Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation
Act 1992
No. 234 of 1992
TABLE OF PROVISIONS |
PART 1—PRELIMINARY |
| Division 1—Short title and commencement |
Section | |
1. | Short title |
2. | Commencement |
| Division 2—Definitions |
3. | General definitions |
4. | Employees |
5. | Employees lost at sea |
6. | Injuries suffered by employees |
7. | Injuries etc. resulting from medical treatment |
8. | Incapacity for work |
9. | Injury arising out of, or in the course of, employment |
10. | Provisions relating to diseases |
11. | Hearing impairment—time when suffered |
12. | Serious and wilful misconduct |
13. | Normal weekly earnings |
14. | Recovery of damages |
15. | Persons who are wholly or partly dependent |
16. | Ex-nuptial and adoptive relationships |
17. | Persons caring for prescribed children |
| Division 3—Miscellaneous preliminary provisions |
18. | Extent of Act |
19. | Application of Act |
TABLE OF PROVISIONS—continued
Section | |
20. | Act not to apply to CERC Act employees |
21. | Act binds Crown etc. |
22. | Amounts of compensation |
23. | Indexation |
24. | Liability to pay compensation |
25. | Compensation to be paid in full |
| PART 2—COMPENSATION |
| Division 1—Injuries, property loss or damage, medical expenses |
26. | Compensation for injuries |
27. | Compensation for property loss or damage |
28. | Compensation for medical and related expenses |
| Division 2—Injuries resulting in death |
29. | Compensation for injuries resulting in death |
30. | Compensation in respect of funeral expenses |
| Division 3—Injuries resulting in incapacity for work |
31. | Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity |
32. | Determination of suitable employment |
33. | Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee is in receipt of a superannuation pension |
34. | Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee is in receipt of a lump sum benefit |
35. | Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee rolled-over part of a lump sum benefit |
36. | Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where the employee rolled-over the whole of a lump sum benefit |
37. | Compensation where employee is maintained in a hospital |
38. | Compensation for incapacity not payable in certain cases |
| Division 4—Injuries resulting in permanent impairment |
39. | Compensation for injuries resulting in permanent impairment |
40. | Interim payment of compensation |
41. | Compensation for non-economic loss |
42. | Approved Guide |
| Division 5—Household and attendant care services |
43. | Compensation for household services and attendant care services |
| Division 6—Miscellaneous |
44. | Redemption of compensation |
45. | Recurrent payments after payment of lump sum |
46. | Cancelled determinations not to affect certain payments of compensation |
47. | Reduction of compensation in certain cases |
| PART 3—REHABILITATION |
48. | Approved rehabilitation program providers |
49. | Assessment of capability of undertaking rehabilitation program |
50. | Provision of rehabilitation programs |
51. | Compensation payable in respect of certain alterations etc. |
52. | Duty to provide suitable employment |
TABLE OF PROVISIONS—continued
Section | |
| PART 4—LIABILITIES ARISING APART FROM THIS ACT |
53. | Interpretation |
54. | Employee not to have right to bring action for damages against employer etc. in certain cases |
55. | Actions for damages—election by employees |
56. | Notice of proceedings against third party |
57. | Notice of proceedings against employer |
58. | Compensation not payable if damages recovered |
59. | Proceedings against third parties |
60. | Payment of damages by persons to employer |
61. | Compensation not payable both under Act and under award |
| PART 5—NOTICES AND CLAIMS |
62. | Notice of injury or loss of, or damage to, property |
63. | Claims for compensation |
64. | Survival of claims |
65. | Claims may not be made in certain cases |
66. | Power to require medical examination |
67. | Power to request the provision of information relevant to claim |
68. | Certain documents to be supplied on request |
69. | Neither section 67 nor 68 to affect legal professional privilege |
70. | Legal professional privilege not to apply to medical reports |
71. | Bankruptcy etc. of actual employer |
72. | Time limit for determining claims relating to the death of an employee |
73. | Time limit for determining liability for claims relating to injuries to employees other than injuries resulting in death |
74. | Employer may seek review of Authority’s decision |
75. | Sections 72 to 74 (inclusive) not to apply to Authority if declaration made under section 100 |
| PART 6—RECONSIDERATION OF DETERMINATIONS AND REVIEW OF DECISIONS BY THE ADMINISTRATIVE APPEALS TRIBUNAL |
| Division 1—Definitions |
76. | Interpretation |
| Division 2—Reconsideration of determinations by employers |
77. | Determinations to be notified in writing |
78. | Reconsiderations of determinations |
79. | Time limit for reconsideration of determinations |
80. | Employer may seek review of Authority’s decision |
81. | Sections 79 and 80 not to apply to Authority if declaration made under section 100 |
82. | Industry panel or Comcare to give copy of report to employer to claimant |
83. | Power to request the provision of information relevant to reconsideration |
84. | Section 83 not to affect legal professional privilege |
85. | Legal professional privilege not to apply to medical reports |
86. | Bankruptcy etc. of employer |
87. | Reviewable decision to be notified in writing |
88. | Applications to the AAT |
| Division 3—AAT review of reviewable decisions and extension of time decisions |
89. | Modified AAT Act to apply |
90. | Evidence in proceedings before AAT |
91. | Costs of proceedings before AAT—general |
92. | Costs of proceedings before AAT—when costs payable by employer |
TABLE OF PROVISIONS—continued
Section | |
| PART 7—COMPULSORY INSURANCE AND THE FUND |
| Division 1—Compulsory insurance |
93. | Compulsory insurance |
94. | Employer to give details of insurance or indemnity arrangements to Authority |
95. | Authority may require evidence from employer |
| Division 2—The Fund |
96. | The Fund |
97. | Fund to insure |
98. | Fund to provide Authority with financial information |
99. | Minister may revoke approval under section 96 |
| Division 3—Reserve function of Authority |
100. | Ministerial declaration |
101. | Effect of Ministerial declaration |
102. | Authority to insure if declaration made under section 100 |
| PART 8—ADMINISTRATION AND FINANCE |
| Division 1—Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation Authority |
103. | Establishment |
104. | Functions |
105. | Powers |
106. | Power to obtain information |
107. | Directions by Minister |
| Division 2—Constitution and Meetings of Authority |
108. | Authority is body corporate |
109. | Constitution |
110. | Appointment of members |
111. | Term of office |
112. | Deputies of members |
113. | Persons acting as Chairperson or Deputy Chairperson |
114. | Remuneration and allowances |
115. | Leave of absence |
116. | Disclosure of interests |
117. | Resignation |
118. | Termination of appointment |
119. | Meetings |
| Division 3—Finance |
120. | Application of Division 3 of Part XI of the Audit Act |
121. | Money of Authority |
122. | Estimates of receipts and expenditure |
123. | Exemption from taxation |
124. | Borrowings |
| Division 4—Miscellaneous |
125. | Delegation by Authority |
TABLE OF PROVISIONS—continued
Section | |
| PART 9—MISCELLANEOUS |
126. | Employee to give information about prior employers |
127. | Determinations to be in writing |
128. | Shared liability |
129. | Subrogation of rights of actual employer to Fund |
130. | Payment of compensation |
131. | Employee to notify other employers that compensation has been paid |
132. | Recovery of compensation payments |
133. | Money paid for benefit of person |
134. | Provisions applicable on death of beneficiary |
135. | Assignment, set-off or attachment of compensation |
136. | Recovery of overpayments |
137. | Employees on compensation leave |
138. | Double benefits |
139. | Compensation where State compensation payable |
140. | Notice of departure from Australia etc. |
141. | Comcare may charge for officer’s services provided to employer |
142. | Disallowable instruments |
143. | Regulations |

Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation
Act 1992
No. 234 of 1992

 An Act relating to rehabilitation and workers’ compensation for seafarers and certain other persons, and for related purposes
An Act relating to rehabilitation and workers’ compensation for seafarers and certain other persons, and for related purposes
[Assented to 24 December 1992]
The Parliament of Australia enacts:
PART 1—PRELIMINARY
Division 1—Short title and commencement
Short title
1. This Act may be cited as the Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1992.
Commencement
2.(1) Sections 1, 2 and 3 and Part 8 commence on the day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the remaining provisions of this Act commence on a day or days to be fixed by Proclamation.
(3) If a provision referred to in subsection (2) does not commence within the period of 6 months beginning on the day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent, it commences on the first day after the end of that period.
Division 2—Definitions
General definitions
3. In this Act, unless the contrary intention appears:
“adoption” means adoption under a law of a State or Territory or of a foreign country;
“aggravation” includes acceleration or recurrence;
“ailment” means any physical or mental ailment, disorder, defect or morbid condition (whether of sudden onset or gradual development);
“approved Guide” means:
(a) the document, prepared by the Authority in accordance with section 42 under the title ‘Guide to the Assessment of the Degree of Permanent Impairment’, that has been approved by the Minister and is for the time being in force; and
(b) if an instrument varying the document has been approved by the Minister—that document as so varied;
“approved industry training course” means an industry training course approved in writing by the Authority for the purposes of this definition;
“approved program provider” has the meaning given by section 48;
“attendant care services”, in relation to an employee, means services (other than household services, medical or surgical services or nursing care) required for the essential and regular personal care of the employee;
“Authority” means the Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation Authority established by section 103;
“CERC Act” means the Commonwealth Employees’ Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988;
“certified agreement” has the same meaning as in the Industrial Relations Act 1988;
“Chairperson” means the Chairperson of the Authority;
“claim” means a claim under Part 5;
“claimant”, in relation to a time after the death of a claimant, means the claimant’s legal personal representative;
“Comcare” has the same meaning as in the CERC Act;
“Comcare officer” means a person referred to in subsection 88(1) of the CERC Act;
“compensation leave” means any period during which an employee is absent from his or her employment due to an incapacity for work resulting from an injury in respect of which compensation is payable under section 31 or 37;
“damages” includes any amount paid under a compromise or settlement of a claim for damages, whether or not legal proceedings have been instituted, but does not include an amount paid in respect of costs incurred in connection with legal proceedings;
“default event”, in relation to an employer, happens when:
(a) the employer:
(i) becomes bankrupt or insolvent; or
(ii) applies to take the benefit of any law for the relief of insolvents; or
(iii) compounds with the employer’s creditors for their benefit; or
(iv) if the employer is a body corporate—is being wound-up; or
(v) if the employer is a body corporate—ceases to exist; or
(vi) no longer engages in trade or commerce in Australia; and
(b) the employer is unable to meet the employer’s liabilities under this Act;
“dependant”, in relation to a deceased employee, means a person:
(a) who is the spouse of the employee; or
(b) who is the father, mother, step-father, step-mother, father-in-law, mother-in-law, grandfather, grandmother, son, daughter, step-son, step-daughter, grandson, grand-daughter, brother, sister, half-brother or half-sister of the employee; or
(c) in relation to whom the employee stood in the position of a parent or who stood in the position of a parent to the employee;
being a person who was wholly or partly dependent on the employee at the date of the employee’s death;
Note: see also section 16.
“dependent” means dependent for economic support;
“disease” means:
(a) any ailment suffered by an employee; or
(b) the aggravation of any such ailment;
being an ailment or an aggravation that was contributed to in a material degree by the employee’s employment;
“employee” has the meaning given in section 4;
“financial corporation” means a financial corporation within the meaning of paragraph 51(xx) of the Constitution;
“foreign corporation” means a foreign corporation within the meaning of paragraph 51(xx) of the Constitution and includes a body that is incorporated in an external Territory;
“Fund” has the meaning given in section 96;
“Government ship” means a ship:
(a) that belongs to the Commonwealth or a State or Territory; or
(b) the beneficial interest in which is vested in the Commonwealth or a State or Territory; or
(c) that is for the time being demised or sub-demised to, or in the exclusive possession of, the Commonwealth or a State or Territory;
and includes a ship that belongs to an arm of the Defence Force, but does not include a ship:
(d) that belongs to a trading corporation that is an authority or agency of the Commonwealth or of a State or a Territory; or
(e) the beneficial interest in which is vested in such a trading corporation; or
(f) that is for the time being demised or sub-demised to, or in the exclusive possession of, such a trading corporation; or
(g) that is operated by seafarers supplied (directly or indirectly) by a corporation under a contract with the Commonwealth or a State or Territory;
“household services”, in relation to an employee, means services of a domestic nature (including cooking, house cleaning, laundry and gardening services) required for the proper running and maintenance of the employee’s household;
“impairment” means the loss, the loss of the use, or the damage or malfunction, of any part of the body or of the whole or part of any bodily system or function;
“injury” means:
(a) a disease; or
(b) an injury (other than a disease) suffered by an employee, being a physical or mental injury arising out of, or in the course of, the employee’s employment; or
(c) an aggravation of a physical or mental injury (other than a disease) suffered by an employee (whether or not that injury arose out of, or in the course of, the employee’s employment), being an aggravation that arose out of, or in the course of, that employment;
but does not include anything suffered by an employee as a result of reasonable disciplinary action taken against the employee, or failure by the employee to obtain a promotion, transfer or benefit in connection with his or her employment;
“loss”, in relation to property used by an employee, includes destruction;
“medical treatment” means:
(a) medical or surgical treatment by, or under the supervision of, a legally qualified medical practitioner; or
(b) therapeutic treatment obtained at the direction of a legally qualified medical practitioner; or
(c) dental treatment by, or under the supervision of, a legally qualified dentist; or
(d) therapeutic treatment by, or under the supervision of, a physiotherapist, osteopath, masseur or chiropractor registered as such under the law of a State or Territory; or
(e) an examination, test or analysis carried out at the request or direction of a legally qualified medical practitioner or dentist, and the provision of a report in respect of it; or
(f) the supply, replacement or repair of an artificial limb or other artificial substitute or of a medical, surgical or other similar aid or appliance; or
(g) treatment and maintenance as a patient at a hospital; or
(h) nursing care, and the provision of medicines, medical and surgical supplies and curative apparatus, whether in a hospital or not;
“member” means a member of the Authority;
“Navigation Act” means the Navigation Act 1912;
“non-economic loss”, in relation to an employee who has suffered an injury resulting in a permanent impairment, means loss or damage of a non-economic kind suffered by the employee (including pain and suffering, a loss of expectation of life or a loss of the amenities or enjoyment of life) as a result of that injury or impairment and of which the employee is aware;
“normal weekly earnings” means the normal weekly earnings of an employee worked out under section 13;
“permanent” means likely to continue indefinitely;
“place of residence”, in relation to an employee, means:
(a) the place in Australia where the employee normally resides; or
(b) a place in Australia, other than the place mentioned in paragraph (a), where the employee resides temporarily, as a matter of necessity or convenience, for the purposes of his or her employment; or
(c) any other place in Australia where the employee stays, or intends to stay, overnight, if a journey to it from the employee’s place of work does not substantially increase the risk of sustaining an injury when compared with the journey from his or her place of work to the place referred to in paragraph (a) or (b);
“place of work”, in relation to an employee, means any place at which the employee is required to attend for the purpose of carrying out the duties of his or her employment and:
(a) if the employee is a seafarer—includes the prescribed ship on which the seafarer is employed or engaged; and
(b) if the employee is a trainee—includes a ship on which the trainee is required to train as part of an approved industry training course;
“prescribed child” means:
(a) a person under 16; or
(b) a person who:
(i) is 16 or over but under 25; and
(ii) is receiving full-time education at a school, college, university or other educational institution; and
(iii) is not ordinarily in employment or engaged in work on his or her own account;
“prescribed person”, in relation to an employee, means:
(a) the spouse of the employee; or
(b) any of the following who is 16 or over:
(i) the father, mother, step-father, step-mother, father-in-law, mother-in-law, grandfather, grandmother, son, daughter, step-son, step-daughter, grandson, granddaughter, brother, sister, half-brother or half-sister of the employee;
(ii) a person in relation to whom the employee stands in the position of a parent or who stands in the position of a parent to the employee;
(iii) a person (other than the spouse of the employee or a person referred to in subparagraph (i) or (ii)) who is wholly or mainly dependent on the employee and has the care of a prescribed child who is wholly or mainly dependent on the employee;
Note: see also sections 16 and 17.
