
Childcare Rebate Act 1993
An Act to provide for the payment of rebates for a
proportion of certain child care expenses incurred
by families
[Assented to 24 December 1993]
The Parliament of Australia enacts:
PART 1—PRELIMINARY
Short title
1. This Act may be cited as the Childcare Rebate Act 1993.
Commencement
2.(1) Subject to subsection (2), this Act commences on a day to be fixed by Proclamation.
(2) If this Act does not commence under subsection (1) within the period of 6 months beginning on the day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent, it commences on the first day after the end of that period.
Outline of this Act
3.(1) This Act establishes the childcare rebate. It is about who is entitled to the rebate, how it can be claimed and the amount of the rebate.
(2) Part 2 is about which families are eligible to receive the rebate. It provides for the registration of these families by the Health Insurance Commission.
(3) Part 3 is about the eligibility of registered families for the rebate. It also deals with how claims for the rebate are made.
(4) Part 4 is about payment of the rebate. It deals with the circumstances in which the rebate is, and is not payable, and also sets out how amounts of rebate are worked out.
(5) Part 5 is about administration of the rebate. It deals with the general administrative responsibility for this Act, registration of child care providers, appeals against decisions by the Commission under this Act and the consequences of making false or misleading statements.
(6) Part 6 deals with miscellaneous matters.
Definitions
4. In this Act, unless the contrary intention appears:
“approved form” means a form approved in writing by the Managing Director for the purposes of the provision in which the expression occurs;
“Australia”, when referred to in its geographical sense, includes the Territory of Christmas Island and the Territory of Cocos (Keeling) Islands;
“child care” has the meaning given in section 27;
“Child Care Provider Number” means a number issued under subsection 49(4);
“childcare rebate” means the rebate payable under this Act;
“claim” means a claim made under section 32 for payment of the childcare rebate;
“Commission” means the Health Insurance Commission;
“dependent child” has the meaning given in section 11;
“family” has the meaning given in section 5;
“Family Registration Number” means a number issued under subsection 19(3);
“fee relief” means fee relief granted under section 12A of the Child Care Act 1972;
“Managing Director” means the Managing Director of the Commission;
“maximum claimable amount” has the meaning given in section 44;
“minimum weekly threshold” has the meaning given in subsection 43(2);
“parent” has the meaning given in section 10;
“parental member”, in relation to a family, means:
(a) a member of the family who is a parent of a dependent child who is a member of the family; or
(b) a partner (within the meaning of subsection 5(2)) of such a parent;
“registered carer” means a person who is registered under section 49;
“registered family” means a family that is registered under section 19;
“reviewable decision” means a decision of a kind referred to in section 53;
“tax file number” has the same meaning as in Part VA of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936;
“week” means a period of 7 days starting at the beginning of a Monday and ending at the end of the following Sunday;
“weekly child care expenditure” has the meaning given in section 41.
Definition of family
5.(1) Subject to subsection (4), for the purposes of this Act, a family means a group of people that is made up of:
(a) a person and any dependent children of the person; and
(b) the partner (if any) of the person and any dependent children of the partner.
(2) For the purpose of paragraph (1)(b), a person is the partner of another person if:
(a) the person is legally married to the other person and is not, in the Managing Director’s opinion (formed as mentioned in subsection (3)), living separately and apart from the other person on a permanent basis; or
(b) all of the following conditions are met:
(i) the person is living with the other person;
(ii) the other person is of the opposite sex;
(iii) the person is not legally married to the other person;
(iv) the relationship between the person and the other person is, in the Managing Director’s opinion (formed as mentioned in subsection (3)), a marriage-like relationship;
(v) the person and the other person are not within a prohibited relationship for the purposes of section 23B of the Marriage Act 1961.
Note: A prohibited relationship for the purposes of section 23B of the Marriage Act 1961 is a relationship between a person and:
• an ancestor of the person; or
• a descendant of the person; or
• a brother or sister of the person (whether of the whole blood or the part-blood).
