
Child Care Payments Act 1997
No. 195, 1997

Child Care Payments Act 1997
No. 195, 1997

Child Care Payments Act 1997
No. 195, 1997
An Act to provide for payments in respect of child care, and for related purposes
Contents
Chapter 1—Preliminary matters and interpretation 2
Part 1—Preliminary matters 2
1 Short title..................................2
2 Commencement..............................2
3 Identifying defined terms.........................2
4 Overview..................................2
Part 2—Interpretation 2
5 Definitions.................................2
6 Meaning of comply with a tax file number request—request for person’s tax file number 2
7 Meaning of comply with a tax file number request—request for tax file number of person’s partner 2
8 Meaning of conscientious objection...................2
9 Extended meaning of inhabitant of Australia—students receiving financial assistance 2
10 Extended meaning of inhabitant of Australia—hardship and special circumstances 2
11 Meaning of member of a couple.....................2
12 Meaning of payment commencement day................2
13 Meaning of receiving...........................2
14 Meaning of satisfies the work/training/study test...........2
15 Work/training/study test—recognised work or work related commitments 2
16 Work/training/study test—recognised training commitments....2
17 Work/training/study test—recognised study commitments......2
18 Minister’s power to make determinations for the purposes of other definitions 2
Chapter 2—Child care assistance 2
Part 1—Entitlement 2
19 Entitlement to child care assistance...................2
Part 2—Qualification 2
20 Qualification for child care assistance..................2
21 Meaning of dependent child.......................2
22 The immunisation requirement—prospective claimants and recipients 2
23 The immunisation requirement—retrospective claimants......2
24 Sessions of care in respect of which emergency child care assistance generally not to count 2
25 Treatment of absences of child from care................2
Part 3—Limitations on payability 2
26 Part sets out limits on payability.....................2
27 Assets test..................................2
28 Assets test—determining value of assets................2
29 Assets test—indexation of assets limit.................2
30 Non-temporary cessation of qualification criteria...........2
31 No payment unless proper claim made.................2
32 Nil rate of payment.............................2
33 Prospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after the maximum assistance period 2
34 Prospective claims—provision of tax file numbers..........2
35 Prospective claims—provision of information required by recipient reconciliation notice 2
36 Retrospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after maximum assistance period 2
Part 4—Claims for child care assistance 2
37 Prospective and retrospective claims..................2
38 Need for a claim..............................2
39 Secretary may also treat claim as claim for child care rebate....2
40 Form of claim................................2
41 Lodgment of claim.............................2
42 Claim may be withdrawn.........................2
43 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised..2
44 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of tax file number 2
45 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of partner’s tax file number 2
Part 5—Determination of claims 2
Division 1—Prospective claims 2
46 Division applies if person makes a prospective claim that is a proper claim 2
47 Secretary to determine claim.......................2
48 Maximum assistance period.......................2
Division 2—Retrospective claims 2
49 Division applies if person makes a retrospective claim that is a proper claim 2
50 Secretary to determine claim.......................2
51 Maximum assistance period.......................2
Division 3—Date of effect etc. of determinations 2
52 Date of effect etc. of determinations may be dealt with in regulations2
Part 6—Rate of child care assistance 2
53 Rate of child care assistance.......................2
Part 7—Payment of child care assistance 2
Division 1—General provisions about payment 2
54 Payment by instalments..........................2
55 Prospective claims payment system...................2
56 Retrospective claims payment system..................2
Division 2—Payment pursuant to prospective claims 2
57 Division deals with payment pursuant to prospective claims....2
58 Commencement of payment.......................2
59 Payment by instalments..........................2
60 Payments generally to be made to operator of child care assistance service 2
61 Payment may be made to the person...................2
62 Payment into bank etc. account.....................2
63 Where payday would fall on public holiday etc.............2
64 Payment after death of person......................2
Division 3—Payment pursuant to retrospective claims 2
65 Division deals with payment pursuant to retrospective claims....2
66 Payment in lump sum...........................2
67 Payment into bank etc. account.....................2
68 Payment after death of person......................2
Part 8—Recipient obligations 2
69 Part deals with obligations of people paid pursuant to prospective claims 2
70 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised..2
71 Secretary may request person to give statement of tax file number.2
72 Secretary may request person to give statement of partner’s tax file number 2
73 Secretary may require notice of the happening of an event or a change of circumstances 2
74 Secretary may require person to give particular information relevant to payment of child care assistance 2
75 Secretary may require person to give information relating to entitlement to child care assistance in a past period 2
76 Secretary may require person to give notice of change of address.2
Chapter 3—Child care rebate 2
Part 1—Entitlement 2
77 Entitlement to child care rebate.....................2
Part 2—Qualification 2
78 Qualification for child care rebate....................2
79 Meaning of dependent child.......................2
80 The immunisation requirement—prospective claimants and recipients 2
81 The immunisation requirement—retrospective claimants......2
82 Treatment of absences of child from care................2
Part 3—Limitations on payability 2
83 Part sets out limits on payability.....................2
84 Non-temporary cessation of qualification criteria...........2
85 No payment unless proper claim made.................2
86 Nil rate of payment.............................2
87 Prospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after the maximum rebate period 2
88 Prospective claims—provision of information required by recipient reconciliation notice 2
89 Retrospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after maximum rebate period 2
Part 4—Claims for child care rebate 2
90 Prospective and retrospective claims..................2
91 Need for a claim..............................2
92 Secretary may also treat claim as claim for child care assistance..2
93 Form of claim................................2
94 Lodgment of claim.............................2
95 Claim may be withdrawn.........................2
96 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised..2
97 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of tax file number 2
98 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of partner’s tax file number 2
Part 5—Determination of claims 2
Division 1—Prospective claims 2
99 Division applies if person makes a prospective claim that is a proper claim 2
100 Secretary to determine claim.......................2
101 Maximum rebate period..........................2
Division 2—Retrospective claims 2
102 Division applies if person makes a retrospective claim that is a proper claim 2
103 Secretary to determine claim.......................2
104 Maximum rebate period..........................2
Division 3—Date of effect etc. of determinations 2
105 Date of effect etc. of determinations may be dealt with in regulations2
Part 6—Rate of child care rebate 2
106 Rate of child care rebate..........................2
Part 7—Payment of child care rebate 2
Division 1—General provisions about payment 2
107 Payment by instalments..........................2
108 Prospective claims payment system...................2
109 Retrospective claims payment system..................2
Division 2—Payment pursuant to prospective claims 2
110 Division deals with payment pursuant to prospective claims....2
111 Commencement of payment.......................2
112 Payment by instalments..........................2
113 Payments to be made to person......................2
114 Payment into person’s bank etc. account................2
115 Where payday would fall on public holiday etc.............2
116 Payment after death of person......................2
Division 3—Payment pursuant to retrospective claims 2
117 Division deals with payment pursuant to retrospective claims....2
118 Payment in lump sum...........................2
119 Payment into bank etc. account.....................2
120 Payment after death of person......................2
Part 8—Recipient obligations 2
121 Part deals with obligations of people paid pursuant to prospective claims 2
122 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised..2
123 Secretary may request person to give statement of tax file number.2
124 Secretary may request person to give statement of partner’s tax file number 2
125 Secretary may require notice of the happening of an event or a change of circumstances 2
126 Secretary may require person to give particular information relevant to payment of child care rebate 2
127 Secretary may require person to give information relating to entitlement to child care rebate in a past period 2
128 Secretary may require person to give notice of change of address.2
Chapter 4—Overpayments and debt recovery 2
Part 1—Preliminary 2
129 Amount paid to person includes amount paid on person’s behalf to another person 2
130 Special provisions relating to operators of child care assistance services 2
131 Chapter does not apply to emergency child care assistance.....2
Part 2—Amounts recoverable under this Act 2
132 Debts due to the Commonwealth....................2
133 Debts arising under this Act.......................2
134 Debts arising from AAT stay orders...................2
135 Debts arising from recipient’s contravention of this Act.......2
136 Person other than payee obtaining payment of a cheque.......2
137 Debts arising from conviction of person for involvement in contravention of this Act by debtor 2
138 Data-matching Program (Assistance and Tax) Act debts.......2
139 Interest payable on debt for failure to enter agreement to pay debt.2
140 Interest payable on debt for breach of agreement to pay debt....2
141 Penalty interest rate............................2
142 Debt from failure to comply with garnishee notice..........2
143 Overseas application of provisions...................2
144 Recoverable debts.............................2
Part 3—Methods of recovery 2
145 Deductions generally...........................2
146 Deductions from debtor’s child care payment.............2
147 Deductions from group payments made to child care assistance service 2
148 Time limits on recovery action under sections 146 and 147.....2
149 Legal proceedings.............................2
150 Garnishee notice..............................2
151 Time limits on recovery action under section 150...........2
152 Secretary may allow payment of debt by instalments.........2
153 Deductions by consent from child care payment of person who is not a debtor 2
Part 4—Non-recovery of debts 2
154 Meaning of debt..............................2
155 Secretary may write off debt.......................2
156 Power to waive Commonwealth’s right to recover debt.......2
157 Waiver of debt arising from error....................2
158 Waiver of debt relating to an offence..................2
159 Waiver of small debt............................2
160 Waiver in relation to settlements.....................2
161 Waiver where debtor or debtor’s partner would have been entitled to child care rebate 2
162 Waiver in special circumstances.....................2
163 Secretary may waive debts of a particular class............2
164 Determination that penalty interest not payable in relation to particular periods 2
Chapter 5—Emergency child care assistance 2
165 Definitions.................................2
166 What is emergency child care assistance?...............2
167 Minister may make guidelines......................2
168 Application.................................2
169 Consequences of failure to comply with requirement for other information 2
170 Children in respect of whom emergency child care assistance is not payable 2
171 Payability and rate of payment of emergency child care assistance.2
172 Duration of payment of emergency child care assistance.......2
Chapter 6—Approval and registration of child care services 2
Part 1—Approval for child care assistance purposes 2
Division 1—Obtaining approval and conditions of approval 2
173 What is the significance of approval of a child care service?....2
174 Application.................................2
175 Approval of child care services.....................2
176 Statement that applicant has tax file number..............2
177 Conditions of approval..........................2
178 Allocation of hours condition ceases to apply to centre based long day care services after 31 December 1999 2
179 Consequences of breach of conditions of approval..........2
180 Procedure for imposing a sanction....................2
181 Cancellation.................................2
182 Procedure for cancellation........................2
183 Effect of cancellation of approval on child care rebate service status 2
184 Notification of matters affecting eligibility for approval.......2
185 Eligibility rules—centre based long day care services........2
186 Eligibility rules—family day care services...............2
187 Eligibility rules—occasional care services...............2
188 Eligibility rules—outside school hours care services.........2
189 Exemption from eligibility rules.....................2
190 Eligibility rules may deal with who may operate a service and change of operator of a service 2
191 Determinations disallowable.......................2
Division 2—Allocation of child care assistance hours 2
Subdivision 1—General 2
192 Purpose of Division............................2
193 Secretary to allocate child care assistance hours............2
194 Allocation guidelines...........................2
195 Notice of allocation............................2
196 Re-allocation of surrendered child care assistance hours.......2
197 Application for new child care assistance hours............2
198 Determination of application.......................2
Subdivision 2—New child care assistance hours for centre based long day care services 2
199 Allocation of new child care assistance hours—1998 and 1999...2
200 Total number to be divided on regional basis.............2
201 Allocation within a region limited to hours available in region...2
202 Other factors affecting allocation....................2
Subdivision 3—New child care assistance hours for other services 2
203 Allocation of new child care assistance hours.............2
204 Factors affecting allocation of new hours................2
Part 2—Registration for child care rebate purposes 2
205 What is the significance of registration of a child care service?...2
206 Application.................................2
207 Registration of child care services....................2
208 Statement that applicant has tax file number..............2
209 When does registration take effect?...................2
210 Conditions of registration.........................2
211 Consequences of breach of conditions of registration.........2
212 Procedure for imposing a sanction....................2
213 Cancellation.................................2
214 Procedure for cancellation........................2
215 Notification of matters affecting eligibility for registration.....2
216 Eligibility rules...............................2
217 Exemption from eligibility rules.....................2
218 Determinations disallowable.......................2
Part 3—Review of decisions 2
219 Review by the AAT............................2
220 Internal review...............................2
Chapter 7—Information management 2
Part 1—Information gathering 2
221 General power to obtain information..................2
222 Power to obtain information from a person who owes a debt to the Commonwealth 2
223 Power to obtain information about a person who owes a debt to the Commonwealth 2
224 General provisions about making requirements under sections 221 to 223 2
225 Power to obtain information to verify claims etc............2
226 General provisions about making requirements under section 225.2
227 Secretary’s obligation in relation to information given under section 225 2
228 State/Territory law does not affect obligations to provide information under this Act 2
229 Part does not create offences in relation to emergency child care assistance 2
Part 2—Confidentiality 2
230 Authorised access to and use of protected information........2
231 Offence—unauthorised access to protected information.......2
232 Offence—unauthorised use of protected information.........2
233 Protection extends to court, tribunal etc. proceedings.........2
234 Secretary’s certificate...........................2
235 Guidelines for exercise of Secretary’s disclosure power.......2
236 Offence—soliciting disclosure of protected information.......2
237 Offence—untrue representations.....................2
238 Offences—offering to supply protected information.........2
239 Officer’s oath or declaration.......................2
240 Freedom of Information Act not affected................2
Chapter 8—General provisions about offences and penalties 2
241 Application of the Criminal Code....................2
242 Crown not liable to be prosecuted for offences............2
243 Conviction of an offence—repayment of child care payment....2
244 Secretary’s certificate...........................2
245 Court certificate..............................2
246 Proceedings against non-corporations..................2
Chapter 9—General provisions about review of decisions 2
Part 1—Internal review 2
247 Decisions to which Part applies.....................2
248 Secretary may review decisions.....................2
249 Application for review...........................2
250 Secretary or CEO may continue payment pending outcome of application for review 2
251 Powers of Secretary, CEO or authorised review officer if application for review 2
252 Certain determinations not to be revived................2
253 Notification of further rights of review.................2
Part 2—Review by Social Security Appeals Tribunal 2
254 Decisions to which Part applies.....................2
255 SSAT objectives..............................2
256 Application for review by SSAT.....................2
257 Secretary may continue payment pending outcome of application for review 2
258 SSAT review powers...........................2
259 Date of effect of SSAT decisions....................2
260 Application requirements.........................2
261 Variation of decision before SSAT review completed........2
262 Parties to SSAT review..........................2
Part 3—Right to review by Administrative Appeals Tribunal 2
263 Review of SSAT decision by AAT...................2
264 Variation of decision before AAT review completed.........2
265 Review of SSAT decision on application by the Secretary......2
266 Secretary may settle proceedings before the AAT...........2
Part 4—Modification of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 2
267 Modification of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act......2
268 Statement of reasons for decision....................2
269 Notice of application for review.....................2
270 Parties to review by the AAT.......................2
271 Lodging documents with the AAT....................2
272 Power of the AAT to obtain additional statements..........2
273 Operation and implementation of the decision under review.....2
274 Power of the AAT if party fails to appear................2
Chapter 10—Administration 2
Part 1—General administration 2
275 Secretary to have general administration of Act............2
276 Delegation by Secretary..........................2
277 Authorised review officers........................2
278 Decisions to be in writing.........................2
279 Notice of decisions under this Act....................2
Part 2—Special provisions about the Agency 2
280 References to the Secretary and the Department—requirements etc. by delegate 2
281 References to the Secretary and the Department—directions by Secretary 2
Chapter 11—Miscellaneous 2
282 Treatment of unincorporated associations...............2
283 Treatment of partnerships.........................2
284 Judicial notice to be taken of certain matters..............2
285 Evidence...................................2
286 Source of payments............................2
287 Regulations.................................2
Schedule 1—Calculation of rate of child care assistance 2
Module A—Interpretation 2
Module B—Overall rate calculation process 2
Module C—Qualifying session of care 2
Module D—Eligible hour of care 2
Module E—Hourly rebateable fee 2
Module F—CA% 2
Module G—Indexation 2
Schedule 2—Calculation of rate of child care rebate 2
Module A—Overall rate calculation process 2
Module B—Qualifying session of care 2
Module C—CCR% 2
Module D—Weekly child care expenditure 2
Module E—Indexation 2

Child Care Payments Act 1997
No. 195, 1997
An Act to provide for payments in respect of child care, and for related purposes
[Assented to 8 December 1997]
The Parliament of Australia enacts:
Chapter 1—Preliminary matters and interpretation
This Act may be cited as the Child Care Payments Act 1997.
This Act commences on the day after the day on which it receives the Royal Assent.
Note: Payments under this Act will only be made in respect of child care occurring on or after the *payment commencement day set under section 12.
(1) Many of the terms in this Act are defined in section 5. Some definitions relevant only to limited areas of this Act are defined in those areas.
(2) Most of the terms that are defined in section 5 are identified by an asterisk appearing at the start of the term: as in “*payment commencement day”. The footnote with the asterisk contains a signpost to section 5.
(3) An asterisk usually identifies the first occurrence of a term in a section (if not divided into subsections), subsection, note or definition. Later occurrences of the term in the same provision are not usually asterisked.
(4) Terms are not asterisked in headings or tables.
(5) The following basic terms used throughout the Act are not identified with an asterisk:
Terms that are not identified | ||
Item | This term | is defined in section |
1 | AAT | 5 |
2 | child care assistance | 5 |
3 | child care rebate | 5 |
4 | child care service | 5 |
5 | partner | 5 |
6 | Secretary | 5 |
7 | SSAT | 5 |
(1) This Act provides for the making of payments in respect of child care.
(2) There are 2 main payment types:
(a) child care assistance; and
(b) child care rebate.
(3) The main provisions relating to child care assistance are in Chapter 2 and Schedule 1. The main provisions relating to child care rebate are in Chapter 3 and Schedule 2.
(4) Subject to the provisions of Chapters 2 and 3, it is possible for a person to be entitled to receive both child care assistance and child care rebate in respect of the same child care.
(5) Provisions dealing with overpayments of, and the recovery of debts relating to, child care assistance and child care rebate are in Chapter 4.
(6) The third payment type is emergency child care assistance. This is a short term payment made to child care services that provide emergency care for children at risk. The main provisions relating to emergency child care assistance are in Chapter 5.
(7) All 3 payment types are only payable in respect of care provided by child care services that are either approved or registered under Chapter 6.
(8) The other Chapters of this Act deal with the following matters:
(a) Chapter 7—information gathering and confidentiality;
(b) Chapter 8—general provisions about offences and penalties;
(c) Chapter 9—general provisions about review of decisions;
(d) Chapter 10—administration of the Act;
(e) Chapter 11—miscellaneous matters.
In this Act:
AAT is short for the Administrative Appeals Tribunal.
absence, in relation to a child and a child care service, does not include any period after the service has stopped providing care for the child (otherwise than temporarily).
Agency means the Commonwealth Services Delivery Agency established by the Agency Act.
Agency Act means the Commonwealth Services Delivery Agency Act 1997.
Australian Immunisation Handbook means the latest edition of the Australian Immunisation Handbook published by the Australian Government Publishing Service.
authorised review officer means an *officer authorised under section 277 to perform duties as an authorised review officer for the purposes of this Act.
centre based long day care service means a child care service approved as a centre based long day care service under Part 1 of Chapter 6.
CEO, in relation to the *Agency, means the Chief Executive Officer of the Agency.
child care assistance hours means child care assistance hours that are, or are to be, allocated to *child care assistance services under Part 1 of Chapter 6.
child care assistance means child care assistance under Chapter 2.
child care assistance service means a child care service that has been approved as a service of one of the following kinds under Part 1 of Chapter 6:
(a) a centre based long day care service;
(b) a family day care service;
(c) an occasional care service;
(d) an outside school hours care service.
child care payment means:
(a) child care assistance (see Chapter 2); or
(b) child care rebate (see Chapter 3); or
(c) emergency child care assistance (see Chapter 5).
Note: Emergency child care assistance is not a child care payment to which Chapter 4 applies.
child care rebate means child care rebate under Chapter 3.
child care rebate service means:
(a) a *child care assistance service; or
(b) a child care service that is registered under Part 2 of Chapter 6 as a child care rebate service.
child care service means a service that provides child care. For the purposes of Part 2 of Chapter 6, an individual who cares for a child is taken to operate a child care service.
comply with a tax file number request has the meaning given by sections 6 and 7.
conscientious objection, in relation to the immunisation of a child, has the meaning given by section 8.
dependent child:
(a) when used in relation to child care assistance, has the meaning given by section 21; and
(b) when used in relation to child care rebate, has the meaning given by section 79.
eligibility rules means:
(a) in Part 1 of Chapter 6—rules made under section 185, 186, 187 or 188; or
(b) in Part 2 of Chapter 6—rules made under section 216.
emergency child care assistance means emergency child care assistance under Chapter 5.
employee, in relation to the *Agency, has the same meaning as in the *Agency Act.
entitled:
(a) when used in relation to child care assistance, has the meaning given by section 19; and
(b) when used in relation to child care rebate, has the meaning given by section 77.
family day care service means a child care service approved as a family day care service under Part 1 of Chapter 6.
group payment has the meaning given by subsection 60(2).
group payment notice, in relation to a *group payment, has the meaning given by subsection 60(3).
immunised, in relation to a child, means the child is immunised in accordance with:
(a) a standard vaccination schedule determined under subsection 18(1); or
(b) a catch up vaccination schedule determined under subsection 18(1).
information includes estimates.
inhabitant of Australia means:
(a) a person who is an inhabitant of Australia for the purposes of the Social Security Act 1991; or
(b) a person described in section 9 or 10.
Note: The definition relevant to paragraph (a) is in subsection 23(1) of the Social Security Act 1991.
maximum assistance period, in relation to a claim for child care assistance, means:
(a) if it is a *prospective claim:
(i) the period specified in accordance with section 48; or
(ii) if that period has been extended under section 33—that period as so extended; or
(b) if it is a *retrospective claim—the period specified in accordance with section 51.
maximum rebate period, in relation to a claim for child care rebate, means:
(a) if it is a prospective claim:
(i) the period specified in accordance with section 101; or
(ii) if that period has been extended under section 87—that period as so extended; or
(b) if it is a retrospective claim—the period specified in accordance with section 104.
medical practitioner means a person registered or licensed as a medical practitioner under a State or Territory law that provides for the registration or licensing of medical practitioners.
member of a couple has the meaning given by section 11.
National Convener means the National Convener of the Social Security Appeals Tribunal.
occasional care service means a child care service approved as an occasional care service under Part 1 of Chapter 6.
officer means a person performing duties, or exercising powers or functions, under or in relation to this Act and, in relation to a provision of Part 2 of Chapter 7, includes:
(a) a person who has been such a person; and
(b) a person who is or has been appointed or employed by the Commonwealth and who, as a result of that appointment or employment, may acquire or has acquired *information about a person under this Act; and
(c) a person who, although not appointed or employed by the Commonwealth, performs or did perform services for the Commonwealth and who, as a result of performing those services, may acquire or has acquired information about a person under this Act.
outside school hours care service means a child care service approved as an outside school hours care service under Part 1 of Chapter 6.
partner, in relation to a person who is a *member of a couple, means the other member of the couple.
payday means a day that is a family payment payday for the purposes of the Social Security Act 1991.
payment commencement day means the day that is, under section 12, the payment commencement day.
payment period means the period of 2 weeks starting on the Monday that is the *payment commencement day and the period of 2 weeks starting on each succeeding alternate Monday.
prospective claim:
(a) when used in relation to child care assistance, has the meaning given by paragraph 37(1)(a); and
(b) when used in relation to child care rebate, has the meaning given by paragraph 90(1)(a).
protected information means:
(a) *information about a person or a child care service that is or was held in the records of the Department or the Agency; or
(b) information that there is no information about a person or a child care service held in the records of the Department or the *Agency.
receiving has a meaning affected by section 13.
recipient notification notice means a notice under section 73 or 125.
recipient reconciliation notice means a notice under section 75 or 127.
recipient statement notice means a notice under section 74 or 126.
recognised immunisation provider has the same meaning as in section 46A of the Health Insurance Act 1973.
retrospective claim:
(a) when used in relation to child care assistance, has the meaning given by paragraph 37(1)(b); and
(b) when used in relation to child care rebate, has the meaning given by paragraph 90(1)(b).
satisfies the work/training/study test has the meaning given by section 14.
Secretary means the Secretary of the Department.
service arrangements has the same meaning as in the *Agency Act.
session of care has the meaning given by a determination in force under subsection 18(2).
SSAT is short for the Social Security Appeals Tribunal.
tax file number has the same meaning as in Part VA of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936.
tax file number request means a request under subsection 44(1), 45(1), 71(1), 72(1), 97(1), 98(1), 123(1) or 124(1).
tax year has the same meaning as year of income has in the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936.
Note: The relevant definition is in section 6 of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936.
6 Meaning of comply with a tax file number request—request for person’s tax file number
(1) This section deals with how a *tax file number request may be complied with if it is a request under section 44, 71, 97 or 123 (these are requests for a person’s *tax file number).
(2) To comply with a *tax file number request, the person may:
(a) give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s *tax file number; or
(b) give the Secretary a declaration by the person in a form approved in writing by the Secretary and satisfy either subsection (3) or (4).
(3) The person satisfies this subsection if:
(a) the person’s declaration states that the person:
(i) has a *tax file number but does not know what it is; and
(ii) has asked the Commissioner of Taxation to inform the person of the person’s tax file number; and
(b) the person has given the Secretary a document by the person that authorises the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Secretary:
(i) whether the person has a tax file number; and
(ii) if the person has a tax file number—the tax file number; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Secretary that the person has no tax file number.
(4) The person satisfies this subsection if:
(a) the person’s declaration states that the person has applied for a *tax file number; and
(b) the person has given the Secretary a document by the person that authorises the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Secretary:
(i) if a tax file number is issued to the person—the tax file number; or
(ii) if the application is refused—that the application has been refused; or
(iii) if the application is withdrawn—that the application has been withdrawn; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Secretary that the person has not applied for a tax file number; and
(d) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Secretary that an application by the person for a tax file number has been refused; and
(e) the application for a tax file number has not been withdrawn.
7 Meaning of comply with a tax file number request—request for tax file number of person’s partner
(1) This section deals with how a *tax file number request may be complied with if it is a request under section 45, 72, 98 or 124 (these are requests to a person for his or her partner’s *tax file number).
(2) To comply with a *tax file number request, the person may:
(a) give the Secretary a written statement of the partner’s *tax file number; or
(b) give the Secretary a declaration by the partner in a form approved in writing by the Secretary and satisfy either subsection (3) or (4).
(3) The person satisfies this subsection if:
(a) the partner’s declaration states that the partner:
(i) has a *tax file number but does not know what it is; and
(ii) has asked the Commissioner of Taxation to inform the partner of the partner’s tax file number; and
(b) the person has given the Secretary a document by the partner that authorises the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Secretary:
(i) whether the partner has a tax file number; and
(ii) if the partner has a tax file number—the tax file number; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Secretary that the partner has no tax file number.