“prescribed ship” means:
(a) a ship to which Part II of the Navigation Act applies; or
(b) an off-shore industry vessel in relation to which a declaration under subsection 8A(2) of that Act is in force; or
(c) a trading ship in relation to which a declaration under subsection 8AA(2) of that Act is in force;
but does not include a Government ship;
“property used by an employee” means an artificial limb or other artificial substitute, or a medical, surgical or other similar aid or appliance, used by the employee;
“rehabilitation program” includes medical, dental, psychiatric and hospital services (whether on an in-patient or out-patient basis), physical training and exercise, physiotherapy, occupational therapy and vocational training;
“seafarer” means a person employed in any capacity on a prescribed ship, on the business of the ship, other than:
(a) a pilot; or
(b) a person temporarily employed on the ship in port; or
(c) a person included in the class of persons defined as “special personnel” in section 283 of the Navigation Act;
“seafarer berth” means a berth on a prescribed ship that is normally used by a seafarer;
“spouse” includes:
(a) in relation to an employee or a deceased employee—a person of the opposite sex to the employee who lives with, or immediately before the date of the employee’s death lived with, the employee as the spouse of the employee on a genuine domestic basis although not legally married to the employee; and
(b) in relation to an employee or a deceased employee who is or was a member of the Aboriginal race of Australia or a descendant of indigenous inhabitants of the Torres Strait Islands—a person who is or was recognised as the employee’s husband or wife by the custom prevailing in the tribe or group to which the employee belongs or belonged;
“suitable employment”, in relation to an employee who has suffered an injury in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act, means any employment (including self-employment) for which the employee is suited having regard to:
(a) the employee’s age, experience, training, language and other skills; and
(b) the employee’s suitability for rehabilitation or vocational retraining; and
(c) if employment is available in a place that would require the employee to change his or her place of residence—whether it is reasonable to expect the employee to change his or her place of residence; and
(d) any other relevant matter;
“superannuation amount”, in relation to a pension received by an employee in respect of a week, or a lump sum benefit received by an employee, being a pension or benefit under a superannuation scheme, means an amount equal to:
(a) if the scheme identifies a part of the pension or lump sum as attributable to the contributions made under the scheme by the
employee’s employer or any former employer—the amount of that part; or
(b) in any other case—the amount assessed by the person administering the superannuation scheme to be the part of the pension or lump sum that is so attributable;
“superannuation scheme” means any superannuation scheme or superannuation fund under which an employer makes contributions on behalf of his or her employees;
“therapeutic treatment” includes:
(a) an examination, test or analysis done for the purpose of diagnosing an injury; and
(b) treatment given for the purpose of alleviating an injury;
“trading corporation” means a trading corporation within the meaning of paragraph 51(xx) of the Constitution;
“trainee” means a person who:
(a) although ordinarily employed or engaged as a seafarer, is not so employed or engaged but is undergoing an approved industry training course; or
(b) is undergoing an approved industry training course before becoming a seafarer.
Employees
4.(1) In this Act, unless the contrary intention appears:
“employee” means:
(a) a seafarer; or
(b) a trainee; or
(c) a person who, although ordinarily employed or engaged as a seafarer, is not so employed or engaged but is required under an award to attend at a Seafarers Engagement Centre for the purpose of registering availability for employment or engagement on a prescribed ship.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, an employee who is not a seafarer is taken to be employed by the Fund until he or she next becomes a seafarer, and his or her employment is taken to be constituted by his or her attendance:
(a) at an approved industry training course; or
(b) at a Seafarers Engagement Centre for the purpose of registering availability for employment or engagement on a prescribed ship.
(3) If a default event occurs in relation to the employer of a seafarer, then, for the purposes of this Act, the seafarer is taken to be employed by the Fund.
(4) If a provision of this Act applies to an employee after an employer has incurred a liability in relation to the employee under this
Act, then, unless the contrary intention appears, a reference in that provision to an employee includes a reference to that person even after he or she ceases to be an employee.
Employees lost at sea
5.(1) In a claim for compensation under section 29, if it is established that a prescribed ship has not been heard of for at least 3 months the ship is taken to have been lost with all on board immediately after the ship was last heard of.
(2) A copy of:
(a) an agreement; or
(b) a list of the employees on a prescribed ship; or
(c) another document showing changes in the employees on a prescribed ship;
which has been prepared for a legal purpose is, in the absence of proof to the contrary, sufficient proof that the employees named in the document were on board the prescribed ship at the time of the loss.
Injuries suffered by employees
6. A reference in this Act to an injury suffered by an employee is, unless the contrary intention appears, a reference to an injury suffered by the employee for which compensation is payable under this Act.
Injuries etc. resulting from medical treatment
7. For the purposes of this Act, an injury or ailment suffered by an employee as a result of medical treatment of an injury is taken to be an injury if, but only if:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act for the injury that was treated; and
(b) it was reasonable for the employee to have obtained that treatment in the circumstances.
Incapacity for work
8. A reference in this Act to an incapacity for work is a reference to an incapacity suffered by an employee as a result of an injury, being:
(a) an incapacity to engage in any work; or
(b) an incapacity to engage in work as an employee at the same rank or level at which he or she was engaged immediately before the injury happened.
Injury arising out of, or in the course of, employment
9.(1) This section does not limit the circumstances in which an injury to an employee may be treated as having arisen out of, or in the course of, his or her employment.
(2) An injury is also to be treated as having so arisen, for the purposes of this Act, if it happened:
(a) as a result of an act of violence that would not have occurred apart from the employment, or the performance by the employee of the duties or functions of his or her employment; or
(b) if the employee is a seafarer:
(i) while the employee was on board the prescribed ship on which he or she was employed or engaged; or
(ii) while the employee was temporarily absent from that ship during an ordinary recess in that employment and not at his or her place of residence; or
(c) if the employee is a trainee—while the trainee was undergoing a prescribed course of training, or was in any other place (other than his or her place of residence) during an ordinary recess in that course of training; or
(d) while the employee was attending at a Seafarers Engagement Centre for the purpose of registering availability for employment or engagement on a prescribed ship; or
(e) while the employee:
(i) was travelling between his or her place of residence and place of work; or
(ii) was travelling between his or her place of residence and a place, where he or she resides temporarily, as a matter of necessity or convenience for the purposes of his or her employment; or
(iii) was travelling between his or her place of residence and a Seafarers Engagement Centre for the purpose of registering availability for employment or engagement on a prescribed ship; or
(iv) was travelling between one of his or her places of work and another of his or her places of work; or
(v) was travelling between his or her place of work or place of residence and a place where an approved industry training course was being conducted; or
(vi) was travelling between his or her place of work or place of residence and any other place for the purpose of:
(A) obtaining a medical certificate for the purposes of this Act; or
(B) receiving medical treatment for an injury; or
(C) undergoing a rehabilitation program provided under this Act; or
(D) receiving a payment of compensation under this Act; or
(E) undergoing a medical examination or rehabilitation assessment in accordance with a requirement made under this Act; or
(F) receiving money due under the terms of his or her
employment, being money that, under the terms of that employment or any agreement or arrangement between the employee and his or her employer, was available, or reasonably expected by the employee to be available, for collection at that place; or
(vii) was at a place for a purpose referred to in subparagraph (vi).
(3) Subparagraph (1)(e)(i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) or (vi) does not apply if the travel:
(a) was by a route that substantially increased the risk of sustaining an injury when compared with a more direct route; or
(b) was interrupted in a way that substantially increased the risk of sustaining an injury.
(4) Subsection (1) does not apply if an employee is injured:
(a) while at a place referred to in that subsection; or
(b) during an ordinary recess in his or her employment; because he or she voluntarily and unreasonably submitted to an abnormal risk of injury.
Provisions relating to diseases
10.(1) If:
(a) an employee has suffered, or is suffering, from a disease, or the death of an employee results from a disease; and
(b) the disease is of a kind specified by the Minister, by written notice, as a disease related to employment of a kind specified in the notice; and
(c) the employee was, at any time before symptoms of the disease first became apparent, engaged in employment of that kind in the maritime industry;
the employment in which the employee was so engaged is taken, for the purposes of this Act, to have contributed in a material degree to the contraction of the disease, unless the contrary is established.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee contracts a disease, any employment in the maritime industry in which he or she was engaged at any time before symptoms of the disease first became apparent is taken, unless the contrary is established, to have contributed in a material degree to the contraction of the disease if the incidence of the disease among people who have engaged in such employment is significantly greater than it is among people who have engaged in other employment.
(3) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee suffers an aggravation of a disease, any employment in the maritime industry in which he or she was engaged at any time before symptoms of the
aggravation first became apparent is taken, unless the contrary is established, to have contributed in a material degree to the aggravation if the incidence of the aggravation of the disease among people suffering from it who have engaged in such employment is significantly greater than it is among people suffering from the disease who have engaged in other employment.
(4) If:
(a) an employee suffers an injury (other than one resulting in a hearing impairment); and
(b) the injury is a disease or an aggravation of a disease;
the employee is taken, for the purposes of this Act, to have suffered the injury on the day when:
(c) the employee first sought medical treatment for the disease or aggravation; or
(d) the disease or aggravation resulted in the death of the employee or first resulted in his or her impairment or incapacity for work;
whichever happens first.
(5) For the purposes of this Act, the death of an employee is taken to have resulted from a disease, or an aggravation of a disease, if, apart from that disease or aggravation, as the case may be, the death of the employee would have happened at a significantly later time.
(6) For the purposes of this Act, an incapacity for work, or an impairment, of an employee is taken to have resulted from a disease, or an aggravation of a disease, if, apart from that disease or aggravation, as the case may be:
(a) the incapacity or impairment would not have occurred; or
(b) the incapacity would have started, or the impairment would have happened, at a significantly later time; or
(c) the extent of the incapacity or impairment would have been significantly less.
(7) For the purposes of this Act, a disease suffered by an employee, or an aggravation of such a disease, is not taken to be an injury to the employee if the employee has at any time, for purposes connected with his or her employment or proposed employment in the maritime industry, made a wilful and false representation that he or she did not suffer, or had not previously suffered, from that disease.
Hearing impairment—time when suffered
11. If an employee suffers a hearing impairment as a result of an injury, the employee is taken, for the purposes of this Act, to suffer the injury on the day on which the employee gives a notice of the injury under section 62.
Serious and wilful misconduct
12. For the purposes of this Act, an employee who is under the influence of alcohol or a drug (other than a drug prescribed for the employee by a legally qualified medical practitioner or dentist and used by the employee in accordance with that prescription) is taken to have engaged in serious and wilful misconduct.
Normal weekly earnings
13.(1) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee who is a seafarer suffers an injury, the employee’s normal weekly earnings are an amount equal to the amount payable weekly to the employee by way of salary under the contract of employment that applied to his or her employment immediately before the injury happened.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee who is a trainee suffers an injury, the employee’s normal weekly earnings are an amount equal to the amount that would have been payable weekly to the employee by way of salary under the award, determination or certified agreement that, apart from the injury, would have applied to his or her employment immediately after the completion of the training course.
(3) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee who is attending a Seafarers Engagement Centre suffers an injury, the employee’s normal weekly earnings are an amount equal to the amount specified in a certified agreement for the purposes of this subsection.
(4) For the purposes of this Act, if an employee (other than an employee to whom subsection (1), (2) or (3) applies) suffers an injury, the employee’s normal weekly earnings are an amount equal to the amount that was payable weekly to the employee by way of salary under the contract of employment that applied to his or her employment immediately before the injury happened.
(5) If the amount per week payable to an employee in respect of his or her employment before the injury is increased, or would have been increased, because of the operation of an award, determination, industrial agreement or contract of employment if the employee had continued in that employment, because the employee:
(a) reaches a particular age; or
(b) completes a particular period of service; or
(c) receives an increase in salary, by way of an increment in a range of salary that applies to the employee;
the normal weekly earnings of the employee before the injury, as worked out under the preceding subsections, must be increased by the same percentage as that by which that amount per week is increased or would have been increased, as the case may be.