(3) In forming an opinion about the relationship between 2 people for the purposes of paragraph (2)(a) or subparagraph (2)(b)(iii), the Managing Director is to have regard to all the circumstances of the relationship including, in particular, the following matters:
(a) the financial aspects of the relationship, including:
(i) any joint ownership of real estate or other major assets and any joint liabilities; and
(ii) any significant pooling of financial resources especially in relation to major financial commitments; and
(iii) any legal obligations owed by one person in respect of the other person; and
(iv) the basis of any sharing of day-to-day household expenses;
(b) the nature of the household, including:
(i) any joint responsibility for providing care or support of children; and
(ii) the living arrangements of the people; and
(iii) the basis on which responsibility for housework is distributed;
(c) the social aspects of the relationship, including:
(i) whether the people hold themselves out as married to each other; and
(ii) the assessment of friends and regular associates of the people about the nature of their relationship; and
(iii) the basis on which the people make plans for, or engage in, joint social activities;
(d) any sexual relationship between the people;
(e) the nature of the people’s commitment to each other, including:
(i) the length of the relationship; and
(ii) the nature of any companionship and emotional support that the people provide to each other; and
(iii) whether the people consider that the relationship is likely to continue indefinitely; and
(iv) whether the people see their relationship as a marriage-like relationship.
(4) A person is not to be simultaneously treated as a member of more than one family unless:
(a) the person is a child; and
(b) members of more than one family jointly share the right to have, and to make decisions concerning, the daily care and control of the child.
Act to bind the Crown
6. This Act binds the Crown in each of its capacities.
Extension to external Territories
7. This Act extends to the Territory of Christmas Island and the Territory of Cocos (Keeling) Islands.
PART 2—ELIGIBILITY OF FAMILIES TO REGISTER FOR THE CHILDCARE REBATE
Outline of this Part
8.(1) This Part is about the eligibility of families to register for the childcare rebate, and the registration process.
(2) Division 1 is about the requirements for parental responsibility within the family.
(3) Division 2 is about the requirements relating to residency in Australia.
(4) Division 3 provides for the registration of families by the Commission.
Division 1—Parental responsibility
Parental responsibility requirements for registration
9. A family is not eligible to register for the childcare rebate unless the family includes:
(a) at least one person who is a parent within the meaning of section 10; and
(b) at least one other person who is a dependent child of that parent within the meaning of section 11.
Definition of parent
10. A parent is a person who:
(a) has the right (whether alone or jointly with another person):
(i) to have the daily care and control of a child; and
(ii) to make decisions about the daily care and control of the child; and
(b) has the care and control of the child.
Definition of dependent child
11.(1) Subject to subsection (2), a child is a dependent child of another person if:
(a) the other person has the right (whether alone or jointly with a third person):
(i) to have the daily care and control of the child; and
(ii) to make decisions about the daily care and control of the child; and the child is in the other person’s care and control; or
(b) the child:
(i) is not a dependent child of someone else under paragraph (a); and
(ii) is wholly or substantially in the other person’s care and control.
(2) A child cannot be a dependent child if he or she has turned 13.
Dependent children may have more than one family
12. Section 11 does not prevent a child from being a dependent child of persons who are not members of the same family.
Division 2—Residency
Residency requirements for registration
13. A family is not eligible to register for the childcare rebate unless at least one of the parents:
(a) is an Australian resident within the meaning of section 14; or
(b) is taken to be an Australian resident because of section 15 or 16.
Australian residents
14.(1) An Australian resident is a person who resides in Australia and who:
(a) is an Australian citizen; or
(b) is, within the meaning of the Migration Act 1958, the holder of a valid permanent entry permit; or
(c) has been granted, or is included in, a return endorsement, or a resident return visa, in force under that Act.
(2) In deciding for the purposes of this Act whether or not a person resides in Australia, regard must be had to:
(a) the nature of the accommodation used by the person in Australia; and
(b) the nature and extent of the family relationship the person has in Australia; and
(c) the nature and extent of the person’s employment, business or financial ties in Australia; and
(d) the nature and extent of the person’s assets located in Australia; and
(e) the frequency and duration of the person’s travel outside of Australia; and
(f) any other matter relevant to determining whether the person intends to remain permanently in Australia.
Certain overseas students are to be treated as Australian residents
15.(1) A person who is not an Australian resident within the meaning of section 14 is taken to be an Australian resident if the person:
(a) is undertaking a course of study at an educational institution in Australia; and
(b) is receiving from the Commonwealth for the purpose of undertaking that course of study, financial assistance of a kind specified in a determination under subsection (2).
(2) The Minister may make determinations as to the kinds of financial assistance to which paragraph (1)(b) applies.
(3) Determinations under subsection (2) are disallowable instruments for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Other people may be treated as Australian residents
16.(1) A person who is not an Australian resident within the meaning of section 14 is taken to be an Australian resident if the Commission so determines in writing.
(2) The Commission may so determine if it is satisfied that:
(a) hardship would be caused to the applicant if the applicant were not treated as an Australian resident; or
(b) because of the special circumstances of the particular case, the applicant should be treated as an Australian resident.