(4) The person satisfies this subsection if:
(a) the partner’s declaration states that an application by the partner for a *tax file number is pending; and
(b) the person has given the Secretary a document by the partner that authorises the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Secretary:
(i) if a tax file number is issued to the partner—the tax file number; or
(ii) if the application is refused—that the application has been refused; or
(iii) if the application is withdrawn—that the application has been withdrawn; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Secretary that an application by the partner for a tax file number has been refused; and
(d) the application for a tax file number has not been withdrawn.
8 Meaning of conscientious objection
A person has a conscientious objection to a child being *immunised if the person’s objection is based on a personal, philosophical, religious or medical belief involving a conviction that vaccination under the latest edition of the Standard Vaccination Schedule should not take place.
9 Extended meaning of inhabitant of Australia—students receiving financial assistance
A person is an inhabitant of Australia if the person:
(a) is undertaking a course of study in Australia; and
(b) is receiving financial assistance directly from the Commonwealth for the purpose of undertaking that course of study.
10 Extended meaning of inhabitant of Australia—hardship and special circumstances
(1) A person is an inhabitant of Australia if the Secretary determines in writing that the person is an inhabitant of Australia for the purposes of this Act.
(2) The Secretary may make a determination under subsection (1) if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) hardship would be caused to the applicant if the applicant were not treated as an inhabitant of Australia; or
(b) because of the special circumstances of the particular case, the applicant should be treated as an inhabitant of Australia.
(3) In making a determination under subsection (1), the Secretary must comply with any guidelines in force under subsection (4) in relation to the making of such declarations.
(4) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines relating to the making of determinations under subsection (1).
(5) A determination under subsection (4) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
11 Meaning of member of a couple
(1) Subject to subsection (2), a person is a member of a couple for the purposes of this Act if:
(a) the person is legally married to another person and is not, in the Secretary’s opinion (formed as mentioned in subsection (2)), living separately and apart from the other person on a permanent or indefinite basis; or
(b) all of the following conditions are met:
(i) the person has a relationship with a person of the opposite sex (in this paragraph called the partner);
(ii) the person is not legally married to the partner;
(iii) the relationship between the person and the partner is, in the Secretary’s opinion (formed as mentioned in subsections (2) and (3)), a marriage‑like relationship;
(iv) both the person and the partner are over the age of consent applicable in the State or Territory in which they live;
(v) the person and the partner are not within a prohibited relationship for the purposes of section 23B of the Marriage Act 1961.
Note: A prohibited relationship for the purposes of section 23B of the Marriage Act 1961 is a relationship between a person and:
(a) an ancestor of the person; or
(b) a descendant of the person; or
(c) a brother or sister of the person (whether of the whole blood or the part-blood).
(2) In forming an opinion about the relationship between 2 people for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a) or subparagraph (1)(b)(iii), the Secretary is to have regard to all the circumstances of the relationship including, in particular, the following matters:
(a) the financial aspects of the relationship, including:
(i) any joint ownership of real estate or other major assets and any joint liabilities; and
(ii) any significant pooling of financial resources, especially in relation to major financial commitments; and
(iii) any legal obligations owed by one person in respect of the other person; and
(iv) the basis of any sharing of day-to-day household expenses;
(b) the nature of the household, including:
(i) any joint responsibility for providing care or support of children; and
(ii) the living arrangements of the people; and
(iii) the basis on which responsibility for housework is distributed;
(c) the social aspects of the relationship, including:
(i) whether the people hold themselves out as married to each other; and
(ii) the assessment of friends and regular associates of the people about the nature of their relationship; and
(iii) the basis on which the people make plans for, or engage in, joint social activities;
(d) any sexual relationship between the people;
(e) the nature of the people’s commitment to each other, including:
(i) the length of the relationship; and
(ii) the nature of any companionship and emotional support that the people provide to each other; and
(iii) whether the people consider that the relationship is likely to continue indefinitely; and
(iv) whether the people see their relationship as a marriage‑like relationship.
(3) The Secretary must not form the opinion that the relationship between a person and his or her partner is a marriage‑like relationship if the person is living separately and apart from the partner on a permanent or indefinite basis.
(4) A person is not a member of a couple if a determination under subsection (5) or (6) is in force in relation to the person.
(5) If:
(a) a person is legally married to another person; and
(b) the person is not living separately and apart from the other person on a permanent or indefinite basis; and
(c) the Secretary is satisfied that the person should, for a special reason in the particular case, not be treated as a member of a couple;
the Secretary may determine, in writing, that the person is not to be treated as a member of a couple for the purposes of this Act.
(6) If:
(a) a person has a relationship with a person of the opposite sex (the partner); and
(b) the person is not legally married to the partner; and
(c) the relationship between the person and the partner is a marriage‑like relationship; and
(d) the Secretary is satisfied that the person should, for a special reason in the particular case, not be treated as a member of a couple;
the Secretary may determine, in writing, that the person is not to be treated as a member of a couple for the purposes of this Act.
12 Meaning of payment commencement day
(1) Subject to subsections (2), (3) and (4), the payment commencement day is the day fixed by Proclamation as the payment commencement day for the purposes of this Act.
(2) The day fixed by Proclamation under subsection (1):
(a) must not be more than 6 months after the day on which this Act commences; and
(b) must be a Monday next following a day that is a family payment payday for the purposes of the Social Security Act 1991.
(3) If the payment commencement day is not fixed by a Proclamation under subsection (1) within the period of 6 months beginning on the day on which this Act commences, the payment commencement day is the first Monday after the end of that period that is a Monday next following a day that is a family payment payday for the purposes of the Social Security Act 1991.
(4) The payment commencement date will not be earlier than 27 April 1998.
(1) A person is taken to be receiving a *child care payment from the earliest day on which the payment is payable to the person, regardless of whether the first instalment of the payment is paid on an earlier or later day.
(2) A person is taken to be receiving a *child care payment until the latest day on which the payment is payable to the person, regardless of whether the last instalment of the payment is paid on an earlier or later day.
(3) A person is taken to be receiving a *child care payment even if amounts of the payment are being paid, on the person’s behalf, to another person (for example, the operator of a *child care assistance service).
14 Meaning of satisfies the work/training/study test
(1) A person satisfies the work/training/study test if:
(a) the person has recognised work or work related commitments within the meaning of section 15; or
(b) the person has recognised training commitments within the meaning of section 16; or
(c) the person has recognised study commitments within the meaning of section 17.
(2) The Minister may, in writing, determine that any person included in a specified class of persons is exempt from the requirements of paragraphs (1)(a), (b) and (c).
(3) A person covered by a determination under subsection (2) is taken to satisfy the work/training/study test while the determination is in force.
(4) A determination under subsection (2) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
15 Work/training/study test—recognised work or work related commitments
(1) A person has recognised work or work related commitments if the person:
(a) is in paid work (whether or not the person performs the work as an employee); or
(b) receives a carer payment under Part 2.5 of the Social Security Act 1991; or
(c) receives domiciliary nursing care benefit under Part VB of the National Health Act 1953; or
(d) is registered with the Commonwealth Employment Service in an allowance category as being unemployed; or
(e) is a member of a class of persons determined in writing by the Minister to be a class of persons who are taken to have recognised work or work related commitments for the purposes of this section.
(2) For the purpose of paragraph (1)(d), a person is registered in an allowance category if:
(a) the person is registered in a category approved under subsection 23(4A) of the Social Security Act 1991 for the purposes of Part 2.12 of that Act as being unemployed; or
(b) the person is registered in a category approved under subsection 58(2) of the Student and Youth Assistance Act 1973 for the purposes of Part 8 of that Act as being unemployed.
Note: The Commonwealth Employment Service registers the unemployed in various categories. The relevant categories here are the categories that are relevant for the purposes of receiving a newstart allowance under the Social Security Act 1991 or a youth training allowance under Part 8 of the Student and Youth Assistance Act 1973.
(3) A determination under paragraph (1)(e) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
16 Work/training/study test—recognised training commitments
A person has recognised training commitments if the person is undertaking a training course for the purpose of improving his or her work skills and/or employment prospects.
17 Work/training/study test—recognised study commitments
A person has recognised study commitments if the person:
(a) receives assistance under the Student and Youth Assistance Act 1973 by way of a benefit under the AUSTUDY scheme; or
(b) receives assistance under the scheme administered by the Department of Employment, Education, Training and Youth Affairs that is known as the ABSTUDY scheme; or
(c) is enrolled in an Adult Migrant English Program administered by the Department of Immigration and Multicultural Affairs; or
(d) is undertaking any other course of education for the purposes of improving his or her work skills and/or employment prospects.
18 Minister’s power to make determinations for the purposes of other definitions
Immunised
(1) The Minister may, for the purpose of the definition of immunised in section 5, determine, in writing:
(a) one or more standard vaccination schedules for the immunisation of children; and
(b) one or more catch up vaccination schedules for the immunisation of children who have not been immunised in accordance with a standard vaccination schedule.
Session of care
(2) The Minister may, in writing, determine what constitutes a session of care for the purposes of this Act.
(3) A determination under subsection (2) may also deal with how a session of care that starts on one day and ends on another day is to be treated for the purposes of this Act. The determination has effect accordingly.
Determinations under this section are disallowable
(4) A determination under this section is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Chapter 2—Child care assistance
19 Entitlement to child care assistance
(1) A person is entitled to child care assistance in respect of a *payment period if:
(a) the person is qualified for child care assistance in respect of the payment period (see Part 2); and
(b) the payability rules (see Part 3) do not preclude payment of child care assistance to the person in respect of the whole payment period.
Note: A person may also be entitled, in respect of the same payment period, to child care rebate (see Chapter 3).
(2) The payability rules preclude payment of child care assistance in respect of the *whole payment period if, in respect of all times in the payment period, a provision or provisions of Part 3 applies to make child care assistance not payable to the person.
Note: If the payability rules preclude payment of child care assistance to the person in respect of part of the payment period, sessions of care in that part of the period are not qualifying sessions of care for the purposes of Schedule 1 (calculation of rate of child care assistance).
20 Qualification for child care assistance
(1) A person is qualified for child care assistance in respect of a *payment period if the conditions set out in subsection (2) are satisfied in relation to a *session of care for a child, or a number of sessions of care for a child, during the payment period.
(2) The conditions to be satisfied in relation to a *session of care are:
(a) the child is a *dependent child of the person, or the person’s partner, during the session; and
(b) the care is provided in Australia by a *child care assistance service; and
(c) the person, or the person’s partner, incurs or has incurred a liability to pay for the session (whether or not the liability has been discharged); and
(d) none of the following provisions apply to make the person not qualified to receive child care assistance in respect of the session of care:
(i) section 22;
(ii) section 23;
(iii) section 24; and
(e) the person, or the person’s partner, is an *inhabitant of Australia during the session; and
(f) the session starts on or after the *payment commencement day.
Note: See section 25 for treatment of a session of care when the child is absent from some or all of the session.
(1) A child is a dependent child of another person for the purposes of child care assistance if:
(a) the child is a dependent child of the person for the purposes of Part 2.17 of the Social Security Act 1991; or
(b) a determination by the Secretary under subsection (2) is in force in relation to the child and the person.
Note: The definition relevant to paragraph (a) is in section 5 of the Social Security Act 1991.
(2) The Secretary may determine in writing that, because of special circumstances, a child is to be treated as a dependent child of another person for the purposes of child care assistance.
22 The immunisation requirement—prospective claimants and recipients
If:
(a) a person is given a notice under subsection 43(1) relating to the immunisation of a child under 7 in respect of whom the person has made a *prospective claim for child care assistance; or
(b) a person is given a notice under subsection 70(1) relating to the immunisation of a child under 7 in respect of whom the person is *receiving child care assistance;
the person is not qualified to receive child care assistance in respect of a *session of care for the child that occurs after the end of the period of 28 days after the notice is given, unless, at the end of that period, the Secretary is satisfied that:
(c) the child is *immunised; or
(d) both of the following have occurred:
(i) a *recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that he or she has discussed with the person the benefits and risks of immunising the child;
(ii) the person has declared in writing that he or she has a *conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(e) if the child is a *dependent child of another person, both of the following have occurred:
(i) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that he or she has discussed with the other person the benefits and risks of immunising the child;
(ii) the other person has declared in writing that he or she has a conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(f) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the immunisation of the child would be medically contraindicated under the specifications set out in the *Australian Immunisation Handbook; or
(g) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the vaccine for immunising the child is not, or will not be, available immediately before or during a session of care in respect of which a claim would otherwise be payable; or
(h) a registered medical practitioner has certified in writing that the child has recovered from the relevant disease, has developed a natural immunity and does not require immunisation.
Note 1: During the 28 days, the person may still be qualified to receive child care assistance.
Note 2: *Retrospective claims are dealt with differently—see section 23.
23 The immunisation requirement—retrospective claimants
(1) A person who makes a *retrospective claim for child care assistance in respect of a *session of care for a child under 7 is not qualified to receive child care assistance in respect of that session of care unless the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the child was *immunised at the time the session occurred; or
(b) the session of care occurred after:
(i) a *recognised immunisation provider certified in writing that he or she had discussed with the person the benefits and risks of immunising the child; and
(ii) the person declared in writing that he or she had a *conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(c) if the child is a *dependent child of another person, the session of care occurred after:
(i) a recognised immunisation provider certified in writing that he or she had discussed with the other person the benefits and risks of immunising the child; and
(ii) the other person declared in writing that he or she had a conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(d) both of the following conditions are satisfied:
(i) at the time of the session of care, the immunisation of the child was medically contraindicated under the specifications set out in the *Australian Immunisation Handbook;
(ii) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the immunisation is medically contraindicated under those specifications; or
(e) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the vaccine for immunising the child was not available immediately before or during the session of care for which a claim has been made; or
(f) a registered medical practitioner has certified in writing that the child has recovered from the relevant disease, has developed a natural immunity and does not require immunisation.
(2) If:
(a) neither the person nor the person’s partner has made an earlier claim under this Act (whether retrospective or prospective, whether for child care assistance or child care rebate, and whether relating to the same or a different child); and
(b) the Secretary is not satisfied as mentioned in subsection (1) in respect of a session of care to which the claim relates;
the Secretary may give the person a notice to the effect that the child must be *immunised if the person is to receive child care assistance in respect of the child. The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available under paragraphs (1)(b) to (f).
(3) If the Secretary gives the person a notice under subsection (2), the Secretary may apply subsection (1) to the claim and the session of care as if:
(a) references in subsection (1) to particular requirements being satisfied at the time of the session of care were instead references to those requirements being satisfied at a time during the period starting after the session of care and ending at the end of the 28th day after the day on which the notice is given; and
(b) references in subsection (1) to particular requirements being satisfied before the session of care were instead references to those requirements being satisfied at a time during the period referred to in paragraph (a).
The determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period referred to in paragraph (a).
(4) If:
(a) the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in a paragraph of subsection (1) (including as applied under subsection (3)) in relation to the child; and
(b) the person or the person’s partner later makes another *retrospective claim for child care assistance in relation to the child;
the Secretary is to regard that paragraph as also being satisfied in relation to the child and the later claim, unless the Secretary considers that there is reason to require the matter in the paragraph to be re-established.
24 Sessions of care in respect of which emergency child care assistance generally not to count
(1) A person is not qualified to receive child care assistance in respect of a *session of care for a child if *emergency child care assistance is paid in respect of the same care to the operator of the *child care assistance service that provides the care.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to a *session of care if the guidelines in force under section 167 provide that child care assistance and *emergency child care assistance may both be paid in respect of that care.
25 Treatment of absences of child from care
(1) The *absence of a child from part only of a *session of care does not prevent the whole session counting as a session of care for the child for the purposes of the application of section 20 to a person, the child and a *payment period.
(2) The *absence of a child from all of a *session of care provided by an *occasional care service prevents the session counting as a session of care for the child for the purposes of section 20.
(3) The *absence of a child from all of a *session of care, other than a session provided by an *occasional care service, does not prevent the whole session counting as a session of care for the child for the purposes of the application of section 20 to a person, the child and a *payment period if, and only if:
(a) the child’s absence is covered by subsection (4); or
(b) the child’s absence is within the limit for other absences that applies to the person, the child and the calendar year in which the absence occurs (see subsection (5)).
(4) The child’s *absence is covered by this subsection if:
(a) the absence is due to the illness of the child, the person or his or her partner, or another person with whom the child lives, and a medical certificate covering that illness is obtained from a *medical practitioner; or
(b) the absence is due to the child’s attendance at a pre-school; or
(c) the absence is due to alternative care arrangements being made for the child because the child does not have to be at school on a pupil-free day; or
(d) the absence is due to the person or his or her partner not being at work:
(i) because of a public holiday; or
(ii) because of a rostered day off; or
(iii) because he or she is a shift worker who works a rotating shift.
(5) The limit for other *absences that applies to the person, the child and a calendar year is 30 days of other absences per calendar year. A day is to be counted towards this limit if the following conditions are satisfied:
(a) the child is absent for all of a *session of care on the day (even if the child attends some or all of another session of care on the day); and
(b) the absence is not covered by subsection (4); and
(c) the session of care is taken into account in calculating the rate of child care assistance payable to the person, or to the person’s partner, in respect of the child; and
(d) that rate is not a nil rate.
(6) In determining if the conditions set out in subsection 20(2) are satisfied in relation to a *session of care from which the child is *absent (wholly or partly) as mentioned in subsection (1) or (3):
(a) subject to paragraph (b), apply subsection 20(2) to the facts as they would be if the child attended all of the session of care; but
(b) the liability referred to in paragraph 20(2)(c) must be a liability actually incurred, despite the child’s absence.
Part 3—Limitations on payability
26 Part sets out limits on payability
This Part sets out circumstances in which, although a person is qualified for child care assistance under Part 2, child care assistance is not payable to the person.
(1) Child care assistance is not payable to a person in respect of any time when the value of the person’s assets exceeds $406,000.
(2) The regulations may provide for child care assistance to be payable to people, despite subsection (1), in situations of hardship.
28 Assets test—determining value of assets
(1) For the purposes of section 27, the value of a person’s assets is to be worked out in accordance with the regulations.
(2) Without limiting subsection (1), the regulations may:
(a) provide that a person’s assets are to include the assets of another person (for example, the person’s partner); and
(b) identify things to be included in a person’s assets; and
(c) identify things not to be included in a person’s assets.
(3) Regulations made for the purposes of this section may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
29 Assets test—indexation of assets limit
(1) The amount specified in subsection 27(1) is to be indexed.
(2) The Minister may, in writing, before the day on which the amount is first indexed, determine that a higher amount is to be substituted for that amount. The determination has effect accordingly.
(3) A determination under subsection (2) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(4) The regulations may prescribe:
(a) when the amount is to be indexed; and
(b) the way in which the amount is to be indexed.
(5) Regulations made for the purposes of this section may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
(6) If an amount (the indexable amount) is indexed in accordance with the regulations, subsection 27(1) has effect as if the new amount (as indexed) were substituted for the indexable amount on the day when the indexation takes effect.
30 Non-temporary cessation of qualification criteria
Child care assistance is not payable to a person in respect of any time after there have ceased (otherwise than temporarily) to be sessions of care in relation to the person in relation to which the conditions specified in subsection 20(2) are satisfied.
Note: Cessations due to a child being on holidays or being ill would generally be only temporary.
31 No payment unless proper claim made
Child care assistance is not payable to a person unless the person has made a proper claim for child care assistance.
Child care assistance is not payable to a person if the rate calculated in respect of a *payment period would be nil.
33 Prospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after the maximum assistance period
(1) Child care assistance is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim in respect of any period before the start of, or after the end of, the *maximum assistance period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 48), or that period as extended under this section.
(2) The Secretary may extend the *maximum assistance period (including as previously extended under this subsection) by a period of at least 4 weeks and not more than 12 months if, before the end of the period:
(a) the person has provided the Secretary with *information relating to the period of the extension in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that the information provides a sufficient basis for the determination of the child care assistance that will be payable to the person in respect of that period.
(3) There is no limit to the number of times that the *maximum assistance period may be extended.
34 Prospective claims—provision of tax file numbers
(1) Child care assistance is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim if:
(a) the person is requested under section 44 or 71 to:
(i) give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s *tax file number; or
(ii) apply for a tax file number and give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number once it has been issued; and
(b) at the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made, the person has not complied with the request; and
(c) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
Note 1: See section 6 for how to comply with a request.
Note 2: During the 28 days, child care assistance may still be payable to the person.
Note 3: *Retrospective claims are dealt with differently—see subsection 44(5).
(2) Child care assistance is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim if:
(a) the person is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the person is requested under section 45 or 72 to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the person’s partner; and
(c) at the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made the person has not complied with the request; and
(d) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
Note 1: See section 7 for how to comply with a request.
Note 2: During the 28 days, child care assistance may still be payable to the person.
Note 3: *Retrospective claims are dealt with differently—see subsection 45(6).
35 Prospective claims—provision of information required by recipient reconciliation notice
(1) Child care assistance is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim if:
(a) the person is, by a *recipient reconciliation notice under section 75, required to provide *information or evidence to the Department; and
(b) at the end of the period specified in the notice, the person has not provided the information or evidence.
Note: During the period, child care assistance may still be payable to the person.
(2) Child care assistance continues not to be payable to the person (even pursuant to a later claim) until the *information or evidence is provided to the Department.
36 Retrospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after maximum assistance period
Child care assistance is not payable to a person pursuant to a *retrospective claim in respect of any period before the start of, or after the end of, the *maximum assistance period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 50).
Part 4—Claims for child care assistance
37 Prospective and retrospective claims
(1) A person may claim child care assistance in one of 2 ways:
(a) the claim may be for payment on an ongoing basis (see subsection (2))—this is a prospective claim; or
(b) the claim may be for payment in respect of a past period (see subsection (3))—this is a retrospective claim.
Note: Child care assistance is only payable in respect of sessions of care that occur on or after the *payment commencement day. This applies both to prospective and retrospective claims.
(2) Payment on an ongoing basis is payment starting from the *payment period in which the claim is made or from a payment period that starts within 4 weeks after the claim is made.
(3) The past period to which a *retrospective claim may relate must be a period:
(a) starting not more than 26 weeks before the claim is made; and
(b) ending not later than the end of the last *payment period before the claim is made.
It must not include any part of the *maximum assistance period in relation to an earlier claim made by the person.
(4) If a *retrospective claim relates to a period contrary to subsection (3), the claim is taken not to relate to that period.
A person who wants to be paid child care assistance must make a proper claim for that payment.
Note 1: For what is a proper claim, see:
(a) section 40 (form of claim); and
(b) section 41 (lodgment of claim).
Note 2: The Secretary has power to treat a proper claim for child care rebate as though it were also a proper claim for child care assistance—see section 92.
39 Secretary may also treat claim as claim for child care rebate
The Secretary may, if the Secretary thinks it is appropriate to do so, treat a proper claim for child care assistance as though it were also a proper claim for child care rebate.
To be a proper claim, a claim must:
(a) be in writing in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) include, or be accompanied by, the *information required by the form.
(1) To be a proper claim, a claim must be lodged:
(a) at an office of the Department; or
(b) at a place approved in writing for the purpose by the Secretary; or
(c) with a person approved in writing for the purpose by the Secretary.
(2) A place or person approved by the Secretary must be a place or person in Australia.
(1) A claimant for child care assistance, or a person on behalf of a claimant, may withdraw a claim that has not been determined.
(2) A claim that is withdrawn is taken to have not been made.
(3) A withdrawal may be made orally or in writing.
43 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised
(1) The Secretary may give a person who makes a *prospective claim for child care assistance a notice stating that a child under 7 to whom the claim relates must be *immunised if the person is to receive child care assistance in respect of sessions of care for the child.
(2) The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available.
Note: The alternatives to immunisation are set out in paragraphs 22(d) to (h).
44 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of tax file number
(1) If a claimant for child care assistance is in Australia, the Secretary may request but not compel the claimant:
(a) if the claimant has a *tax file number—to give the Secretary a written statement of the claimant’s tax file number; or
(b) if the claimant does not have a tax file number:
(i) to apply to the Commissioner of Taxation for a tax file number; and
(ii) to give the Secretary a written statement of the claimant’s tax file number after the Commissioner of Taxation has issued it.
(2) Section 6 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to comply with the request.
(4) If the claim is a *prospective claim, the consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in subsection 34(1).
(5) If the claim is a *retrospective claim:
(a) the determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made; and
(b) the claim is taken not to have been made if:
(i) at the end of that period, the person has not complied with the request; and
(ii) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
45 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of partner’s tax file number
(1) If:
(a) a claimant for child care assistance is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the claimant’s partner is in Australia;
the Secretary may request but not compel the claimant to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the claimant’s partner.
(2) Section 7 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to comply with the request.
(4) Without limiting subsection (3), the Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to satisfy the request if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the claimant does not know the partner’s *tax file number; and
(b) the claimant can obtain none of the following from the partner:
(i) the partner’s tax file number;
(ii) a statement of the partner’s tax file number;
(iii) a declaration by the partner under paragraph 7(2)(b).
(5) If the claim is a *prospective claim, the consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in subsection 34(2).
(6) If the claim is a *retrospective claim:
(a) the determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made; and
(b) the claim is taken not to have been made if:
(i) at the end of that period, the person has not complied with the request; and
(ii) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
Part 5—Determination of claims
46 Division applies if person makes a prospective claim that is a proper claim
This Division applies if a person makes a *prospective claim for child care assistance and the claim is a proper claim.
47 Secretary to determine claim
(1) The Secretary must determine the claim in accordance with subsection (2).
(2) The Secretary must grant the claim if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the person is *entitled to child care assistance in respect of a *payment period that starts at some time in the period:
(i) starting at the beginning of the payment period in which the claim is made; and
(ii) ending 4 weeks after the day on which the claim is made; and
(b) the *information provided by the claimant in relation to the claim provides a sufficient basis for the determination of the child care assistance that is or will be payable to the person in respect of a period consisting of at least the payment period referred to in paragraph (a) and the next payment period.
Otherwise, the Secretary must reject the claim.
Note: For the application of this subsection to claims lodged before the *payment commencement day, see subsection (5).
(3) If the Secretary grants the claim, the determination must specify:
(a) the *maximum assistance period (see section 48); and
(b) the rate or rates at which child care assistance is to be paid to the person during that period.
Note: The determination will specify more than one rate if the amount to be paid to the person in respect of the *payment periods in the *maximum assistance period will not always be the same (for example, because of variations in the level of usage of *child care assistance services).
(4) A determination is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with subsection (3).
(5) The Secretary may, in relation to a claim lodged before the *payment commencement day, apply subsection (2) to the claim as if:
(a) the reference in subparagraph (2)(a)(i) to the *payment period in which the claim is made were instead a reference to the payment period that starts on the payment commencement day; and
(b) the reference in subparagraph (2)(a)(ii) to the day on which the claim is made were instead a reference to the payment commencement day.
The maximum assistance period to be specified in a determination granting the claim is the lesser of:
(a) the period in respect of which the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in paragraph 47(2)(b); and
(b) the period of 12 months starting at the beginning of that period.
Note: The maximum assistance period may be extended under section 33.
Division 2—Retrospective claims
49 Division applies if person makes a retrospective claim that is a proper claim
This Division applies if a person makes a *retrospective claim for child care assistance and the claim is a proper claim.
50 Secretary to determine claim
(1) The Secretary must determine the claim in accordance with subsection (2).