(6) If the amount per week payable to employees in a class to which the employee belonged when the injury happened is later increased or reduced as a result of:
(a) the operation of a law of the Commonwealth, or of a State or Territory; or
(b) the making, alteration or operation of an award, determination or industrial agreement, or the doing of any other act or thing under such a law;
the normal weekly earnings of the employee before the injury, as worked out under the preceding subsections, must be increased or reduced by the same percentage as that by which that amount per week was so increased or reduced, as the case may be.
Recovery of damages
14. For the purposes of this Act, damages are taken to have been recovered by an employee, or by or for the benefit of a dependant of a deceased employee, when the amount of the damages was paid to, or for the benefit of, the employee or dependant, as the case may be.
Persons who are wholly or partly dependent
15.(1) For the purposes of this Act, a person is taken to have been wholly or partly dependent on an employee at the date of the employee’s death if the person would have been so dependent apart from an incapacity of the employee that resulted from an injury.
(2) For the purposes of this Act, a person who, immediately before the date of an employee’s death, lived with the employee and was:
(a) the employee’s spouse; or
(b) a prescribed child of the employee;
is taken to be a person who was wholly dependent on the employee at that date.
(3) For the purposes of this Act, other than subsection 29(5), a son or daughter of a deceased employee who was born alive after the employee’s death must be treated as if he or she had been born immediately before the employee’s death and was wholly dependent on the employee at the date of the employee’s death.
(4) In determining, for the purposes of this Act, whether a child is or was dependent on an employee, the following are not to be taken into account:
(a) an amount of allowance under Part 2.17, 2.18 or 2.19 of the Social Security Act 1991; or
(b) an amount of pension under Part 2.20 of that Act.
Ex-nuptial and adoptive relationships
16. Relationships mentioned in:
(a) paragraph (b) of the definition of “dependant” in section 3; or
(b) subparagraph (b)(i) of the definition of “prescribed person” in that section;
are, for the purposes of this Act, taken to include:
(c) ex-nuptial relationships; and
(d) relationships by adoption; and
(e) relationships traced through ex-nuptial relationships or relationships by adoption.
Persons caring for prescribed children
17. For the purposes of the definition of “prescribed person” in section 3, a person who has the care of a child referred to in subparagraph (b)(iii) of that definition must not be treated as not wholly or mainly maintained by the relevant employee merely because the employee pays the person remuneration for caring for the child.
Division 3—Miscellaneous preliminary provisions
Extent of Act
18. This Act extends to all places outside Australia, including the external Territories.
Application of Act
19.(1) This Act applies to the employment of employees on a prescribed ship that is engaged in trade or commerce:
(a) between Australia and places outside Australia; or
(b) among the States; or
(c) within a Territory, between a State and a Territory or between 2 Territories.
(2) This Act also has the effect it would have if:
(a) a reference to an employer were limited to a reference to a trading corporation formed within the limits of the Commonwealth; and
(b) a reference to an employee were limited to a reference to an employee employed by a trading corporation formed within the limits of the Commonwealth.
(3) This Act also has the effect it would have if:
(a) a reference to an employer were limited to a reference to a financial corporation formed within the limits of the Commonwealth; and
(b) a reference to an employee were limited to a reference to an employee employed by a financial corporation formed within the limits of the Commonwealth.
(4) This Act also has the effect it would have if:
(a) a reference to an employer were limited to a reference to a foreign corporation; and
(b) a reference to an employee were limited to a reference to an employee employed by a foreign corporation.
(5) This Act does not apply with respect to:
(a) State banking that does not extend beyond the limits of the State concerned; or
(b) State insurance that does not so extend.
Act not to apply to CERC Act employees
20. Despite any other provision of this Act, this Act does not apply to a person who is an employee within the meaning of the CERC Act.
Act binds Crown etc.
21.(1) This Act binds the Crown in right of the Commonwealth.
(2) This Act does not permit the Crown to be prosecuted for an offence.
Amounts of compensation
22. An amount of compensation payable under a provision of this Act in respect of an injury is, unless the contrary intention appears, in addition to an amount of compensation paid or payable under any other provision of this Act in respect of that injury.
Indexation
23.(1) In this section:
“commencing day” means the day on which this section commences;
“index number”, in relation to a quarter, means the All Groups Consumer Price Index number, being the weighted average of the 8 capital cities, published by the Australian Statistician in respect of that quarter;
“relevant amount” means the amount specified in subsection 29(3), (4) or (5), 30(2), 31(9), (10) or (11), 39(9), 41(2), 43(2) or (4) or 44(1);
“relevant year” means the period of 12 months starting on 1 July 1992, and each later period of 12 months.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), if (whether before, on or after the commencing day) the Australian Statistician has published or publishes an index number in respect of a quarter in substitution for an index number previously published in respect of that quarter, the publication of the later index number must be disregarded for the purposes of this section.
(3) If (whether before, on or after the commencing day) the Australian Statistician has changed or changes the reference base for the Consumer Price Index, then, for the purposes of the application of this section after the change took place or takes place, regard must only be had to the index number published in terms of the new reference base.
(4) If the factor worked out under subsection (5) in relation to a relevant year is greater than one, this Act has effect as if for each relevant amount there were substituted, on the first day of that relevant year, an amount worked out by multiplying by that factor:
(a) if, because of one or more other applications of this section, this Act has effect as if another amount or amounts were substituted for the relevant amount—the substituted amount or the last substituted amount; or
(b) in any other case—the relevant amount.
(5) The factor worked out in relation to a relevant year is the number (calculated to 3 decimal places) worked out by dividing the index number of the December quarter immediately before the relevant year by the index number for the December quarter immediately before that first-mentioned December quarter.
(6) If the factor worked out in relation to a relevant year would, if it were calculated to 4 decimal places, end with a number greater than 4, the factor in relation to that relevant year is taken to be the factor calculated to 3 decimal places in accordance with that subsection and increased by 0.001.
Liability to pay compensation
24. The liability of an employer to pay compensation to a person under this Act is the liability of the employer to pay the amount or amounts that the employer determines, in accordance with this Act, to be payable to the person.
Compensation to be paid in full
25. Subject to subsection 29(4) and sections 30 to 37 (inclusive), 47, 55, 58 and 139, compensation in respect of an injury must be paid in full by an employer whose employment has made a material contribution to the injury.
PART 2—COMPENSATION
Division 1—Injuries, property loss or damage, medical expenses
Compensation for injuries
26.(1) If an employee suffers an injury that results in his or her death, incapacity for work, or impairment, compensation is payable for the injury.
(2) Compensation is not payable for an intentionally self-inflicted injury.
(3) Compensation is not payable for an injury that is not intentionally self-inflicted but is caused by the serious and wilful
misconduct of the employee, unless the injury results in death, or serious and permanent impairment.
Compensation for property loss or damage
27.(1) If:
(a) an employee has an accident arising out of, or in the course of, his or her employment; and
(b) the accident does not cause injury to the employee but results in the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee;
compensation of an amount equal to the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee in the necessary replacement or repair of the property is payable to the employee.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), expenditure incurred by an employee in the necessary replacement or repair of property is taken to include any fees or charges paid or payable by the employee to a legally qualified medical practitioner or dentist, or other qualified person, for a consultation, examination, prescription, or other service reasonably rendered in connection with the replacement or repair.
(3) Compensation is not payable under this section if the loss or damage is caused by the serious and wilful misconduct of the employee.
Compensation for medical and related expenses
28.(1) If an employee:
(a) suffers an injury; and
(b) obtains medical treatment for the injury, being treatment that it was reasonable for the employee to obtain in the circumstances;
compensation is payable for the cost of the medical treatment, of such amount as is appropriate, having regard to the nature of the treatment.
(2) Subsection (1) applies whether or not the injury results in death, incapacity for work, or impairment.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (1), the cost of medical treatment involving the supply, replacement or repair of property used by an employee, is taken to include any fees or charges paid or payable by the employee to a legally qualified medical practitioner or dentist, or other qualified person, for a consultation, examination, prescription or other service reasonably required in connection with that supply, replacement or repair.
(4) An amount of compensation under subsection (1) is payable:
(a) to, or in accordance with the directions of, the employee; or
(b) if the employee dies before the compensation is paid and without having paid the cost referred to in subsection (1) and another person (who is not the legal personal representative of the employee) has paid that cost—to that other person; or
(c) if that cost has not been paid and the employee, or the legal personal representative of the employee, does not claim the compensation—to the person to whom the cost is payable.
(5) If an employer is liable to pay any cost referred to in subsection (1), any amount paid under subsection (4) to the person to whom that cost is payable is, to the extent of the payment, a discharge of the liability of the employer.
(6) Subject to subsection (7), if compensation for the cost of medical treatment is payable, compensation is payable to the employee of an amount equal to the amount of the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee:
(a) in making a necessary journey for the purpose of obtaining the treatment; or
(b) in remaining, for the purpose of obtaining the treatment, at a place to which the employee has made a journey for that purpose.
(7) Compensation is not payable under subsection (6) unless:
(a) the journey covered a substantial distance; or
(b) if the journey involved the use of public transport or ambulance service—the employee’s injury reasonably required the use of such transport or service, regardless of the distance involved.
(8) The matters to be taken into account in deciding questions arising under subsections (6) and (7) include:
(a) the place or places where appropriate medical treatment was available to the employee; and
(b) the means of transport available to the employee for the journey; and
(c) the route or routes by which the employee could have travelled; and
(d) the accommodation available to the employee.
(9) If:
(a) an employee suffers an injury; and
(b) a person has reasonably incurred expenditure in connection with the transportation of the employee, or, if the employee has died, of the employee’s body, from the place where the injury was sustained to a hospital or similar place, or to a mortuary; and
(c) an employee, or the legal personal representative of the employee, does not make a claim for compensation for that expenditure;
compensation of an amount equal to that expenditure is payable to the person who incurred the expenditure.
Division 2—Injuries resulting in death
Compensation for injuries resulting in death
29.(1) This section applies if an injury to an employee results in the employee’s death.
(2) Subject to this section and sections 28 and 30, if the employee dies without leaving dependants, compensation is not payable for the injury.
(3) If the employee dies leaving dependants some or all of whom were, at the date of the employee’s death, wholly dependent on the employee:
(a) subject to this section and to sections 28 and 30, compensation of $151,167.84 is payable for the injury; and
(b) that compensation is payable for the benefit of those dependants.
(4) If the employee dies without leaving dependants who were wholly dependent on the employee at the date of the employee’s death, but leaving dependants who were partly dependent on the employee at that date:
(a) subject to this section and to sections 28 and 30, compensation is payable for the injury of such amount, not exceeding $151,167.84, as is appropriate, having regard to any losses suffered by those dependants as a result of the cessation of the employee’s earnings; and
(b) that compensation is payable for the benefit of those dependants.
(5) If:
(a) a prescribed child was, at the date of the injury or at the date of the employee’s death, wholly or mainly dependent on the employee; or
(b) a prescribed child, being a child of the employee, was born after the employee’s death; or
(c) a prescribed child would, if the employee had not died, have been wholly or mainly dependent on the employee;
compensation is payable at the rate of $50.38 per week and that compensation is payable to, or in accordance with the directions of:
(d) if the prescribed child is 18 or over—the child; or
(e) if the prescribed child is under 18—the Authority for the benefit of the child;
from the date of the employee’s death or the date of the birth of the child, whichever is later.
(6) Compensation is not payable under subsection (5) in respect of:
(a) any period during which the child is not a prescribed child; and
(b) in the case of a child referred to in paragraph (5)(c)—any period
during which, if the employee had not died, the child would not have been wholly or mainly dependent upon the employee.
(7) An amount of compensation paid or payable under this Act before the death of an employee:
(a) is not affected by subsection (2); and
(b) must not be deducted from the compensation payable under subsection (3); and
(c) must not be taken into account in determining the compensation payable under subsection (4).
(8) If an amount of compensation is payable under subsection (3) or (4) for the benefit of 2 or more dependants of the deceased employee, the employer must determine the shares of those dependants in that amount as it thinks fit, having regard to any losses suffered by those dependants as a result of the cessation of the employee’s earnings.
(9) A reference in this section to a dependant of a deceased employee is a reference to a dependant by or on behalf of whom a claim is made for compensation under this section.
(10) If claims for compensation under this section are made by or on behalf of 2 or more dependants of a deceased employee, the employer must make one determination in respect of those claims.
Compensation in respect of funeral expenses
30.(1) If an injury to an employee results in death, compensation is payable for the cost of the employee’s funeral to the person who paid the cost of the funeral or, if that cost has not been paid, to the person who carried out the funeral.
(2) The amount of compensation is such amount, not exceeding $1,889.60, as the employer determines is reasonable, having regard to:
(a) the charges ordinarily made for funerals in the place where the funeral was carried out; and
(b) any amount paid or payable in respect of the cost of the funeral under any other law of the Commonwealth.
(3) If an employer is liable to pay the cost of the funeral of an employee, any amount paid under this section to the person who carried out the funeral is, to the extent of the payment, a discharge of the liability of the employer.
Division 3—Injuries resulting in incapacity for work
Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity
31.(1) This section applies to an employee who is incapacitated for work as a result of an injury, other than an employee to whom section 33, 34, 35, 36 or 37 applies.
(2) Subject to subsection (3) and this Part (other than this section), compensation for the injury is payable to the employee, for each of the first 45 weeks (whether consecutive or otherwise) during which the employee is incapacitated, of an amount worked out using the formula:
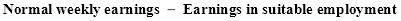
where:
“Normal weekly earnings” means the amount of the employee’s normal weekly earnings;
“Earnings in suitable employment” means the amount per week (if any) that the employee is able to earn in suitable employment.
(3) If the employee is a seafarer, the compensation payable under subsection (2) is payable for each of the first 45 weeks (whether consecutive or otherwise) after the date on which the seafarer is left on shore at, or returned to, his or her proper return port.
(4) Subject to this Part (other than this section), compensation for the injury is payable to the employee, for each week during which the employee is incapacitated, being a week to which subsection (2) does not apply.