(3) A person may apply in writing to the Commission for such a determination.
Note: Refusals to make determinations are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Guidelines for making determinations
17.(1) The Minister may issue guidelines about making determinations under section 16.
(2) In making a determination under section 16, the Commission must comply with any such guidelines.
(3) The guidelines are disallowable instruments for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Division 3—Registration of families
Applying for registration
18.(1) A person may apply in writing to the Commission for registration of the family of which he or she is a member.
(2) The application must:
(a) list the names of all the members of the family; and
(b) be in the approved form.
Note: Subsection 5(1) sets out who the members of a family are for the purposes of this Act.
(3) The Minister may determine that, in order for an applicant to establish a particular matter specified in the determination that is relevant to deciding whether to register a family, the application must contain one or both of the following:
(a) a statement of the kind specified in the determination;
(b) evidence of the kind specified in the determination.
(4) Determinations under subsection (3) are disallowable instruments for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Registration by the Commission
19.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Commission must register the family of a person who makes an application under section 18 if and only if it is satisfied that the family meets the requirements of Divisions 1 and 2.
(2) Without limiting the circumstances under which the Commission must reject an application, the Commission must reject such an application if:
(a) the circumstances are such that a matter in respect of which the Commission must be satisfied in order to be satisfied that the family meets the requirements of Division 1 or 2 is a matter specified in a determination made for the purposes of subsection 18(3); and
(b) the application does not comply with the requirements imposed by the determination in relation to the establishment of that matter.
(3) If the Commission registers the family, it must:
(a) issue the family with a number to be known as the family’s Family Registration Number; and
(b) notify the applicant, in writing, of the number.
Note: Refusals to register families are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Variation of registration
20.(1) If a person becomes a member of a registered family, that person or any other member of the family may apply to the Commission for a variation in the registration to add the new family member, and the Commission must vary the registration accordingly.
(2) If a person ceases to be a member of a registered family, that person or any other member of the family may apply to the Commission for a variation in the registration to delete that person’s name, and the Commission must vary the registration accordingly.
Note: Refusals to vary registrations under this section are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Variation of registration without application
21. If the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) a person has ceased to be a member of a registered family; and
(b) the family nevertheless still meets the requirements of Divisions 1 and 2;
the Commission must vary the registration by deleting the person’s name.
Note: Variations of registration under this section are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Cancellation of registration
22.(1) The Commission must cancel a family’s registration if each parental member of the family requests the Commission in writing to do so.
(2) The Commission must cancel a family’s registration if:
(a) it is satisfied that the family no longer meets the requirements of Divisions 1 and 2; or
(b) on the basis of information it has received since the family was registered, it is satisfied that the family did not meet the requirements of Divisions 1 and 2 at the time it was registered.
(3) The Commission may cancel a family’s registration if it is satisfied that the Commission was given incorrect or misleading information in connection with the application for registration of the family.
Note: Cancellations of registration under subsection (2) or (3) are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Procedure for variation or cancellation
23.(1) Before varying a family’s registration under section 21 or cancelling a family’s registration under subsection 22(2) or (3), the Commission must give notice in writing, to a parental member of the family, that:
(a) states that the Commission is considering varying or cancelling the family’s registration; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which variation or cancellation is being considered; and
(c) invites any member of the family to make written submissions to the Commission, within 28 days, stating why the family’s registration should not be varied or cancelled.
(2) Within the 28 day period commencing on the day on which the notice was given, any member of the family may make such written submissions to the Commission.
(3) In deciding whether to vary or cancel the family’s registration, the Commission must have regard to any such written submissions made by any member of the family during that period.
(4) The Commission must give written notice of its decision, to a member of the family who is an adult, as soon as practicable after the decision is made.
Automatic variation or cancellation of registration as children turn 13
24.(1) This section applies if, on the basis of information given to it in applications made under this Division, the Commission is satisfied that a person who was a member of a registered family as a dependent child has since turned 13.
(2) The Commission must vary the registration accordingly if it is satisfied that there are still one or more dependent children in the family.
(3) The Commission must cancel the registration if it is satisfied that there are no longer any dependent children in the family.
(4) This section does not affect the Commission’s power to vary or cancel a family’s registration under section 20, 21 or 22.
PART 3—CLAIMING THE CHILDCARE REBATE
Outline of this Part
25.(1) This Part is about when registered families can claim the childcare rebate, and how claims are made.
(2) Division 1 is about the requirements relating to the provision of child care for dependent children of registered families.