(2) The Secretary must grant the claim if the Secretary is satisfied that the claimant is *entitled to child care assistance in respect of some or all of the period to which the claim relates. Otherwise, the Secretary must reject the claim.
Note: Subsection 37(3) limits the period to which a *retrospective claim may relate.
(3) If the Secretary grants the claim, the determination must specify:
(a) the *maximum assistance period (see section 51); and
(b) the amount of child care assistance to be paid to the person in respect of that period.
(4) A determination is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with subsection (3).
The maximum assistance period to be specified in a determination is the period in respect of which the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in subsection 50(2).
Division 3—Date of effect etc. of determinations
52 Date of effect etc. of determinations may be dealt with in regulations
(1) The regulations may make provision in relation to the following matters:
(a) the date of effect of a determination granting a claim or of a determination of the rate at which child care assistance is payable;
(b) the continuing effect of a determination granting a claim, and the suspension, cancellation or resumption of such a determination and the date from which a suspension, cancellation or resumption takes effect;
(c) the continuing effect of a determination of the rate at which child care assistance is payable, and the variation of such a determination and the date from which a variation takes effect.
(2) Decisions made, or taken to be made, under regulations made for the purposes of subsection (1) are, for the purposes of Chapter 9 (review of decisions), taken to be made under this Act, unless the regulations provide otherwise.
Part 6—Rate of child care assistance
53 Rate of child care assistance
The rate at which child care assistance is payable to a person is to be worked out in accordance with Schedule 1.
Part 7—Payment of child care assistance
Division 1—General provisions about payment
An instalment of child care assistance (worked out in accordance with Part 6) is payable to a person in respect of each *payment period in respect of which the person is *entitled to child care assistance.
55 Prospective claims payment system
Payment of child care assistance pursuant to a *prospective claim is to be made by instalments payable in advance of the *payment periods to which they relate (see Division 2).
56 Retrospective claims payment system
Payment of child care assistance pursuant to a *retrospective claim is to be made by a lump sum payment consisting of the sum of the instalments payable to the person in respect of the relevant *payment periods (see Division 3).
Division 2—Payment pursuant to prospective claims
57 Division deals with payment pursuant to prospective claims
This Division deals with the payment of child care assistance to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim.
Child care assistance becomes payable to the person from the start of the *maximum assistance period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 48).
(1) Child care assistance is to be paid to the person by instalments in accordance with this section.
(2) An instalment of child care assistance is to be paid to the person on each *payday after child care assistance becomes payable to the person.
(3) The instalment to be paid to the person on a *payday is a payment in advance, in respect of the next *payment period to start after the payday, at the rate that will apply to that period.
(4) If it is not practicable to pay the instalment in respect of a *payment period on a *payday as required by subsections (2) and (3) because the payday occurs before or soon after the claim is determined, that instalment is instead to be paid as soon as practicable after the payday, or the determination of the claim, whichever is later.
60 Payments generally to be made to operator of child care assistance service
(1) Subject to section 61, each amount of child care assistance is to be paid, on behalf of the person, to the operator of the *child care assistance service providing the relevant child care. If there is more than one such service, the amount is to be apportioned between the operators of those services as directed by the Secretary.
(2) An amount paid to a *child care assistance service on the person’s behalf is to be paid to the operator of the service as part of a lump sum, known as a group payment, consisting of that amount and amounts of child care assistance paid to the service on behalf of other people.
(3) If a *group payment is paid to the operator, the operator is to be given a notice (a group payment notice):
(a) specifying the total amount payable, and giving particulars of how that amount is made up of amounts to be paid to the service on behalf of other people; and
(b) specifying how that total amount is to be applied to discharge or reduce liabilities owed to the service by, or by partners of, those people; and
(c) specifying the amount (if any) by which that total amount has been reduced by a deduction or deductions under section 147, and the debt or debts in respect of which the deduction or deductions was or were made; and
(d) if paragraph (c) applies—the net amount actually paid to the service.
(4) The operator must, in accordance with the *group payment notice, apply the *group payment to discharge or reduce liabilities owed to the service by, or by partners of, the people identified in the group payment notice.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(5) The people identified in the *group payment notice are taken to have paid the operator the amounts specified as mentioned in paragraph (3)(a), even if the net amount actually paid to the operator is, because of a deduction or deductions under section 147, less than the total of those amounts.
61 Payment may be made to the person
Section 60 does not apply to all or part of an amount if the Secretary directs that the amount, or the part of the amount, is to be paid directly to the person:
(a) because the liability in respect of the relevant care has already been discharged; or
(b) because of some other special circumstance.
The direction has effect accordingly.
62 Payment into bank etc. account
(1) An amount that is, under section 60, to be paid to the operator of a *child care assistance service on the person’s behalf is to be paid to the credit of a bank account, credit union account or building society account nominated and maintained by the operator.
(2) An amount that is, under section 61, to be paid directly to the person is to be paid to the credit of a bank account, credit union account or building society account nominated and maintained by the person.
(3) An account into which amounts are paid under this section may be maintained by the operator or person either alone or jointly or in common with another person or body.
(4) The Secretary may direct that the whole or a part of an amount is to be paid to the operator or person in a way that is different from that required by subsection (1) or (2). The direction has effect accordingly.
63 Where payday would fall on public holiday etc.
If the Secretary is satisfied that an amount of child care assistance that would normally be paid on a particular day cannot reasonably be paid on that day (because, for example, it is a public holiday or a bank holiday), the Secretary may direct that the amount is to be paid on an earlier day. The direction has effect accordingly.
64 Payment after death of person
(1) If:
(a) the person dies; and
(b) at the date of the person’s death the person had not *received an amount of child care assistance to be paid directly to him or her; and
(c) another person applies to receive the amount; and
(d) the application is made:
(i) within 26 weeks after the death; or
(ii) within a further period allowed by the Secretary in special circumstances;
the Secretary may pay the amount to the person who, in the Secretary’s opinion, is best entitled to it.
(2) If the Secretary pays an amount of child care assistance under subsection (1), the Commonwealth has no further liability to anyone in respect of that child care assistance.
Division 3—Payment pursuant to retrospective claims
65 Division deals with payment pursuant to retrospective claims
This Division deals with the payment of child care assistance to a person pursuant to a *retrospective claim.
(1) The child care assistance is to be paid to the person in a lump sum as soon as practicable after the determination of the claim.
(2) The amount of the lump sum is the sum of the instalments to be paid to the person in respect of the relevant *payment periods.
(3) The instalment to be paid to a person in respect of a *payment period is a payment in respect of that period at the rate that applies to that period.
67 Payment into bank etc. account
(1) The child care assistance is to be paid to the credit of a bank account, credit union account or building society account nominated and maintained by the person.
(2) The account may be maintained by the person either alone or jointly or in common with another person or body.
(3) The Secretary may direct that the whole or a part of an amount of the child care assistance is to be paid to the person in a way that is different from that required by subsection (1). The direction has effect accordingly.
68 Payment after death of person
(1) If:
(a) the person dies; and
(b) at the date of the person’s death the person had not *received an amount of child care assistance to be paid to him or her; and
(c) another person applies to receive the amount; and
(d) the application is made:
(i) within 26 weeks after the death; or
(ii) within a further period allowed by the Secretary in special circumstances;
the Secretary may pay the amount to the person who, in the Secretary’s opinion, is best entitled to it.
(2) If the Secretary pays an amount of child care assistance under subsection (1), the Commonwealth has no further liability to anyone in respect of that child care assistance.
69 Part deals with obligations of people paid pursuant to prospective claims
This Part deals with the obligations of a person who is *receiving child care assistance pursuant to a *prospective claim.
70 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice stating that a child under 7 in respect of whom the child care assistance is being paid must be *immunised if the person is to continue to receive child care assistance in respect of sessions of care for the child.
Note: See section 22 for the consequences of a child not being immunised.
(2) The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available.
Note: The alternatives to immunisation are set out in paragraphs 22(d) to (h).
71 Secretary may request person to give statement of tax file number
(1) If the person is in Australia, the Secretary may request but not compel the person:
(a) if the person has a *tax file number—to give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number; or
(b) if the person does not have a tax file number:
(i) to apply to the Commissioner of Taxation for a tax file number; and
(ii) to give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number after the Commissioner of Taxation has issued it.
(2) Section 6 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the person from having to comply with the request.
(4) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in subsection 34(1).
72 Secretary may request person to give statement of partner’s tax file number
(1) If:
(a) the person is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the person’s partner is in Australia;
the Secretary may request but not compel the person to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the person’s partner.
(2) Section 7 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the person from having to comply with the request.
(4) Without limiting subsection (3), the Secretary may exempt the person from having to satisfy the request if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the person does not know the partner’s *tax file number; and
(b) the person can obtain none of the following from the partner:
(i) the partner’s tax file number;
(ii) a statement of the partner’s tax file number;
(iii) a declaration by the partner under paragraph 7(2)(b).
(5) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in subsection 34(2).
73 Secretary may require notice of the happening of an event or a change of circumstances
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to inform the Department if:
(a) a specified event or change of circumstances occurs; or
(b) the person becomes aware that a specified event or change of circumstances is likely to occur.
(2) An event or change of circumstances is not to be specified in the notice unless the occurrence of the event or change of circumstances might affect the payment of the child care assistance.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the person is to give the *information to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient notification notice given under this Act.
(4) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (3)(c) or (e).
(5) The period specified under paragraph (3)(d) must end at least 14 days after:
(a) the day on which the event or change of circumstances occurs; or
(b) the day on which the person becomes aware that the event or change of circumstances is likely to occur.
(6) If the notice requires the person to inform the Department of any proposal by the person to leave Australia, subsection (5) does not apply to that requirement.
(7) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibilities.
(8) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
74 Secretary may require person to give particular information relevant to payment of child care assistance
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to give the Department a statement about a specified matter that might affect the payment of child care assistance to the person.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the statement is to be given to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the statement to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient statement notice given under this Act.
(3) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (2)(c) or (e).
(4) The period specified under paragraph (2)(d) must end at least 14 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) A statement given in response to the notice must be in writing and in accordance with a form approved in writing by the Secretary.
(6) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(7) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
75 Secretary may require person to give information relating to entitlement to child care assistance in a past period
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to give the Department *information about specified matters relating to the person’s entitlement to be paid child care assistance, or the rate at which child care assistance was payable to the person, in respect of a specified past period.
(2) The notice may also require the person to produce evidence of liabilities of a kind referred to in paragraph 20(2)(c) incurred in respect of the period.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the *information or evidence is to be given to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information or evidence to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient reconciliation notice given under this Act.
(4) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (3)(c) or (e).
(5) The period specified under paragraph (3)(d) must end at least 14 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(6) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(7) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
76 Secretary may require person to give notice of change of address
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to inform the Department if the person has changed or changes his or her address.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the person is to give the *information to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a notice given under this Act.
(3) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (2)(c) or (e).
(4) The period specified under paragraph (2)(d) must end at least 14 days after the later of:
(a) the day on which the person changes address; or
(b) the day on which the notice is given.
77 Entitlement to child care rebate
(1) A person is entitled to child care rebate in respect of a *payment period if:
(a) the person is qualified for child care rebate in respect of the payment period (see Part 2); and
(b) the payability rules (see Part 3) do not preclude payment of child care rebate to the person in respect of the whole payment period.
Note: A person may also be entitled, in respect of the same payment period, to child care assistance (see Chapter 2).
(2) The payability rules preclude payment of child care rebate in respect of the whole *payment period if, in respect of all times in the payment period, a provision or provisions of Part 3 applies to make child care rebate not payable to the person.
Note: If the payability rules preclude payment of child care rebate to the person in respect of part of the payment period, sessions of care in that part of the period are not qualifying sessions of care for the purposes of Schedule 2 (calculation of rate of child care rebate).
78 Qualification for child care rebate
(1) A person is qualified for child care rebate in respect of a *payment period if the conditions set out in subsection (2) are satisfied in relation to a *session of care for a child, or a number of sessions of care for a child, during the payment period.
(2) The conditions to be satisfied in relation to a *session of care are:
(a) the child is a *dependent child of the person, or the person’s partner, during the session; and
(b) the care is provided in Australia by a *child care rebate service; and
(c) the child is not a dependent child of a person who is, or of the partner of a person who is:
(i) the operator of the service; or
(ii) a member of a business partnership that operates the service; and
(d) the person, or the person’s partner, incurs or has incurred a liability to pay for the session (whether or not that liability has been discharged); and
(e) the person, and the person’s partner (if any), *satisfy the work/training/study test at some time during the week of the *payment period in which the session occurs; and
(f) none of the following provisions apply to make the person not qualified to receive child care rebate in respect of the session of care:
(i) section 80;
(ii) section 81; and
(g) the person, or the person’s partner, is an *inhabitant of Australia during the session; and
(h) the session starts on or after the *payment commencement day.
Note: See section 82 for treatment of a session of care when the child is absent from some or all of the session.
(3) In this section:
business partnership means a partnership between 2 or more persons carrying on a business of providing child care.
(1) A child is a dependent child of another person for the purposes of child care rebate if:
(a) the child:
(i) is under 13; or
(ii) has turned 13 but is under 17, and is a disabled child as defined in subsection (2); and
(b) the relationship between the child and the other person satisfies one of the conditions set out in subsection (3).
(2) A child is a disabled child if:
(a) the child has a physical, intellectual or psychiatric disability; and
(b) because of that disability:
(i) the child needs care and attention from another person on a daily basis; and
(ii) the care and attention needed by the child is substantially more than that needed by a child of the same age who does not have a physical, intellectual or psychiatric disability; and
(c) the child is likely to need that care and attention permanently or for an extended period.
(3) The conditions relating to the relationship between the child and the other person are:
(a) the other person is legally responsible (whether alone or jointly with a third person) for the day-to-day care, welfare and development of the child, and the child is in the other person’s care; or
(b) the child is wholly or substantially in the other person’s care, and there is no one else who is in a relationship with the child as described in paragraph (a); or
(c) a determination by the Secretary under subsection (4) is in force in relation to the relationship between the child and the other person.
(4) The Secretary may, in writing, determine that the relationship between the child and the other person is sufficient for the purposes of this section if the other person has the day-to-day care of the child on a long term basis (otherwise than in the course of carrying on a business of providing care or a business of a pre‑school).
80 The immunisation requirement—prospective claimants and recipients
If:
(a) a person is given a notice under subsection 96(1) relating to the immunisation of a child under 7 in respect of whom the person has made a *prospective claim for child care rebate; or
(b) a person is given a notice under subsection 122(1) relating to the immunisation of a child under 7 in respect of whom the person is *receiving child care rebate;
the person is not qualified to receive child care rebate in respect of a *session of care for the child that occurs after the end of the period of 28 days after the notice is given, unless, at the end of that period, the Secretary is satisfied that:
(c) the child is *immunised; or
(d) both of the following have occurred:
(i) a *recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that he or she has discussed with the person the benefits and risks of immunising the child;
(ii) the person has declared in writing that he or she has a *conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(e) if the child is a *dependent child of another person, both of the following have occurred:
(i) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that he or she has discussed with the other person the benefits and risks of immunising the child;
(ii) the other person has declared in writing that he or she has a conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(f) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the immunisation of the child would be medically contraindicated under the specifications set out in the *Australian Immunisation Handbook; or
(g) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the vaccine for immunising the child is not available immediately before or during a session of care in respect of which a claim would otherwise be payable; or
(h) a registered medical practitioner has certified in writing that the child has recovered from the relevant disease, has developed a natural immunity and does not require immunisation.
Note 1: During the 28 days, the person may still be qualified to receive child care rebate.
Note 2: *Retrospective claims are dealt with differently—see section 81.
81 The immunisation requirement—retrospective claimants
(1) A person who makes a *retrospective claim for child care rebate in respect of a *session of care for a child under 7 is not qualified to receive child care rebate in respect of that session of care unless the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the child was *immunised at the time the session occurred; or
(b) the session of care occurred after:
(i) a *recognised immunisation provider certified in writing that he or she had discussed with the person the benefits and risks of immunising the child; and
(ii) the person declared in writing that he or she had a *conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(c) if the child is a *dependent child of another person, the session of care occurred after:
(i) a recognised immunisation provider certified in writing that he or she had discussed with the other person the benefits and risks of immunising the child; and
(ii) the other person declared in writing that he or she had a conscientious objection to the child being immunised; or
(d) both of the following conditions are satisfied:
(i) at the time of the session of care the immunisation of the child was medically contraindicated under the specifications set out in the *Australian Immunisation Handbook;
(ii) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the immunisation is medically contraindicated under those specifications; or
(e) a recognised immunisation provider has certified in writing that the vaccine for immunising the child was not available immediately before or during the session of care for which a claim has been made; or
(f) a registered medical practitioner has certified in writing that the child has recovered from the relevant disease, has developed a natural immunity and does not require immunisation.
(2) If:
(a) neither the person nor the person’s partner has made an earlier claim under this Act (whether retrospective or prospective, whether for child care assistance or child care rebate, and whether relating to the same or a different child); and
(b) the Secretary is not satisfied as mentioned in subsection (1) in respect of a session of care to which the claim relates;
the Secretary may give the person a notice to the effect that the child must be *immunised if the person is to receive child care rebate in respect of the child. The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available under paragraphs (1)(b) to (f).
(3) If the Secretary gives the person a notice under subsection (2), the Secretary may apply subsection (1) to the claim and the session of care as if:
(a) references in subsection (1) to particular requirements being satisfied at the time of the session of care were instead references to those requirements being satisfied at a time during the period starting after the session of care and ending at the end of the 28th day after the day on which the notice is given; and
(b) references in subsection (1) to particular requirements being satisfied before the session of care were instead references to those requirements being satisfied at a time during the period referred to in paragraph (a).
The determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period referred to in paragraph (a).
(4) If:
(a) the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in a paragraph of subsection (1) (including as applied under subsection (3)) in relation to the child; and
(b) the person or the person’s partner later makes another *retrospective claim for child care rebate in relation to the child;
the Secretary is to regard that paragraph as also being satisfied in relation to the child and the later claim, unless the Secretary considers that there is reason to require the matter in the paragraph to be re-established.
82 Treatment of absences of child from care
(1) The *absence of a child from all or part of a *session of care does not prevent the whole session of care counting as a session of care for the child for the purposes of the application of section 78 to a person, the child and a *payment period.
(2) In determining if the conditions set out in subsection 78(2) are satisfied in relation to a *session of care during some or all of which the child is *absent:
(a) subject to paragraph (b), apply the subsection to the facts as they would be if the child attended all of the session of care; but
(b) the liability referred to in paragraph 78(2)(d) must be a liability actually incurred, despite the child’s absence.
Part 3—Limitations on payability
83 Part sets out limits on payability
This Part sets out circumstances in which, although a person is qualified for child care rebate under Part 2, child care rebate is not payable to the person.
84 Non-temporary cessation of qualification criteria
Child care rebate is not payable to a person in respect of any time after there have ceased (otherwise than temporarily) to be sessions of care in relation to the person in relation to which the conditions specified in subsection 78(2) are satisfied.
Note: Cessations due to a child being on holidays or being ill would generally be only temporary.
85 No payment unless proper claim made
Child care rebate is not payable to a person unless the person has made a proper claim for child care rebate.
Child care rebate is not payable to a person if the rate calculated in respect of a *payment period would be nil.
87 Prospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after the maximum rebate period
(1) Child care rebate is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim in respect of any period before the start of, or after the end of, the *maximum rebate period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 101), or that period as extended under this section.
(2) The Secretary may extend the *maximum rebate period (including as previously extended under this subsection) by a period of at least 4 weeks and not more than 12 months if, before the end of the period:
(a) the person has provided the Secretary with *information relating to the period of the extension in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that the information provides a sufficient basis for the determination of the child care rebate that will be payable to the person in respect of that period.
(3) There is no limit to the number of times that the *maximum rebate period may be extended.
88 Prospective claims—provision of information required by recipient reconciliation notice
(1) Child care rebate is not payable to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim if:
(a) the person is, by a *recipient reconciliation notice under section 127, required to provide *information or evidence to the Department; and
(b) at the end of the period specified in the notice, the person has not provided the information or evidence.
Note: During the period, child care rebate may still be payable to the person.
(2) Child care rebate continues to be not payable to the person (even pursuant to a later claim) until the *information or evidence is provided to the Department.
89 Retrospective claims—no payment in respect of periods before or after maximum rebate period
Child care rebate is not payable to a person pursuant to a *retrospective claim in respect of any period before the start of, or after the end of, the *maximum rebate period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 103).
Part 4—Claims for child care rebate
90 Prospective and retrospective claims
(1) A person may claim child care rebate in one of 2 ways:
(a) the claim may be for payment on an ongoing basis (see subsection (2))—this is a prospective claim; or
(b) the claim may be for payment in respect of a past period (see subsection (3))—this is a retrospective claim.
Note: Child care rebate is only payable in respect of sessions of care that occur on or after the *payment commencement day. This applies both to prospective and retrospective claims.
(2) Payment on an ongoing basis is payment starting from the *payment period in which the claim is made or from a payment period that starts within 4 weeks after the claim is made.
(3) The past period to which a *retrospective claim may relate must be a period:
(a) starting not more than 26 weeks before the claim is made; and
(b) ending not later than the end of the last *payment period before the claim is made.
It must not include any part of the *maximum rebate period in relation to an earlier claim made by the person.
(4) If a *retrospective claim relates to a period contrary to subsection (3), the claim is taken not to relate to that period.
A person who wants to be paid child care rebate must make a proper claim for that payment.
Note 1: For what is a proper claim, see:
(a) section 93 (form of claim); and
(b) section 94 (lodgment of claim).
Note 2: The Secretary has power to treat a proper claim for child care assistance as though it were also a proper claim for child care rebate—see section 39.
92 Secretary may also treat claim as claim for child care assistance
The Secretary may, if the Secretary thinks it is appropriate to do so, treat a proper claim for child care rebate as though it were also a proper claim for child care assistance.
To be a proper claim, the claim must:
(a) be in writing in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) include, or be accompanied by, the information required by the form.
(1) To be a proper claim, a claim must be lodged:
(a) at an office of the Department; or
(b) at a place approved in writing for the purpose by the Secretary; or
(c) with a person approved in writing for the purpose by the Secretary.
(2) A place or person approved by the Secretary must be a place or person in Australia.
(1) A claimant for child care rebate, or a person on behalf of a claimant, may withdraw a claim that has not been determined.
(2) A claim that is withdrawn is taken to have not been made.
(3) A withdrawal may be made orally or in writing.
96 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised
(1) The Secretary may give a person who makes a *prospective claim for child care rebate a notice stating that a child under 7 to whom the claim relates must be *immunised if the person is to receive child care rebate in respect of sessions of care for the child.
(2) The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available.
Note: The alternatives to immunisation are set out in paragraphs 80(d) to (h).
97 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of tax file number
(1) If a claimant for child care rebate is in Australia, the Secretary may request but not compel the claimant:
(a) if the claimant has a *tax file number—to give the Secretary a written statement of the claimant’s tax file number; or
(b) if the claimant does not have a tax file number:
(i) to apply to the Commissioner of Taxation for a tax file number; and
(ii) to give the Secretary a written statement of the claimant’s tax file number after the Commissioner of Taxation has issued it.
(2) Section 6 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to comply with the request.
(4) If the claim is a *retrospective claim, the determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made.
(5) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in point C2 of Schedule 2 (calculation of rate of child care rebate).
98 Secretary may request claimant to give statement of partner’s tax file number
(1) If:
(a) a claimant for child care rebate is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the claimant’s partner is in Australia;
the Secretary may request but not compel the claimant to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the claimant’s partner.
(2) Section 7 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to comply with the request.
(4) Without limiting subsection (3), the Secretary may exempt the claimant from having to satisfy the request if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the claimant does not know the partner’s *tax file number; and
(b) the claimant can obtain none of the following from the partner:
(i) the partner’s tax file number;
(ii) a statement of the partner’s tax file number;
(iii) a declaration by the partner under paragraph 7(2)(b).
(5) If the claim is a *retrospective claim, the determination of the claim may be deferred until the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made.
(6) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in point C2 of Schedule 2 (calculation of rate of child care rebate).
Part 5—Determination of claims
99 Division applies if person makes a prospective claim that is a proper claim
This Division applies if a person makes a *prospective claim for child care rebate and the claim is a proper claim.
100 Secretary to determine claim
(1) The Secretary must determine the claim in accordance with subsection (2).
(2) The Secretary must grant the claim if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the person is *entitled to child care rebate in respect of a *payment period that starts at some time in the period:
(i) starting at the beginning of the payment period in which the claim is made; and
(ii) ending 4 weeks after the day on which the claim is made; and
(b) the *information provided by the claimant in relation to the claim provides a sufficient basis for the determination of the child care rebate that is or will be payable to the person in respect of a period consisting of at least the payment period referred to in paragraph (a) and the next payment period.
Otherwise, the Secretary must reject the claim.
Note: For the application of this subsection to claims lodged before the *payment commencement day, see subsection (5).
(3) If the Secretary grants the claim, the determination must specify:
(a) the *maximum rebate period (see section 101); and
(b) the rate or rates at which child care rebate is to be paid to the person during that period.
Note: The determination will specify more than one rate if the amount to be paid to the person in respect of the *payment periods in the *maximum rebate period will not always be the same (for example, because of variations in the level of usage of *child care rebate services).
(4) A determination is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with subsection (3).
(5) The Secretary may, in relation to a claim lodged before the *payment commencement day, apply subsection (2) to the claim as if:
(a) the reference in subparagraph (2)(a)(i) to the *payment period in which the claim is made were instead a reference to the payment period that starts on the payment commencement day; and
(b) the reference in subparagraph (2)(a)(ii) to the day on which the claim is made were instead a reference to the payment commencement day.
The maximum rebate period to be specified in a determination granting the claim is the lesser of:
(a) the period in respect of which the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in paragraph 100(2)(b); and
(b) the period of 12 months starting at the beginning of that period.
Note: The maximum rebate period may be extended under section 87.
Division 2—Retrospective claims
102 Division applies if person makes a retrospective claim that is a proper claim
This Division applies if a person makes a *retrospective claim for child care rebate and the claim is a proper claim.
103 Secretary to determine claim
(1) The Secretary must determine the claim in accordance with subsection (2).
(2) The Secretary must grant the claim if the Secretary is satisfied that the claimant is *entitled to child care rebate in respect of some or all of the period to which the claim relates. Otherwise, the Secretary must reject the claim.
Note: Subsection 90(3) limits the period to which a *retrospective claim may relate.
(3) If the Secretary grants the claim, the determination must specify:
(a) the *maximum rebate period (see section 104); and
(b) the amount of child care rebate to be paid to the person in respect of that period.
(4) A determination is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with subsection (3).
The maximum rebate period to be specified in a determination is the period in respect of which the Secretary is satisfied as mentioned in subsection 100(2).
Division 3—Date of effect etc. of determinations
105 Date of effect etc. of determinations may be dealt with in regulations
(1) The regulations may make provision in relation to the following matters:
(a) the date of effect of a determination granting a claim or of a determination of the rate at which child care rebate is payable;
(b) the continuing effect of a determination granting a claim, and the suspension, cancellation or resumption of such a determination and the date from which a suspension, cancellation or resumption takes effect;
(c) the continuing effect of a determination of the rate at which child care rebate is payable, and the variation of such a determination and the date from which a variation takes effect.