(5) The amount of compensation per week payable under subsection (4) to an employee is:
(a) if the employee is not employed during that week—an amount equal to 75% of his or her normal weekly earnings less the amount (if any) that he or she was able to earn during that week in suitable employment; or
(b) if the employee is employed for 25% or less of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—an amount that, when added to the amount that he or she was able to earn during that week in suitable employment, results in an amount equal to 80% of his or her normal weekly earnings; or
(c) if the employee is employed for more than 25% but not more than 50% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—an amount that, when added to the amount that he or she was able to earn during that week in suitable employment, results in an amount equal to 85% of his or her normal weekly earnings; or
(d) if the employee is employed for more than 50% but not more than 75% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—an amount that, when added to the amount that he or she was able to earn during that week in suitable employment, results in an amount equal to 90% of his or her normal weekly earnings; or
(e) if the employee is employed for more than 75% but less than 100% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—an amount that, when added to the amount that he or she was
able to earn during that week in suitable employment, results in an amount equal to 95% of his or her normal weekly earnings; or
(f) if the employee is employed for 100% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—an amount that, when added to the amount that he or she was able to earn during that week in suitable employment, results in an amount equal to 100% of his or her normal weekly earnings.
(6) If:
(a) compensation is payable under subsection (4) to an employee for a week; and
(b) the employee is employed or engaged during the whole or any part of that week as a seafarer;
subsection (5) applies in relation to the employee as if he or she were covered by paragraph (5)(f).
(7) If an amount of compensation worked out under subsection (5) is more than 150% of the amount called the “Average Weekly Ordinary Time Earnings of Fulltime Adults”, as published from time to time by the Australian Statistician, the amount so worked out must be reduced by an amount equal to the excess.
(8) If an amount of compensation worked out under paragraph (5)(a) is less than the minimum earnings, the amount so worked out must be increased by an amount equal to the difference between that amount and the minimum earnings.
(9) For the purposes of subsection (8), the minimum earnings of an employee are taken to be:
(a) $254.46, or, if subsection (10) or (11) applies to the employee, the sum of $254.46 and the amount or amounts required to be added under whichever of those subsections applies; or
(b) an amount equal to 90% of the employee’s normal weekly earnings;
whichever is less.
(10) If there are one or more prescribed persons wholly or mainly dependent on the employee, the amount of $62.99 must be added to the amount of $254.46 specified in paragraph (9)(a).
(11) If there are one or more prescribed children (whether born before, on or after the date of the injury) wholly or mainly dependent on the employee, the amount of $31.50 for each of those children must be added to the amount of $254.46 specified in paragraph (9)(a), but an amount must not be so added for a child in relation to any period before the date of birth of that child.
(12) If a prescribed child is:
(a) a prescribed person in relation to the employee; and
(b) the only prescribed person who is wholly or mainly dependent on the employee; subsection (11) does not apply to the child.
(13) If 2 or more prescribed children are each:
(a) a prescribed person in relation to the employee; and
(b) wholly or mainly dependent on the employee;
subsection (10) applies to one of those children and subsection (11) applies to the rest.
(14) For the purposes of this section the normal weekly hours of an employee who is not employed on a ship are:
(a) if the award, determination or certified agreement that applies to the employee specifies the normal weekly hours of an employee—those hours; or
(b) in any other case—38 hours.
(15) In this section:
“proper return port” has the same meaning as in the Navigation Act.
Determination of suitable employment
32. An employer who determines, for the purposes of section 31, the amount per week that an employee is able to earn in suitable employment must have regard to the following:
(a) if the employee is in employment—the amount per week that the employee is earning in that employment;
(b) if, after becoming incapacitated for work, the employee received an offer of suitable employment and did not accept that offer—the amount per week that the employee would be earning in that employment if he or she were engaged in that employment;
(c) if, after becoming incapacitated for work, the employee received an offer of suitable employment and, having accepted that offer, did not engage, or continue to engage, in that employment—the amount per week that the employee would be earning in that employment if he or she were engaged in that employment;
(d) if, after becoming incapacitated for work, the employee received an offer of suitable employment on condition that the employee completed a reasonable rehabilitation or vocational retraining program and the employee did not fulfil that condition—the amount that the employee would be earning in that employment if he or she were engaged in that employment;
(e) if, after becoming incapacitated for work, the employee has not sought suitable employment—the amount per week that, having regard to the state of the labour-market at the relevant time, the employee could reasonably be expected to earn in such employment if he or she were engaged in such employment;
(f) if paragraph (b), (c), (d) or (e) applies to the employee—whether the employee’s failure to accept an offer of employment, to engage, or to continue to engage, in employment, to undertake, or to complete, a rehabilitation or vocational retraining program or to seek employment, as the case may be, was, in the opinion of the employer, reasonable in all the circumstances;
(g) any other matter that the employer considers relevant.
Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee is in receipt of a superannuation pension
33.(1) This section applies to an employee who:
(a) is incapacitated for work as a result of an injury; and
(b) retires (whether voluntarily or otherwise) from his or her employment at any time after the commencement of this section; and
(c) as a result of the retirement, receives a pension under a superannuation scheme.
(2) Compensation is payable to the employee for the injury under this section for each week after the date of the retirement during which the employee is incapacitated.
(3) The amount of compensation is an amount worked out using the formula:

where:
“Unadjusted amount of compensation” means the amount of compensation that would have been payable to the employee for a week if:
(a) section 31, other than subsection 31(8), had applied to the employee; and
(b) the week were a week referred to in subsection 31(4);
“Superannuation amount” means the superannuation amount received by the employee that week under a superannuation scheme;
“Superannuation contributions” means the amount of superannuation contributions that would have been required to be paid by the employee in that week if he or she were still contributing to the superannuation scheme.
Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee is in receipt of a lump sum benefit
34.(1) This section applies to an employee who:
(a) is incapacitated for work as a result of an injury; and
(b) retires (whether voluntarily or otherwise) from his or her
employment at any time after the commencement of this section; and
(c) as a result of the retirement, receives a lump sum benefit under a superannuation scheme; and
(d) has not rolled-over the lump sum benefit into another superannuation fund or an approved deposit fund.
(2) Compensation is payable to the employee for the injury under this section for each week after the date of the retirement during which the employee is incapacitated.
(3) The amount of compensation is an amount worked out using the formula:

where:
“Unadjusted amount of compensation” means the amount of compensation that would have been payable to the employee for a week if:
(a) section 31, other than subsection 31(8), had applied to the employee; and
(b) the week were a week referred to in subsection 31(4);
“Superannuation amount” means the superannuation amount received by the employee as a lump sum;
“Superannuation contributions” means the amount of superannuation contributions that would have been required to be paid by the employee in that week if he or she were still contributing to the superannuation scheme.
(4) In this section:
“approved deposit fund” has the same meaning as in Subdivision AA of Division 2 of Part III of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936;
“rolled-over” has the same meaning as in Subdivision AA of Division 2 of Part III of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936;
“superannuation fund” has the same meaning as in Subdivision AA of Division 2 of Part III of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936.
Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where employee rolled-over part of a lump sum benefit
35.(1) This section applies to an employee who:
(a) has been incapacitated for work as a result of an injury; and
(b) retired (whether voluntarily or otherwise) from his or her employment at any time after the commencement of this section; and
(c) as a result of the retirement, receives a lump sum benefit under a superannuation scheme; and
(d) rolled-over part of the lump sum benefit into a superannuation fund or an approved deposit fund.
(2) Compensation is payable to the employee for the injury under this section for each week after the date of the retirement during which the employee is incapacitated.
(3) The amount of compensation is an amount worked out using the formula:

where:
“Unadjusted amount of compensation” means the amount of compensation that would have been payable to the employee for a week if:
(a) section 31, other than subsection 31(8), had applied to the employee; and
(b) the week were a week referred to in subsection 31(4);
“Amount not rolled-over” means the amount not rolled-over or withdrawn from the superannuation fund or approved deposit fund to which the lump sum benefit was rolled-over;
“Lump sum benefit” means the amount of the lump sum benefit received by the employee;
“Superannuation amount” means the superannuation amount received by the employee as a lump sum.
(4) In this section:
“approved deposit fund” has the same meaning as in section 34;
“rolled-over” has the same meaning as in section 34;
“superannuation fund” has the same meaning as in section 34.
Compensation for injuries resulting in incapacity where the employee rolled-over the whole of a lump sum benefit
36.(1) This section applies to an employee who:
(a) has been incapacitated for work as a result of an injury; and
(b) retired (whether voluntarily or otherwise) from his or her employment at any time after the commencement of this section; and
(c) as a result of the retirement, receives a lump sum benefit under a superannuation scheme; and
(d) rolled-over the lump sum benefit into a superannuation fund or an approved deposit fund.
(2) Compensation is payable to the employee for the injury under this section for each week after the date of the retirement during which the employee is incapacitated.
(3) The amount of compensation is an amount worked out using the formula:
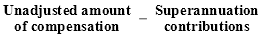
where:
“Unadjusted amount of compensation” means the amount of compensation that would have been payable to the employee for a week if:
(a) section 31, other than subsection 31(8), had applied to the employee; and
(b) the week were a week referred to in subsection 31(4);
“Superannuation contributions” means the amount of superannuation contributions that would have been required to be paid by the employee in that week if he or she were still contributing to the superannuation scheme.
(4) In this section:
“approved deposit fund” has the same meaning as in section 34;
“rolled-over” has the same meaning as in section 34;
“superannuation fund” has the same meaning as in section 34.
Compensation where employee is maintained in a hospital
37.(1) If:
(a) as a result of an injury, an employee (other than an employee to whom section 33, 34, 35 or 36 applies) is maintained as a patient in a hospital, nursing home or similar place, and has been so maintained for a continuous period of not less than one year; and
(b) there are no prescribed persons or prescribed children who are dependent on the employee;
compensation is payable to the employee for the injury of the amount, for each week during which the employee is so maintained, determined by the person liable to pay the compensation, having regard to:
(c) the present and probable future needs and expenses of the employee; and
(d) the period during which the employee is likely to be such a patient.
(2) An amount determined under subsection (1) must not be less than one-half of, nor more than, the amount per week of compensation that would have been payable to the employee under section 31 had that section applied to the employee.
Compensation for incapacity not payable in certain cases
38.(1) If an employee who has not reached 64 suffers an injury, compensation is not payable under this Division for the injury after the person reaches 65.
(2) If an employee who has reached 64 suffers an injury, compensation is not payable under this Division for the injury after the end of the period of 12 months starting on the day on which the injury happened.
(3) Compensation is not payable under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 in respect of any period during which the employee is imprisoned for committing an offence.
(4) Subject to section 45, if a determination is made that an amount of compensation is payable to an employee under section 44 for an injury, compensation is not payable to the employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 in respect of a period of incapacity for work resulting from the injury, being a period after the day on which the determination is made.
Division 4—Injuries resulting in permanent impairment
Compensation for injuries resulting in permanent impairment
39.(1) If an injury to an employee results in a permanent impairment, compensation is payable to the employee for the injury.
(2) For the purpose of determining whether an impairment is permanent, the employer must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the duration of the impairment;
(b) the likelihood of improvement in the employee’s condition;
(c) whether the employee has undertaken all reasonable rehabilitative treatment for the impairment;
(d) any other relevant matters.
(3) Subject to this section, the amount of compensation payable to the employee is an amount assessed under subsection (4) by the employer, being an amount that is not more than the maximum amount at the date of the assessment.
(4) The amount assessed must be an amount that is the same percentage of the maximum amount as the percentage determined under subsection (5).
(5) The employer under this section must determine the degree of permanent impairment of the employee resulting from an injury under the provisions of the approved Guide.
(6) The degree of permanent impairment must be expressed as a percentage.
(7) Subject to section 40, where the degree of permanent impairment of the employee, as determined under this section, is less than 10%, an amount of compensation is not payable to the employee under this section.
(8) Subsection (7) does not apply to an impairment resulting from the loss of, or injury to, a finger or toe.
(9) For the purposes of this section, the maximum amount is $100,778.56.
Interim payment of compensation
40.(1) If an employer:
(a) makes a determination that an employee is suffering from a permanent impairment as a result of an injury; and
(b) is satisfied that the degree of the impairment is equal to or more than 10% but has not made a final determination of the degree of impairment;
the employer must, on the written request of the employee made at any time before the final determination is made, make an interim determination of the degree of permanent impairment under section 39 and assess an amount of compensation payable to the employee.
(2) The amount assessed under subsection (1) must be an amount that is the same percentage of the maximum amount specified in subsection 39(9) as the percentage worked out in the interim determination under subsection (1) to express the degree of permanent impairment of the employee.
(3) If, after an amount of compensation has been paid to an employee following the making of an interim determination, a final determination is made of the degree of permanent impairment of the employee, there is payable to the employee an amount equal to the difference (if any) between the amount payable under section 39 on the making of the final determination and the amount paid to the employee under this section.
(4) If a final assessment is made of the degree of permanent impairment of an employee, no further amounts of compensation are payable to the employee in respect of a subsequent increase in the degree of impairment, unless the increase is 10% or more.
Compensation for non-economic loss
41.(1) If an injury to an employee results in a permanent impairment and compensation is payable for the injury under section 39, the employer is liable to pay additional compensation in accordance with this section to the employee for any non-economic loss suffered by the employee as a result of the injury or impairment.
(2) The amount of compensation is an amount worked out using the formula:

where:
“Degree of permanent impairment” means the percentage finally determined under section 39 to be the degree of permanent impairment of the employee;
“Degree of non-economic loss” means the percentage determined under the approved Guide, by the employer, to be the degree of non-economic loss suffered by the employee.
Approved Guide
42.(1) The Authority may, from time to time, prepare a written document, to be called the “Guide to the Assessment of the Degree of Permanent Impairment”, setting out:
(a) criteria by reference to which the degree of the permanent impairment of an employee resulting from an injury must be determined; and
(b) criteria by reference to which the degree of non-economic loss suffered by an employee as a result of an injury or impairment must be determined; and
(c) methods by which the degree of permanent impairment and the degree of non-economic loss, as determined under those criteria, must be expressed as a percentage.
(2) The Authority may, from time to time, by instrument in writing, vary or revoke the approved Guide.
(3) A document prepared by the Authority under subsection (1), and an instrument under subsection (2), have no force or effect unless and until approved by the Minister.