(3) Division 2 is about the requirements of work, training or study commitments for parental members of registered families.
(4) Division 3 is about the process of claiming the childcare rebate.
Division 1— Child care
Child care requirements for the rebate
26. A family is not eligible for the childcare rebate in respect of a particular period unless:
(a) during some or all of the period, one or more members of the family who are dependent children received child care within the meaning of section 27; and
(b) the child care was provided by one or more registered carers; and
(c) one of the parental members of the family paid for the child care.
Definition of child care
27.(1) Child care is care of a child that is provided:
(a) at the child’s home; or
(b) at the home of a registered carer who is providing the care; or
(c) at a child care centre within the meaning of section 4A of the Child Care Act 1972; or
(d) at premises at which a child care service referred to in subsection (2) is provided.
(2) Paragraph (1)(d) applies to:
(a) a child care service for the operation of which the Commonwealth provides financial assistance (either directly or by payments to a State or Territory); and
(b) a child care service for the operation of which a State or Territory provides financial assistance, other than a service of a kind that the Minister determines not to be a service to which paragraph (1)(d) applies; and
(c) a child care service of a kind that the Minister determines to be a child care service to which paragraph (1)(d) applies.
(3) Determinations under paragraphs (2)(b) and (c) are disallowable instruments for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
(4) Child care provided outside Australia is not taken to be child care for the purposes of this Act.
Division 2—Work, training or study commitments
Work, training or study requirements for the rebate
28. A family is not eligible for the childcare rebate in respect of a particular period unless, during the whole of that period, each parental member of the family is a person to whom one or more of the following applies:
(a) the person has recognised work or work related commitments within the meaning of section 29;
(b) the person has recognised training commitments within the meaning of section 30;
(c) the person has recognised study commitments within the meaning of section 31.
Recognised work or work related commitments
29.(1) A person has recognised work or work related commitments if the person:
(a) is in paid work (whether or not the person performs the work as an employee); or
(b) receives a carer pension under Part 2.5 of the Social Security Act 1991; or
(c) receives domiciliary nursing care benefit under Part VB of the National Health Act 1953; or
(d) is registered with the Commonwealth Employment Service in an allowance category as being unemployed.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(d), a person is registered in an allowance category if the person is registered in a category approved under subsection 23(4A) of the Social Security Act 1991 for the purposes of Parts 2.11 and 2.12 of that Act as being unemployed.
Note: The Commonwealth Employment Service registers the unemployed in various categories. The categories relevant here are the categories that are relevant for the purposes of receiving a job search allowance or a newstart allowance under the Social Security Act 1991.
Recognised training commitments
30. A person has recognised training commitments if the person is undertaking a training course for the purpose of improving his or her work skills and/or employment prospects.
Recognised study commitments
31. A person has recognised study commitments if the person:
(a) receives assistance under the Student Assistance Act 1973 by way of a benefit under the AUSTUDY scheme; or
(b) receives assistance under the scheme administered by the Department of Employment, Education and Training and known as the ABSTUDY scheme; or
(c) is enrolled in an Adult Migrant English Program administered by the Department of Immigration and Ethnic Affairs; or
(d) is undertaking any other course of education for the purpose of improving his or her work skills and/or employment prospects.
Division 3—Claims
Claims for payment of the rebate
32.(1) A parental member of a registered family may lodge with the Commission a claim for childcare rebate in respect of amounts that any parental member of the family has paid to one or more registered carers for providing child care to dependent children who are members of the family.
(2) The claim may relate to expenses incurred in respect of a period of one or more weeks.
(3) The claim must not relate to child care in respect of which the childcare rebate is not payable because of section 36.
(4) The claim must be in writing and must be in the approved form.
Information etc. to be provided in claims
33.(1) The claim must specify:
(a) the name of each dependent child who was provided with the child care to which the claim relates; and
(b) the Family Registration Number of the family to which the claimant and the child or children belong; and
(c) the Child Care Provider Number of each registered carer who provided the child care; and
(d) the period during which the child care was provided; and
(e) the amounts paid to registered carers for the child care; and
(f) such other information as is specified in the approved form for the claim.
(2) The claim must be accompanied by such other documents as are specified in the approved form for the claim.
(3) The amounts specified in the claim as amounts paid to registered carers for the child care must not include any amounts of fee relief that have not yet been deducted from the amounts so paid.
Receipts
34.(1) The claim must be accompanied by receipts that were given to the claimant by or on behalf of the registered carers who provided the child care to which the claim relates.