(2) Decisions made, or taken to be made, under regulations made for the purposes of subsection (1) are, for the purposes of Chapter 9 (review of decisions), taken to be made under this Act, unless the regulations provide otherwise.
Part 6—Rate of child care rebate
The rate at which child care rebate is payable to a person is to be worked out in accordance with Schedule 2.
Part 7—Payment of child care rebate
Division 1—General provisions about payment
An instalment of child care rebate (worked out in accordance with Part 6) is payable to a person in respect of each *payment period in respect of which the person is *entitled to child care rebate.
108 Prospective claims payment system
Payment of child care rebate pursuant to a *prospective claim is to be made by instalments payable after the *payment periods to which they relate (see Division 2).
109 Retrospective claims payment system
Payment of child care rebate pursuant to a *retrospective claim is to be made by a lump sum payment consisting of the sum of the instalments payable to the person in respect of the relevant *payment periods (see Division 3).
Division 2—Payment pursuant to prospective claims
110 Division deals with payment pursuant to prospective claims
This Division deals with the payment of child care rebate to a person pursuant to a *prospective claim.
Child care rebate becomes payable to the person from the start of the *maximum rebate period specified in the determination granting the claim (see section 101).
(1) Child care rebate is to be paid to the person by instalments in accordance with this section.
(2) An instalment of child care rebate is to be paid to the person on each *payday after child care rebate becomes payable to the person.
(3) The instalment to be paid to the person on a *payday is a payment in arrears, in respect of the last *payment period to end before the payday, at the rate that applies to that period.
(4) If it is not practicable to pay the instalment in respect of a *payment period on a *payday as required by subsections (2) and (3) because the payday occurs before or soon after the claim is determined, that instalment is instead to be paid as soon as practicable after the payday, or the determination of the claim, whichever is later.
113 Payments to be made to person
Each amount of child care rebate is to be paid to the person.
114 Payment into person’s bank etc. account
(1) The child care rebate is to be paid to the credit of a bank account, credit union account or building society account nominated and maintained by the person.
(2) The account may be maintained by the person either alone or jointly or in common with another person or body.
(3) The Secretary may direct that the whole or a part of the amount is to be paid to the person in a way that is different from that required by subsection (1). The direction has effect accordingly.
115 Where payday would fall on public holiday etc.
If the Secretary is satisfied that an amount of child care rebate that would normally be paid on a particular day cannot reasonably be paid on that day (because, for example, it is a public holiday or a bank holiday), the Secretary may direct that the amount is to be paid on an earlier day.
116 Payment after death of person
(1) If:
(a) the person dies; and
(b) at the date of the person’s death the person had not *received an amount of child care rebate to be paid to him or her; and
(c) another person applies to receive the amount; and
(d) the application is made:
(i) within 26 weeks after the death; or
(ii) within a further period allowed by the Secretary in special circumstances;
the Secretary may pay the amount to the person who, in the Secretary’s opinion, is best entitled to it.
(2) If the Secretary pays an amount of child care rebate under subsection (1), the Commonwealth has no further liability to anyone in respect of that child care rebate.
Division 3—Payment pursuant to retrospective claims
117 Division deals with payment pursuant to retrospective claims
This Division deals with the payment of child care rebate to a person pursuant to a *retrospective claim.
(1) The child care rebate is to be paid to the person in a lump sum as soon as practicable after the determination of the claim.
(2) The amount of the lump sum is the sum of the instalments to be paid to the person in respect of the relevant *payment periods.
(3) The instalment to be paid to a person in respect of a *payment period is a payment in respect of that period at the rate that applies to that period.
119 Payment into bank etc. account
(1) The child care rebate is to be paid to the credit of a bank account, credit union account or building society account nominated and maintained by the person.
(2) The account may be maintained by the person either alone or jointly or in common with another person or body.
(3) The Secretary may direct that the whole or a part of an amount of the child care rebate is to be paid to the person in a way that is different from that required by subsection (1). The direction has effect accordingly.
120 Payment after death of person
(1) If:
(a) the person dies; and
(b) at the date of the person’s death the person had not *received an amount of child care rebate to be paid to him or her; and
(c) another person applies to receive the amount; and
(d) the application is made:
(i) within 26 weeks after the death; or
(ii) within a further period allowed by the Secretary in special circumstances;
the Secretary may pay the amount to the person who, in the Secretary’s opinion, is best entitled to it.
(2) If the Secretary pays an amount of child care rebate under subsection (1), the Commonwealth has no further liability to anyone in respect of that child care rebate.
121 Part deals with obligations of people paid pursuant to prospective claims
This Part deals with the obligations of a person who is *receiving child care rebate pursuant to a *prospective claim.
122 Secretary may give notice stating that child must be immunised
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice stating that a child under 7 in respect of whom the child care rebate is being paid must be *immunised if the person is to continue to receive child care rebate in respect of sessions of care for the child.
Note: See section 80 for the consequences of a child not being *immunised.
(2) The notice must also explain the alternatives to immunisation that may be available under paragraphs 80(d) to (h).
123 Secretary may request person to give statement of tax file number
(1) If the person is in Australia, the Secretary may request but not compel the person:
(a) if the person has a *tax file number—to give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number; or
(b) if the person does not have a tax file number:
(i) to apply to the Commissioner of Taxation for a tax file number; and
(ii) to give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number after the Commissioner of Taxation has issued it.
(2) Section 6 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the person from having to comply with the request.
(4) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in point C2 of Schedule 2 (calculation of rate of child care rebate).
124 Secretary may request person to give statement of partner’s tax file number
(1) If:
(a) the person is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the person’s partner is in Australia;
the Secretary may request but not compel the person to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the person’s partner.
(2) Section 7 deals with how the request may be complied with.
(3) The Secretary may exempt the person from having to comply with the request.
(4) Without limiting subsection (3), the Secretary may exempt the person from having to satisfy the request if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the person does not know the partner’s *tax file number; and
(b) the person can obtain none of the following from the partner:
(i) the partner’s tax file number;
(ii) a statement of the partner’s tax file number;
(iii) a declaration by the partner under paragraph 7(2)(b).
(5) The consequences of failing to comply with the request are as set out in point C2 of Schedule 2 (calculation of rate of child care rebate).
125 Secretary may require notice of the happening of an event or a change of circumstances
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to inform the Department if:
(a) a specified event or change of circumstances occurs; or
(b) the person becomes aware that a specified event or change of circumstances is likely to occur.
(2) An event or change of circumstances is not to be specified in the notice unless the occurrence of the event or change of circumstances might affect the payment of the child care rebate.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the person is to give the *information to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient notification notice given under this Act.
(4) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (3)(c) or (e).
(5) The period specified under paragraph (3)(d) must end at least 14 days after:
(a) the day on which the event or change of circumstances occurs; or
(b) the day on which the person becomes aware that the event or change of circumstances is likely to occur.
(6) If the notice requires the person to inform the Department of any proposal by the person to leave Australia, subsection (5) does not apply to that requirement.
(7) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(8) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
126 Secretary may require person to give particular information relevant to payment of child care rebate
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to give the Department a statement about a specified matter than might affect the payment of the child care rebate to the person.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the statement is to be given to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the statement to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient statement notice given under this Act.
(3) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (2)(c) or (e).
(4) The period specified under paragraph (2)(d) must end at least 14 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(5) A statement given in response to the notice must be in writing and in accordance with a form approved in writing by the Secretary.
(6) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(7) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
127 Secretary may require person to give information relating to entitlement to child care rebate in a past period
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to give the Department *information about specified matters relating to the person’s entitlement to be paid child care rebate, or the rate at which child care rebate was payable to the person, in respect of a specified past period.
(2) The notice may also require the person to produce evidence of liabilities of a kind referred to in paragraph 78(2)(d) incurred in respect of the period.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the *information or evidence is to be given to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information or evidence to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a recipient reconciliation notice given under this Act.
(4) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (3)(c) or (e).
(5) The period specified under paragraph (3)(d) must end at least 14 days after the day on which the notice is given.
(6) The person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with the notice.
Penalty: 30 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(7) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
128 Secretary may require person to give notice of change of address
(1) The Secretary may give the person a notice that requires the person to inform the Department if the person has changed or changes his or her address.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the notice:
(a) must be in writing; and
(b) may be given personally or by post; and
(c) must specify how the person is to give the *information to the Department; and
(d) must specify the period within which the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(e) must specify that the notice is a notice given under this Act.
(3) The notice is not invalid merely because it fails to comply with paragraph (2)(c) or (e).
(4) The period specified under paragraph (2)(d) must end at least 14 days after the later of:
(a) the day on which the person changes address; or
(b) the day on which the notice is given.
Chapter 4—Overpayments and debt recovery
129 Amount paid to person includes amount paid on person’s behalf to another person
For the purposes of this Chapter, an amount of a *child care payment is taken to be paid to a person even if the amount is paid, on the person’s behalf, to another person (for example, a *child care assistance service).
130 Special provisions relating to operators of child care assistance services
(1) For the purposes of this Chapter, a reference to an amount being paid to the operator of a *child care assistance service includes a reference to an amount being paid to a former operator of a child care assistance service.
(2) Debts under this Chapter are owed by the operator or former operator that incurred the debt, even if the *child care assistance service comes to have a new operator, and references to the operator have effect accordingly.
131 Chapter does not apply to emergency child care assistance
This Chapter does not apply to *emergency child care assistance.
Part 2—Amounts recoverable under this Act
132 Debts due to the Commonwealth
If an amount has been paid by way of a *child care payment, the amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth if, and only if, a provision of this Act or the Data-matching Program (Assistance and Tax) Act 1990 expressly provides that it is.
Note: For the provisions of this Act that create debts due to the Commonwealth, see sections 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139 and 140.
133 Debts arising under this Act
No entitlement to amount—debt generally owed by person
(1) Subject to subsection (2), if:
(a) an amount has been paid to a person by way of a *child care payment in respect of a period; and
(b) the person was not *entitled to the child care payment in respect of that period;
the amount so paid is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the person.
No entitlement to amount—debt may instead be owed by service operator
(2) If:
(a) child care assistance is paid on behalf of a person to the operator of a *child care assistance service; and
(b) the payment is in respect of a period after the service is no longer providing care for any *dependent child of the person or the person’s partner;
the amount so paid:
(c) is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the operator; and
(d) is not a debt due to the Commonwealth by the person under subsection (1).
Note 1: A service may, for example, no longer provide care for a child because the child starts going to another service, because the child dies or because the service ceases to operate.
Note 2: Child care assistance paid on behalf of a person to the operator of a *child care assistance service will be paid as part of a *group payment.
Duplicate instalments—debt generally owed by person
(3) Subject to subsection (4), if:
(a) an amount has been paid to a person by way of an instalment of a *child care payment; and
(b) another amount (the later amount) is paid to the person in respect of the same instalment; and
(c) the later amount is not a payment of arrears; and
(d) the later amount would not otherwise be a debt due to the Commonwealth;
the later amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the person.
Duplicate instalments—modified effect of subsection (3) taking into account payments to service operator
(4) Subsection (3) has effect in relation to child care assistance subject to the following qualifications:
(a) if the first amount and the later amount were both paid to the operator of the same *child care assistance service on a person’s behalf, the later amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the operator, not the person;
(b) if one of the amounts was paid in accordance with the method applicable under section 60 and the other was not, it is that other amount (which may be the first amount or the later amount) that is a debt due to the Commonwealth, and it is due by:
(i) the person, if it was paid directly to a person; or
(ii) the operator of the child care assistance service, if it was paid to the operator of a child care assistance service on a person’s behalf.
Note: Child care assistance paid on behalf of a person to the operator of a *child care assistance service will be paid as part of a *group payment.
Incorrectly calculated amount—debt owed by person
(5) If:
(a) an amount (the received amount) has been paid to a person by way of a *child care payment; and
(b) because the received amount had not been correctly calculated using the relevant rate calculator, or for any other reason, the received amount is greater than the amount (the correct amount) of a child care payment that should have been paid to the person under this Act;
the difference between the received amount and the correct amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth by the person.
Note: The relevant rate calculator is:
(a) for child care assistance—Schedule 1; and
(b) for child care rebate—Schedule 2.
Regulations on date of effect to be taken into account
(6) In determining if there is a debt due to the Commonwealth under this section, the effect of regulations made for the purposes of subsections 52(1) and 105(1) is to be taken into account.
134 Debts arising from AAT stay orders
If:
(a) a person applies to the AAT under section 263 for review of a decision; and
(b) the AAT makes an order under subsection 41(2) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975; and
(c) as a result of the order, the amount that has in fact been paid to the person by way of a *child care payment is greater than the amount that was payable to the person;
the difference between the amount that was in fact paid to the person and the amount that was payable to the person is a debt due to the Commonwealth.
Note: Subsection 43(6) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 provides that the AAT’s decision on the review will generally take effect from the day on which the SSAT’s decision had effect. Since this is the case, the amount payable to the person during the stay period is the amount finally determined by the AAT as being payable and not the amount that was paid in accordance with the terms of the stay order.
135 Debts arising from recipient’s contravention of this Act
If:
(a) an amount has been paid to a recipient by way of a *child care payment; and
(b) the amount was paid because the recipient or another person:
(i) made a false statement or a false representation; or
(ii) failed or omitted to comply with a provision of this Act;
the amount so paid is a debt due by the recipient to the Commonwealth.
136 Person other than payee obtaining payment of a cheque
If:
(a) an instalment of a *child care payment is paid by cheque; and
(b) a person other than the payee obtains possession of the cheque from the payee; and
(c) the cheque is not endorsed by the payee to the person; and
(d) the person obtains value for the cheque;
the amount of the cheque is a debt due by the person to the Commonwealth.
137 Debts arising from conviction of person for involvement in contravention of this Act by debtor
If:
(a) a recipient is liable to pay a debt under section 135 because the recipient contravened this Act; and
(b) another person is convicted of an offence under section 5, 7A or 86 of the Crimes Act 1914 in relation to that contravention;
the recipient and the other person are jointly and severally liable to pay the debt.
Note 1: This section does not create a new debt. It extends liability for a debt that has already arisen under section 135 to a person who is convicted of certain offences.
Note 2: In recovering a debt, the Department may have regard to any view expressed by a court as to the responsibility of a person to pay the debt.
138 Data-matching Program (Assistance and Tax) Act debts
If:
(a) an amount has been paid to a person by way of a *child care payment; and
(b) the amount is a debt due to the Commonwealth under subsection 11(6) of the Data-matching Program (Assistance and Tax) Act 1990;
the amount so paid is recoverable by the Commonwealth.
139 Interest payable on debt for failure to enter agreement to pay debt
Notice may be given about interest becoming payable if person fails to enter agreement to pay debt
(1) If:
(a) a person owes a debt to the Commonwealth under a provision of this Part; and
(b) either:
(i) the person owing the debt is an individual who is not *receiving a *child care payment; or
(ii) the person owing the debt is the operator of a *child care assistance service who is not receiving *group payments; and
(c) the Secretary has given the person a notice asking the person to pay the debt; and
(d) at the end of the period of 21 days after the notice is given, the person:
(i) has not entered into negotiations to pay the debt; or
(ii) has entered into negotiations to pay the debt, but has not entered into an agreement to pay the debt by reasonable instalments;
the Secretary may give the person a notice advising the person of the following:
(e) the amount of the debt;
(f) that, unless the person, within 14 days after the notice is given:
(i) pays the whole of the debt; or
(ii) enters into an agreement to pay the debt by reasonable instalments;
interest may become payable on the debt;
(g) how any interest that becomes payable is to be calculated.
When interest becomes payable
(2) Subject to subsection (3), if:
(a) the whole of the debt is not paid within 14 days after the person is given the notice; or
(b) the person does not enter into an agreement to pay the debt within the 14 day period;
interest is payable by way of penalty on the debt by the person and the amount of the interest is to be worked out under subsection (4).
Secretary may determine interest is not payable
(3) The Secretary may determine that interest is not payable on the debt if the Secretary is satisfied that the person intends to pay the debt as soon as is reasonably practicable having regard to the circumstances of the person.
Note: For general provisions about determinations under this subsection, see section 164.
The interest payable
(4) Interest is payable on the amount of the debt (excluding interest) as remains due from time to time:
(a) on and from the day after the 14 day period ends; and
(b) at the penalty interest rate.
Note: For penalty interest rate see section 141.
Payments in satisfaction of debt and interest
(5) If:
(a) interest is payable on the debt; and
(b) an amount is paid for the purpose of paying the debt and the interest;
the amount so paid is to be applied as follows:
(c) until the debt (excluding interest) is fully paid—in satisfaction of the amount of the debt that is due when the payment is made;
(d) after the debt (excluding interest) is fully paid—in satisfaction of the interest that had become payable on the debt before the debt was fully paid.
Interest ceases to be payable if agreement entered into
(6) If a person enters into an agreement to pay the debt by reasonable instalments, interest that would, apart from this subsection, become payable on the debt on and from the day on which the agreement is entered into is not payable.
Effect of compliance with garnishee notice
(7) If 2 or more payments are made in reduction of the debt in compliance with a garnishee notice under subsection 150(1), interest that would, apart from this subsection, become payable on the debt during the garnishee notice period is not payable.
Meaning of garnishee notice period
(8) In this section, garnishee notice period means the period that begins on the day the first payment is made in compliance with a garnishee notice and ends on the day the last payment is made in compliance with that notice (whether or not the debt is satisfied).
Interest payable is a debt due to the Commonwealth
(9) The interest that is payable on the debt is a debt due to the Commonwealth.
140 Interest payable on debt for breach of agreement to pay debt
Notice may be given about interest becoming payable if person breaches agreement to pay debt
(1) If:
(a) a person owes a debt to the Commonwealth under a provision of this Part; and
(b) either:
(i) the person owing the debt is an individual who is not *receiving a *child care payment; or
(ii) the person owing the debt is the operator of a *child care assistance service who is not receiving *group payments; and
(c) the person enters into an agreement to pay the debt by reasonable instalments; and
(d) the person does not pay an instalment;
the Secretary may give the person a notice advising the person of the following:
(e) the amount of the debt;
(f) that, unless the person pays the instalment within 14 days after the notice is given, interest may become payable on the debt;
(g) how any interest that becomes payable is to be calculated.
When interest becomes payable
(2) Subject to subsections (3) and (4), if the instalment is not paid within 14 days after the person is given the notice, interest is payable by way of penalty on the debt by the person and the amount of interest is to be worked out under subsection (5).
Secretary may determine interest is not payable
(3) The Secretary may determine that interest is not payable on the debt if the Secretary is satisfied that the person intends to pay the instalment as soon as is reasonably practicable having regard to the person’s circumstances.
Note: For general provisions about determinations under this subsection, see section 164.
Interest may cease to accrue
(4) Interest payable under subsection (2) ceases to accrue on and from the day the person:
(a) next pays the instalment due under an agreement; or
(b) enters into a new agreement;
whichever first occurs.
The interest payable
(5) Interest is payable on the amount of the debt (excluding interest) as remains due from time to time:
(a) on and from the day after the 14 day period ends; and
(b) at the penalty interest rate.
Note: For penalty interest rate see section 141.
Payments in satisfaction of debt and interest
(6) If:
(a) interest is payable on the debt; and
(b) an amount is paid for the purpose of paying the debt and interest;
the amount is to be applied as follows:
(c) until the debt (excluding interest) is fully paid—in satisfaction of the amount of the debt that is due when the payment is made;
(d) after the debt (excluding interest) is fully paid—in satisfaction of the interest that had become payable on the debt before it was fully paid.
Interest payable is a debt due to the Commonwealth
(7) The interest payable on the debt is a debt due to the Commonwealth.
(1) The penalty interest rate is:
(a) 20% per year; or
(b) if a lower rate is determined under subsection (2)—that lower rate.
(2) The Minister may determine, in writing, a rate of less than 20% per year that is to be the penalty interest rate for the purposes of sections 139 and 140.
(3) A determination under subsection (2) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
142 Debt from failure to comply with garnishee notice
(1) If:
(a) a person (the garnishee debtor) is given a notice under section 150 in respect of a debt due by another person (the original debtor) under this Act; and
(b) the garnishee debtor fails to comply with the notice to the extent that he or she is capable of complying with it;
then the amount of the debt outstanding (worked out under subsection (2)) is recoverable from the garnishee debtor by the Commonwealth by means of:
(c) legal proceedings; or
(d) garnishee notice.
Note: If the person does not pay the debt or enter into an agreement to pay the debt within a certain time, interest may become payable on the debt (see section 139). If the person enters into an agreement to pay the debt and breaches the agreement, interest may become payable on the debt (see section 140).
(2) The amount of the debt outstanding is the amount equal to:
(a) as much of the amount required by the notice under section 150 to be paid by the garnishee debtor as the garnishee debtor was able to pay; or
(b) as much of the debt due by the original debtor at the time when the notice was given as remains due from time to time;
whichever is the lesser.
(3) If the Commonwealth recovers:
(a) the whole or part of the debt due by the garnishee debtor under subsection (1); or
(b) the whole or part of the debt due by the original debtor;
then:
(c) both debts are reduced by the amount that the Commonwealth has so recovered; and
(d) the amount specified in the notice under section 150 is to be taken to be reduced by the amount so recovered.
(4) This section applies to an amount in spite of any law of a State or Territory (however expressed) under which the amount is inalienable.
(5) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
143 Overseas application of provisions
Sections 133, 135, 136 and 137 extend to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia, whether in a foreign country or not; and
(b) all persons irrespective of nationality or citizenship.
(1) A debt owed by a person, other than the operator of a *child care assistance service, is recoverable by the Commonwealth by means of:
(a) if the person is *receiving a *child care payment—deductions from that person’s child care payment; or
(b) if section 153 applies to another person who is receiving a child care payment—deductions from that other person’s child care payment; or
(c) legal proceedings; or
(d) garnishee notice.
Note: The debt is also recoverable by the Commonwealth by deductions from social security payments—see section 1228 of the Social Security Act 1991.
(2) A debt owed by the operator of a *child care assistance service is recoverable by the Commonwealth by means of:
(a) if *group payments are being made to the service—deductions from those payments; or
(b) legal proceedings; or
(c) garnishee notice.
(3) In this section:
debt means:
(a) a debt due to the Commonwealth under section 133, 134, 135, 136, 138, 139 or 140; or
(b) a debt due to the Commonwealth for which a person is liable because of section 137.
(1) Sections 146, 147 and 153 provide for debt recovery by deductions in the following situations:
(a) section 146—recovery of a debt owed by a person who is *receiving a *child care payment;
(b) section 147—recovery of a debt owed by the operator of a *child care assistance service who is receiving *group payments;
(c) section 153—recovery of a debt by consent from a person other than the debtor.
(2) For the purposes of this Part, a person is taken to be *receiving a *child care payment even if the person is only to be paid a single payment (for example, a lump sum payment paid pursuant to a *retrospective claim). In such a case, a deduction from the single payment may be made under the relevant section.
146 Deductions from debtor’s child care payment
(1) This section applies to a debt if, under section 144, the debt is recoverable by the Commonwealth by means of deductions from a *child care payment being *received by a person.
(2) The debt is to be deducted from the person’s *child care payment in the following way:
Method statement
Step 1. Take the amount, decided under subsection (3), by which each payment of the person’s *child care payment is to be reduced.
Step 2. Each payment of the person’s *child care payment is to be reduced by that amount, until the sum of those amounts is equal to the debt.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the maximum amount by which each payment of the person’s *child care payment may be reduced is worked out as follows:
![]()
(4) If a person makes a request in writing to the Secretary for a higher or lower rate of reduction, the Secretary may decide the amount by which each payment of the person’s *child care payment is to be reduced, and, if requested by the person, may vary the amount from time to time.
(5) Subject to section 148, the debt must be deducted unless:
(a) the Secretary takes action under Part 4 in relation to the amount; or
(b) the amount is recovered by the Commonwealth under another provision of this Chapter.
(6) If the person is *receiving both child care assistance and child care rebate, the debt is to be deducted from the *child care payment in relation to which it was incurred until the person is no longer receiving that payment. Then, any remaining part of the debt is to be deducted in accordance with subsection (2) from the other child care payment, if it is still being received by the person.
147 Deductions from group payments made to child care assistance service
(1) This section applies to a debt if, under section 144, the debt is recoverable by the Commonwealth by means of deductions from *group payments being received by the operator of a *child care assistance service.
(2) The debt is to be deducted from the *group payments made to the operator in the following way:
Method statement
Step 1. Take the amount, decided under subsection (3), by which each *group payment made to the operator is to be reduced.
Step 2. Each group payment to the operator is to be reduced by that amount, until the sum of those amounts is equal to the debt.
Note 1: The deduction of an amount does not have the effect of reducing the extent to which the group payment is to be applied in reducing or extinguishing liabilities owed to the service—see subsections 60(4) and (5).
Note 2: The amount of a deduction is to be specified in the relevant *group payment notice—see paragraph 60(3)(c).
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the maximum amount by which each *group payment made to an operator may be reduced is worked out as follows:
![]()
(4) If an operator makes a request in writing to the Secretary for a higher or lower rate of reduction, the Secretary may decide the amount by which each *group payment is to be reduced, and, if requested by the operator, may vary the amount from time to time.
(5) Subject to section 148, the debt must be deducted unless:
(a) the Secretary takes action under Part 4 in relation to the amount; or
(b) the amount is recovered by the Commonwealth under another provision of this Chapter.
148 Time limits on recovery action under sections 146 and 147
(1) Subject to subsections (2), (3), (4) and (5), action under this section, or section 146 or 147, for the recovery of a debt is not to be commenced after the end of the period of 6 years starting on the day on which the debt arose.
(2) If the debt arose under section 135, action under section 146 for the recovery of the debt may be commenced at any time within the period of 6 years starting on the first day on which an *officer becomes aware, or could reasonably be expected to have become aware, of the circumstances that gave rise to the debt.
Note: The time limit in subsection (2) also applies to action for recovery against a person who is liable because of section 137 for a debt that arises under section 135.
(3) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 146 or 147 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period part of the amount owing is paid;
action under that section for the recovery of the balance of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of payment.
(4) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 146 or 147 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period, the person who owes the amount acknowledges that he or she owes it;
action under that section for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of acknowledgment.
(5) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 146 or 147 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period:
(i) action is taken under this section, or section 149 or 150, for the recovery of the debt; or
(ii) a review of a file relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs; or
(iii) other internal Departmental activity relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs;
action under section 146 or 147 for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years after the end of the activity or action referred to in paragraph (b).
(1) If, under section 144, a debt is recoverable by the Commonwealth by means of legal proceedings, the debt is recoverable by the Commonwealth in a court of competent jurisdiction.
(2) Subject to subsections (3), (4), (5) and (6), legal proceedings for the recovery of the debt are not to be commenced after the end of the period of 6 years starting on the day on which the debt arose.
(3) If the debt arose under section 135, legal proceedings for the recovery of the debt may be commenced at any time within the period of 6 years starting on the first day on which an *officer becomes aware, or could reasonably be expected to have become aware, of the circumstances giving rise to the debt.
Note: The time limit in subsection (3) also applies to legal proceedings for recovery against a person who is liable because of section 137 for a debt that arises under section 135.