(4) If an employer or the Administrative Appeals Tribunal is required to assess or reassess, or review the assessment or reassessment of, the degree of permanent impairment of an employee resulting from an injury, or the degree of non-economic loss suffered by an employee, the assessment, reassessment or review must be made in accordance with the approved Guide.
(5) The percentage of permanent impairment or non-economic loss suffered by an employee as a result of an injury ascertained under the methods referred to in paragraph (1)(c) may be 0%.
(6) In preparing criteria for the purposes of paragraphs (1)(a) and (b), or in varying those criteria, the Authority must have regard to medical opinion concerning the nature and effect (including possible effect) of the injury and the extent (if any) to which impairment resulting from the injury, or non-economic loss resulting from the injury or impairment, may reasonably be capable of being reduced or removed.
(7) When a document prepared by the Authority in accordance with subsection (1), or an instrument under subsection (2), has been approved by the Minister, the Authority must cause copies of the document or instrument, as the case may be, to be laid before each House of the Parliament within 15 sitting days of that House after the Minister receives those copies.
(8) The Authority must make copies of the approved Guide and of any approved variation of that Guide, available upon application by a person and payment of the prescribed fee (if any).
(9) Sections 48 (other than paragraphs (1)(a) and (b) and subsection (2)), 49 and 50 of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 apply in relation to a document, being the approved Guide or an instrument varying or revoking that Guide that has been approved by the Minister, as if, in those sections, references to regulations were references to such a document and references to a regulation were references to a provision of such a document.
(10) For the purpose of the application of the provisions of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 in accordance with subsection (9), a document referred to in that subsection is taken to have been made on the date on which it was approved by the Minister under this section.
Division 5—Household and attendant care services
Compensation for household services and attendant care services
43.(1) If, as a result of an injury to an employee, the employee obtains household services that he or she reasonably requires, compensation is payable at the rate of such amount per week as is reasonable in the circumstances.
(2) The amount of compensation payable per week under subsection (1) for household services:
(a) must not be more than $251.94; and
(b) must not be less than 50% of the amount per week paid or payable by the employee for those services, unless the amount per week so paid or payable is more than $503.88.
(3) Without limiting the matters that may be taken into account in determining the household services that are reasonably required in a particular case, the employer must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the extent to which household services were provided by the employee before the date of the injury and the extent to which he or she is able to provide those services after that date;
(b) the number of persons living with the employee as members of his or her household, their ages and their need for household services;
(c) the extent to which household services were provided by the persons referred to in paragraph (b) before the injury;
(d) the extent to which the persons referred to in paragraph (b), or any other members of the employee’s family, might reasonably be expected to provide household services for themselves and for the employee after the injury;
(e) the need to avoid substantial disruption to the employment or other activities of the persons referred to in paragraph (b).
(4) If, as a result of an injury to an employee, the employee obtains attendant care services that he or she reasonably requires, compensation is payable at the rate of:
(a) $251.94 per week; or
(b) an amount per week equal to the amount per week paid or payable by the employee for the services;
whichever is less.
(5) Without limiting the matters that may be taken into account in determining the attendant care services that are reasonably required in a particular case, the employer must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the nature of the employee’s injury and the degree to which that injury impairs the employee’s ability to provide for his or her personal care;
(b) the extent to which any medical service or nursing care received by the employee provides for his or her essential and regular personal care;
(c) the extent to which it is reasonable to meet any wish by the employee to live outside an institution;
(d) the extent to which attendant care services are necessary to enable the employee to undertake or continue employment;
(e) any assessment made in relation to the rehabilitation of the employee;
(f) the extent to which a relative of the employee might reasonably be expected to provide attendant care services.
(6) An employer is not liable to pay compensation under subsection (1) in respect of any week within the period of 28 days starting on the
day of the injury unless the employer determines otherwise in a particular case on the ground of financial hardship or the need to provide for adequate supervision of dependent children.
(7) An amount of compensation payable under subsection (1) or (4) is payable:
(a) if the employee has paid for the household services or attendant care services, as the case may be—to the employee; or
(b) in any other case—to the person who provided those services.
(8) If an amount of compensation is paid to a person who provided household services or attendant care services to an employee, the payment of the amount is, to the extent of the payment, a discharge of the liability of the employee to pay for those services.
Division 6—Miscellaneous
Redemption of compensation
44.(1) If:
(a) an employer is liable to make weekly payments under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 to an employee for an injury resulting in an incapacity; and
(b) the amount of those payments is $62.99 per week or less; and
(c) the employer is satisfied that the degree of the employee’s incapacity is unlikely to change;
the employer must make a determination that any liability to make further payments to the employee under that section be redeemed by the payment to the employee of a lump sum.
(2) The amount of the lump sum is the amount worked out using the formula:
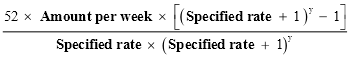
where:
“Amount per week” means the amount per week payable to the employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 as the case may be, at the date of the determination;
“Specified rate” means the specified rate, expressed as a decimal fraction, applicable at the date of the determination;
“y” [Number of years] means the number worked out by dividing by 365 the number of days between the date of the determination and the day on which the employee reaches 65 (rounded to 3 decimal places).
(3) The Minister may, from time to time, by notice in writing, specify a rate for the purposes of subsection (2).
Recurrent payments after payment of lump sum
45.(1) If:
(a) at any time after a lump sum is paid to an employee under section 44 for an injury, the injury results in the employee being incapacitated for work to the extent that the employee is not able to engage in suitable employment; and
(b) the incapacity is likely to continue indefinitely;
compensation is payable to the employee under this section during the period of the incapacity.
(2) The amount of compensation is an amount per week equal to the amount per week that would, but for the payment of the lump sum, have been payable to the employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 as the case may be, for the incapacity, less the amount per week that was redeemed at the date of the determination under section 44.
Cancelled determinations not to affect certain payments of compensation
46.(1) For the purposes of subsections 38(4) and 45(2), account must not be taken of a determination that the liability of an employer to make further payments to an employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 is to be redeemed if the determination:
(a) is revoked by the employer; or
(b) is set aside by a tribunal or court.
(2) Paragraph (1)(b) does not apply if a further determination is made by a tribunal or court, being a determination under which the liability of the employer to make further payments to the employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35 or 36 is to be redeemed.
Reduction of compensation in certain cases
47.(1) Subject to subsection (2), if, in relation to a day in respect of which compensation is payable to an employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 or 45, an amount is paid or payable to the employee by the employer by way of salary, wages or pay, the amount of compensation payable under that section in respect of that day must be reduced by the amount so paid or payable to the employee.
(2) If, in relation to a day in respect of which compensation is payable to an employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 or 45, an amount is payable to the employee in relation to recreation leave, the amount must not be paid and the employee must be recredited with a day’s recreation leave.
(3) In this section, a reference to an amount paid or payable to an employee by the employer does not include a reference to:
(a) an amount by way of pay in respect of a period of long service leave that is granted, or instead of the grant of a period of long service leave; or
(b) any amount that the employee is able to earn in suitable employment, being an amount that has been taken into account for the purposes of working out the amount of compensation payable to the employee under section 31.
PART 3—REHABILITATION
Approved rehabilitation program providers
48. In this Part:
“approved program provider” has the same meaning as in the CERC Act.
Assessment of capability of undertaking rehabilitation program
49.(1) If an employee suffers an injury that lasts, or is expected to last, 28 days, which results in an impairment or an incapacity for work, the employee’s employer must, within 28 days after receiving notice of the injury, arrange for the assessment of the employee’s capability of undertaking a rehabilitation program.
(2) An assessment must be made by:
(a) a legally qualified medical practitioner nominated by the employer; or
(b) a suitably qualified person (other than a medical practitioner) nominated by the employer; or
(c) a panel comprising legally qualified medical practitioners or other suitably qualified persons (or both) nominated by the employer.
(3) The employer may require the employee to undergo an examination by the person or panel of persons making the assessment.
(4) If an employee, without reasonable excuse, does not undergo an examination in accordance with a requirement, or in any way obstructs such an examination, the employee’s rights to compensation under this Act, and to institute or continue any proceedings under this Act in relation to compensation, are suspended until the examination takes place.
(5) If an employee’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (4), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
(6) The employer must pay the cost of conducting any examination of an employee and is liable to pay to the employee:
(a) an amount equal to the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee in making a necessary journey in connection with the examination; and
(b) an amount equal to the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee in remaining (if necessary), for the purpose of the
examination, at a place to which the employee has made a journey for that purpose.
(7) In deciding questions arising under subsection (6), the employer must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the means of transport available to the employee for the journey;
(b) the route or routes by which the employee could have travelled;
(c) the accommodation available to the employee.
(8) If an examination is carried out, the person or persons who carried out the examination must give the employer a written assessment of the employee’s capability of undertaking a rehabilitation program, specifying, where appropriate, the kind of program which he or she is capable of undertaking and containing any other information relating to the provision of a rehabilitation program for the employee that the employer may require.
Provision of rehabilitation programs
50.(1) If an employee of an employer is assessed under section 49 as capable of undertaking a rehabilitation program, the employer must, after consulting the employee in relation to:
(a) the selection of an approved program provider; and
(b) the development of an appropriate rehabilitation program by an approved program provider;
make arrangements with an approved program provider for the provision of an appropriate rehabilitation program.
(2) The cost of any rehabilitation program provided for an employee under this section must be paid by the employer.
(3) If an employee is undertaking a rehabilitation program under this section, compensation is not payable to the employee under section 31, 33, 34, 35, 36 or 45 but:
(a) if the employee is undertaking a full-time program—compensation is payable to the employee of an amount per week equal to the amount per week of the compensation that would, but for this subsection, have been payable under section 31, 33, 34, 35, 36 or 45 if the incapacity referred to in that section had continued throughout the period of the program; or
(b) if the employee is undertaking a part-time program—compensation is payable to the employee of such amount per week as the employer determines, being an amount not less than the amount per week of the compensation that, apart from this subsection, would have been payable to the employee under this Act and not greater than the amount per week of the compensation that would have been payable under paragraph (a) if the employee had been undertaking a full-time program.
(4) An employee who is entitled to compensation under subsection (3) during a period is not entitled to receive an amount under Part 2.10 of the Social Security Act 1991 during that period.
(5) If an employee, without reasonable excuse, does not undertake a rehabilitation program provided for the employee under this section, the employee’s rights to compensation under this Act, and to institute or continue any proceedings under this Act in relation to compensation, are suspended until the employee starts to undertake the program.
(6) If an employee’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (5), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
Compensation payable in respect of certain alterations etc.
51.(1) If:
(a) an employee suffers an injury resulting in an impairment; and
(b) the employee is undertaking, or has completed, a rehabilitation program, or has been assessed as not capable of undertaking such a program;
compensation is payable of such amount as is reasonable for the costs, payable by the employee, of:
(c) any alteration of the employee’s place of residence or place of work; or
(d) any modifications of a vehicle or article used by the employee; or
(e) any aids or appliances for the use of the employee, or the repair or replacement of such aids or appliances;
being alterations, modifications or aids or appliances reasonably required by the employee, having regard to the nature of the employee’s impairment and, where appropriate, the requirements of the rehabilitation program.
(2) Without limiting the matters that may be taken into account in determining the amount of compensation payable in a particular case under subsection (1), the employer making the determination must have regard to such of the following matters as are relevant in that case:
(a) the likely period during which the alteration, modification, aid or appliance will be required;
(b) any difficulties faced by the employee in gaining access to, or enjoying reasonable freedom of movement in, his or her place of residence or work;
(c) any difficulties faced by the employee in gaining access to, or enjoying reasonable freedom of movement in, a vehicle used by the employee;
(d) any alternative means of transport available to the employee;
(e) whether arrangements can be made for hiring the relevant aid or appliance;
(f) if the employee has previously received compensation under this section in respect of an alteration of his or her place of residence or a modification of a vehicle and has later disposed of that place of residence or vehicle—whether the value of that place of residence or vehicle was increased as a result of the alteration or modification.
(3) An amount of compensation payable under this section is payable:
(a) to, or in accordance with the directions of, the employee; or
(b) if the employee dies before the compensation is paid and without having paid the cost referred to in subsection (1) and another person (not being the legal personal representative of the employee) has paid that cost—to that other person; or
(c) if that cost has not been paid and the employee (or the legal personal representative of the employee) cannot or does not make a claim for the compensation—to the person to whom that cost is payable.
(4) If an employer is liable to pay any cost referred to in subsection (1), any amount paid under subsection (3) to the person to whom that cost is payable is, to the extent of the payment, a discharge of the liability of the employer.
Duty to provide suitable employment
52. If an employee is undertaking, or has completed, a rehabilitation program, his or her employer must take all reasonable steps to provide the employee with suitable employment, or to assist the employee to find such employment.
PART 4—LIABILITIES ARISING APART FROM THIS ACT
Interpretation
53.(1) In this Part:
(a) a reference to the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee is a reference to the loss of, or damage to, the property in circumstances referred to in section 27; and
(b) a reference to an employee is, if the employee has died, a reference to his or her legal personal representative; and
(c) a reference to a dependant of a deceased employee is, if the dependant has died, a reference to the dependant’s legal personal representative; and
(d) a reference to an employer, being a body corporate, includes a reference to a related body corporate that:
(i) owns the prescribed ship; or
(ii) manages the prescribed ship; or
(iii) is chartering the prescribed ship; or
(iv) operates the prescribed ship; and
(e) a reference to an employee includes a reference to an employee of a related body corporate that:
(i) is performing duties on the prescribed ship; or
(ii) is performing duties in connection with the prescribed ship.
(2) For the purposes of paragraphs (l)(d) and (e), the question whether bodies corporate are related to each other is to be determined in the same manner as the question whether bodies corporate (within the meaning of the Corporations Law) are related to each other is determined under the Corporations Law.
Employee not to have right to bring action for damages against employer etc. in certain cases
54.(1) Subject to section 55, a person does not have a right to bring an action or other proceedings against his or her employer, or an employee of the employer in respect of:
(a) an injury sustained by an employee in the course of his or her employment, being an injury in respect of which the employer would, apart from this subsection, be liable (whether vicariously or otherwise) for damages; or
(b) the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee resulting from such an injury.