(2) Each receipt must be signed by:
(a) the registered carer who provided the child care to which the receipt relates; or
(b) a person duly authorised by that registered carer to sign such receipts.
(3) Each receipt must state:
(a) the name of the child or children to whom was provided the child care to which the receipt relates; and
(b) the period during which the child care was provided; and
(c) the registered carer’s Child Care Provider Number; and
(d) the registered carer’s name and address, and telephone number (if any); and
(e) the amount paid for the child care; and
(f) the name of the person who paid the amount.
(4) This section does not limit the scope of subsection 33(2).
PART 4—PAYMENT OF THE CHILDCARE REBATE
Division 1—Determining whether the rebate is payable
Note: Decisions on whether the rebate is payable in respect of claims are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Claims in respect of which the rebate is payable
35. Subject to section 36, childcare rebate is payable in respect of a claim if and only if:
(a) the claimant, and each child specified in the claim as required under paragraph 33(1)(a), are members of the same registered family; and
(b) the claim complies with the requirements of section 33; and
(c) the information provided under Division 3 of Part 3 in relation to the claim is correct.
Claims in respect of which the rebate is not payable
36. Childcare rebate is not payable in respect of a claim if:
(a) the claim relates to child care that has not yet been provided; or
(b) the claim relates to child care provided more than 2 years before the claim was lodged; or
(c) the claim relates to child care provided by a registered carer to dependent children of the registered carer; or
(d) the claimant, or another person who is a member of the same family as the claimant, has made another claim for payment of the rebate in relation to child care provided, to a child specified in the claim, at one or more times that overlap with one or more of the times at which child care to which the claim relates was provided; or
(e) in none of the weeks during which the child care to which the claim relates was provided did the claimant’s weekly child care expenditure exceed the minimum weekly threshold; or
(f) all of the days on which the child care was provided occurred before 1 July 1994.
Note: Section 41 describes how the claimant’s weekly child care expenditure is worked out. For the minimum weekly threshold, see section 43.
Child care provided before 1 July 1994
37. Childcare rebate is not payable in respect of child care provided before 1 July 1994.
Children who are members of more than one family
38. If a child is a member of more than one family, this Division does not prevent parents of the child who are members of different families from claiming, in respect of the same week, childcare rebate for payments to registered carers for providing care to the child. However, the claims must not relate to provision of child care to the same child during the same hours on the same day.
Paying the rebate
39.(1) If childcare rebate is payable, the Managing Director must, on behalf of the Commonwealth, pay the claimant the amount worked out under Division 2 in respect of the claim.
(2) The amount is to be paid in the way determined by the Managing Director.
Division 2—The amount of the rebate
Note: Decisions about the amounts of childcare rebate payable, and decisions that no amount of childcare rebate is payable, are reviewable under Division 3 of Part 5.
Subdivision A—General
Overall calculation of the amount payable
40.(1) The amount of childcare rebate payable in respect of a claim is the amount equal to the sum of each of the amounts payable under Subdivision C in respect of a week to which the claim relates.
Note: Under Subdivision C, amounts of rebate are worked out for each week, based on each weekly child care expenditure worked out under Subdivision B. To work out the claimant’s entitlement, the Commission adds together all the amounts of rebate for the weeks covered by the claim.
(2) The amount is to be rounded upwards to the nearest 5 cents.
Subdivision B—Working out the weekly child care expenditure
Weekly child care expenditure
41.(1) A claimant’s weekly child care expenditure for a week during which child care to which a claim relates was provided is:
(a) if the child care was provided to only one dependent child—the amount of child care expenditure for the week worked out under subsections (2) and (3) in relation to the child; or
(b) if the child care was provided to more than one dependent child—the sum of the amounts of child care expenditure for the week worked out under subsections (2) and (3) in relation to each of the children.
(2) The amount of child care expenditure for the week in relation to a child is:
(a) if all of the child care to which the claim relates was provided in that week—the amount specified in the claim as the amount paid to one or more registered carers for providing the child care; or
(b) if it was provided in more than one week—the amount worked out using the formula in subsection (3).
(3) The formula is as follows:

where:
“Amount paid” is the amount specified in the claim as the amount paid to one or more registered carers for providing the child care;
“Total period of care” means the number of days in the period starting at the beginning of the first day on which that child care was provided and ending on the last day on which it was provided (whether or not the child care was provided on each of the days during the period);
“Period of care in the week” means the number of the days in that period that occurred during the week in question.