(4) If:
(a) subsection (2) or (3) applies so that legal proceedings for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period part of the amount owing is paid;
legal proceedings for the recovery of the balance of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of payment.
(5) If:
(a) subsection (2) or (3) applies so that legal proceedings for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period, the person who owes the amount acknowledges that he or she owes it;
legal proceedings for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of acknowledgment.
(6) If:
(a) subsection (2) or (3) applies so that action under this section for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period:
(i) action is taken under this section, or section 146, 147 or section 150, for the recovery of the debt; or
(ii) a review of a file relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs; or
(iii) other internal Departmental activity relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs;
action under this section for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years after the end of the activity or action referred to in paragraph (b).
(1) If, under section 144, a debt is recoverable from a person (the debtor) by the Commonwealth by means of a garnishee notice, the Secretary may by written notice given to another person:
(a) by whom any money is due or accruing, or may become due, to the debtor; or
(b) who holds or may subsequently hold money for or on account of the debtor; or
(c) who holds or may subsequently hold money on account of some other person for payment to the debtor; or
(d) who has authority from some other person to pay money to the debtor;
require the person to whom the notice is given to pay the Commonwealth:
(e) an amount specified in the notice, not exceeding the amount of the debt or the amount of the money referred to in the preceding paragraph that is applicable; or
(f) such amount as is specified in the notice out of each payment that the person becomes liable from time to time to make to the debtor until that debt is satisfied; or
(g) such percentage as is specified in the notice of each payment that the person becomes liable from time to time to make to the debtor until that debt is satisfied.
(2) The time for making a payment in compliance with a notice under subsection (1) is such time as is specified in the notice, not being a time before the money concerned becomes due or is held or before the end of the period of 14 days after the notice is given.
(3) A person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with a notice under subsection (1).
Penalty: Imprisonment for 12 months.
Note 1: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
Note 2: See also section 142 for other consequences of failure to comply with a notice under this section.
(4) If the Secretary gives a notice to a person under subsection (1), the Secretary must give a copy of the notice to the debtor.
(5) A person who makes a payment to the Commonwealth in compliance with a notice under subsection (1) is to be taken to have made the payment under the authority of the debtor and of any other person concerned.
(6) If:
(a) a notice is given to a person under subsection (1) in respect of a debt; and
(b) an amount is paid by another person in reduction or in satisfaction of the debt;
the Secretary must notify the first-mentioned person accordingly, and the amount specified in the notice is to be taken to be reduced by the amount so paid.
(7) If, apart from this subsection, money is not due or repayable on demand to a person unless a condition is fulfilled, the money is to be taken, for the purposes of this section, to be due or repayable on demand, as the case may be, even though the condition has not been fulfilled.
(8) This section applies to money in spite of any law of a State or Territory (however expressed) under which the amount is inalienable.
(9) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
151 Time limits on recovery action under section 150
(1) Subject to subsections (2), (3), (4) and (5), action under section 150 for the recovery of a debt is not to be commenced after the end of the period of 6 years starting on the day on which the debt arose.
(2) If the debt arose under section 135, action under section 150 for the recovery of the debt may be commenced at any time within the period of 6 years starting on the first day on which an *officer becomes aware, or could reasonably be expected to have become aware, of the circumstances that gave rise to the debt.
Note: The time limit in subsection (2) also applies to action for recovery against a person who is liable because of section 137 for a debt that arises under section 135.
(3) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 150 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period part of the amount owing is paid;
action under that section for the recovery of the balance of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of payment.
(4) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 150 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period, the person who owes the amount acknowledges that he or she owes it;
action under that section for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years starting on the day of acknowledgment.
(5) If:
(a) subsection (1) or (2) applies so that action under section 150 for the recovery of a debt must be commenced within a particular period; and
(b) within that period:
(i) action is taken under this section, or section 146, 147 or 149, for the recovery of the debt; or
(ii) a review of a file relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs; or
(iii) other internal Departmental activity relating to action for the recovery of the debt occurs;
action under section 150 for the recovery of the debt may be commenced within the period of 6 years after the end of the activity or action referred to in paragraph (b).
152 Secretary may allow payment of debt by instalments
(1) The Secretary may, on behalf of the Commonwealth, decide to allow a person to pay a debt in one or more instalments.
(2) A decision made under subsection (1) takes effect:
(a) if no day is specified in the decision—on the day on which the decision is made; or
(b) if a day is specified in the decision—on the day so specified (whether that day is before, after or on the day on which the decision is made).
(3) In subsection (1):
debt means a debt recoverable by the Commonwealth under Part 2.
153 Deductions by consent from child care payment of person who is not a debtor
(1) If:
(a) a person (the debtor) incurs a debt under this Act; and
(b) another person (the consenting person) is *receiving a *child care payment; and
(c) for the purpose of the recovery of the debt, the consenting person consents to the deduction of an amount from the consenting person’s child care payment;
the Secretary may deduct the amount from the consenting person’s child care payment.
(2) The debtor’s debt is reduced by an amount equal to the amount deducted from the consenting person’s *child care payment.
(3) The consenting person may revoke the consent at any time.
In this Part:
debt means a debt recoverable by the Commonwealth under Part 2.
155 Secretary may write off debt
(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Secretary may, on behalf of the Commonwealth, decide to write off a debt, for a stated period or otherwise.
(2) The Secretary may decide to write off a debt under subsection (1) if, and only if:
(a) the debt is irrecoverable at law; or
(b) the debtor has no capacity to repay the debt; or
(c) the debtor’s whereabouts are unknown after all reasonable efforts have been made to locate the debtor; or
(d) the debt cannot be recovered by deductions under this Act or the Social Security Act 1991 and it is not cost effective for the Commonwealth to take action to recover the debt.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(a), a debt is taken to be irrecoverable at law if, and only if:
(a) the debt cannot be recovered by means of deductions under section 146 or 147, or legal proceedings under section 149, or garnishee notice under section 150, because the relevant time limit for recovery action under that section has elapsed; or
(b) there is no proof of the debt capable of sustaining legal proceedings for its recovery; or
(c) the debtor is discharged from bankruptcy and the debt was incurred before the discharge and was not incurred by fraud; or
(d) the debtor has died leaving no estate or insufficient funds in the debtor’s estate to repay the debt.
(4) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(b), if a debt is recoverable by means of deductions under section 146 or 147, the person is taken to have a capacity to repay the debt unless recovery by those means would cause the person severe financial hardship.
(5) A decision made under subsection (1) takes effect:
(a) if no day is specified in the decision—on the day on which the decision is made; or
(b) if a day is specified in the decision—on the day so specified (whether that day is before, after or on the day on which the decision is made).
(6) Nothing in this section prevents anything being done at any time to recover a debt that has been written off under this section.
156 Power to waive Commonwealth’s right to recover debt
(1) On behalf of the Commonwealth, the Secretary may waive the Commonwealth’s right to recover the whole or a part of a debt from a debtor only in the circumstances described in section 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162 or 163.
(2) A waiver takes effect:
(a) on the day specified in the waiver (whether that day is before, after or on the day on which the decision to waive is made); or
(b) if the waiver does not specify when it takes effect—on the day on which the decision to waive is made.
Note: If the Secretary waives the Commonwealth’s right to recover all or part of a debt, this is a permanent bar to recovery of the debt or part of the debt—the debt or part of the debt effectively ceases to exist.
157 Waiver of debt arising from error
(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Secretary must waive the right to recover the proportion of a debt that is attributable solely to an administrative error made by the Commonwealth if the debtor *received in good faith the payment or payments that gave rise to that proportion of the debt.
Note: Subsection (1) does not allow waiver of a part of a debt that was caused partly by administrative error and partly by one or more other factors (such as error by the debtor).
(2) Subsection (1) only applies if:
(a) the debt is not raised within a period of 6 weeks from the first payment that caused the debt; or
(b) if the debt arose because a person has complied with a notification obligation, the debt is not raised within a period of 6 weeks from the end of the notification period;
whichever is the later.
(3) If:
(a) a debt arose because the debtor or the debtor’s partner underestimated the value of particular property of the debtor or partner; and
(b) the estimate was made in good faith; and
(c) the value of the property was not able to be easily determined when the estimate was made;
the Secretary must waive the right to recover the proportion of the debt attributable to the underestimate.
(4) For the purposes of this section, a proportion of a debt may be 100% of the debt.
158 Waiver of debt relating to an offence
(1) If:
(a) a debtor has been convicted of an offence that gave rise to a proportion of a debt; and
(b) the court indicated in sentencing the debtor that it imposed a longer custodial sentence on the debtor because he or she was unable or unwilling to pay the debt;
the Secretary must waive the right to recover the proportion of the debt that arose in connection with the offence.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a proportion of a debt may be 100% of the debt.
(1) The Secretary must waive the right to recover a debt if:
(a) the debt is, or is likely to be, less than $200; and
(b) it is not cost effective for the Commonwealth to take action to recover the debt.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply if the debt is at least $50 and could be recovered by deductions under section 146 or 147.
160 Waiver in relation to settlements
Settlement of civil action
(1) If the Commonwealth has agreed to settle a civil action against a debtor for recovery of a debt for less than the full amount of the debt, the Secretary must waive the right to recover the difference between the debt and the amount that is the subject of the settlement.
Settlement of proceedings before the AAT
(2) If the Secretary has agreed to settle proceedings before the AAT relating to recovery of a debt on the basis that the debtor will pay less than the full amount of the debt, the Secretary must waive the right to recover the difference between the debt and the amount that is the subject of the settlement.
Waiver where at least 80% of debt recovered and debtor cannot pay more
(3) If:
(a) the Commonwealth has recovered at least 80% of the original value of a debt from a debtor; and
(b) the Commonwealth and the debtor agree that the recovery is in full satisfaction for the whole of the debt; and
(c) the debtor cannot repay a greater proportion of the debt;
the Secretary must waive the remaining 20% or less of the value of the original debt.
Agreement for part-payment in satisfaction of outstanding debt
(4) If the Secretary and a debtor agree that the debtor’s debt will be fully satisfied if the debtor pays the Commonwealth an agreed amount less than the amount of the debt outstanding at the time of the agreement (the unpaid amount), the Secretary must waive the right to recover the difference between the unpaid amount and the agreed amount.
Limits on agreement to accept part-payment in satisfaction of outstanding debt
(5) The Secretary must not make an agreement described in subsection (4) unless the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the debtor cannot repay more of the debt than the agreed amount; and
(b) the agreed amount is at least the present value of the unpaid amount repaid in instalments whose amount and timing is determined by the Secretary; and
(c) it would take at least a year to recover the unpaid amount under Part 2 if subsection (4) did not apply.
Formula for working out present value of unpaid amount
(6) For the purposes of subsection (5), the present value of the unpaid amount is the amount worked out in accordance with the following formula:

where:
annual repayment is the amount of the debt that the Secretary believes would be recovered under Part 2 in a year if subsection (4) did not apply in relation to the debt.
interest is the annual rate of interest specified by the Minister by determination in writing.
rp (repayment period) is the number of years needed to repay the unpaid amount if repayments equal to the annual repayment were made each year.
Determination is a disallowable instrument
(7) A determination for the purposes of the definition of interest in subsection (6) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
161 Waiver where debtor or debtor’s partner would have been entitled to child care rebate
(1) If:
(a) a debt arises under this Act from overpayments of child care assistance made to the debtor; and
(b) the debtor or the debtor’s partner does not claim child care rebate for the period when the overpayments were made; and
(c) an amount of child care rebate would have been payable for the period when the overpayments were made if the debtor or the debtor’s partner had lodged a claim;
the Secretary must waive the right to recover the debt to the extent set out in subsection (2).
(2) The Secretary must waive under subsection (1) the right to recover the amount of debt equal to the amount of child care rebate that would have been payable to the debtor or the debtor’s partner in the 3 year period ending on the day the overpayment is stopped if:
(a) the overpayments had not been made to the debtor; and
(b) the debtor or the debtor’s partner had lodged a claim for the payment.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (2), the amount of child care rebate that would have been payable to the debtor or the debtor’s partner is to be worked out on the basis that the CCR% applicable was 20%.
Note: The CCR% is used in calculating the rate of child care rebate—see Module C of Schedule 2.
162 Waiver in special circumstances
The Secretary may waive the right to recover all or part of a debt if the Secretary is satisfied that:
(a) the debt did not result wholly or partly from the debtor or another person knowingly:
(i) making a false statement or a false representation; or
(ii) failing or omitting to comply with a provision of this Act; and
(b) there are special circumstances (other than financial hardship alone) that make it desirable to waive; and
(c) it is more appropriate to waive than to write off the debt or part of the debt.
Note: Section 155 allows the Secretary to write off a debt on behalf of the Commonwealth.
163 Secretary may waive debts of a particular class
(1) The Secretary may, on behalf of the Commonwealth, decide to waive the Commonwealth’s right to recover debts arising under or as a result of this Act that are included in a class of debts specified by the Minister by determination in writing.
(2) A decision under subsection (1) takes effect:
(a) if no day is specified in the decision—on the day on which the decision is made; or
(b) if a day is specified in the decision—on the day so specified (whether that day is before, after or on the day on which the decision is made).
(3) A determination under subsection (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
164 Determination that penalty interest not payable in relation to particular periods
(1) This section deals with the making of determinations under subsections 139(3) and 140(3). These are determinations that interest is not payable in certain circumstances.
(2) The determination may relate to a period before the making of the determination.
(3) The determination may be expressed to be subject to the person complying with specified conditions.
(4) The Secretary must give a copy of the determination to the person as soon as practicable after making the determination.
(5) A failure to comply with subsection (4) does not invalidate the determination.
(6) If:
(a) the determination is expressed to be subject to the person complying with specified conditions; and
(b) the person contravenes a condition;
the determination ceases to have effect.
(7) The Secretary may cancel or vary the determination by written notice to the person.
Chapter 5—Emergency child care assistance
In this Chapter:
child at risk means a child that is at risk of physical, emotional or psychological abuse.
ECA is short for *emergency child care assistance.
guidelines means guidelines in force under section 167.
166 What is emergency child care assistance?
ECA is a payment made to the operator of a *child care assistance service who, believing a child to be a child at risk, provides child care for the child on or after the *payment commencement day.
167 Minister may make guidelines
(1) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines providing for matters:
(a) required by this Chapter to be provided; or
(b) necessary or convenient to be made for the purposes of this Chapter.
(2) The guidelines may also provide that ECA and child care assistance may both be paid in respect of a *session of care for a child in specified circumstances.
(3) A determination under subsection (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(1) The operator of a *child care assistance service who believes that a child is a child at risk may apply to the Secretary to be paid ECA in respect of child care provided by the service for the child on or after the *payment commencement day.
(2) The application:
(a) must be in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) must include the *information required by the form; and
(c) must include any other information relating to the application that the Secretary requires.
169 Consequences of failure to comply with requirement for other information
If:
(a) the Secretary requires further *information under paragraph 168(2)(c) in relation to an application; and
(b) the operator of the service concerned does not provide the information within 28 days after the request is made, or within such shorter period as the Secretary specifies in the request;
then:
(c) any payment of ECA made to the operator in relation to the application may be recovered from the operator as provided for in the guidelines as a debt due to the Commonwealth; and
(d) no further payment of ECA is to be made to the operator in relation to the application.
170 Children in respect of whom emergency child care assistance is not payable
(1) ECA is not payable in respect of child care provided for a child:
(a) who is under the care (however described) of a person under a child welfare law of a State or Territory; or
(b) who is a member of a class of children specified in the guidelines for the purposes of this section.
(2) The guidelines may specify laws of a State or Territory that are to be child welfare laws for the purposes of subsection (1).
171 Payability and rate of payment of emergency child care assistance
(1) The Secretary must determine, in writing, an application made under section 168.
(2) The Secretary must determine that ECA is payable, unless section 170 or 172 makes it not payable.
(3) If the determination is that ECA is payable then it is payable at the rate and in the manner provided for in the guidelines.
172 Duration of payment of emergency child care assistance
(1) ECA is payable in respect of child care for a child:
(a) for a single continuous period of up to 4 weeks; and
(b) not more than once in any 12 month period.
(2) Despite subsection (1), if the Secretary believes that a child is a child at risk, the Secretary may determine that ECA is payable for the child even though ECA has already been paid within the period of the preceding 12 months for the child.
(3) If:
(a) the Secretary has made a determination granting ECA to an operator in respect of a child; and
(b) ECA has already been paid within the period of the preceding 12 months in respect of the child; and
(c) the Secretary has not made a determination under subsection (2) in respect of child care provided by the operator for the child;
the Secretary must determine in writing that no further payment is to be made under the determination granting ECA to the operator.
(4) The Secretary must inform the operator that the determination under subsection (3) has been made.
(5) The determination takes effect on the day the operator is so informed.
Chapter 6—Approval and registration of child care services
Part 1—Approval for child care assistance purposes
Division 1—Obtaining approval and conditions of approval
173 What is the significance of approval of a child care service?
Payments of child care assistance can only be made in respect of child care provided for a child in a child care service approved under this Part (see section 20).
(1) A person or body who operates, or proposes to operate, a child care service may apply to the Secretary to have the service approved as a service of one of the following kinds:
(a) a centre based long day care service;
(b) a family day care service;
(c) an occasional care service;
(d) an outside school hours care service.
(2) The application:
(a) must be in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) must include the *information required by the form; and
(c) must include any other information relating to the application that the Secretary requires.
175 Approval of child care services
(1) The Secretary must approve a child care service as a service of a particular kind if:
(a) an application has been made to approve the service as a service of that kind; and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that the service satisfies the *eligibility rules for services to become approved as services of that kind; and
(c) the Secretary is satisfied that the applicant meets the requirements of section 176.
Note: The Secretary may exempt a child care service from complying with an eligibility rule (see section 189).
(2) If the Secretary approves the service, the Secretary must give the applicant a certificate of approval.
176 Statement that applicant has tax file number
(1) An applicant meets the requirements of this section if:
(a) the applicant has a *tax file number; and
(b) the application contains a statement to that effect.
(2) The Secretary must accept a statement made under paragraph (1)(b) unless the Commissioner of Taxation has informed the Secretary that the applicant does not have a *tax file number.
(3) This section does not authorise the Secretary:
(a) to require or request a person to quote the person’s *tax file number; or
(b) to seek or obtain, in any way, a person’s tax file number; or
(c) to record a person’s tax file number.
(4) The Secretary may ask the Commissioner of Taxation to provide information on whether an applicant or a *child care assistance service has a *tax file number.
(5) Subsection (1) does not apply if the Secretary is satisfied that the applicant is a body whose income is, under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936, exempt from tax.
Eligibility requirements
(1) It is a condition of a *child care assistance service’s approval that the service satisfies the *eligibility rules for services to continue to be approved as services of that kind.
Note 1: See sections 185, 186, 187 and 188 for the eligibility rules.
Note 2: The Secretary may exempt a child care service from complying with an eligibility rule (see section 189).
Allocation of child care assistance hours
(2) It is a condition of a *child care assistance service’s approval that the service holds an allocation of *child care assistance hours per fortnight.
Note: Division 2 of this Part (sections 192 to 204) deals with the allocation of *child care assistance hours.
Allocation not to be exceeded
(3) It is a condition of a *child care assistance service’s approval that the service does not exceed its *child care assistance hours limit.
Meaning of exceeding child care assistance hours limit
(4) A *child care assistance service exceeds its child care assistance hours limit if:
(a) in a *payment period, it provides a number of hours of child care; and
(b) child care assistance is paid in respect of those hours of child care; and
(c) that number of hours is greater than the number of hours in the service’s allocation of *child care assistance hours.
Compliance with child care laws
(5) It is a condition of the approval of a *child care assistance service that the provision of care by the service complies with all applicable requirements imposed by a law of the Commonwealth, or of the State or Territory in which the service is situated, relating to child care.
Conditions imposed by notice to operator
(6) The Secretary may impose other conditions on the approval of a *child care assistance service by notice in writing to the operator of the service.
Conditions imposed by notice in Gazette
(7) The Minister may at any time impose other conditions on the approval of a class of *child care assistance services by determination in writing published in the Gazette.
178 Allocation of hours condition ceases to apply to centre based long day care services after 31 December 1999
After 31 December 1999, subsection 177(2) ceases to apply to *centre based long day care services.
179 Consequences of breach of conditions of approval
(1) The Secretary may impose one or more of the following sanctions on a *child care assistance service if the Secretary is satisfied that the service has breached a condition of approval of the service:
(a) vary the conditions of approval imposed under subsection 177(6);
(b) impose additional conditions on the service’s approval;
(c) reduce the number of hours in the service’s allocation of *child care assistance hours per fortnight;
(d) suspend the service’s approval as a child care assistance service;
(e) cancel the service’s approval as a child care assistance service.
(2) The Minister may determine, in writing, factors to be taken into account in imposing a sanction under this section.
180 Procedure for imposing a sanction
(1) Before imposing a sanction on a service under section 179, the Secretary must give notice in writing to the operator of the service that:
(a) states that the Secretary is considering imposing the sanction; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which imposition of the sanction is being considered; and
(c) summarises the evidence and other material on which those grounds are based; and
(d) summarises the effect of the notice (including the review process provided for under this Act) on a person’s entitlement to child care assistance in respect of child care provided by the service; and
(e) invites the operator to make written submissions to the Secretary, within 28 days, stating why the sanction should not be imposed.
(2) In deciding whether to impose the sanction, the Secretary must have regard to any submissions made by the operator as mentioned in paragraph (1)(e).
(1) The Secretary must cancel a *child care assistance service’s approval if the operator of the service requests the Secretary in writing to do so.
(2) The Secretary must cancel a *child care assistance service’s approval if the Secretary is satisfied that the service should not have been approved.
(3) The Secretary must cancel a *child care assistance service’s approval if the service fails to provide child care for a continuous period of 3 months unless the Secretary is satisfied that, because of special circumstances affecting the service, the approval should not be cancelled.
Note: The Secretary may also cancel under section 179.
182 Procedure for cancellation
(1) Before cancelling an approval under subsection 181(2) or (3), the Secretary must give notice in writing to the operator of the service that:
(a) states that the Secretary is considering cancelling the service’s approval; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which the cancellation is being considered; and
(c) summarises the evidence and other material on which those grounds are based; and
(d) summarises the effect of the notice (including the review processes provided for under this Act) on a person’s entitlement to child care assistance in respect of child care provided by the service; and
(e) invites the operator to make written submissions to the Secretary, within 28 days, stating why the approval should not be cancelled.
(2) In deciding whether to cancel the approval the Secretary must have regard to any submissions made by the operator as mentioned in paragraph (1)(e).
183 Effect of cancellation of approval on child care rebate service status
If a *child care assistance service’s approval is cancelled under paragraph 179(1)(e) or subsection 181(2) or (3), the service is taken to be registered under Part 2 as a child care rebate service.
184 Notification of matters affecting eligibility for approval
The operator of a *child care assistance service is guilty of an offence if the operator:
(a) has:
(i) after the service was approved, become aware of any matter existing when the service was approved as a result of which the service should not have been approved; or
(ii) become aware of any matter occurring after the service was approved as a result of which a condition of the service’s approval has been breached; and
(b) has failed to notify the Secretary in writing of the matter as soon as practicable after becoming aware of it.
Penalty: 20 penalty units
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
185 Eligibility rules—centre based long day care services
The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) rules relating to the eligibility of child care services to become approved as centre based long day care services; and
(b) rules relating to the eligibility of these services to continue to be so approved.
186 Eligibility rules—family day care services
The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) rules relating to the eligibility of child care services to become approved as family day care services; and
(b) rules relating to the eligibility of these services to continue to be so approved.
187 Eligibility rules—occasional care services
The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) rules relating to the eligibility of child care services to become approved as occasional care services; and
(b) rules relating to the eligibility of these services to continue to be so approved.
188 Eligibility rules—outside school hours care services
The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) rules relating to the eligibility of child care services to become approved as outside school hours care services; and
(b) rules relating to the eligibility of these services to continue to be so approved.
189 Exemption from eligibility rules
The Secretary may, by determination in writing, exempt a specified child care service, or a specified class of child care services, from a specified *eligibility rule, or specified eligibility rules.
Note: The *eligibility rules may relate to a child care service becoming approved or continuing to be approved as a service of a particular kind.
190 Eligibility rules may deal with who may operate a service and change of operator of a service
Without limiting sections 185, 186, 187 and 188, rules made under those sections may specify requirements:
(a) to be met by the operators and staff of services, including requirements relating to individual suitability to provide child care; and
(b) to be met by the operator of a service if the operation of the service is proposed to be transferred from one operator to another.
191 Determinations disallowable
A determination under subsection 177(7) or 179(2) or section 185, 186, 187 or 188 is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Division 2—Allocation of child care assistance hours
This Division deals mainly with the allocation of new child care assistance hours. Other child care assistance hours may be allocated under the guidelines to take account of arrangements in existence before the payment commencement day.
193 Secretary to allocate child care assistance hours
The Secretary is to allocate child care assistance hours per fortnight to *child care assistance services under this Division and the guidelines.
Note: It is a condition of a *child care assistance service’s approval that the service holds an allocation of child care assistance hours per fortnight—see subsection 177(2). However, this rule ceases to apply to *centre based long day care services after 31 December 1999—see section 178.
(1) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines specifying:
(a) procedures relating to the allocation (including re-allocation) of child care assistance hours; and
(b) matters to be taken into account in making such an allocation; and
(c) any other matter authorised under this Division to be specified in the guidelines.
(2) A determination under subsection (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
The Secretary must give written notice to each *child care assistance service to whom an allocation of child care assistance hours is made, giving details of the allocation of hours to that service.
196 Re-allocation of surrendered child care assistance hours
(1) If a *child care assistance service’s allocation of hours under this Division is reduced for any reason by a number of hours (the surrendered hours), the Secretary may re-allocate the surrendered hours in accordance with the guidelines.
(2) A re-allocation of surrendered hours is taken not to be an allocation of new child care assistance hours.
Note: Subdivisions 2 and 3 deal with the allocation of new child care assistance hours.
197 Application for new child care assistance hours
(1) A person seeking an allocation of new child care assistance hours to a *child care assistance service must apply to the Secretary.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) must include the *information required by the form; and
(c) must include any other information relating to the application that the Secretary requires; and
(d) must be accompanied by the prescribed application fee (if any).
(3) The regulations may prescribe an application fee, or a method for working out an application fee.
(4) The amount of any application fee:
(a) must be reasonably related to the expenses incurred, or to be incurred, by the Commonwealth in relation to the application; and
(b) must not be such as to amount to taxation.
198 Determination of application
(1) The Secretary must determine whether to grant or refuse an application under section 197.
(2) The determination must be in writing.
Subdivision 2—New child care assistance hours for centre based long day care services
199 Allocation of new child care assistance hours—1998 and 1999
(1) For the calendar year 1998, the total number of new child care assistance hours available for allocation to *centre based long day care services is not to exceed 1,008,000 per fortnight.
(2) For the calendar year 1999, the total number of new child care assistance hours available for allocation to *centre based long day care services is not to exceed 1,008,000 per fortnight.
200 Total number to be divided on regional basis
(1) For the purposes of allocating new child care assistance hours for *centre based long day care services in 1998 and 1999, the Minister must make a determination:
(a) specifying the regions in respect of which allocations of new child care assistance hours are to be made; and
(b) dividing the total number of 1,008,000 hours referred to in section 199 into numbers of hours available for allocation to centre based long day care services in each of those regions.
