials
For the purpose of column 2 of items 44 to 47 of Part 2, if explosive materials of different hazard divisions are present in the same area of a major hazard facility or a potential major hazard facility, the Subclass of each explosive material present must be determined in accordance with the following table and the notes to the table.
HAZARD DIVISION | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
1.3 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
1.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
1.5 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
1.6 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
Notes to the table
Note 1 If explosive materials of more than 2 Divisions are present, any 2 of those Divisions are to be considered in determining a resultant Division, which must then be considered with the next Division, and so on until all Divisions present have been considered.
Note 2 If 2 or more explosive materials of Division 1.6 are present, the subclass of those materials may be determined to be Division 1.6 only if it is proved by testing or analogy that there is no additional risk of sympathetic detonation between the materials. Otherwise, the subclass of those materials must be determined to be Division 1.1.
Part 2 Threshold quantities
Item | Material | UN number | Threshold quantity
(tonnes) |
General |
1 | Acetone cyanohydrin | 1541 | 20 |
2 | Acetylene | 1001 | 50 |
3 | Acrolein | 1092 | 200 |
4 | Acrylonitrile | 1093 | 200 |
5 | Allyl alcohol | 1098 | 20 |
6 | Allylamine | 2334 | 200 |
7 | Ammonia — anhydrous, liquefied or ammonia solutions, relative density less than 0.880 at 15 C in water, with more than 50% ammonia | 1005 | 200 |
8 | Ammonium nitrate fertilisers | 2067 2068 2069 2070 | 5 000 |
9 | Ammonium nitrate, with no more than 0.2% combustible substances, including any organic substance calculated as carbon, to the exclusion of any other added substance | 1942 | 2 500 |
10 | Arsenic pentoxide, Arsenic (V) acid and other salts | 1559 | 10 |
11 | Arsenic trioxide, Arsenious (III) acid and other salts | 1561 | 0.10 |
12 | Arsine | 2188 | 0.01 |
13 | Bromine or Bromine solutions | 1744 | 100 |
14 | Carbon disulfide | 1131 | 200 |
15 | Chlorine | 1017 | 25 |
16 | Dioxins | | 0.10 |
17 | Ethyl nitrate | | 50 |
18 | Ethylene dibromide | 1605 | 50 |
19 | Ethylene oxide | 1040 | 50 |
20 | Ehtyleneimine | 1185 | 50 |
21 | Fluorine | 1045 | 25 |
22 | Formaldehyde | 1198 2209 | 50 |
23 | Hydrofluoric acid solution (greater than 50%) | 1790 | 50 |
24 | Hydrogen | 1049 | 50 |
25 | Hydrogen chloride: (a) anhydrous; | 1050 | 250 |
| (b) refrigerated liquid | 2186 | 250 |
26 | Hydrogen cyanide | 1051 1614 | 20 |
27 | Hydrogen fluoride | 1052 | 50 |
28 | Hydrogen sulfide | 1053 | 50 |
29 | LP gases | 1011 1012 1075 1077 1978 | 200 |
30 | Methyl bromide | 1062 | 200 |
31 | Methane, or natural gas | 1971 1972 | 200 |
32 | Methyl isocyanate | 2480 | 0.15 |
33 | Oxides of nitrogen, including nitrous oxide, nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen trioxide | 1067 1070 1660 1975 2201 2421 | 50 |
34 | Oxygen | 1072 1073 | 2 000 |
35 | Phosgene | 1076 | 0.75 |
36 | Propyleneimine | 1921 | 200 |
37 | Propylene oxide | 1280 | 50 |
38 | Sodium chlorate, solid | 1495 | 200 |
39 | Sulfuric anhydride (syn. Sulphur trioxide) | 1829 | 75 |
40 | Sulfur dichloride | 1828 | 1 |
41 | Sulfur dioxide, liquefied | 1079 | 200 |
42 | Titanium tetrachloride | 1838 | 500 |
43 | Toluene diisocyanate | 2078 | 200 |
Explosive materials |
44 | Explosive materials of Subclass 1.1A | | 10 |
45 | Explosive materials of Subclass 1.1 (other than explosive materials mentioned in item 44) | | 50 |
46 | Explosive materials of Subclass 1.2 | | 200 |
47 | Explosive materials of Subclass 1.3 | | 200 |
Compressed and liquefied gases |
48 | Compressed or liquefied gases of: (a) Subclass 2.1; or (b) Subsidiary Risk 2.1 | | 200 |
49 | Liquefied gases of Subsidiary Risk 5 | | 200 |