Expenditure covered by other claims
42. If the claimant, or another member of the claimant’s family, has previously made any other claims relating to child care provided during that week, the weekly child care expenditure worked out in respect of the claim referred to in section 41 is increased by adding to it all the amounts of weekly child care expenditure, for that week, worked out under section 41 in respect of all such other claims.
Subdivision C—Working out the amount of the rebate for a week
The minimum weekly threshold
43.(1) No amount of childcare rebate is payable to the claimant in respect of a week for which the claimant’s weekly child care expenditure did not exceed the minimum weekly threshold.
(2) The minimum weekly threshold is the amount equal to the lowest weekly fee that a child care centre (within the meaning of the Child Care Act 1972) may charge for providing to one child 50 hours of child care in respect of which the minimum amount of fee relief would be payable under the guidelines in force under section 12A of the Child Care Act 1972.
Note: The Health Insurance Commission can tell you what the current minimum weekly threshold is.
The maximum claimable amounts
44.(1) The claimant’s maximum claimable amount for a week is the amount specified in subsection (2) or (3) (whichever is applicable).
(2) The maximum claimable amount is the fee relief ceiling if the claimant paid amounts to one or more registered carers for providing child care during that week to only one dependent child of the claimant.
(3) The maximum claimable amount is twice the fee relief ceiling if the claimant paid amounts to one or more registered carers for providing child care during that week to more than one dependent child of the claimant.
(4) In this section:
“fee relief ceiling” means the lowest weekly fee that a child care centre (within the meaning of the Child Care Act 1972) may charge for providing 50 hours of child care in respect of which the maximum amount of fee relief would be payable under the guidelines in force under section 12A of the Child Care Act 1972.
Note: The Health Insurance Commission can tell you what the current fee relief ceiling is.
Claims up to the maximum claimable amount
45.(1) If the claimant’s weekly child care expenditure for a week exceeds the minimum weekly threshold and is less than the claimant’s maximum claimable amount for the week, the amount of childcare rebate payable on the claim in respect of that week is the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) If the claimant, or another member of the claimant’s family, has previously made any other claims relating to childcare provided during that week, the amount of childcare rebate that would otherwise have been payable under subsection (1) is reduced by the amounts of childcare rebate that have been paid, or are payable, in respect of such other claims.
Claims equal to or exceeding the maximum claimable amount
46.(1) If the claimant’s weekly child care expenditure for a week equals or exceeds the claimant’s maximum claimable amount for the week, the amount of childcare rebate payable on the claim in respect of that week is the amount worked out using the following formula:
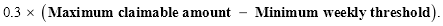
(2) If the claimant, or another member of the claimant’s family, has previously made any other claims relating to child care provided during that week, the amount of childcare rebate that would otherwise have been payable under subsection (1) is reduced by the amounts of childcare rebate that have been paid, or are payable, in respect of such other claims.
PART 5—ADMINISTRATION
Division 1—General
General administration of this Act
47. The Commission has the general administration of this Act.
Additional functions of the Commission
48.(1) In addition to the functions of the Commission under the Health Insurance Commission Act 1973, the Commission has such additional functions as are conferred on the Commission under this Act.
(2) Anything done by or on behalf of the Commission in the performance of such additional functions is taken, for all purposes, to have been done in the performance of its functions under the Health Insurance Commission Act 1973.
Division 2—Registered carers
Registration of carers
49.(1) A person or body may apply in writing to the Commission for registration as a carer.
(2) The application must be in the approved form.
(3) The Commission must register the applicant if and only if it is satisfied that the applicant is eligible for registration.
(4) If the Commission registers the applicant, it must:
(a) issue the applicant with a number to be known as the person’s Child Care Provider Number; and
(b) notify the applicant, in writing, of the number and the day on which the registration takes effect.
Note: Refusals to register carers are reviewable under Division 3.
Eligibility for registration
50.(1) Subject to subsection (2), an applicant is eligible for registration if:
(a) the applicant is providing, or intends within a reasonable time after making the application to provide, child care to children other than the applicant’s own dependent children; and
(b) provision of the child care complies, or (if the child care is not being provided at the time the application is made) will comply, with any requirements imposed on the provision of the child care by a law of the Commonwealth or a State or Territory relating to child care; and
(c) in the case of an individual—the applicant has turned 18; and
(d) in the case of a body corporate—the applicant’s powers extend to providing the child care that is being, or (if the child care is not being provided at the time the application is made) is intended to be provided.
(2) An applicant is not eligible for registration unless:
(a) the applicant has a tax file number; and
(b) the application contains a statement to that effect.