(2) Subsection (1) applies whether that injury, loss or damage occurred before or after the commencement of this section.
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply in relation to an action or proceeding instituted before the commencement of this section.
Actions for damages—election by employees
55.(1) If:
(a) compensation is payable under section 39, 40 or 41 in respect of an injury to an employee; and
(b) the employee’s employer or another employee would, apart from subsection 54(1), be liable for damages for any non-economic loss suffered by the employee because of the injury;
the employee may make an election in accordance with subsection (2) to institute an action or proceeding against the employer or other employee for damages for that non-economic loss.
(2) An election:
(a) must be made before an amount of compensation is paid to an employee under section 39, 40 or 41 in respect of the injury; and
(b) must be given to the employer in respect of the injury; and
(c) must be in writing.
(3) An election is irrevocable.
(4) If an employee makes an election:
(a) subsection 54(1) does not apply in relation to an action or other proceeding subsequently instituted by the employee against the employer or another employee for damages for the non-economic loss to which the election relates; and
(b) compensation is not payable after the date of the election under section 39, 40 or 41 in respect of the injury.
(5) In any action or proceeding instituted because of an election made by an employee, the court is not to award the employee damages of an amount exceeding $138,570.52 for any non-economic loss suffered by the employee.
Notice of proceedings against third party
56. If:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act in respect of the death of an employee, an injury to an employee or the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee; and
(b) the death, injury, loss or damage occurred in circumstances that appear to create a legal liability in a person (other than the employee’s employer or another employee) to pay damages in respect of the death, injury, loss or damage; and
(c) the employee, or a dependant of the deceased employee, as the case may be, institutes proceedings against that person for the recovery of such damages;
the employee or dependant must notify the employer in writing of those proceedings as soon as practicable but in any event not later than 7 days after the day on which he or she first became aware that those proceedings had been instituted.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
Notice of proceedings against employer
57. If:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act in respect of the death of an employee or an injury to an employee; and
(b) the employee, or a dependant of the deceased employee, as the case may be, institutes proceedings against the employee’s employer or another employee for the recovery of damages in respect of the death or injury;
the employee or dependant must notify the employer in writing of those proceedings as soon as practicable but in any event not later than
7 days after the day on which he or she first became aware that those proceedings had been instituted.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
Compensation not payable if damages recovered
58.(1) This section applies if:
(a) an employee recovers damages in respect of an injury to the employee or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee, being an injury, loss or damage in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act; or
(b) damages are recovered by, or for the benefit of, a dependant of a deceased employee in respect of the death of the employee and compensation is payable under this Act in respect of the injury that resulted in that death.
(2) The employee or dependant must, not later than 28 days after the day on which the damages were recovered, notify the employer in writing of the recovery of the damages and the amount of the damages. Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(3) If, before the recovery of the damages by, or for the benefit of, the employee or dependant, any compensation under this Act was paid to the employee in respect of the injury, loss or damage, or to, or for the benefit of, the dependant in respect of the injury that resulted in the death of the employee, as the case may be, the employee or dependant is liable to pay to the employer an amount equal to:
(a) the amount of that compensation; or
(b) the amount of the damages;
whichever is less.
(4) Compensation is not payable under this Act to the employee in respect of the injury, loss or damage, or to, or for the benefit of, the dependant in respect of the injury that resulted in the death of the employee, after the date on which the damages were recovered by the employee or by, or for the benefit of, the dependant, as the case may be.
(5) Subsection (3) does not apply if the damages were recovered in proceedings instituted by the employee as a result of an election by the employee under section 55, or by way of a settlement of such proceedings.
(6) Subsection (4) does not apply if the damages were recovered:
(a) as a result of proceedings, or fresh proceedings, instituted by the employer under section 59; or
(b) as a result of proceedings the conduct of which is taken over by the employer under that section; or
(c) as a result of proceedings instituted by the employee as a result of an election by the employee under section 55; or
(d) by way of settlement of those proceedings.
(7) A reference in subsection (3) to compensation under this Act that was paid for the benefit of a dependant does not include a reference to compensation paid under subsection 29(5).
(8) If an employee, or a dependant of an employee, establishes to the satisfaction of the employer that a part of the damages referred to in subsection (1) did not relate to an injury, loss or damage in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act, subsection (3) applies in relation to that employee or dependant as if the amount of the damages were an amount equal to so much of the amount of the damages as did relate to an injury, loss or damage in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act.
Proceedings against third parties
59.(1) This section applies if:
(a) an amount of compensation under this Act:
(i) is paid to an employee in respect of an injury to the employee or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee; or
(ii) is paid for the benefit of a dependant of a deceased employee in respect of an injury that resulted in the death of the employee; and
(b) the injury, loss, damage or death occurred in circumstances that appear to create a legal liability in a person to pay damages in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death.
(2) If:
(a) this section applies; and
(b) the employee or dependant consents, in writing, to the employer instituting proceedings, or taking over the conduct of proceedings against the person, for the purposes of recovering the damages in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death;
the employer may institute proceedings or fresh proceedings against the person in the name of the employee or dependant for the recovery of damages in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death or may take over the conduct of the proceedings, as the case requires.
(3) If:
(a) this section applies; and
(b) the employee or dependant does not consent to the employer instituting proceedings, or taking over the conduct of proceedings against the person, for the purposes of recovering the damages in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death; and
(c) proceedings against the person for the purpose of recovering such damages:
(i) have not been instituted by the employee or by or for the benefit of the dependant and the delay in instituting the proceedings is unreasonable; or
(ii) have been so instituted but have not been properly prosecuted;
the employer may institute proceedings or fresh proceedings against the person in the name of the employee or dependant for the recovery of damages in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death or may take over the conduct of the proceedings, as the case requires.
(4) If the employer institutes proceedings or fresh proceedings or takes over the conduct of proceedings under subsection (2) or (3) the employer must conduct the proceedings in the interests of the person in whose name the proceedings were instituted.
(5) The employer is liable to pay all costs of, or incidental to, any proceedings taken over by it, being costs payable by the plaintiff in those proceedings, other than those costs unreasonably incurred by the plaintiff.
(6) If the employer institutes, or takes over the conduct of, proceedings under this section, the employer may:
(a) subject to subsection (7), settle the proceedings, either with or without obtaining judgment; and
(b) if a judgment is obtained in the proceedings in favour of the plaintiff—take such steps as are necessary to enforce the judgment.
(7) The employer may only settle the proceedings:
(a) with the written consent of the employee or dependant in whose name the proceedings were instituted; or
(b) without the consent of the employee or dependant in whose name the proceedings were instituted if the employee or dependant withholds consent unreasonably.
(8) Subject to subsection (7), if the employer requires the employee or dependant to sign any document relevant to proceedings instituted or taken over by the employer under this section (including the settlement of the proceedings), the employee or dependant must sign it and, if he or she fails to do so, the court or tribunal in which the proceedings are taken may direct that the document may be signed on his or her behalf by a person appointed by the employer for the purpose.
(9) If the employer institutes, or takes over the conduct of, proceedings under this section, the employee or dependant must comply with any reasonable requirement of the employer for the purpose of the proceedings and, if the employee or dependant fails do so, the right of the employee or dependant to compensation under this Act in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death to which the proceedings
relate is suspended until such time as the employee or dependant complies with that requirement.
(10) If a right to compensation is suspended under subsection (9), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
(11) Any damages awarded under a judgment obtained in proceedings referred to in this section, or payable as a result of the settlement of such proceedings, must be paid to the employer and the employer must deduct from the amount of those damages:
(a) an amount equal to the total of all amounts of compensation paid to the employee or dependant under this Act in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death to which the proceedings relate; and
(b) the amount of any costs of or incidental to those proceedings paid by the employer;
and must pay the balance (if any) to the employee or dependant.
(12) If the employer pays an amount to an employee or dependant under subsection (11), the employee or dependant is not entitled to receive any further amounts of compensation under this Act in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death to which the proceedings related until the amount of compensation that would, apart from this subsection, have been payable to the employee or dependant in respect of the injury, loss, damage or death equals the amount paid by the employer to the employee or dependant under subsection (11).
(13) In this section:
“person” does not include the employer or an employee.
Payment of damages by persons to employer
60.(1) If a person appears to be liable:
(a) to pay damages to an employee in respect of an injury to the employee, or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee, being an injury, loss or damage in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act; or
(b) to pay damages to a dependant of a deceased employee in respect of the death of the employee, if that death resulted from an injury in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act;
the employer may, by notice in writing given to the person, require that:
(c) if the person agrees to pay damages to the employee in respect of the injury, loss or damage or to the dependant in respect of the death; or
(d) if damages against the person are awarded to the employee in the proceedings instituted in respect of the injury, loss or
damage, or to the dependant in proceedings instituted in respect of the death;
the person pay to the employer so much of the amount of the damages as does not exceed the amount that would be payable by the employee or dependant to the employer under section 58 if the damages had been paid to the employee or dependant.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), if:
(a) a person has agreed:
(i) to pay damages to an employee in respect of an injury to the employee, or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee, being an injury, loss or damage in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act; or
(ii) to pay damages to a dependant of a deceased employee in respect of the death of the employee, if that death resulted from an injury in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act; or
(b) damages against a person have been awarded:
(i) to an employee in proceedings instituted in respect of an injury to the employee or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee, being an injury, loss or damage in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act; or
(ii) to a dependant of a deceased employee in proceedings instituted in respect of the death of the employee, if that death resulted from an injury in respect of which an amount of compensation has been paid under this Act;
the employer may, by notice in writing given to the person, require the person to pay to the employer so much of the amount of the damages as does not exceed the amount that would have been payable by the employee or dependant to the employer under section 58 if the damages had been paid to or in respect of the employee or dependant.
(3) If, before a notice under subsection (2) was received by a person, the person had paid to or in respect of the employee or dependant, all or part of the damages to which the notice related:
(a) if all of the damages had been paid—the notice has no force or effect; or
(b) if part only of the damages had been paid—the reference in that subsection to the amount of the damages is to be read as a reference to so much of that amount as had not been paid.
(4) If a person fails to pay an amount to the employer in accordance with a notice under this section, the employer may recover that amount from the person as a debt due to the employer.
(5) Payment of an amount to the employer by a person in accordance with a notice under this section is, to the extent of the amount paid, a discharge of the liability of that person to the employee or dependant and of the liability (if any) of the employee or dependant to the employer under section 58.
(6) In this section:
“person” does not include the employer or an employee.
Compensation not payable both under Act and under award
61.(1) A person who would, apart from this section, be entitled to compensation under this Act and benefits under an award in respect of the same injury, or in respect of the same loss of, or damage to, property, is not entitled to both but must elect whether to receive the compensation or the benefits.
(2) An election made by an employee is irrevocable.
(3) If an employee makes an election to receive either compensation under this Act or benefits under the award but compensation is not payable under this Act, or benefits are not payable under the award, as the case may be, in respect of the injury, or the loss of, or damage to, property, the election has no effect.
(4) If an employee has made an election to receive compensation under this Act, that compensation is not payable unless the employee makes a claim under section 63.
(5) If an employee who has made an election dies, the election does not have effect in relation to his or her dependants.
(6) In this section:
“award” means an award, determination or order by which provision is made for, or in relation to, the grant of any benefits to or in relation to employees or their dependants in respect of injury or disease causing death or incapacity, or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property, in circumstances connected with the employment of those employees, being an award or order made under a law of the Commonwealth relating to conciliation and arbitration.
PART 5—NOTICES AND CLAIMS
Notice of injury or loss of, or damage to, property
62.(1) Subject to subsection (2), this Act does not apply to an injury suffered by an employee unless a written notice of the injury is given to the employer:
(a) as soon as practicable after the employee becomes aware of the injury; or
(b) if the employee dies without having become so aware or before it is practicable to serve such a notice—as soon as practicable after the employee’s death.
(2) This Act does not apply in relation to the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee, being loss or damage caused in circumstances referred to in section 27, unless a written notice of the accident that resulted in the loss or damage is given to the employer:
(a) as soon as practicable after the employee becomes aware that the accident had resulted in the loss or damage; or
(b) if the employee dies without having become so aware or before it is practicable to serve such a notice—as soon as practicable after the employee’s death.
(3) For the purposes of subsections (1) and (2), if the injury was suffered by an employee on a prescribed ship, a notice given to the master of the ship is taken to be given to the employer.
(4) If:
(a) a written notice, purporting to be a notice under this section, has been given to an employer; and
(b) the notice, or the giving of the notice, does not comply with this section;
the notice is taken to have been given under this section if:
(c) the employer to whom it was given would not thereby be prejudiced; or
(d) the non-compliance resulted from the death, or absence from Australia, of a person, or from ignorance, or mistake, or any other reasonable cause.
Claims for compensation
63.(1) Compensation is not payable to a person under this Act unless a claim for compensation is made by or on behalf of the person under this section.
(2) A claim must be made by giving the employer:
(a) a written claim, in accordance with a form approved by the Authority for the purposes of this paragraph; and
(b) except where the claim is for compensation under section 28, 29 or 30—a certificate by a legally qualified medical practitioner in accordance with the form approved by the Authority for the purposes of this paragraph; and
(c) a notice setting out:
(i) the name and address of any other employer who has been given, or to whom it is intended to give, a claim under paragraph (2)(a) in relation to the injury; and
(ii) the name and address of any other employer whose employment is believed to have materially contributed to the injury.
(3) If a written claim (other than a claim for compensation under section 28, 29 or 30) is given to a person under paragraph (2)(a) and the claim is not accompanied by a certificate of the kind referred to in paragraph (2)(b), the claim is taken not to have been made until such a certificate is given to that employer.
(4) Strict compliance with an approved form referred to in subsection (2) is not required and substantial compliance is sufficient.
Survival of claims
64.(1) If a person who is entitled to make a claim for compensation under this Act dies without making a claim, a claim may be made by the person’s legal personal representative.
(2) A claim is not affected by the death of the claimant after the claim was served.
(3) Section 134 applies to an amount payable under a determination made in respect of a claim referred to in this section as if the deceased person had died after the determination was made.