50 | Compressed or liquefied gases that meet the criteria for Very Toxic in Part 3 of this Schedule | | 20 |
51 | Compressed or liquefied gases that meet the criteria for Toxic in Part 3 of this Schedule | | 200 |
Flammable materials |
52 | Liquids of Class 3 and Packing Group I (other than the materials mentioned in item 53) | | 200 |
53 | Crude oil, in remote locations, of Class 3 and Packing Group I | | 2 000 |
54 | Liquids of: (a) Class 3; and (b) either: (i) Packing Group I; or (ii) Packing Group II | | 50 000 |
55 | Liquids with flashpoints of less than 61 C kept above their boiling points at ambient conditions | | 200 |
56 | Combustible solids of Subclass 4.1 and Packing Group I | | 200 |
57 | Spontaneously combustible dangerous goods of: (a) Subclass 4.2; and (b) either: (i) Packing Group I; or (ii) Packing Group II | | 200 |
58 | Dangerous goods that: (a) either: (i) liberate flammable gases; or (ii) react violently on contact with water; and (b) are of: (i) Subclass 4.3; and (ii) either: (A) Packing Group I; or (B) Packing Group II | | 200 |
59 | Dangerous goods that: (a) have Hazchem codes of 4WE (materials that react violently with water); and (b) are of: (i) either: (A) Class 3; or (B) Class 8; and (ii) either: (A) Packing Group I; or (B) Packing Group II | | 500 |
Oxidising materials |
60 | Oxidising material listed in Appendix 5 to the ADG Code | | 50 |
61 | Oxidising materials of: (a) Subclass 5.1; and (b) either: (i) Packing Group I; and (ii) Packing Group II | | 200 |
Peroxides |
62 | Peroxides listed in Appendix 5 to the ADG Code | | 50 |
63 | Organic peroxides of Subclass 5.2 | | 200 |
Toxic liquids and solids |
64 | Materials that meet the criteria for Very Toxic in Part 3 of this Schedule | | 20 |
65 | Materials that meet the criteria for Toxic in Part 3 of this Schedule | | 200 |
| | | | |
Note 1 The UN number listed for a material specified in an item in this Part is for information only. The listing of the UN number is not intended to restrict the meaning of the name of the material, which may also apply to material that does not come within the scope of the UN number, for example, because the material is too dangerous to transport or is part of a mixture covered by another UN number. However, any material that is covered by the UN number listed in the table must be included in the quantity of the material named.
Note 2 If a material specified in an item in this Part is part of a mixture, the equivalent quantity is to be calculated in accordance with Example 2 in Chapter 16 of the National Code of Practice for the Control of Major Hazard Facilities [NOHSC:2016 (1996)], as in existence at the commencement of this Schedule.
Part 3 Criteria for toxicity
Description | Oral toxicity in rabbits LD50 (mg/kg) | Dermal toxicity in rats or rabbits LD50 (mg/kg) | Inhalation toxicity (4 hours in rabbits) LC 50 (mg/L) |
Very toxic | LD50 < 5 | LD50 < 40 | LC50 < 0.5 |
Toxic | 5 < LD50 < 50 | 40 < LD50 < 200 | 0.5 < LC50 < 2 |
Part 4 Aggregation formula
For Part 9, the aggregation formula is as follows:
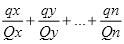
where:
qx, qy, … qn is the total amount of each material (x, y, … n) that is present, that will be present, or that is likely to be present, in an isolated amount that is more than 2% of the threshold quantity for the material.
Qx, Qy, … Qn is the threshold quantity for each material.
Schedule 9A Information to be included in safety report
(paragraph 9.47 (4) (c))
Part 1 Definitions
101 In this Schedule:
critical operating parameters means the upper and lower performance limits of any equipment, process or procedure, if compliance with that equipment, process or procedure is necessary to avoid a major accident.
failure, in relation to a control measure, means:
(a) if the control measure is a positive action or event — the non‑occurrence, or the defective occurrence, of the action or event; and
(b) if the control measure is a limitation on an operational activity, process or procedure — a breach of that limitation.