(3) The Commission must accept a statement made under paragraph (2)(b) unless the Commissioner of Taxation has informed the Commission that the applicant does not have a tax file number.
(4) This section does not authorise the Commission:
(a) to require or request a person to quote the person’s tax file number; or
(b) to seek or obtain, in any other way, a person’s tax file number; or
(c) to record a person’s tax file number.
Note: See sections 8WA and 8WB of the Taxation Administration Act 1953 concerning unauthorised activities relating to a person’s tax file number.
(5) The Commission may ask the Commissioner of Taxation to provide information on whether an applicant or a registered carer has a tax file number.
(6) The Commission must not, in asking the Commissioner of Taxation to provide such information, provide to the Commissioner of Taxation a registered carer’s Child Care Provider Number.
(7) Subsection (2) does not apply if the Commission is satisfied that the applicant is a body whose income is, under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936, exempt from income tax.
Cancellation of registration
51.(1) The Commission must cancel a registered carer’s registration if the registered carer requests the Commission in writing to do so.
(2) The Comission must cancel a registered carer’s registration if:
(a) it is satisfied that the registered carer is no longer eligible for registration; or
(b) on the basis of information it has received since the registration, it is satisfied that the registered carer was not eligible for registration at the time of registration.
(3) The Commission may cancel a registered carer’s registration if it is satisfied that the Commission was given incorrect or misleading information in connection with the registered carer’s application for registration.
Note: Cancellations of registration under subsection (2) or (3) are reviewable under Division 3.
Procedure for cancellation
52.(1) Before cancelling a registered carer’s registration under subsection 51(2) or (3), the Commission must give notice in writing to the person that:
(a) states that the Commission is considering cancelling the registered carer’s registration; and
(b) sets out the grounds on which cancellation is being considered; and
(c) invites the registered carer to make written submissions to the Commission, within 28 days, stating why his or her registration should not be cancelled.
(2) Within the 28 day period commencing on the day on which the notice was given, the registered carer may make such written submissions to the Commission.
(3) In deciding whether to cancel the registered carer’s registration, the Commission must have regard to any such written submissions the registered carer made during that period.
Division 3—Review of decisions
Decisions that may be subject to reconsideration by the Commission
53. An application may be made to the Commission for reconsideration of any of the following decisions:
(a) refusal to make a determination under section 16 that a person is taken to be an Australian resident;
(b) refusal to register a family under section 19;
(c) refusal to vary the registration of a family under section 20;
(d) variation of a family’s registration under section 21 without application from a member of the family;
(e) cancellation of a family’s registration under subsection 22(2) or (3);
(f) a decision under Part 4 that childcare rebate is not payable in respect of a claim;
(g) a decision under Division 2 of Part 4 as to the amount (if any) of childcare rebate payable in respect of a claim;
(h) refusal to register a person as a carer under section 49;
(i) cancellation of a person’s registration as a carer under subsection 51(2) or (3).
Deadline for reaching decisions
54.(1) If this Act provides for a person to apply to the Commission for a reviewable decision, the Commission must make the decision:
(a) within 28 days after receiving the application; or
(b) if the Commission has, within those 28 days, given the applicant a written request for further information about the application—within 28 days after receiving that further information.
(2) The Commission is taken, for the purposes of this Division, to have made a decision to refuse the application if it has not informed the applicant in writing of its decision before the end of the relevant period of 28 days.
(3) In this section:
“application” includes a claim.
Note: Section 27A of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 requires the decision-maker to notify persons whose interests are affected by the decision of the making of the decision and their right to have the decision reviewed. In so notifying, the decision-maker must have regard to the Code of Practice determined under section 27B of that Act.
Applications for reconsideration of decisions
55.(1) A person affected by a reviewable decision who is dissatisfied with the decision may apply to the Commission for the Commission to reconsider the decision.
(2) The application must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) set out the reasons for the application.
(3) The application must be made within:
(a) 28 days after the applicant is informed of the decision; or
(b) if, either before or after the expiration of that period of 28 days, the Commission extends the period within which the application may be made—the extended period for making the application.
(4) An approved form of application may provide for verification by statutory declaration of statements in applications.
Reconsideration by the Commission
56.(1) Upon receiving such an application, the Commission must:
(a) reconsider the decision; and
(b) affirm, vary or revoke the decision.
(2) If the Commission revokes a decision that was a decision refusing to do something, revocation is taken to be a decision to do that thing.
(3) The Commission’s decision on reconsideration of a decision has the effect as if it had been made under the application under which the original decision was made.