(4) This section does not apply to a claim for compensation under section 41.
Claims may not be made in certain cases
65. If an amount is paid to, or in accordance with the directions of, the Authority under subsection 29(3) or (4), for the benefit of a dependant of a deceased employee, by whom, or on whose behalf, a claim was made for compensation under section 29, no other dependant of that employee is entitled to claim compensation under that section after the day on which that amount is so paid.
Power to require medical examination
66.(1) If:
(a) a notice has been given under section 62 in relation to an injury to an employee; or
(b) an employee has made a claim for compensation under section 63;
the employer to whom the notice of claim is given may require the employee to undergo an examination by a legally qualified medical practitioner nominated by the employer.
(2) If an employee, without reasonable excuse, does not undergo an examination, or in any way obstructs an examination, the employee’s rights to compensation under this Act, and to institute or continue any proceedings under this Act in relation to compensation, are suspended until the examination takes place.
(3) If an employee’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (2), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
(4) An employer who requires an employee to undergo an examination under this section must pay the cost of the examination and is liable to pay to the employee:
(a) an amount equal to the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee in making a necessary journey in connection with the examination; and
(b) an amount equal to the expenditure reasonably incurred by the employee in remaining (if necessary), for the purpose of the examination, at a place to which the employee has made a journey for that purpose.
(5) Without limiting the matters that may be taken into account in deciding questions arising under subsection (4), the employer making the decision must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the means of transport available to the employee for the journey;
(b) the route or routes by which the employee could have travelled;
(c) the accommodation available to the employee.
(6) An employee must not be required to undergo an examination under this section at more frequent intervals than are specified by the Minister by written notice.
Power to request the provision of information relevant to claim
67.(1) Subject to section 69, if an employer who has been given a claim is satisfied that the claimant:
(a) has information or a document that is relevant to the claim; or
(b) may obtain such information or a copy of such a document without unreasonable expense or inconvenience;
the employer may, by written notice given to the claimant, ask the claimant to give the information, or a copy of the document, to the employer within 28 days after the date of the notice, or within such further period (if any) as the employer, on the request of the claimant, allows.
(2) A claimant who has received a notice under subsection (1) is taken to have complied with the notice if the claimant gives the employer the information, or a copy of the document specified in the notice, within 28 days after the date of the notice or within such further period (if any) as the employer has allowed.
(3) If a claimant, without reasonable excuse, does not comply with a notice under subsection (1), the employer may refuse to deal with the claim until the claimant gives the employer the information, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice.
Certain documents to be supplied on request
68.(1) Subject to section 69, an employer must not, without reasonable excuse, fail to comply with a written request by a claimant for the employer to give the claimant any documents held by the employer that relate to the claimant’s claim.
Penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) This section also applies to the determination of a request under section 40, and for that purpose:
(a) a reference to a claim is to be read as a reference to the request under that section; and
(b) a reference to the claimant is to be read as a reference to the person who made the request.
Neither section 67 nor 68 to affect legal professional privilege
69. Subject to section 70, neither section 67 nor 68 affects legal professional privilege.
Legal professional privilege not to apply to medical reports
70. Legal professional privilege does not apply in relation to a medical report in respect of an injury in relation to which an employee is claiming compensation under this Act.
Bankruptcy etc. of actual employer
71.(1) If:
(a) a claim in respect of an injury to an employee or in respect of the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee, has been made under section 63; and
(b) the Fund has become the employer of the employee because of subsection 4(3);
then:
(c) the claimant must give the Fund:
(i) a copy of any notices given to the actual employer in respect of the claim; or
(ii) new notices in respect of the claim; and
(d) section 72 or 73 applies as if the claim was given to the Fund on the day when:
(i) the copy of the claim was given to the Fund under subparagraph (1)(c)(i); or
(ii) a new claim notice was given to the Fund under subparagraph (1)(c)(ii).
(2) If:
(a) paragraph (1)(b) applies; and
(b) the actual employer has given a notice to the claimant under section 67; and
(c) the claimant has not given the information to the actual employer;
then the claimant must give the information to the Fund.
Time limit for determining claims relating to the death of an employee
72.(1) An employer must determine a claim for compensation under Division 2 of Part 2 by the later of the following times:
(a) the end of the period (“original 60-day period”) of 60 days after the employer receives the claim;
(b) if the employer, by written notice under section 67 served on the claimant within the original 60-day period, asks the claimant to give information, or a copy of a document—the end of the period of 60 days after the employer receives the information;
(c) if, at the written request of the employer, the Authority by written notice within the original 60-day period makes a decision allowing a period longer than the original 60-day period—the end of that longer period.
(2) If the employer has not determined the claim by the end of the period allowed by subsection (1), then, at the end of that period the employer is taken to have made a decision disallowing the claim.
(3) A request under paragraph (1)(c) must state fully and in detail the circumstances concerning, and the reasons for, the employer’s request for the Authority to allow a longer period than the original 60-day period.
Time limit for determining liability for claims relating to injuries to employees other than injuries resulting in death
73.(1) If the claim relates to an injury to an employee other than an injury resulting in death, the employee’s employer must determine its liability in relation to the claim for compensation by the later of the following times:
(a) the end of the period (“original 12-day period”) of 12 days after the employer receives the claim;
(b) if the employer, by written notice under section 67 served on the claimant, within the original 12-day period, asks the claimant to give information, or a copy of a document—the end of the period of 12 days after the employer receives the information;
(c) if, at the written request of the employer, the Authority by written notice within the original 12-day period makes a decision allowing a period longer than the original 12-day period—the end of that longer period.
(2) If the employer has not determined the claim by the end of the period allowed by subsection (1), then, at the end of that period the employer is taken to have made a decision disallowing the claim.
(3) If the injury under subsection (1) results in the employee being incapacitated for work, compensation is payable in respect of the claim for the incapacity from the day liability arose under section 31.
(4) If the injury under subsection (1) results in permanent impairment to the employee compensation is payable in accordance with section 39 or 40.
(5) A request under paragraph (1)(c) must state fully and in detail the circumstances concerning, and the reasons for, the employer’s request for the Authority to allow a longer period than the original 12-day period.
Employer may seek review of Authority’s decision
74. If an employer is dissatisfied with a decision of the Authority under paragraph 72(1)(c) or 73(1)(c), the employer may apply to the AAT for review of the decision.
Sections 72 to 74 (inclusive) not to apply to Authority if declaration made under section 100
75. If a declaration is made under section 100, sections 72 to 74 (inclusive) do not apply to the Authority.
PART 6—RECONSIDERATION OF DETERMINATIONS AND REVIEW OF DECISIONS BY THE ADMINISTRATIVE APPEALS TRIBUNAL
Division 1—Definitions
Interpretation
76.(1) In this Part:
“AAT” means the Administrative Appeals Tribunal;
“AAT Act” means the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975;
“AAT extension application” means an application under subsection 29(7) of the AAT Act that relates to a review of a reviewable decision or an extension of time decision;
“claimant” means a person in respect of whom a determination is made;
“decision” has the same meaning as in the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975;
“determination” means a determination, decision or requirement made by the employer under section 13, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 39, 40, 41, 43, 44, 45, 49, 50, 51, 66 or 126;
“extension of time decision” means a decision of the Authority under paragraph 72(1)(c) or 73(1)(c);
“reviewable decision” means a decision made under section 78.
(2) For the purposes of this Part, the parties to proceedings instituted under this Part are:
(a) the applicant; and
(b) where the applicant is not the claimant—the claimant; and
(c) the employer.
Division 2—Reconsideration of determinations by employers
Determinations to be notified in writing
77.(1) As soon as practicable after an employer makes a determination, the employer must cause to be served on the claimant a notice in writing setting out:
(a) the terms of the determination; and
(b) the reasons for the determination; and
(c) a statement to the effect that the claimant may, if dissatisfied with the determination, request a reconsideration of the determination under subsection 78(2).
(2) This section does not apply in relation to a determination under subsection 28(1) that compensation of an amount equal to the full amount of the cost of medical treatment obtained by an employee is payable if that amount of compensation is payable to a person other than the employee.
Reconsiderations of determinations
78.(1) An employer may, on the employer’s own initiative, reconsider a determination made by the employer, whether or not a proceeding has been instituted or completed under this Part in respect of a reviewable decision made in relation to that determination.
(2) A claimant may, by notice in writing given to an employer, request the employer to reconsider a determination made by the employer.
(3) A request for reconsideration of a determination must:
(a) set out the reasons for the request; and
(b) be given to the employer within 30 days after the day on which the determination first came to the notice of the claimant, or within such further period (if any) as the employer, either before or after the end of that 30 day period, allows.
(4) On receipt of a request, the employer must for the purposes of this section:
(a) if the employer is a party to a certified agreement that relates to industry panels—arrange for an industry panel; or
(b) in any other case—arrange with Comcare for a Comcare officer;
to assist the employer in reconsidering the determination under subsection (5).
(5) After making arrangements under paragraph (4)(a) or (b), the employer must, with the assistance of the industry panel or the Comcare officer, reconsider the determination.
(6) After an employer reconsiders a determination, the employer must make a decision affirming or revoking the determination or varying the determination in such manner as the employer thinks fit.
(7) In this section:
“certified agreement” has the same meaning as in the Industrial Relations Act 1988;
“industry panel” means an industry panel established under a certified agreement for the purposes of assisting the employer in reconsidering a determination under this section.
Time limit for reconsideration of determinations
79.(1) If a claimant requests an employer to reconsider a determination made by the employer, the employer must reconsider the determination before the later of the following times:
(a) the end of the period (“original 35-day period”) of 35 days after the employer receives the request;
(b) if the employer, by notice under section 83 served on the claimant within the original 35-day period, asks the claimant to give information, or a copy of a document—the end of the period of 35 days after the employer receives the information;
(c) if, at the written request of the employer, the Authority by written notice within the original 35-day period makes a decision allowing a period longer than the original 35-day period—the end of that longer period.
(2) If the employer has not determined the claim by the end of the period allowed by subsection (1), then, at the end of that period the employer is taken to have made a decision disallowing the claim.
(3) A request under paragraph (l)(c) must state fully and in detail the circumstances concerning, and the reasons for, the employer’s request for the Authority to allow a longer period than the original 35-day period.
Employer may seek review of Authority’s decision
80. If an employer is dissatisfied with a decision of the Authority under paragraph 79(1)(c), the employer may apply to the AAT for review of the decision.
Sections 79 and 80 not to apply to Authority if declaration made under section 100
81. If a declaration is made under section 100, sections 79 and 80 do not apply to the Authority.
Industry panel or Comcare to give copy of report to employer to claimant
82. The industry panel or Comcare, as the case requires, must give a copy of any report it gives to an employer in relation to the reconsideration of a determination under subsection 78(5) to the claimant.
Power to request the provision of information relevant to reconsideration
83.(1) Subject to section 84, if:
(a) a claimant has requested the employer to reconsider a determination under subsection 78(2); and
(b) the employer is satisfied that the claimant:
(i) has information or a document that is relevant to the claim; or
(ii) may obtain such information or a copy of such a document without unreasonable expense or inconvenience; the employer may, by written notice given to the claimant, ask the claimant to give the information or a copy of the document, to the employer within 28 days after the date of the notice, or within such further period (if any) as the employer, on the request of the claimant allows.
(2) A claimant who has received a notice under subsection (1) is taken to have complied with the notice if the claimant gives the employer the information, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice within 28 days after the date of the notice or within such further period (if any) as the employer has allowed.
(3) If a claimant, without reasonable excuse, does not comply with a notice under subsection (1), the employer may refuse to reconsider a determination under subsection 78(2) until the claimant gives the employer the information, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice.
Section 83 not to affect legal professional privilege
84. Subject to section 85, section 83 does not affect legal professional privilege.
Legal professional privilege not to apply to medical reports
85. Legal professional privilege does not apply in relation to a medical report in respect of an injury in relation to which an employee is claiming compensation under this Act.
Bankruptcy etc. of employer
86.(1) If:
(a) a claimant has given a notice under subsection 78(2) to the
actual employer within the period specified in subsection 78(3); and
(b) the Fund has become the employer because of subsection 4(3); then:
(c) the claimant must give the Fund:
(i) a copy of the notice given to the actual employer; or
(ii) a new notice under subsection 78(2); and
(d) section 72 or 73 applies as if the notice was given to the Fund on the day when:
(i) a copy of the notice was given to the Fund under subparagraph (1)(c)(i); or
(ii) a new notice was given to the Fund under subparagraph (1)(c)(ii); and
(e) subsection 78(3) does not apply.
(2) If:
(a) paragraph (1)(b) applies; and
(b) the actual employer has given a notice to the claimant under section 83; and
(c) the claimant has not given the information to the actual employer;
the claimant must give the information to the Fund.
Reviewable decision to be notified in writing
87. As soon as practicable after the employer makes a reviewable decision, the employer must cause to be served on the claimant a notice in writing setting out:
(a) the terms of the decision; and
(b) the reasons for the decision; and
(c) a statement to the effect that, subject to the AAT Act, application may be made to the AAT for review of the decision to which the notice relates.
Applications to the AAT
88.(1) Application may be made to the AAT by a claimant for review of a reviewable decision.
(2) Despite section 27 of the AAT Act, no person other than the claimant may make an application under subsection (1).
Division 3—AAT review of reviewable decisions and extension of time decisions
Modified AAT Act to apply
89.(1) The AAT Act applies in relation to:
(a) the review of reviewable decisions; and
(b) the review of extension of time decisions; and
(c) AAT extension applications;
subject to the modifications set out in this section.
(2) Section 24 of the AAT Act has effect as if the reference to any place in Australia or an external Territory were a reference to any place, whether within or outside Australia.
(3) Subsection 29(2) of the AAT Act has effect as if the reference to “the twenty-eighth day” (first occurring) were a reference to “the sixtieth day”.