(2) The determination may also divide the number of hours specified as available for allocation in a particular region into numbers of hours available for allocation in respect of different categories of *centre based long day care service (for example, care provided to children in a particular age group).
(3) The determination must be based on:
(a) the relative needs of different regions of Australia for *centre based long day care; and
(b) any other factor specified in the guidelines.
(4) The determination must be in writing.
(5) A determination under this section is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
201 Allocation within a region limited to hours available in region
(1) This section applies to the allocation of new child care assistance hours to *centre based long day care services for 1998 and 1999.
Note: After 1999, *centre based long day care services are not required to hold an allocation of child care assistance hours—see section 178.
(2) In deciding whether to grant an application for an allocation of new child care assistance hours to a service in a region, the Secretary must:
(a) ensure that the number of hours specified in the determination under section 200 as available for allocation in that region will not be exceeded by more than 15%; and
(b) ensure that if the application relates to a category of child care specified in the determination under section 200 in relation to that region, the number of hours specified for that category will not be exceeded by more than 15%.
(3) Although the Secretary’s allocation to a service or services in respect of a region or a category of child care may exceed, by up to 15%, the numbers of hours specified for that region or category in the determination under section 200, this does not authorise the Secretary to exceed the limit imposed by section 199.
202 Other factors affecting allocation
(1) This section applies to the allocation of new child care assistance hours to *centre based long day care services for 1998 and 1999.
Note: After 1999, *centre based long day care services are not required to hold an allocation of child care assistance hours—see section 178.
(2) In deciding whether to grant an application for an allocation of new child care assistance hours, the Secretary must take into account factors relevant to the nature and quality of the service in respect of which the application is made.
(3) If the total number of hours applied for in relation to a region or a category of *centre based long day care service exceeds the number specified for that region or category in the determination under section 200, the Secretary must allocate the hours available among services that will best meet child care assistance needs for centre based long day care in that region, or in relation to that category (as the case requires).
(4) The guidelines may specify factors to be taken into account by the Secretary for the purposes of subsections (2) and (3).
Subdivision 3—New child care assistance hours for other services
203 Allocation of new child care assistance hours
The Secretary may from time to time determine the number of new child care assistance hours per fortnight available for allocation to each of the following kinds of *child care assistance service:
(a) *family day care services;
(b) *occasional care services;
(c) *outside school hours care services.
The determination must be in writing.
204 Factors affecting allocation of new hours
(1) In deciding whether to grant an application for an allocation of new child care assistance hours to a *family day care service, an *occasional care service or an *outside school hours care service, the Secretary must:
(a) take into account factors relevant to the nature and quality of the service in respect of which the application is made; and
(b) ensure that the number of hours determined for that kind of service under section 203 is not exceeded.
(2) If the total number of new child care assistance hours applied for in respect of a kind of *child care assistance service exceeds the number determined for that kind of service under section 203, the Secretary must allocate the hours available to the service, or services, that will best meet child care assistance needs in relation to that kind of service.
(3) The guidelines may specify factors to be taken into account by the Secretary under this section.
Part 2—Registration for child care rebate purposes
205 What is the significance of registration of a child care service?
Payments of child care rebate can only be made in respect of child care provided for a child in a *child care rebate service (see section 78). A child care service that is registered under this Part is a child care rebate service.
(1) A person or body who operates, or proposes to operate, a child care service that is not a *child care assistance service may apply to the Secretary to have the service registered as a child care rebate service.
Note: A *child care assistance service whose approval has been cancelled is taken to be registered under this Part as a child care rebate service (see section 183).
(2) The application:
(a) must be in the form approved in writing by the Secretary; and
(b) must include the *information required by the form; and
(c) must include such other information relating to the application that the Secretary requires.
207 Registration of child care services
(1) The Secretary must register a child care service as a child care rebate service if:
(a) an application has been made to register the service; and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that the service satisfies the *eligibility rules for a service to become registered as a child care rebate service; and
(c) the Secretary is satisfied that the applicant meets the requirements of section 208.
Note: The Secretary may exempt a child care service from complying with *eligibility rules (see section 217).
(2) If the Secretary registers the service, the Secretary must give the applicant a certificate of registration.
208 Statement that applicant has tax file number
(1) An applicant meets the requirements of this section if:
(a) the applicant has a *tax file number; and
(b) the application contains a statement to that effect.
(2) The Secretary must accept a statement made under paragraph (1)(b) unless the Commissioner of Taxation has informed the Secretary that the applicant does not have a *tax file number.
(3) This section does not authorise the Secretary:
(a) to require or request a person to quote the person’s *tax file number; or
(b) to seek or obtain, in any way, a person’s tax file number; or
(c) to record a person’s tax file number.
(4) The Secretary may ask the Commissioner of Taxation to provide information on whether an applicant or a *child care rebate service has a *tax file number.
(5) Subsection (1) does not apply if the Secretary is satisfied that the applicant is a body whose income is, under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936, exempt from tax.
209 When does registration take effect?
(1) The registration of an applicant takes effect on the later of the following 2 days:
(a) the day on which, in the Secretary’s opinion, the applicant was first eligible to be registered; or
(b) the day occurring 13 weeks before the day on which the application for registration was made.
(2) If the Secretary is satisfied that the applicant was not eligible to be registered during a period occurring after the day the applicant’s registration takes effect but before the day on which the application was made, the Secretary may determine that the registration is not to have had effect during that period.
210 Conditions of registration
Eligibility requirements
(1) It is a condition of the registration of a *child care rebate service that the service satisfies the *eligibility rules for services to continue to be registered as child care rebate services.
Note: The Secretary may exempt a child care service from complying with an eligibility rule (see section 217).
Compliance with child care laws
(2) It is a condition of the registration of a *child care rebate service that the provision of care by the service complies with all applicable requirements imposed by a law of the Commonwealth, or of the State or Territory in which the service is situated, relating to child care.
Qualifications of individual operators
(3) It is a condition of the registration of a *child care rebate service that, if the service is operated by an individual, the operator of the service has turned 18 or has a qualification of a kind specified in a determination under subsection (4).
Determination of qualifications
(4) The Minister may make a written determination that an operator who has not turned 18 must have a qualification of a kind specified in the determination.
Body corporate’s powers
(5) It is a condition of the registration of a *child care rebate service that, if the service is operated by a body corporate, the powers of the body corporate extend to providing the child care.
Conditions imposed by notice on operator
(6) The Secretary may impose other conditions on the registration of a *child care rebate service by notice in writing to the operator of the service.
Conditions imposed by notice in Gazette
(7) The Minister may at any time impose other conditions on the registration of a class of *child care rebate services by determination in writing published in the Gazette.
211 Consequences of breach of conditions of registration
(1) The Secretary may impose one or more of the following sanctions on a *child care rebate service if the Secretary is satisfied that the service has breached a condition of registration of the service:
(a) vary the conditions of registration imposed under subsection 210(6);
(b) impose additional conditions on the service’s registration;
(c) suspend the service’s registration as a child care rebate service;
(d) cancel the service’s registration as a child care rebate service.
(2) The Minister may determine, in writing, factors to be taken into account in imposing a sanction under this section.
212 Procedure for imposing a sanction
(1) Before imposing a sanction on a service under section 211, the Secretary must give notice in writing to the operator of the service that:
(a) states that the Secretary is considering imposing the sanction; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which the imposition of the sanction is being considered; and
(c) summarises the evidence and other material on which those grounds are based; and
(d) summarises the effect of the notice (including the review process provided for under this Act) on a person’s entitlement to child care rebate in respect of child care provided by the service; and
(e) invites the operator to make written submissions to the Secretary, within 28 days, stating why the sanction should not be imposed.
(2) In deciding whether to impose the sanction, the Secretary must have regard to any submissions made by the operator as mentioned in paragraph (1)(e).
(1) The Secretary must cancel a *child care rebate service’s registration if the operator of the service requests the Secretary in writing to do so.
(2) The Secretary must cancel a *child care rebate service’s registration if the Secretary is satisfied that the service should not have been registered.
Note: The Secretary may also cancel under section 211.
214 Procedure for cancellation
(1) Before cancelling a registration under subsection 213(2), the Secretary must give notice in writing to the operator of the service that:
(a) states that the Secretary is considering cancelling the service’s registration; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which the cancellation is being considered; and
(c) summarises the evidence and other material on which those grounds are based; and
(d) summarises the effect of the notice (including the review processes provided for under this Act) on a person’s entitlement to child care rebate in respect of child care provided by the service; and
(e) invites the operator to make written submissions to the Secretary, within 28 days, stating why the registration should not be cancelled.
(2) In deciding whether to cancel the registration, the Secretary must have regard to any submissions made by the operator as mentioned in paragraph (1)(e).
215 Notification of matters affecting eligibility for registration
The operator of a *child care rebate service is guilty of an offence if the operator:
(a) has:
(i) after the service was registered, become aware of any matter existing when the service was registered as a result of which the service should not have been registered; or
(ii) become aware of any matter occurring after the service was registered as a result of which a condition of the service’s registration has been breached; and
(b) has failed to notify the Secretary in writing of the matter as soon as practicable after becoming aware of it.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) rules relating to the eligibility of child care services to become registered as child care rebate services; and
(b) rules relating to the eligibility of the services to continue to be registered as child care rebate services.
217 Exemption from eligibility rules
The Secretary may, by determination in writing, exempt a specified child care service, or a specified class of child care services, from a specified *eligibility rule, or specified eligibility rules.
Note: The *eligibility rules may relate to a child care service becoming registered or continuing to be registered as a child care rebate service.
218 Determinations disallowable
A determination under subsection 210(4) or (7), subsection 211(2) or section 216 is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(1) An application may be made to the AAT for the review of any of the following decisions under this Chapter:
(a) to refuse an application for approval as a service of a particular kind (subsection 175(1));
(b) to impose a condition on the approval of a particular child care assistance service (subsection 177(6));
(c) to impose a sanction on a child care assistance service (subsection 179(1));
(d) to cancel a child care assistance service’s approval under subsection 181(2);
(e) to cancel a child care assistance service’s approval under subsection 181(3), but only if the operator of the service made submissions under paragraph 182(1)(e) in relation to the cancellation;
(f) to refuse to exempt a specified child care service from a specified eligibility rule (section 189);
(g) to refuse an application for an allocation of new *child care assistance hours under section 198, but only to the extent:
(i) in the case of an application for an allocation to a *centre based long day care service—that the decision was based on subsection 202(2) (factors relating to the nature and quality of the service); and
(ii) in any other case—that the decision was based on paragraph 204(1)(a) (factors relating to the nature and quality of the service);
(h) to refuse an application to register a child care service as a child care rebate service (subsection 207(1));
(i) to impose a condition on the registration of a particular child care rebate service (subsection 210(6));
(j) to impose a sanction on a child care rebate service (subsection 211(1));
(k) to cancel a child care rebate service’s approval under subsection (213(2));
(l) to refuse to exempt a specified child care service from a specified eligibility rule (section 217).
(2) An application may be made to the AAT for the review of a decision under subpoint D2(7) of Schedule 1 (exemption of a service from the 20 hour limit).
(1) The regulations may provide for internal reconsideration of a decision that is reviewable by the AAT under section 219.
(2) The regulations may provide for reconsideration by the Secretary or by an *authorised review officer.
Chapter 7—Information management
221 General power to obtain information
(1) The Secretary may require a person to give *information, or produce a document that is in the person’s custody or under the person’s control, to the Department if the Secretary considers that the information or document may be relevant to the question of:
(a) whether a person is or was *entitled to a *child care payment the person is *receiving or has received; or
(b) whether a person who has made a claim for a child care payment is, was or will be entitled to the child care payment in respect of a period; or
(c) the rate of child care payment that is, was or will be applicable to a person; or
(d) whether an amount of a child care payment has been received by a particular person, or has been paid into a particular account.
Note: See section 224 for general provisions about making requirements under this section.
(2) A person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with a notice imposing a requirement under this section.
Penalty: 60 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(3) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
(4) This section does not require a person to give *information or produce a document to the extent that in doing so the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (other than a law of a Territory).
(5) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia, whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are making or who have made a claim for a *child care payment; and
(c) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are *receiving, or have received, a payment of a child care payment.
Note: State or Territory law does not affect a person’s obligations under this section—see section 228.
222 Power to obtain information from a person who owes a debt to the Commonwealth
(1) The Secretary may require a person who owes a debt to the Commonwealth under or as a result of this Act:
(a) either to:
(i) give to the Department *information that is relevant to the person’s financial situation; or
(ii) produce to the Department a document that is in the person’s custody or under the person’s control and is relevant to the person’s financial situation; and
(b) if the person’s address changes—to notify the Department of the new address within 14 days of the change.
Note: See section 224 for general provisions about making requirements under this section.
(2) A person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with a notice imposing a requirement under this section.
Penalty: 60 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(3) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
(4) This section does not require a person to provide *information or produce a document to the extent that in doing so the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (other than a law of a Territory).
Note: State or Territory law does not affect a person’s obligations under this section—see section 228.
(5) This section does not limit section 221.
(6) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia, whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are making or who have made a claim for a *child care payment; and
(c) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are *receiving, or have received, a payment of a child care payment.
223 Power to obtain information about a person who owes a debt to the Commonwealth
(1) If the Secretary believes that a person may have *information or a document:
(a) that would help the Department locate another person (the debtor) who owes a debt to the Commonwealth under or as a result of this Act; or
(b) that is relevant to the debtor’s financial situation;
the Secretary may require the person to give the information, or produce the documents, to the Department.
Note: See section 224 for general provisions about making requirements under this section.
(2) A person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with a notice imposing a requirement under this section.
Penalty: 60 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(3) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
(4) This section does not require a person to provide *information or produce a document to the extent that in doing so the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (other than a law of a Territory).
Note: State or Territory law does not affect a person’s obligations under this section—see section 228.
(5) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia, whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are making or who have made a claim for a *child care payment; and
(c) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are *receiving, or have received, a payment of a child care payment.
224 General provisions about making requirements under sections 221 to 223
(1) This section contains general provisions relating to requiring a person, under section 221, 222 or 223, to give *information or produce a document.
(2) The requirement is to be made by notice in writing given to the person.
(3) The notice must specify:
(a) how the person is to give the *information, or produce the document, to the Department; and
(b) the period within which the person is to give the information, or produce the document, to the Department; and
(c) the *officer (if any) to whom the information is to be given or the document is to be produced; and
(d) the section under which the notice is given.
(4) The period specified under paragraph (3)(b) must end at least 14 days after the notice is given.
(5) The notice may require the person to give the *information by appearing before a specified *officer to answer questions.
(6) If the notice requires the person to appear before an *officer, the notice must specify a time and a place for the person to appear, and the time must be at least 14 days after the notice is given.
225 Power to obtain information to verify claims etc.
(1) The Secretary may require a person to give *information about a class of persons to the Department for either or both of the following purposes:
(a) detecting cases in which amounts of *child care payment have been paid when they should not have been paid;
(b) verifying the entitlement of persons who have made claims for child care payments.
Note 1: See section 226 for general provisions about making requirements under this section.
Note 2: See section 227 for provisions relating to the Secretary’s obligations to consider the relevance of *information given in response to a requirement under this section.
(2) The *information that the Secretary may require about each person in the class of persons is all or any of the following information (but no other information):
(a) full name and any previous name;
(b) address;
(c) sex;
(d) marital status;
(e) date of birth;
(f) date of death;
(g) dates of entries into and departures from Australia;
(h) any payments received by the person from the person required to provide the information, in a specified period (not being a period starting more than 12 months before the notice is given), and the account number of any account into which any of those payments were paid;
(i) in relation to a course of study or training being undertaken by the person:
(i) the date on which the person started the course; and
(ii) the date on which the person completed the course;
(j) in relation to any employment of the person by the person given the notice:
(i) the date on which the person’s employment started; and
(ii) the date on which the person’s employment ended.
(3) A person commits an offence if the person refuses or fails to comply with a notice imposing a requirement under this section.
Penalty: 60 penalty units.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(4) This section binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth, of each of the States, of the Australian Capital Territory, of the Northern Territory and of Norfolk Island.
Note: The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence—see section 242.
(5) This section does not require a person to give *information to the extent that in doing so the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (other than a law of a Territory).
Note: State or Territory law does not affect a person’s obligations under this section—see section 228.
(6) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia, whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are making or who have made a claim for a *child care payment; and
(c) all persons, irrespective of their nationality, who are *receiving, or have received, a payment of a child care payment.
226 General provisions about making requirements under section 225
(1) This section contains general provisions relating to requiring a person, under section 225, to give *information.
(2) The person must be in a class of persons specified in a determination in force under paragraph (11)(a).
(3) The requirement is to be made by notice in writing given to the person.
(4) The notice must specify:
(a) the class of persons about whom the *information is to be given; and
(b) how the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(c) the period within which the person is to give the information to the Department; and
(d) the *officer (if any) to whom the information is to be given; and
(e) that the notice is given under section 225.
(5) The notice must also ask the person to take steps, that are reasonable in the circumstances, to inform persons about whom *information is to be given that information about them has been, is being or may be given to the Department.
(6) The class of persons specified in the notice must be some or all of the members of a class of persons specified in a determination in force under paragraph (11)(b).
(7) The Secretary may specify a class of persons in the notice whether or not the Secretary is able to identify any of the persons in that class as being persons who have *received, are receiving, or have made claims for, *child care payments.
(8) The period specified under paragraph (4)(c) must be at least 14 days after the notice is given.
(9) The notice may require the person to give the *information by appearing before a specified *officer to answer questions.
(10) If the notice requires the person to appear before an *officer, the notice must specify a time and a place for the person to appear, and the time must be at least 14 days after the notice is given.
(11) The Minister may, by determination in writing:
(a) specify a class or classes of persons who may be required to give information; and
(b) specify a class or classes of persons about whom information may be required to be given.
(12) A determination under subsection (11) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
227 Secretary’s obligation in relation to information given under section 225
(1) This section applies to *information given to the Secretary in response to a requirement under section 225.
(2) Within 3 months after the *information is given, the Secretary must decide which (if any) of the information is, or is likely to be, relevant to the matters referred to in subsection 225(1).
(3) If the Secretary decides, within the 3 month period, that some or all of the *information is not, or is not likely to be, relevant to the matters referred to in subsection 225(1), the Secretary must ensure that any record of the irrelevant information is destroyed.
(4) If the Secretary has not made a decision under subsection (3) at the end of the 3 month period, the Secretary must ensure that any record of all or any part of the *information is destroyed.
228 State/Territory law does not affect obligations to provide information under this Act
(1) Nothing contained in any law of a State or a Territory operates to prevent a person from:
(a) giving *information; or
(b) producing documents; or
(c) giving evidence;
that the person is required to give or produce to the Department or to an *officer for the purposes of this Act.
(2) This section extends to:
(a) acts, omissions, matters and things outside Australia whether or not in a foreign country; and
(b) all persons irrespective of their nationality or citizenship.
229 Part does not create offences in relation to emergency child care assistance
Nothing in this Part creates an offence in relation to the provision of *information relating to *emergency child care assistance, or relating to debts that relate to emergency child care assistance.
230 Authorised access to and use of protected information
(1) A person may obtain *protected information if the information is obtained for the purposes of this Act or the Social Security Act 1991.
Note: In certain circumstances it is an offence for a person to obtain *protected information without authority (see section 231).
(2) A person may:
(a) make a record of *protected information; or
(b) disclose protected information to any person; or
(c) otherwise use protected information;
if the record, disclosure or use made of the information by the person is made:
(d) for the purposes of this Act or the Social Security Act 1991; or
(e) for the purpose for which the information was disclosed to the person under section 233 or 234.
Note: In certain circumstances it is an offence for a person to use *protected information without authority (see section 232).
231 Offence—unauthorised access to protected information
A person is guilty of an offence if:
(a) the person obtains *information; and
(b) the information is *protected information; and
(c) the person:
(i) is not authorised or required by or under this Act or the Social Security Act 1991; and
(ii) has no other lawful authority;
to obtain the information; and
(d) the person knows, or is reckless as to whether, the information is protected information.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
232 Offence—unauthorised use of protected information
A person is guilty of an offence if:
(a) the person:
(i) makes a record of; or
(ii) discloses to any other person; or
(iii) otherwise makes use of;
*information; and
(b) the information is *protected information; and
(c) the person:
(i) is not authorised or required by or under this Act or the Social Security Act 1991; and
(ii) has no other lawful authority;
to make the record, disclosure or use of the information that is made by the person; and
(d) the person knows, or is reckless as to whether, the information is protected information.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
233 Protection extends to court, tribunal etc. proceedings
(1) An *officer must not, except for the purposes of this Act, the Social Security Act 1991 or the former payments legislation, be required:
(a) to produce any document in his or her possession; or
(b) to disclose any matter or thing of which he or she had notice;
by reason of the performance or exercise of his or her duties, functions or powers under this Act, or the Social Security Act 1991 or the former payments legislation to:
(c) a court; or
(d) a tribunal; or
(e) an authority; or
(f) a person;
that has power to require the production of documents or the answering of questions.
(2) In this section:
former payments legislation means the Child Care Act 1972 or the Childcare Rebate Act 1993.
(1) Despite sections 232 and 233, the Secretary may:
(a) if the Secretary certifies that it is necessary in the public interest to do so in a particular case or class of cases—disclose *information acquired by an *officer in the performance of his or her functions or duties or in the exercise of his or her powers under this Act or the Social Security Act 1991 to such persons and for such purposes as the Secretary determines; or
(b) disclose any such information to the Secretary of a Department of State of the Commonwealth or to the head of an authority of the Commonwealth for the purposes of that Department or authority; or
(c) disclose any such information to a person who is expressly or impliedly authorised by the person to whom the information relates to obtain it.
Note: A person to whom information is disclosed may commit an offence if the person uses the information without authority (see section 232).
(2) In giving certificates for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a), the Secretary must act in accordance with guidelines in force under subsection 235(1).
(3) In disclosing *information under paragraph (1)(b), the Secretary must act in accordance with guidelines in force under subsection 235(1).
235 Guidelines for exercise of Secretary’s disclosure power
(1) The Minister, by determination in writing:
(a) must make guidelines for the exercise of the Secretary’s power to give certificates for the purposes of paragraph 234(1)(a); and
(b) must make guidelines for the exercise of the Secretary’s power under paragraph 234(1)(b).
(2) The guidelines must not be inconsistent with the provisions of the Privacy Act 1988.
(3) Before making a determination under subsection (1), the Minister must consult the Privacy Commissioner.
(4) A determination under subsection (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
236 Offence—soliciting disclosure of protected information
A person is guilty of an offence if:
(a) the person solicits the disclosure of *information from an *officer or another person; and
(b) the disclosure would be in contravention of this Part; and
(c) the first-mentioned person knows, or is reckless as to whether, the information is *protected information.
The offence is committed whether or not any protected information is actually disclosed.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
237 Offence—untrue representations
A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person solicits the disclosure of *protected information from an *officer; and
(b) for that purpose makes representations which the person knows are untrue.
The offence is committed whether or not any protected information is actually disclosed.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
238 Offences—offering to supply protected information
(1) A person is guilty of an offence if the person:
(a) offers to supply (whether to a particular person or otherwise) *information about another person; and
(b) knows that the information is *protected information.
The offence is committed whether or not any protected information is actually supplied.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(2) A person is guilty of an offence if the person:
(a) holds himself or herself out as being able to supply (whether to a particular person or otherwise) *information about another person; and
(b) knows that the information is *protected information.
The offence is committed whether or not any protected information is actually supplied.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 2 years.
Note: Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code sets out the general principles of criminal responsibility.
(3) Nothing in subsection (1) or (2) renders an *officer acting in the exercise or performance of his or her duties, functions or powers under this Act or the Social Security Act 1991 guilty of an offence.
239 Officer’s oath or declaration
An *officer must make an oath or declaration in a form approved by the Minister or the Secretary if required to do so by the Minister or the Secretary.
240 Freedom of Information Act not affected
The provisions of this Part that relate to the disclosure of *information do not affect the operation of the Freedom of Information Act 1982.
Chapter 8—General provisions about offences and penalties
241 Application of the Criminal Code
Chapter 2 of the Criminal Code applies to all offences against this Act.
242 Crown not liable to be prosecuted for offences
The Crown is not liable to be prosecuted for an offence against, or arising out of, this Act.
243 Conviction of an offence—repayment of child care payment
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person is convicted of an offence against section 29A, 29B, 29C or 29D of the Crimes Act 1914; and
(b) the offence relates to a *child care payment.
(2) The court may:
(a) impose a penalty in respect of the offence; and
(b) order the person to pay the Commonwealth an amount equal to any amount paid by way of *child care payment because of the act, failure or omission for which the person is convicted.
Note: The amount referred to in paragraph (b) will be evidenced by a certificate prepared by the Secretary under section 244.
(3) In spite of anything in this Act, or any other law, a person is not to be imprisoned for failing to pay an amount payable to the Commonwealth under paragraph (2)(b).
(1) For the purposes of paragraph 243(2)(b), a certificate signed by the Secretary is evidence of the matters specified in the certificate.
(2) The certificate may specify:
(a) a person; and
(b) an amount that has been paid to the person by way of *child care payment because of:
(i) an act; or
(ii) a failure; or
(iii) an omission; and
(c) the act, failure or omission which caused the amount to be paid to the person.
If:
(a) the court makes an order under paragraph 243(2)(b) for the payment to the Commonwealth of an amount of money; and
(b) the clerk or other appropriate officer of the court signs a certificate specifying:
(i) the amount ordered to be paid to the Commonwealth; and
(ii) the person by whom the amount is to be paid; and
(c) the certificate is filed in a court (which may be the court that made the order) that has civil jurisdiction to the extent of the amount to be paid;
the certificate is enforceable in all respects as a final judgment of the court in which the certificate is filed.
246 Proceedings against non-corporations
(1) If, in proceedings for an offence against this Act in respect of conduct engaged in by a person other than a body corporate, it is necessary to establish the state of mind of the person, it is sufficient to show that:
(a) the conduct was engaged in by an employee or agent of the person within the scope of his or her actual or apparent authority; and
(b) the employee or agent had that state of mind.
(2) If:
(a) conduct is engaged in on behalf of a person other than a body corporate by an employee or agent of the person; and
(b) the conduct is within the employee’s or agent’s actual or apparent authority;
the conduct is taken, for the purposes of a prosecution for an offence against this Act, to have been engaged in by the person unless the person establishes that he or she took reasonable precautions and exercised due diligence to avoid the conduct.
(3) Despite any other provision in this Act, if:
(a) a person is convicted of an offence; and
(b) the person would not have been convicted of the offence if subsections (1) and (2) had not been in force;
the person is not liable to be punished by imprisonment for that offence.
(4) A reference in this section to the state of mind of a person includes a reference to:
(a) the knowledge, intention, opinion, belief or purpose of the person; and
(b) the person’s reasons for the intention, opinion, belief or purpose.
(5) A reference in this section to engaging in conduct includes a reference to failing or refusing to engage in conduct.
(6) A reference in this section to an offence against this Act includes a reference to an offence created by section 5, 6, 7 or 7A, or subsection 86 (1), of the Crimes Act 1914 that relates to this Act.