(4) The Commission must give to the applicant a notice stating its decision on the reconsideration together with a statement of its reasons for its decision.
Deadline for reconsiderations
57.(1) The Commission must make its decision on reconsideration of a decision within 28 days after receiving an application for reconsideration.
(2) The Commission is taken, for the purposes of this Division, to have made a decision confirming the original decision if it has not informed the applicant of its decision on the reconsideration before the expiration of the period of 28 days.
Note: Section 27A of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 requires the decision-maker to notify persons whose interests are affected by the decision of the making of the decision and their right to have the decision reviewed. In so notifying, the decision-maker must have regard to the Code of Practice determined under section 27B of that Act.
Review by the AAT
58. Applications may be made to the AAT for a review of a reviewable decision if the Commission has confirmed or varied the decision under section 56.
Division 4—False or misleading statements
References to making statements
59. A reference in this Division to making a statement includes a reference to issuing or presenting a document, and a reference to a statement is to be construed accordingly.
Knowingly making false or misleading statements
60.(1) A person must not make, or authorise the making of, a statement (whether oral or in writing) if the person knows that the statement is:
(a) false or misleading in a material particular; and
(b) capable of being used in connection with a claim or an application under this Act.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 6 months.
(2) If:
(a) a person makes a statement (whether oral or in writing) that is false or misleading in a material particular; and
(b) the statement is capable of being used in connection with a claim or an application under this Act; and
(c) the material particular in respect of which the statement is false or misleading is substantially based upon a statement made, either orally or in writing, to the person or to an agent of the person by another person who is an employee or agent of the first-mentioned person; and
(d) the other person knew that his or her statement was false or misleading in a material particular; and
(e) the other person knew, or had reasonable grounds to suspect, that his or her statement would be used in preparing a statement of the kind referred to in paragraph (b);
the other person is guilty of an offence.
Penalty: Imprisonment for 6 months.
(3) The reference in subsection (2) to an employee of a person is a reference, if the person is a corporation, to:
(a) a director, secretary, manager or employee of the corporation; or
(b) a receiver and manager of any part of the undertaking of the corporation appointed under a power contained in any instrument; or
(c) a liquidator of the corporation appointed in voluntary winding up.
Recovery of amounts paid because of false statements
61.(1) This section applies if, as a result of a false or misleading statement, an amount paid, purportedly by way of childcare rebate, exceeds the amount of childcare rebate (if any) that should have been paid.
(2) The amount of the excess is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from the person by or on behalf of whom the statement was made, or from the estate of that person.
(3) The amount is so recoverable whether or not it was paid to that person, and whether or not any person has been convicted of an offence relating to the statement.
(4) If the Managing Director of the Commission has served a notice on the person, or on the estate, claiming the excess as a debt due to the Commonwealth and:
(a) within the period referred to in subsection (6), an arrangement has been entered into between the Managing Director and the person or estate for the repayment of the excess, and there has been a default in payment of an amount required to be paid under the arrangement; or
(b) at the end of that period, such an arrangement has not been entered into and all or part of the excess remains unpaid;
then, from the day after the end of the period, interest at the rate specified in the regulations becomes payable on so much of the excess as from time to time remains unpaid.
(5) The interest so payable is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from the person or the person’s estate.
(6) The period for entering into an arrangement under paragraph (4)(a) is a period of 3 months following the service of the notice under subsection (4), or such longer period as the Managing Director allows.
(7) Despite subsections (4) and (5), in any proceedings instituted by the Commonwealth for the recovery of an amount due under subsection (5), the court may order that the interest payable under that subsection is, and is taken to have been, so payable from a day later than the day referred to in that subsection.
Offsetting overpayments against future payments of the rebate
62.(1) Despite section 61, if an amount paid to a person, purportedly by way of childcare rebate under this Act, exceeds the amount of childcare rebate (if any) that should have been paid to that person (the “excess amount”) the Managing Director may, if the person so agrees, reduce the amount of any childcare rebate that subsequently becomes payable to that person under this Act.
(2) The amount of any reduction must not exceed the amount by which the sum of the excess amount and any excess amounts previously paid to that person is greater than the sum of any amounts recovered by the Commission by one or more previous applications of section 61 or this section.
PART 6—MISCELLANEOUS
Appropriation
63. Payment of childcare rebate under this Act must be made out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund, which is appropriated accordingly.
Regulations
64. The Governor-General may make regulations prescribing matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed; or
(b) necessary or convenient for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
[Minister’s second reading speech made in—
House of Representatives on 29 September 1993
Senate on 26 October 1993]