Part 2 Specified information
Division 1 Facility description
Details of the facility
201 A description of the main activities and products of the major hazard facility, particularly those activities associated with the following materials:
(a) a material specified in Part 2 of Schedule 9;
(b) biological materials;
(c) radioactive materials.
202 If a material mentioned in paragraph 201 (a), (b) or (c) is present, or is likely to be present at the facility — the following information in relation to the material:
(a) sufficient information to identify the material (including, if applicable, the information mentioned in subparagraphs 9.06 (2) (i) (i) to (v));
(b) the maximum quantity in which the material is, or is likely to be, present at the facility;
(c) the physical, chemical and toxicological characteristics of the material, both immediate and delayed;
(d) any other hazardous characteristics of the material, both immediate and delayed;
(e) the physical and chemical behaviour of the material, under:
(i) normal conditions of use; and
(ii) foreseeable abnormal conditions.
203 A description of the chemical and physical processes associated with a material mentioned in paragraph 201 (a), (b) or (c), including:
(a) a description of the main units of process equipment used in those processes; and
(b) a process flow drawing, or a set of such drawings.
204 A drawing of the major hazard facility’s general layout, including the location of:
(a) the main process units; and
(b) the main storage areas; and
(c) hazard and major accident initiators.
205 If:
(a) a change is proposed to the major hazard facility; and
(b) no new control measures will be adopted in relation to the proposed change; and
(c) the proposed change will:
(i) alter the production capacity or profile of the major hazard facility; or
(ii) involve the deletion, addition or modification of any processes;
a description of the proposed change.
206 If:
(a) a change is proposed to a major hazard facility; and
(b) no new control measures will be adopted in relation to the proposed change;
a statement about whether, and the way in which (if applicable), existing control measures and safety management systems are capable of maintaining the safe operation of the major hazard facility while the proposed change is being made and after the proposed change is made.
Details of the surrounding area
207 A scaled plan of the facility and its surrounding area, showing:
(a) the location of the facility within the surrounding area; and
(b) topographical information; and
(c) surrounding land uses; and
(d) the location of any identified external threats, including:
(i) other major hazard facilities; or
(ii) other facilities that could affect the safety of the major hazard facility.
208 Graphically presented demographic information for the local community, including land uses permitted by the local planning authority.
209 Meteorological data relevant to the estimation of the effects of any major accident.
Division 2 Safety information
Control measures
210 A detailed description of the following:
(a) the instrumentation and other equipment installed in the facility;
(b) the procedures in place that are the control measures for preventing or limiting the consequences of major accidents;
(c) the critical operating parameters for the control measures mentioned in paragraph (b);
(d) key personnel and resources (both internal and external) available to intervene in the event of any failure of a control measure, whether or not that failure could result in a major accident;
(e) the emergency plan for the major hazard facility, including specific information about how compliance with the plan can be expected to limit the consequences of a major accident;
(f) the means by which the employer in control of the major hazard facility will ensure:
(i) that there is, at all times, a command structure in place for the major hazard facility that will apply in the event of an emergency; and
(ii) that details of the command structure is communicated throughout the facility.
Performance monitoring
211 A detailed description of:
(a) the performance standards that must be met by the safety management system; and
(b) any performance indicators relevant to those performance standards.
Safety management system
212 If a matter addressed in the safety report is covered by the safety management system — a clear reference to the relevant part of the document prepared under subregulation 9.429.43 (2) that addresses the matter.
213 A description of the parts of the safety management system that address the maintenance of the system.
Safety and reliability of plant
214 A description of the steps taken to ensure that safety and reliability are incorporated into the design and construction of all aspects of the major hazard facility (whether or not the employer in control of the facility is or was directly engaged in the design and construction of the facility).
Accident history
215 A summary of each major accident that has occurred at the facility in the preceding 5 years.
Schedule 3 Further amendment of Occupational Health and Safety (Commonwealth Employment) (National Standards) Regulations 1994
(regulation 5)
[1] Regulation 1
substitute
1.01 Name of Regulations
These Regulations are the Occupational Health and Safety (Safety Standards) Regulations 1994.