Note 1: For other provisions about how this Act applies to non-corporations, see section 282 (treatment of unincorporated associations) and section 283 (treatment of partnerships).
Note 2: For proceedings for an offence in respect of conduct engaged in by a body corporate, see Part 2.5 of the Criminal Code.
Chapter 9—General provisions about review of decisions
247 Decisions to which Part applies
(1) This Part applies to any decision of an *officer under this Act, other than a decision specified in subsection (2) or (3).
(2) This Part does not apply to a decision under:
(a) section 40, 41, 93 or 94 (form or place of lodgment of claim); or
(b) section 70, 73, 74, 75, 76, 122, 125, 126, 127 or 128 (notices requiring the provision of information etc.); or
(c) subsection 44(1), 45(1), 71(1), 72(1), 97(1), 98(1), 123(1) or 124(1) (tax file number requests); or
(d) section 43, 70, 96 or 122 (immunisation notices); or
(e) Chapter 6 (registration and approval of services); or
(f) section 221, 222, 223 or 225 (requirements to provide information or documents); or
(g) section 250 or 257 (continuing a payment); or
(h) section 266 (settling proceedings); or
(i) Chapter 8 (offences and penalties), Chapter 10 (administration) or Chapter 11 (miscellaneous); or
(j) subpoint D2(7) of Schedule 1 (exemption from the 20 hour limit).
Note: For the review of decisions under Chapter 6 (registration and approval of services) and subpoint D2(7) of Schedule 1 (exemption from the 20 hour limit), see section 219.
(3) This Part does not apply to a decision to make, revoke or vary any instrument that is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 or to make, amend or repeal any regulations.
248 Secretary may review decisions
(1) The Secretary may review a decision to which this Part applies if the Secretary is satisfied that there is sufficient reason to review the decision.
(2) The Secretary may review a decision even if an application has been made to the SSAT or the AAT for review of the decision.
(3) The Secretary may:
(a) affirm the decision; or
(b) vary the decision; or
(c) set the decision aside and substitute a new decision.
(4) If:
(a) the Secretary makes a decision under subsection (3); and
(b) when the Secretary makes that decision, a person has applied to the SSAT for review of the decision that was reviewed by the Secretary;
the Secretary must give the *National Convener written notice of the Secretary’s decision under subsection (3).
(5) If:
(a) the Secretary makes a decision under subsection (3); and
(b) when the Secretary makes that decision, a person has applied to the AAT for review of the decision that was reviewed by the Secretary;
the Secretary must give the Registrar of the AAT written notice of the Secretary’s decision under subsection (3).
(6) If:
(a) the Secretary sets a decision aside under subsection (3); and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that an event that did not occur would have occurred if the decision had not been made;
the Secretary may, if satisfied that it is reasonable to do so, treat the event as having occurred for the purposes of this Act.
(1) Subject to subsections (2) and (3), a person affected by a decision to which this Part applies may apply to the Secretary for review of the decision.
(2) If a decision to which this Part applies is made by an *employee of the *Agency in the exercise of a delegated power, a person affected by the decision may apply to the *CEO for review of the decision.
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply to a decision made by:
(a) the Secretary personally; or
(b) the *CEO personally.
(4) If a person applies under subsection (1) for review of a decision, the Secretary or an *authorised review officer may review the decision under section 251.
(5) If a person applies under subsection (2) for review of a decision, the *CEO, or an *authorised review officer, may review the decision under section 251.
(6) If a person applies under subsection (2) for the review of a decision made by an *employee of the *Agency, the reference in subsection (5) to an *authorised review officer is taken to be a reference to an authorised review officer who is another employee of the Agency.
(7) Despite subsections (4) and (5), an *authorised review officer cannot review a decision whether to exercise the Secretary’s power under section 266.
(8) If:
(a) a person who may apply to the Secretary for review of a decision under subsection (1), or to the *CEO for review of the decision under subsection (2), has not so applied; and
(b) the person applies to the SSAT for review of the decision;
the person is taken to apply to the Secretary or CEO for review of the decision under subsection (1) or (2), as the case may be, on the day on which the person applies to the SSAT.
250 Secretary or CEO may continue payment pending outcome of application for review
(1) If:
(a) an adverse decision is made in relation to a *child care payment; and
(b) the adverse decision depends on:
(i) the exercise of a discretion by a person; or
(ii) the holding of an opinion by a person; and
(c) a person applies to the Secretary or the *CEO under subsection 249(1) or (2) for review of the adverse decision;
the person to whom the application is made may, in writing, declare that payment of the child care payment is to continue, pending the determination of the review, as if the adverse decision had not been made.
(2) While a declaration under subsection (1) is in force in relation to the adverse decision, this Act (other than this Chapter) applies as if the adverse decision had not been made.
(3) A declaration under subsection (1) in relation to an adverse decision:
(a) starts to have effect on the day on which the declaration is made or on the earlier day (if any) stated in the declaration; and
(b) stops having effect if:
(i) the application for review of the adverse decision is withdrawn; or
(ii) the review of the adverse decision is determined; or
(iii) the declaration is revoked.
(4) A reference in subsection (1) to a person’s holding of an opinion is a reference to the person’s holding the opinion whether or not this Act expressly requires the opinion to be held before making the decision concerned.
(5) In this section:
adverse decision, in relation to a *child care payment, means:
(a) a decision to cancel or suspend the child care payment; or
(b) a decision to reduce the rate of the child care payment.
251 Powers of Secretary, CEO or authorised review officer if application for review
(1) If an application for review of a decision is made under subsection 249(1) or (2), the Secretary, the *CEO or an *authorised review officer must:
(a) affirm the decision; or
(b) vary the decision; or
(c) set the decision aside and substitute a new decision.
(2) If a person makes a decision under subsection (1), the person must give the applicant written notice of the decision.
(3) If:
(a) a person sets a decision aside under subsection (1); and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that an event that did not occur would have occurred if the decision had not been made;
the Secretary may, if satisfied that it is reasonable to do so, treat the event as having occurred for the purposes of this Act.
252 Certain determinations not to be revived
(1) If:
(a) the Secretary makes a determination (the first determination) that:
(i) a person is *entitled to a *child care payment; or
(ii) a child care payment is payable at a particular rate to a person; and
(b) the Secretary makes a determination (the second determination):
(i) to cancel the child care payment; or
(ii) to reduce the rate at which the child care payment is payable; and
(c) notice of the second determination is given to the person; and
(d) the person applies under section 249 for review of the second determination; and
(e) the application is made more than 13 weeks after the notice is given; and
(f) a decision (the review decision) is made by the Secretary, the *CEO, an *authorised review officer, the SSAT or the AAT; and
(g) the review decision, or the effect of the review decision, is:
(i) to set aside the second determination; or
(ii) to affirm a decision setting aside the second determination;
the following provisions have effect:
(h) the second determination does not become void from the time when it was made;
(i) the mere setting aside of the second determination does not of itself revive the first determination.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a person is taken to have applied for review of a determination (the primary determination) if:
(a) the person applies for review of another determination or decision; and
(b) an examination of the primary determination is necessary to resolve the issues raised by the review of the other determination or decision.
253 Notification of further rights of review
(1) If a person gives the applicant notice under subsection 251(2), the notice must include:
(a) a statement to the effect that the applicant may, subject to this Act, apply to the SSAT for review of the person’s decision; and
(b) a statement about the person’s decision that:
(i) sets out the reasons for the decision; and
(ii) sets out the findings by the person on material questions of fact; and
(iii) refers to the evidence or other material on which those findings were based; and
(c) a statement to the effect that, if the person is dissatisfied with the SSAT’s decision, application may, subject to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975, be made to the AAT for review of the SSAT’s decision.
(2) A contravention of subsection (1) in relation to a decision does not affect the validity of the decision.
Part 2—Review by Social Security Appeals Tribunal
254 Decisions to which Part applies
(1) This Part applies to any decision of an *officer under this Act, other than a decision specified in subsection (2) or (3).
(2) This Part does not apply to a decision under:
(a) section 40, 41, 93 or 94 (form or place of lodgment of claim); or
(b) section 70, 73, 74, 75, 76, 122, 125, 126, 127 or 128 (notices requiring the provision of information etc.); or
(c) subsection 44(1), 45(1), 71(1), 72(1), 97(1), 98(1), 123(1) or 124(1) (tax file number requests); or
(d) section 43, 70, 96 or 122 (immunisation notices); or
(e) Chapter 6 (registration and approval of services); or
(f) section 221, 222, 223 or 225 (requirements to provide information or documents); or
(g) section 250 or 257 (continuing a payment); or
(h) section 266 (settling proceedings); or
(i) Chapter 8 (offences and penalties), Chapter 10 (administration) or Chapter 11 (miscellaneous); or
(j) subpoint D2(7) of Schedule 1 (exemption from the 20 hour limit).
Note: For the review of decisions under Chapter 6 (registration and approval of services) and subpoint D2(7) of Schedule 1 (exemption from the 20 hour limit), see section 219.
(3) This Part does not apply to a decision to make, revoke or vary any instrument that is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 or to make, amend or repeal any regulations.
The SSAT must, in carrying out its functions under this Act, pursue the objective of providing a mechanism of review that is fair, just, economical, informal and quick.
Note: For the establishment and membership of the SSAT, see Division 1 of Part 7.3 of the Social Security Act 1991. For the procedures for review by the SSAT, see Part 6.3 of that Act.
256 Application for review by SSAT
(1) If:
(a) a decision to which this Part applies has been made by the Secretary or the *CEO personally; or
(b) a decision to which this Part applies has been:
(i) reviewed by the Secretary, the CEO or an *authorised review officer under section 251; and
(ii) the decision has been affirmed, varied or set aside;
a person affected by the decision of the Secretary, the CEO or the authorised review officer may apply to the SSAT for review of that decision.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), the decision made by the Secretary, the *CEO or the *authorised review officer is taken to be:
(a) if the Secretary, the CEO or the authorised review officer affirms a decision—the decision as affirmed; and
(b) if the Secretary, the CEO or the authorised review officer varies a decision—the decision as varied; and
(c) if the Secretary, the CEO or the authorised review officer sets a decision aside and substitutes a new decision—the new decision.
257 Secretary may continue payment pending outcome of application for review
(1) If:
(a) an adverse decision is made in relation to a *child care payment; and
(b) the adverse decision depends on:
(i) the exercise of a discretion by a person; or
(ii) the holding of an opinion by a person; and
(c) a person applies to the SSAT under subsection 256(1) for review of the adverse decision;
the Secretary may, in writing, declare that payment of the child care payment is to continue, pending the determination of the review, as if the adverse decision had not been made.
(2) While a declaration under subsection (1) is in force in relation to the adverse decision, this Act (other than this Chapter) applies as if the adverse decision had not been made.
(3) A declaration under subsection (1) in relation to an adverse decision:
(a) starts to have effect on the day on which the declaration is made or on the earlier day (if any) stated in the declaration; and
(b) stops having effect if:
(i) the application to the SSAT for review of the adverse decision is withdrawn; or
(ii) the review of the adverse decision is determined by the SSAT; or
(iii) the declaration is revoked by the Secretary.
(4) A reference in subsection (1) to a person’s holding of an opinion is a reference to the person’s holding that opinion whether or not this Act expressly requires the opinion to be held before making the decision concerned.
(5) In this section:
adverse decision, in relation to a *child care payment, means:
(a) a decision to cancel or suspend the child care payment; or
(b) a decision to reduce the rate of the child care payment.
(1) If a person applies to the SSAT for review of a decision to which this Part applies, the SSAT must:
(a) affirm the decision; or
(b) vary the decision; or
(c) set the decision aside; and
(i) substitute a new decision; or
(ii) send the matter back to the Secretary or the *CEO, as the case requires, for reconsideration in accordance with any directions or recommendations of the SSAT.
(2) If the SSAT sets a decision aside and substitutes for it a decision that a person is *entitled to a *child care payment, the SSAT must:
(a) assess the rate at which child care payment is to be paid to the person; or
(b) ask the Secretary or the *CEO, as the case requires, to assess the rate at which the child care payment is to be paid to the person.
(3) Subject to subsection (4), the SSAT may, for the purpose of reviewing a decision under this Act, exercise all the powers and discretions that are conferred by this Act on the Secretary.
(4) The reference in subsection (3) to powers and discretions conferred by this Act does not include a reference to powers and discretions conferred by:
(a) section 40, 41, 93 or 94 (form or place of lodgment of claim); or
(b) section 70, 73, 74, 75, 76, 122, 125, 126, 127 or 128 (notices requiring the provision of information etc.); or
(c) section 44, 45, 71, 72, 97, 98, 123 or 124 (tax file number requests); or
(d) section 43, 70, 96 or 122 (immunisation notices); or
(e) Part 7 of Chapter 2 or Part 7 of Chapter 3 (manner of payment); or
(f) section 150 (garnishee notice); or
(g) Chapter 6 (registration and approval of services); or
(h) section 221, 222, 223 or 225 (requirements to provide information or documents); or
(i) section 250 or 257 (continuing a payment); or
(j) section 266 (settling proceedings); or
(k) Chapter 8 (offences and penalties), Chapter 10 (administration) or Chapter 11 (miscellaneous).
(5) If:
(a) the SSAT sets a decision aside under subsection (1); and
(b) the Secretary, or the SSAT, is satisfied that an event that did not occur would have occurred if the decision had not been made;
the Secretary or the SSAT (as the case may be) may, if satisfied that it is reasonable to do so, treat the event as having occurred for the purposes of this Act.
259 Date of effect of SSAT decisions
(1) Subject to subsections (2) and (3), a decision by the SSAT comes into operation immediately on the giving of the decision.
(2) The SSAT may provide in a decision that the decision is not to come into operation until a later day stated in the decision and, if it does so, the decision comes into operation on that later day.
(3) Subject to subsections (4) and (5), if the SSAT:
(a) varies the decision under review; or
(b) sets aside the decision under review and substitutes a new decision for the decision under review;
the decision as varied or the new decision (as the case may be) has effect, or is taken to have had effect, on and from the day on which the decision under review has or had effect.
(4) If:
(a) a person is given written notice of a decision to which this Part applies; and
(b) the person applies to the SSAT more than 3 months after the notice was given for review of the decision; and
(c) the SSAT varies the decision or sets the decision aside and substitutes a new decision; and
(d) the effect of the SSAT’s decision is:
(i) to grant the person’s claim for a *child care payment; or
(ii) to direct the making of a payment of a child care payment to the person; or
(iii) to increase the rate of the person’s child care payment;
subsection (3) applies as if references in that subsection to the day on which the decision under review had effect were references to the day on which the application was made to the SSAT for review of the decision under review.
(5) The SSAT may order:
(a) that subsection (3) not apply to a decision to which this Part applies by the SSAT on a review; and
(b) that subsections (1) and (2) apply instead.
(1) A person may apply to the SSAT for review of a decision to which this Part applies by:
(a) sending or delivering a written application to:
(i) an office of the SSAT; or
(ii) an office of the Department; or
(iii) if the decision was made by the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency—an office of the Agency; or
(b) going to an office of the SSAT and making an oral application; or
(c) telephoning an office of the SSAT and making an oral application.
(2) If a person makes an oral application under paragraph (1)(b) or (c), the person receiving the oral application must make a written record of the details of the oral application and note on the record the date on which the application is made.
(3) If a written record of an oral application is made under subsection (2), the written record is taken to be a written application by the applicant and to be delivered to an office of the SSAT on the day on which the oral application is made.
(4) An application may include a statement of the reasons for seeking a review of the decision.
261 Variation of decision before SSAT review completed
(1) If an *officer varies a decision after an application has been made to the SSAT for review of the decision but before determination of the review, the application is to be treated as if it were an application for review of the decision as varied.
(2) If an *officer sets a decision aside and substitutes a new decision after an application has been made to the SSAT for review of the decision set aside but before determination of the review, the application is to be treated as if it were an application for review of the new decision.
(3) If:
(a) a person applies to the SSAT for a review of a decision; and
(b) before determination of the review, an *officer varies the decision or sets the decision aside and substitutes a new decision;
the person may either:
(c) proceed with the application for review of the decision as varied or the new decision; or
(d) withdraw the application under section 1274 of the Social Security Act 1991.
(1) The parties to a review by the SSAT of a decision are:
(a) the applicant; and
(b) the Secretary; and
(c) if the decision was made by the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency in the exercise of a delegated power—the CEO; and
(d) any other person who has been made a party to the review under subsection (4).
(2) If a person has applied under subsection 256(1) for review of a decision, any other person whose interests are affected by the decision may apply to the *National Convener to be made a party to the review.
(3) An application under subsection (2) must be in writing.
(4) The *National Convener may order that a person who has applied under subsection (2) be made a party to the review.
Note: For the role of *National Convener, see section 1323 of the Social Security Act 1991.
Part 3—Right to review by Administrative Appeals Tribunal
263 Review of SSAT decision by AAT
(1) If a decision has been reviewed by the SSAT and has been affirmed, varied or set aside, application may be made to the AAT for a review of the decision of the SSAT.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), the decision made by the SSAT is taken to be:
(a) if the SSAT affirms a decision—the decision as affirmed; and
(b) if the SSAT varies a decision—the decision as varied; and
(c) if the SSAT sets a decision aside and substitutes a new decision—the new decision; and
(d) if the SSAT sets a decision aside and sends the matter back to the Secretary for reconsideration in accordance with any directions or recommendations of the SSAT—the directions or recommendations of the SSAT.
(3) Subsection (1) has effect subject to section 29 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975.
Note: Section 29 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 sets out the manner in which an application of the AAT for review of a decision must be made.
(4) If:
(a) the AAT sets a decision aside; and
(b) the Secretary is satisfied that an event that did not occur would have occurred if the decision had not been made;
the Secretary may, if satisfied that it is reasonable to do so, treat the event as having occurred for the purposes of this Act.
264 Variation of decision before AAT review completed
(1) If an *officer varies a decision after an application has been made to the AAT for review of the decision but before the determination of the review, the application is to be treated as if it were an application for review of the decision as varied.
(2) If an *officer sets a decision aside and substitutes a new decision after an application has been made to the AAT for review of the decision set aside but before determination of the review, the application is to be treated as if it were an application for review of the new decision.
(3) If:
(a) a person applies to the AAT for review of a decision; and
(b) before determination of the review, an *officer varies the decision or sets the decision aside and substitutes a new decision;
the person may either:
(c) proceed with the application for review of the decision as varied or the new decision; or
(d) withdraw the application.
265 Review of SSAT decision on application by the Secretary
(1) If a decision has been reviewed by the SSAT and has been varied or set aside, the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to a review under section 263 of the SSAT’s decision as if the Secretary were, for the purposes of section 27 of that Act, a person whose interests are affected by the SSAT’s decision.
Note: Section 27 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 provides that, if an Act provides that an application may be made to the AAT for a review of a decision, the application may be made by or on behalf of any person whose interests are affected by the decision.
(2) If the decision reviewed by the SSAT was made by the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency, subsection (1) applies as if the reference to the Secretary were a reference to the CEO.
266 Secretary may settle proceedings before the AAT
(1) The Secretary may agree, with other parties to proceedings before the AAT that relate to recovering a debt, to settle the proceedings. The agreement must be in writing.
(2) If the proceedings are settled and the Secretary gives the AAT a copy of the agreement to settle the proceedings, the application for review of the decision that was the subject of the proceedings is taken to have been dismissed.
Part 4—Modification of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975
267 Modification of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act
This Part sets out the modifications of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 that need to be made for applications for review under section 263.
268 Statement of reasons for decision
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application under section 263 for review of a decision as if references in section 28 of that Act to the person who made the decision were references to the *National Convener.
Note: Section 28 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 sets out the rights of a person affected by a decision in obtaining reasons for the decision.
269 Notice of application for review
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application under section 263 for review of a decision as if the reference in subsection 29(11) of that Act to the person who made the decision were a reference to each party to a review by the SSAT (other than a party making the application under section 263).
Note: Subsection 29(11) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 requires notice of an application to the AAT for review of a decision to be given to the person who made the decision.
270 Parties to review by the AAT
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review under section 263 as if the reference in paragraph 30(1)(b) of that Act to the person who made the decision were a reference to each person who was a party to the review by the SSAT.
Note: Paragraph 30(1)(b) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 provides that the person who made the decision under review is a party to the proceeding before the AAT for review of the decision.
271 Lodging documents with the AAT
(1) The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review under section 263 as if references in section 37 of that Act to the person who made the decision that is the subject of an application for review by the AAT were references to:
(a) if the original decision was made by the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency—the CEO; or
(b) in any other case—the Secretary.
Note: Subsection 37(1) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 requires a person who has made a decision that is under review by the AAT to give the AAT copies of:
(a) a statement setting out the findings on material questions of fact, referring to the evidence or other material on which those findings were based and giving the reasons for the decision; and
(b) every other document or part of a document that is in the person’s possession or under the person’s control and is considered by the person to be relevant to the review.
(2) If a person applies to the AAT under section 263 for a review of a decision, the Secretary is taken to have complied with his or her obligations under paragraph 37(1)(a) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 in relation to the decision if he or she gives the AAT the prescribed number of copies of the statement prepared by the SSAT under paragraph 1281(1)(a) of the Social Security Act 1991.
Note: Paragraph 1281(1)(a) of the Social Security Act 1991 requires the SSAT to give the parties to the SSAT review a written statement setting out the decision of the SSAT on review, the reasons for the decision, findings on any material questions of fact and a reference to the evidence or other material on which the findings were based.
(3) Subsection (2) does not limit the AAT’s powers under section 38 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975.
Note: Section 38 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 allows the AAT to order the person who lodged a statement under paragraph 37(1)(a) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975, to lodge an additional statement containing further and better particulars.
(4) If:
(a) a person applies to the AAT under section 263 for review of a decision; and
(b) the original decision was made by the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency;
subsection (2) applies as if references to the Secretary were references to the CEO.
(5) In this section:
original decision means the decision that was reviewed by the SSAT.
272 Power of the AAT to obtain additional statements
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review under section 263 as if references in section 38 of that Act to the person who lodges a statement referred to in paragraph 37(1)(a) of that Act with the AAT were references to the *National Convener.
273 Operation and implementation of the decision under review
(1) The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review under section 263 as if the references in subsection 41(4) of that Act to the person who made the decision were references to each party to the review by the SSAT.
Note: Section 41 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 deals with the operation and implementation of a decision under review by the AAT.
(2) The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review under section 263 as if the references in section 41 of that Act to the decision to which the relevant proceeding relates were references to:
(a) if the SSAT affirmed the original decision—the original decision; or
(b) if the SSAT varied the original decision:
(i) the original decision as varied by the SSAT; and
(ii) the original decision; or
(c) if the SSAT set aside the original decision and substituted a new decision:
(i) the new decision; and
(ii) the original decision; or
(d) if the SSAT set aside the original decision and sent the matter back to the Secretary for reconsideration in accordance with any directions or recommendations of the SSAT:
(i) any decision made as a result of that reconsideration; and
(ii) the original decision.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (2), the original decision is the decision that was reviewed by the SSAT.
274 Power of the AAT if party fails to appear
The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to a review under section 263 as if the reference in subsection 42A(2) of that Act to the person who made the decision were a reference to the Secretary.
Note: Subsection 42A(2) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 empowers the AAT to direct that, if a person fails to appear (other than the person who made the decision that is under review), that person is to cease to be a party to the proceedings before the AAT or the application for review is to be dismissed.
275 Secretary to have general administration of Act
The Secretary is, subject to any direction of the Minister, to have the general administration of this Act.
(1) The Secretary may by signed instrument delegate to an *officer all or any of the powers of the Secretary under this Act.
(2) The Secretary may, in accordance with *service arrangements, by signed instrument, delegate to the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency all or any of the Secretary’s powers under this Act.
277 Authorised review officers
The Secretary may, in writing, authorise an *officer to perform duties as an authorised review officer for the purposes of this Act.
278 Decisions to be in writing
(1) A decision of an *officer under this Act must be in writing.
(2) A decision under this Act is taken to be in writing if it is entered into, or recorded with the use of, a computer.
279 Notice of decisions under this Act
(1) If notice of a decision under this Act is:
(a) delivered to a person personally; or
(b) left at the address of the place of residence or business of the person last known to the Secretary; or
(c) sent by pre-paid post to the postal address of the person last known to the Secretary;
notice of the decision is taken, for the purposes of this Act, to have been given to the person.
(2) Notice of a decision under this Act may be given to a person by properly addressing, prepaying and posting the document as a letter.
(3) If notice of a decision under this Act is given in accordance with subsection (2), notice of the decision is taken to have been given to the person at the time at which the letter would be delivered in the ordinary course of the post unless the contrary is proved.
(4) This section only applies to notices of decisions and nothing in this section affects the operation of sections 28A and 29 of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 in relation to other notices under this Act (for example, a notice that requires a person to inform the Department about some matter or a notice that requires a person to give the Secretary a statement about some matter).
Part 2—Special provisions about the Agency
280 References to the Secretary and the Department—requirements etc. by delegate
(1) If the Secretary delegates to the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency a power under this Act to require or request a person to give the Secretary a document or *information, the delegate may, in exercising the power, require or request the person to give the document or information to the CEO instead of the Secretary.
(2) If the Secretary delegates to the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency a power under this Act to require or request a person to give or send to, or lodge with, the Department a document or *information, the delegate may, in exercising the power, require or request the person to give or send the document or information to the Agency, or lodge it with the Agency, instead of the Department.
(3) A person who:
(a) gives a document or *information to the *CEO; or
(b) gives or sends a document or information to the *Agency, or lodges it with the Agency;
in compliance with a requirement or a request by a delegate of the Secretary is to be treated for all purposes as if the person had:
(c) given the document or information to the Secretary; or
(d) given or sent the document or information to the Department, or lodged it with the Department;
as the case may be, in compliance with a requirement or request by the Secretary.
(4) A person who:
(a) does not give a document or *information to the *CEO; or
(b) does not give or send a document or information to the *Agency, or lodge it with the Agency;
in compliance with a requirement or request by a delegate of the Secretary is to be treated for all purposes as if the person:
(c) had not given the document or information to the Secretary; or
(d) had not given or sent the document or information to the Department, or lodged it with the Department;
as the case may be, in compliance with a requirement or request by the Secretary.
281 References to the Secretary and the Department—directions by Secretary
(1) If:
(a) the Secretary delegates to the *CEO of the *Agency or an *employee of the Agency all or any of the Secretary’s powers under this Act; and
(b) because of the delegation, a reference to the Secretary, the Department, or an officer of the Department, in another provision of this Act is inappropriate, whether for administrative reasons or any other reason;
the Secretary may, in writing, direct that the provision is to have effect as if:
(c) the reference to the Secretary were a reference to the *CEO of the *Agency; or
(d) the reference to the Department were a reference to the Agency; or
(e) the reference to an officer of the Department were a reference to an employee of the Agency;
as the case requires.
Note: See section 276 for the Secretary’s power to delegate to the *CEO or an *employee of the *Agency.
(2) If the Secretary gives a direction in relation to a provision, the provision has effect in accordance with the direction while the direction is in force.
(3) A direction comes into force on the day it is notified in the Gazette, or on such later days as is specified in it, and remains in force until it is revoked.
(4) A direction is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
282 Treatment of unincorporated associations
This Act applies to an unincorporated association as if the association were a person, but it applies with the following changes:
(a) obligations that would be imposed on the unincorporated association are imposed instead on each member of the committee of management of the association, but may be discharged by any of those members;
(b) an offence against this Act that would be committed by an unincorporated association is taken instead to have been committed by each member of the committee of management of the association who:
(i) aided, abetted, counselled or procured the relevant act or omission; or
(ii) was in any way knowingly concerned in, or party to, the relevant act or omission (whether directly or indirectly and whether by any act or omission of the member).
(1) This Act applies to a partnership as if the partnership were a person, but it applies with the following changes:
(a) obligations that would be imposed on the partnership are imposed instead on each partner, but may be discharged by any of the partners;
(b) any offence against this Act that would be committed by the partnership is taken instead to have been committed by each partner who:
(i) aided, abetted, counselled or procured the relevant act or omission; or
(ii) was in any way knowingly concerned in, or party to, the relevant act or omission (whether directly or indirectly and whether by any act or omission of the partner).
(2) For the purposes of this Act, a change in the composition of a partnership does not affect the continuity of the partnership.
284 Judicial notice to be taken of certain matters
(1) All courts must take judicial notice of a signature that purports to be attached or appended to any official document if the signature is of a person who:
(a) holds or has held the office of Secretary; or
(b) is or was an *officer.
(2) If the signature of a person referred to in subsection (1) purports to be attached or appended to any official document, all courts must take judicial notice of the fact that the person holds, or has held, the office referred to in subsection (1) or is or was an *officer.
(1) If the signature of any person who:
(a) holds or has held the office of Secretary; or
(b) is or was an *officer;
purports to be attached or appended to any official document, the document must be received in all courts as prima facie evidence of the facts and statements contained in it.
(2) A statement in writing signed by a person referred to in subsection (1) that a person is or was *receiving a *child care payment on a certain date at a certain rate must be received in all courts as prima facie evidence that the person is or was receiving the payment on the date and at the rate stated.
(1) Payments of child care assistance and of *emergency child care assistance are to be made out of money appropriated by the Parliament for the purposes of such payments.
(2) Payments of child care rebate are to be made out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund, which is appropriated accordingly.
The Governor-General may make regulations, not inconsistent with this Act, prescribing matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed; or
(b) necessary or convenient for carrying out or giving effect to this Act and, in particular, may make regulations prescribing penalties not exceeding 5 penalty units for any breach of the regulations.
Schedule 1—Calculation of rate of child care assistance
Note: See section 53.
Definitions
A1 In this Schedule:
minimum family payment rate, in relation to a person, has the same meaning as in the Social Security Act 1991.
Note: The relevant definition is in subsection 6(1) of the Social Security Act 1991.
non-school child means a child who is not a school child.
non-standard hours family day care means hours of care provided by a *family day care service at times that are identified in the service’s conditions of approval as being non-standard hours of the service.
part-time family day care means standard hours family day care provided by a *family day care service for a child in a week during which the service provides a total of less than 50 hours of standard hours family day care for the child.
school child has the meaning given by point A2.
standard hours family day care means hours of care provided by a *family day care service at times that are identified in the service’s conditions of approval as being standard hours of care.
week means the first or second week of a *payment period.
A2(1) A child is a school child for the purposes of this Schedule if the child is attending primary or secondary school, or is on a break from school (for example, school holidays) and will be attending primary or secondary school after that break.
(2) The Minister may determine in writing that children in a specified class are to be treated as though they were attending primary or secondary school for the purposes of this Schedule. The determination has effect accordingly.
(3) The Minister may determine in writing that children in a specified class are to be treated as though they were not attending primary or secondary school for the purposes of this Schedule. The determination has effect accordingly.
(4) A determination under subpoints (2) and (3) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Module B—Overall rate calculation process
Method of calculating rate
B1 The rate of child care assistance is a rate per *payment period worked out in accordance with Method statement B1.
Method statement B1
Step 1. Identify the qualifying sessions of care for the person and for each week of the *payment period (see Module C).
Step 2. Identify the eligible hours of care (see Module D) in relation to:
(a) the first week of the payment period; and
(b) the second week of the payment period.
Step 3. Work out the amount calculated in accordance with the formula set out in point B2 in relation to:
(a) each of the eligible hours of care in the first week; and
(b) each of the eligible hours of care in the second week.
Step 4. Add together the total of those amounts for each week.
Step 5. The rate of child care assistance is worked out by adding together the amounts worked out under Step 4 and then rounding the total in accordance with point B3.
The main formula
B2(1) The formula to be applied in relation to an eligible hour of care for the purposes of Step 3 in Method statement B1 is:
![]()
Note: For how this formula applies in cases of hardship, see point B4.
(2) In this formula:
hourly rebateable fee has the meaning given by Module E.
CA% has the meaning given by Module F.
Rounding amounts
B3 Amounts worked out under Step 5 in Method statement B1 are to be rounded to the nearest 10 cents (rounding 5 cents upwards).
Payment of child care assistance at maximum rate to people in hardship
B4(1) The Secretary may, in writing, determine that a person should receive child care assistance at the maximum rate because the person is or was in hardship. The determination:
(a) is to comply with subpoint (3); and
(b) is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (4).
(2) The formula in subpoint B2(1) applies to the person in respect of the period to which a determination under subpoint (1) applies subject to the following modifications:
(a) the hourly rebateable fee, in relation to an eligible hour of care, is the fee charged by the *child care assistance service for the hour of care; and
(b) the CA% is 100%.
(3) A determination under subpoint (1) applies in respect of the period specified in the determination (which may be a period starting before or after the determination is made). Unless there are exceptional circumstances, the period specified must not be such that the total of that period, and the period specified in each other determination (if any) under this point in relation to the person and the same calendar year, exceeds 13 weeks.
(4) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines relating to the making of determinations under subpoint (1).
(5) A determination under subpoint (4) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Module C—Qualifying session of care
Qualifying session of care—basic meaning
C1 Subject to points C2 and C3, a *session of care for a child is a qualifying session of care in relation to a person and a *payment period if:
(a) it is a session of care in the payment period in relation to which the conditions specified in subsection 20(2) are satisfied; and
(b) no provision of Part 3 of Chapter 2 applies to make child care assistance not payable to the person in respect of the time of the session.
Session cannot be counted twice as a qualifying session of care
C2 Once a *session of care for a child has been counted (for the purposes of this Schedule) as a qualifying session of care in relation to a person, it cannot be counted again as a qualifying session of care for the purposes of determining the child care assistance payable to the person, or another person, pursuant to another claim.
Dealing with session of care in respect of which 2 people have made claims
C3(1) If 2 people claim child care assistance in respect of the same *session of care for a child, the Secretary is to decide in writing which of them is to receive any child care assistance payable in respect of the session. The session is not a qualifying session of care in relation to the other person.
(2) In making the decision, the Secretary must have regard to whether one of the people is the primary carer for the child.
(3) The Secretary is to give notice of the decision to each of the people.
Module D—Eligible hour of care
Eligible hour of care—basic meaning
D1(1) Each of the hours in a qualifying session of care is, subject to points D2 and D3, an eligible hour of care.
Note: A *session of care can still be a qualifying session of care (and each of its hours an eligible hour of care) even if the child is *absent from some or all of the session—see section 25.
(2) If a qualifying session of care includes part only of an hour, and the service charges only for that part of that hour (rather than for the whole of that hour), this Schedule applies, with appropriate modifications, to that part of that hour.
(3) If a qualifying session of care includes part only of an hour, and the service charges for the whole of that hour, the whole of that hour is, subject to points D2 and D3, an eligible hour of care.
Eligible hour of care—the 20 hour per week per child limit if work/training/study test not satisfied
D2(1) This point applies to a person in respect of a week unless:
(a) one of the following subparagraphs applies:
(i) if the person is not a *member of a couple—the person *satisfies the work/training/study test at some time in the week; or
(ii) if the person is a member of a couple—both the person and the person’s partner satisfy the work/training/study test at some time in the week; or
(b) child disability allowance under the Social Security Act 1991 is payable to the person or the person’s partner in respect of some or all of the week:
(i) in respect of a dependent child of the person or the person’s partner; and
(ii) pursuant to a claim that was determined before the week.
(2) This point applies in relation to qualifying sessions of care in the week, other than:
(a) any session provided by an *occasional care service; or
(b) any session provided by a service at a time in relation to which a determination under subpoint (7) applies.
(3) Subject to subpoint (6), it is only the first 20 hours of care in the qualifying sessions of care for a child in a week that are eligible hours of care in those sessions.
(4) The Secretary may, in writing, determine which of the hours in the qualifying sessions of care for a child in a week are to count as the first 20 hours. The determination is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (10).
(5) The Secretary may, in writing, determine that a child needs or needed access to a specified higher total number of hours of care per week because:
(a) the child is or was at risk of neglect or abuse; or
(b) the child’s family is or was in crisis; or
(c) the child is or was a dependent child of a person who is or was disabled and whose partner (if any) is or was also disabled.
The determination is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (10).
(6) Subpoint (3) has effect in respect of the period to which a determination under subpoint (5) applies as if the reference in that subpoint to 20 hours were instead a reference to the higher number of hours specified in the determination.
(7) The Minister may, by determination in writing, exempt a specified *child care assistance service from the limit imposed by this point if:
(a) the service is the sole provider in an area of the kind of care the service provides; and
(b) not to grant the exemption would be likely to result in the closure of the service.
Note: Decisions under this subpoint are reviewable under Part 3 of Chapter 6, rather than under Chapter 9.
(8) A determination under subpoint (7):
(a) is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (10); and
(b) may be expressed so that the exemption is made subject to conditions.
(9) A determination under subpoint (5) or (7) applies in respect of the period specified in the determination (which may be a period starting before or after the determination is made).
(10) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines relating to making of determinations under subpoints (4), (5) and (7).
(11) A determination under subpoint (10) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Eligible hour of care—the 50 hour limit per week per child
D3(1) Subject to subpoint (5), it is only the first 50 hours of care in the qualifying sessions of care for a child in a week that are eligible hours of care in those sessions.
(2) The Secretary may, in writing, determine which of the hours in the qualifying sessions of care for a child in a week are to count as the first 50 hours. The determination is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (7).
(3) The Secretary may, in writing, determine that, because of work related commitments, the person needs or needed a specified higher total number of hours of care per week for the child. The determination is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (7).
(4) The Secretary may, in writing, determine that a child needs or needed access to a specified higher total number of hours of care per week because:
(a) the child is or was at risk of neglect or abuse; or
(b) the child’s family is or was in crisis.
The determination is to be made in accordance with guidelines in force under subpoint (7).
(5) Subpoint (1) has effect in respect of the period to which a determination under subpoint (3) or (4) applies as if the reference in it to 50 hours were instead a reference to the higher number of hours specified in the determination.
(6) A determination under subpoint (3) or (4) applies in respect of the period specified in the determination (which may be a period starting before or after the determination is made).
(7) The Minister may, by determination in writing, make guidelines relating to the making of determinations under subpoints (2), (3) and (4).
(8) A determination under subpoint (7) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Module E—Hourly rebateable fee
Hourly rebateable fee—basic meaning
E1(1) The hourly rebateable fee in relation to an eligible hour of care is the lesser of:
(a) the fee charged by the *child care assistance service for the hour of care, or if point E2 (reimbursements) applies, that fee as reduced under that point; and
(b) the applicable fee limit set out in the table below.
Applicable fee limit | ||
Item | Kind of care provided in hour | Fee limit |
1 | Care for a non-school child, other than part‑time family day care or non-standard hours family day care | $2.30 |
2 | Care for a school child, other than part-time family day care or non-standard hours family day care | $1.95 |
3 | Part-time family day care for a non-school child | the lesser of $3.05 and the ceiling rate (see subpoint (2)) |
4 | Part-time family day care for a school child | the lesser of $2.60 and the ceiling rate (see subpoint (3)) |
5 | Non-standard hours family day care for a non‑school child | $3.05 |
6 | Non-standard hours family day care for a school child | $2.60 |
Note: The amounts specified in this table are to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
(2) For the purposes of item 3 of the table in subpoint (1), the ceiling rate is the amount worked out by dividing $115 by the total number of eligible hours of care of the kind referred to in that item that were provided for the child during the week.
Note: The amount specified in this subpoint is to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
(3) For the purposes of item 4 of the table in subpoint (1), the ceiling rate is the amount worked out by dividing $97.50 by the total number of eligible hours of care of the kind referred to in that item that were provided for the child during the week.
Note: The amount specified in this subpoint is to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
Treatment of reimbursements
E2(1) This point applies if the person, or the person’s partner, is reimbursed for some or all of the fee charged by a *child care assistance service in respect of one or more eligible hours of care in a week.
(2) In respect of each eligible hour of care in the week (not just the hours to which the reimbursement relates), the fee charged by the *child care assistance service for the hour of care is, for the purposes of point E1, to be reduced by the amount worked out in accordance with Method statement E1.
Method statement E1
Step 1. Work out the total amount reimbursed to the person, or the person’s partner, as mentioned in subpoint (1) in respect of the week.
Step 2. Divide the amount by the total number of eligible hours of care in the week.
Step 3. The fee charged by the *child care assistance service for each of those eligible hours of care is to be reduced by the amount worked out under Step 2.
(3) The Minister may determine in writing:
(a) the circumstances in which a person is taken to be reimbursed for the purposes of this point; and
(b) a mechanism for working out the amount taken to be reimbursed to a person for the purposes of this point.
(4) A determination under subpoint (3) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Method of calculating CA%
F1 The CA % in relation to a person and an eligible hour of care is worked out in accordance with Method statement F1.
Method statement F1
Step 1. Work out if the person is receiving family payment at more than the minimum family payment rate. The following rules then apply:
(a) if the person is receiving family payment at more than that rate—the CA% is to be worked out in accordance with point F5;
(b) in any other case—go to Step 2.
Step 2. Work out the person’s annual income (see point F2). The following rules then apply:
(a) if the person’s annual income is at or below the income cut out point (see point F3), go to Step 3;
(b) if the person’s annual income exceeds the income cut out point, the CA% is 0% (resulting in a nil rate of payment).
Step 3. Divide the person’s annual income by 52 to produce a weekly rate of income. The following rules then apply:
(a) if the person’s weekly income is at or below the threshold amount (see point F4), the CA% is to be worked out in accordance with point F5;
(b) if the person’s weekly income exceeds the threshold amount, the CA% is to be worked out in accordance with point F6.
The person’s annual income
F2(1) For the purpose of this Module, the person’s annual income is to be worked out in accordance with the regulations.
(2) Without limiting subpoint (1), the regulations may:
(a) provide that a person’s annual income is to include the income of another person (for example, the person’s partner); and
(b) identify amounts to be included in a person’s income; and
(c) identify amounts not to be included in a person’s income; and
(d) provide for the use of estimates in determining a person’s income; and
(e) provide for a person’s income to be recalculated in certain circumstances; and
(f) make different provision in respect of different classes of people.
(3) Regulations made for the purposes of this point may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
The income cut out point
F3 The income cut out point, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, is:
(a) if the number of children in care of that kind is 1—$65,743; or
(b) if the number of children in care of that kind is 2—$77,084; or
(c) if the number of children in care of that kind is 3 or more—$94,095.
Note 1: See point F7 for the meaning of number of children in care of that kind.
Note 2: The amounts specified in this subpoint are to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
The threshold amount
F4 The threshold amount is $522.
Note: The amount specified in this subpoint is to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
Calculation of CA%—maximum income tested rate
F5(1) The CA% in relation to a person and an eligible hour of care is to be worked out in accordance with the formula in subpoint (2) if:
(a) paragraph (a) of Step 1 in Method statement F1 applies; or
(b) paragraph (a) of Step 3 in Method statement F1 applies.
(2) The formula is:
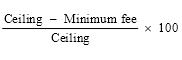
(3) In this formula:
ceiling, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, means the amount worked out by multiplying $115 by the number of children in care of that kind.
minimum fee, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, means:
(a) if the number of children in care of that kind is 1—$19.50; or
(b) if the number of children in care of that kind is 2 or more—$22.
Note 1: See point F7 for the meaning of number of children in care of that kind.
Note 2: The amounts specified in the definitions of ceiling and minimum fee are to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
Calculation of CA%—reduced income tested rate
F6(1) The CA% in relation to a person and an eligible hour of care is to be worked out in accordance with the formula in subpoint (2) if paragraph (b) of Step 3 in Method statement F1 applies.
(2) The formula is:

(3) In this formula:
excess income means the amount of the excess referred to in paragraph (b) of Step 3 in Method statement F1.
withdrawal rate means the amount worked out in accordance with the formula set out in subpoint (4).
minimum fee, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, means:
(a) if the number of children in care of that kind is 1—$19.50; or
(b) if the number of children in care of that kind is 2 or more—$22.
ceiling, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, means the amount worked out by multiplying $115 by the number of children in care of that kind.
Note 1: See point F7 for the meaning of number of children in care of that kind.
Note 2: The amounts specified in the definitions of ceiling and minimum fee are to be indexed in accordance with Module G.
(4) The formula for working out the withdrawal rate is:

(5) In this formula:
ceiling has the same meaning as in subpoint (3).
minimum fee has the same meaning as in subpoint (3).
weekly cut out point means the amount worked out by dividing the income cut out point worked out under point F3 by 52.
threshold amount has the same meaning as in point F4.
Meaning of number of children in care of that kind
F7 For the purposes of applying this Module to a person and an eligible hour of care, the number of children in care of that kind, in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care, is worked out in accordance with Method statement F2.
Method statement F2
Step 1. Work out what kind of care was provided in that hour. For this purpose, the kinds of care are:
(a) care provided for a school child by a *child care assistance service, other than an *occasional care service;
(b) care provided for a non-school child by a child care assistance service, other than an occasional care service;
(c) care provided for a school child by an occasional care service;
(d) care provided for a non-school child by an occasional care service.
Step 2. Work out, in relation to the person, how many children are in qualifying sessions of care of that kind in the week concerned. That number is the number of children in care of that kind in relation to the person and the eligible hour of care.
Amounts to be indexed
G1 The amounts specified in the table below are to be indexed in accordance with the regulations.
Amounts to be indexed | |
Item | Amount |
1 | Each amount specified in the table at the end of subpoint E1(1) |
2 | The amount specified in subpoint E1(2) |
3 | The amount specified in subpoint E1(3) |
4 | Each amount specified in point F3 |
5 | The amount specified in point F4 |
6 | Each amount specified in the definitions of ceiling and minimum fee in subpoint F5(3) |
7 | Each amount specified in the definitions of ceiling and minimum fee in subpoint F6(3) |
Substituting a higher amount before first indexation
G2(1) The Minister may, in writing, before the day on which an amount is first indexed, determine that a higher amount is to be substituted for that amount. The determination has effect accordingly.
(2) A determination under subpoint (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Regulations on indexation
G3(1) The regulations may:
(a) prescribe when an amount is to be indexed; and
(b) prescribe the way in which an amount is to be indexed; and
(c) make different provision in respect of different amounts.
(2) Regulations made for the purposes of this point may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
Consequence of indexing amounts
G4 If an amount (the indexable amount) is indexed in accordance with the regulations, this Schedule has effect as if the new amount (as indexed) were substituted for the indexable amount on the day when the indexation takes effect.
Schedule 2—Calculation of rate of child care rebate
Note: See section 106.
Module A—Overall rate calculation process
Method of calculating rate
A1 The rate of child care rebate is a rate per *payment period worked out in accordance with Method statement A1.
Method statement A1
Step 1. Identify the qualifying sessions of care for the person and for each week of the *payment period (see Module B).
Step 2. Work out the child care rebate for the person for each week of the payment period (see point A2).
Step 3. The rate of child care rebate is worked out by adding together the child care rebate for each week of the payment period and then rounding the total in accordance with point A3.
The weekly child care rebate formula
A2(1) The formula for working out the child care rebate under Step 2 in Method statement A1 is:
![]()
(2) In this formula:
CCR% has the meaning given by Module C.
weekly child care expenditure has the meaning given by Module D.
minimum fee means $19.50. This is the minimum amount that the person must pay for child care for a week before rebate will be paid.
Note: The amount specified in the definition of minimum fee is to be indexed in accordance with Module E.
(3) If the person’s weekly child care expenditure is below the minimum fee, the child care rebate for the week is nil.
Rounding amounts
A3 Amounts worked out under Step 3 in Method statement A1 are to be rounded upwards to the nearest 5 cents.
Module B—Qualifying session of care
Qualifying session of care—basic meaning
B1 Subject to points B2 and B3, a *session of care for a child is a qualifying session of care in relation to a person and a *payment period if:
(a) it is a session of care in the payment period in relation to which the conditions specified in subsection 78(2) are satisfied; and
(b) no provision of Part 3 of Chapter 3 applies to make child care rebate not payable to the person in respect of the time of the session.
Session cannot be counted twice as a qualifying session of care
B2 Once a *session of care for a child has been counted (for the purposes of this Schedule) as a qualifying session of care in relation to a person, it cannot be counted again as a qualifying session of care for the purposes of determining the child care rebate payable to the person, or another person, pursuant to another claim.
Dealing with session of care in respect of which 2 people have made claims
B3(1) If 2 people claim child care rebate in respect of the same *session of care for a child, the Secretary is to decide in writing which of them is to receive any child care rebate payable in respect of the session. The session is not a qualifying session of care in relation to the other person.
(2) In making the decision, the Secretary must have regard to whether one of the people is the primary carer for the child.
(3) The Secretary is to give notice of the decision to each of the people.
The CCR%
C1 The CCR% for a person is:
(a) if the CCR% for the person is set at 20% under point C2 or C3—20%; or
(b) if the person’s annual income exceeds the income cut out point (see points C4 and C5)—20%; or
(c) in any other case—30%.
Non-compliance with tax file number request—CCR% is 20%
C2(1) The CCR% for the person is 20% if:
(a) the person is requested under section 97 or 123 to:
(i) give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s *tax file number; or
(ii) apply for a tax file number and give the Secretary a written statement of the person’s tax file number once it has been issued; and
(b) at the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made, the person has not complied with the request; and
(c) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
Note 1: See section 6 for how to comply with a request.
Note 2: During the 28 days, the CCR% for the person may still be 30%.
(2) The CCR% for the person is 20% if:
(a) the person is a *member of a couple; and
(b) the person is requested under section 98 or 124 to give the Secretary a written statement of the *tax file number of the person’s partner; and
(c) at the end of the period of 28 days after the request is made, the person has not complied with the request; and
(d) the Secretary has not exempted the person from having to comply with the request.
Note 1: See section 7 for how to comply with a request.
Note 2: During the 28 days, the CCR% for the person may still be 30%.
(3) If the person’s claim for child care rebate is a *prospective claim, once the CCR% for the person is 20%, it remains fixed at that rate for the purposes of that claim until the person complies with the request.
(4) If the person’s claim for child care rebate is a *retrospective claim, once the CCR% for the person is 20%, it remains fixed at that rate for the purposes of that claim.
Non-compliance with requirement for information about income
C3(1) The CCR% for the person is 20% if:
(a) the person is requested under the regulations to provide *information relevant to the calculation of annual income for the purposes of this Module; and
(b) the person has not provided the information within the period required by the regulations.
Note: During the period for complying with the request, the CCR% for the person may still be 30%.
(2) If the person’s claim for child care rebate is a *prospective claim, once the CCR% for the person if 20%, it remains fixed at that rate for the purposes of that claim until the person complies with the request.
(3) If the person’s claim for child care rebate is a *retrospective claim, once the CCR% for the person is 20%, it remains fixed at that rate for the purposes of that claim.
The person’s annual income
C4(1) For the purposes of this Module, the person’s annual income is to be worked out in accordance with the regulations.
(2) Without limiting subpoint (1), the regulations may:
(a) provide that a person’s annual income is to include the income of another person (for example, the person’s partner); and
(b) identify amounts to be included in a person’s income; and
(c) identify amounts not to be included in a person’s income; and
(d) provide for the use of estimates in determining a person’s income; and
(e) provide for a person’s income to be recalculated in certain circumstances.
(3) Regulations made for the purposes of this point may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
The income cut out point
C5(1) The income cut out point, in relation to the person and the week, is:
(a) if the person has only one *dependent child in the week—$70,000; or
(b) if the person has more than one dependent child in the week—the amount worked out in accordance with the formula in subpoint (2).
Note: The amount specified in this point is to be indexed in accordance with Module E.
(2) The formula is:
![]()
Note: The amounts specified in this point are to be indexed in accordance with Module E.
(3) In this point:
dependent child, in relation to the person, means a *dependent child of the person or the person’s partner.
Module D—Weekly child care expenditure
Method of calculating weekly child care expenditure
D1 The weekly child care expenditure for a person for a week is worked out in accordance with Method statement D1.
Method statement D1
Step 1. Work out the total of all liabilities that the person, or the person’s partner, has incurred for qualifying sessions of care during the week.
Step 2. Deduct the amounts referred to in point D2. The result is the uncapped weekly child care expenditure.
Step 3. Apply the expenditure ceiling specified in point D3 to the uncapped weekly child care expenditure, then apply the following rules:
(a) if the uncapped weekly child care expenditure is less than the expenditure ceiling, the weekly child care expenditure is equal to the uncapped weekly child care expenditure;
(b) if the uncapped weekly child care expenditure is equal to or greater than the expenditure ceiling, the weekly child care expenditure is equal to the expenditure ceiling.
Amounts to be deducted
D2(1) The amounts to be deducted under Step 2 in Method statement D1 are:
(a) any child care assistance that is paid to or on behalf of the person or the person’s partner for the week; and
(b) any other amount specified in a determination in force under subpoint (2).
(2) The Minister may determine in writing amounts that are to be deducted under Step 2.
(3) A determination under subpoint (2) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
The expenditure ceiling
D3 The expenditure ceiling is as follows:
(a) if rebate is paid in respect of one *dependent child of the person, or the person’s partner, for the week—$115;
(b) if rebate is paid in respect of two or more dependent children of the person, or the person’s partner, for the week—$230.
Note: The amounts specified in this point are to be indexed in accordance with Module E.
Amounts to be indexed
E1 The amounts specified in the table below are to be indexed.
Amounts to be indexed | |
Item | Amount |
1 | The amount specified in subpoint A2(2) (definition of minimum fee) |
2 | Each amount specified in point C5 |
3 | Each amount specified in point D3 |
Substituting a higher amount before first indexation
E2(1) The Minister may, in writing, before the day on which an amount is first indexed, determine that a higher amount is to be substituted for that amount. The determination has effect accordingly.
(2) A determination under subpoint (1) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Regulations on indexation
E3(1) The regulations may:
(a) prescribe when an amount is to be indexed; and
(b) prescribe the way in which an amount is to be indexed; and
(c) make different provision in respect of different amounts.
(2) Regulations made for the purposes of this point may adopt a provision or provisions of the Social Security Act 1991, with or without modification.
Consequence of indexing amounts
E4 If an amount (the indexable amount) is indexed in accordance with the regulations, this Schedule has effect as if the new amount (as indexed) were substituted for the indexable amount on the day when the indexation takes effect.
[Minister's second reading speech made in the
House of Representatives on 26 June 1997
Senate on 29 October 1997]
(110/97)