(4) If:
(a) the AAT has not made a decision under section 43 of the AAT Act; and
(b) the Fund has become the employer of an employee because of subsection 4(3);
then:
(c) subsection 28(1) and paragraph 30(1)(b) of the AAT Act have effect as if a reference to the person who made the decision were a reference to the Fund; and
(d) the AAT must:
(i) if the AAT has begun hearing the proceedings but not completed the hearing of the proceedings—adjourn the proceedings for a period of at least 28 days beginning on the day the AAT becomes aware of the default event in relation to the actual employer; and
(ii) if the AAT has not begun hearing the proceedings—not begin hearing the matter for a period of at least 28 days beginning on the day the AAT becomes aware of the default event in relation to the actual employer.
Evidence in proceedings before AAT
90.(1) If:
(a) a claimant who has instituted proceedings under this Part seeks to adduce any matter in evidence before the AAT in those proceedings; and
(b) the claimant has not disclosed that matter to the AAT at least 28 days before the day fixed for the hearing of those proceedings;
that matter is not admissible in evidence in those proceedings without the leave of the AAT.
(2) If:
(a) an employer has determined a claim and, before doing so, gave the claimant a notice under section 67 or 83 requesting the claimant to give the employer the information, document or copy of the document, specified in the notice; and
(b) the claimant failed to comply with the notice; and
(c) the claimant had the information, document or copy, or could have obtained the information, document or copy without unreasonable expense or inconvenience before the determination was made;
the information, document or copy is not, without leave of the AAT, admissible in proceedings instituted under this Part in relation to the determination.
(3) The AAT must not give leave under subsection (2) unless:
(a) the claimant provides a statement of reasons why he or she failed to comply with a notice under section 67 or 83; and
(b) the AAT is satisfied that there are special circumstances justifying the admission of the information, document or copy in evidence.
Costs of proceedings before AAT—general
91.(1) Subject to this section, the costs incurred by a party to proceedings instituted under this Part in respect of that reviewable decision are to be borne by that party.
(2) Subject to this section, if proceedings instituted under this Part in respect of a reviewable decision relating to a determination are rendered abortive because a decision has been made, following a reconsideration under subsection 78(1), varying or revoking that determination, the employer is liable to reimburse the claimant for costs reasonably incurred by the claimant in connection with that proceeding.
(3) If:
(a) an employer has determined a claim (“original determination”); and
(b) the employer, before making that determination, gave the claimant a notice under section 67 or 83 requesting the claimant to give it the information specified in the notice (“relevant information”); and
(c) the claimant failed to comply with the notice; and
(d) at the time when the employer determined the claim, it did not have the relevant information and the relevant information was not reasonably available to the employer; and
(e) after the claim was determined, the claimant disclosed the relevant information to the employer or to the AAT; and
(f) the employer reconsidered the original determination under subsection 78(1) and made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the original determination; and
(g) the employer is satisfied that, if it had had the relevant information at the time when the original determination was
made, it would have made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the original determination; and (h) the employer would be liable under subsection (2), to reimburse the claimant for costs reasonably incurred by the claimant;
the employer may make a declaration in writing that subsection (2)
does not apply to those costs.
(4) If:
(a) an employer has determined a claim (“original determination”); and
(b) the employer, before making that determination, gave the claimant a notice under section 67 or 83 requesting the claimant to give that employer a document, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice (“relevant document”); and
(c) the claimant failed to comply with the notice; and
(d) at the time when the employer determined the claim, it did not have the information contained in the relevant document and that information was not reasonably available to that employer; and
(e) after the claim was determined, the claimant gave the document, or a copy of the document, or the information contained in the relevant document, to the employer or to the AAT; and
(f) the employer reconsidered the original determination under subsection 78(1), and made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the original determination; and
(g) the employer is satisfied that, if it had had the information contained in the relevant document at the time when the original determination was made, it would have made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the original determination; and
(h) the employer would be liable, under subsection (2), to reimburse the claimant for costs reasonably incurred by the claimant;
the employer may make a declaration, in writing, that subsection (2) does not apply in relation to those costs.
(5) An employer must give a copy of a declaration made by it under subsection (3) or (4) to the claimant.
(6) Application may be made to the AAT for a review of a decision by an employer to make a declaration under subsection (3) or (4).
Costs of proceedings before AAT—when costs payable by employer
92.(1) If, in any proceedings instituted by the claimant, the AAT makes a decision:
(a) varying a reviewable decision in a manner favourable to the claimant; or
(b) setting aside a reviewable decision and making a decision in substitution for the reviewable decision that is more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable decision;
the AAT may, subject to this section, order that the costs of those proceedings incurred by the claimant, or a part of those costs, are to be paid by the employer.
(2) If the AAT gives a decision setting aside a reviewable decision and remitting the case for re-determination by the employer, the AAT must, subject to this section, order that costs of the proceedings before it incurred by the claimant are to be paid by the employer.
(3) Neither subsection (1) nor (2) authorises the AAT to order an employer to pay any costs incurred by a claimant in relation to an application for an extension of time for applying to the AAT for a review of a reviewable decision.
(4) If, in any proceedings, the AAT varies or sets aside a reviewable decision, the AAT must not make an order under subsection (1) or (2) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings if:
(a) the employer, before making the reviewable decision, gave the claimant a notice under section 67 or 83 requesting the claimant to give the authority the information specified in the notice (“relevant information”); and
(b) the AAT is satisfied that:
(i) the claimant failed to comply with that notice; and
(ii) at the time when the employer made the reviewable decision, it did not have the relevant information, and the relevant information was not reasonably available to it; and
(iii) if the employer had had the relevant information at the time when it made the reviewable decision, it would have made a decision more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable decision.
(5) If, in any proceedings, the AAT varies or sets aside a reviewable decision, the AAT must not make an order under subsection (1) or (2) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings if:
(a) the employer, before making the reviewable decision, gave the claimant a notice under section 67 or 83 requesting the claimant to give the employer a copy of the document specified in the notice (“relevant document”); and
(b) the AAT is satisfied that:
(i) the claimant failed to comply with that order; and
(ii) at the time when the employer made the reviewable decision, it did not have the information contained in the relevant document, and that information was not reasonably available to it; and
(iii) if the employer had had the information contained in the relevant document at the time when it made the reviewable decision it would have made a decision more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable decision.
(6) If the AAT orders an employer to pay costs incurred by a claimant, the AAT may, in the absence of agreement between the parties as to the amount of the costs, tax or settle the amount of costs or order that the costs be taxed by the Registrar or a Deputy Registrar of the AAT.
PART 7— COMPULSORY INSURANCE AND THE FUND
Division 1—Compulsory insurance
Compulsory insurance
93.(1) Subject to subsection (2), an employer, other than the Fund, must on each day:
(a) have a policy of insurance or indemnity from an authorised insurer; or
(b) be a member of a protection and indemnity association that:
(i) is approved in writing by the Authority; and
(ii) is a member of the International Group of Protection and Indemnity Associations;
so that the employer is insured or indemnified for the full amount of the employer’s liability under this Act to all employees employed by the employer.
Penalty: 50 penalty units.
(2) A policy of insurance or indemnity, or the terms of membership of a protection and indemnity association, may require that an employer be liable in respect of an amount specified in the policy or terms of membership, as the case may be.
(3) An employer applying to an authorised insurer for the issue or renewal of a policy of insurance or indemnity against liability under this Act must give the insurer a full and correct statement of all salaries or wages paid to employees for the period relevant to working out the premium payable under the policy.
(4) In this section:
“authorised insurer” means a general insurance company under the Insurance Act 1973.
Employer to give details of insurance or indemnity arrangements to Authority
94. An employer must give the Authority the name and address of the authorised insurer or the protection and indemnity association within 14 days of:
(a) being issued with, or renewing, a policy of insurance or indemnity by or with an authorised insurer; or
(b) becoming a member of, or renewing membership of, a protection and indemnity association;
for the purposes of section 93.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Authority may require evidence from employer
95. The Authority may, by notice in writing, require an employer to provide within such reasonable time as is specified in the notice evidence of:
(a) a policy of insurance or indemnity; or
(b) membership of a protection and indemnity association; referred to in section 93.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Division 2—The Fund
The Fund
96. The Minister may, by notice published in the Gazette, approve a trading corporation to be the Fund for the purposes of this Act if the Minister thinks that the following conditions are satisfied in relation to the trading corporation:
(a) its participants represent not less than 80% of the seafarer berths on all prescribed ships;
(b) it has the management and resources to:
(i) quickly process and determine claims for compensation under this Act; and
(ii) develop and manage rehabilitation plans under this Act;
(c) subject to section 97, it has access to sufficient funds to enable the prompt settlement of all liabilities that might arise under this Act.
Fund to insure
97.(1) The Fund must on each day have a policy of insurance or indemnity from an authorised insurer for any amount of the Fund’s liability under this Act that exceeds the prescribed amount for a single event which results in an injury to one or more employees.
(2) Before advising the Governor-General about the making of a regulation prescribing an amount for this section, the Minister must consult the Fund and such organisations which represent employers or employees as the Minister thinks appropriate.
(3) A failure to consult as required by subsection (2) does not affect the validity of a regulation prescribing an amount for the purposes of this section.
(4) In this section:
“authorised insurer” means a general insurance company under the Insurance Act 1973.
Fund to provide Authority with financial information
98. The Fund must give the Authority such financial information as the Authority determines in writing and at such times as the Authority determines.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Minister may revoke approval under section 96
99. The Minister may revoke an approval under section 96:
(a) on the application of the trading corporation approved to be the Fund under section 96; or
(b) if the Minister thinks any of the conditions in section 96 are no longer satisfied; or
(c) if the Minister is satisfied that the Fund has not complied with section 97; or
(d) if the corporation ceases to be a trading corporation.
Division 3—Reserve function of Authority
Ministerial declaration
100. If the Minister:
(a) has not approved a trading corporation to be the Fund under section 96 before the day on which this Part commences; or
(b) has revoked the approval of a trading corporation under section 99;
the Minister may, by notice published in the Gazette, declare that the Authority is to have the Fund’s functions, powers and obligations under this Act.
Effect of Ministerial declaration
101. If the Minister makes a declaration under section 100, subsections 4(2) and (3) and 89(4) and sections 71, 86 and 129 apply as if the references to the Fund were references to the Authority.
Authority to insure if declaration made under section 100
102.(1) If a declaration is made under section 100, the Authority must:
(a) as soon as practicable after the making of the declaration obtain a policy of insurance or indemnity from an authorised insurer for any amount of the Authority’s liability under this Act that exceeds $1,000,000 for a single event which results in an injury to one or more employees; and
(b) have at all times after that time such a policy of insurance or indemnity.
(2) In this section:
“authorised insurer” means a general insurance company under the Insurance Act 1973.
PART 8—ADMINISTRATION AND FINANCE
Division 1—Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation Authority
Establishment
103. The Seafarers Rehabilitation and Compensation Authority is established.
Functions
104. Subject to this Act, the Authority has the following functions, in addition to its other functions under this Act:
(a) to monitor the operation of this Act;
(b) to promote high operational standards of claims management and effective rehabilitation procedures by employers;
(c) to co-operate with other bodies or persons with the aim of reducing the incidence of injuries to employees;
(d) to publish material relating to the functions referred to in paragraphs (a), (b) and (c);
(e) to advise the Minister about anything relating to the Authority’s functions and powers and other matters relating to the compensation and rehabilitation of employees.
Powers
105. The Authority has power to do all things necessary or convenient to be done for, or in connection with, the performance of its functions.
Power to obtain information
106.(1) Without limiting the generality of section 105, the Authority may, by notice in writing, require an employer to give the Authority, within such reasonable period as is specified in the notice, such documents or information (or both) as are specified in the notice, being documents or information in the possession or control of the employer that are relevant to the compilation of statistics for injury prevention purposes.
(2) Without limiting the generality of section 105, if a declaration is made under section 100 the Authority may, by notice in writing, require an employer to give the Authority, within such reasonable period as is specified in the notice, such documents or information (or
both) as are specified in the notice, being documents or information in the possession or control of the employer that are relevant to a claim made by, or in relation to, an employee of the employer.
(3) An employer must not without reasonable excuse fail to comply with a request made under subsection (1) or (2).
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
Directions by Minister
107.(1) Subject to subsection (2), the Minister may, by notice in writing given to the Chairperson, give a direction to the Authority with respect to the performance of its functions or the exercise of its powers.
(2) The Minister is not to give a direction under subsection (1) in relation to a particular case.
(3) The Authority must comply with a direction given under subsection (1).
Division 2—Constitution and Meetings of Authority
Authority is body corporate
108.(1) The Authority:
(a) is a body corporate with perpetual succession; and
(b) is to have a common seal; and
(c) may acquire, hold and dispose of real and personal property; and
(d) may sue and be sued in its corporate name.
(2) The common seal of the Authority is to be kept in such custody as the Authority directs and must not be used except as authorised by the Authority.
(3) All courts, judges and persons acting judicially must take judicial notice of the imprint of the common seal of the Authority appearing on a document and must presume that it was duly affixed.
(4) The Authority is not subject to any requirement, obligation, liability, penalty or disability under a law in force in a State or Territory to which the Commonwealth is not subject.
Constitution
109. The Authority comprises the following members:
(a) a Chairperson;
(b) a Deputy Chairperson;
(c) 2 members representing employers;
(d) 2 members representing employees.
Appointment of members
110.(1) The members are to be appointed by the Minister.
(2) The members referred to in paragraph 109(c) are to be appointed on the nomination of an organisation or organisations that the Minister is satisfied represents the interests of employers.
(3) The members referred to in paragraph 109(d) are to be appointed on the nomination of an organisation or organisations that the Minister is satisfied represents the interests of employees.
(4) A member is to hold office on a part-time basis.
Term of office
111.(1) The Chairperson and Deputy Chairperson are to hold office, subject to this Act, for such term, not exceeding 5 years, as is specified in the instrument of appointment, but are eligible for re-appointment.
(2) A member other than the Chairperson or Deputy Chairperson is to hold office, subject to this Act, for such term, not exceeding 3 years, as is specified in the instrument of appointment, but is eligible for re-appointment.
Deputies of members
112.(1) A member referred to in paragraph 109(c) or (d) may, with the approval of the Minister, appoint a person to be the deputy of that member.
(2) A member may revoke the appointment of his or her deputy but the revocation is not effective until the member has given written notice of the revocation to the Minister.
(3) A deputy is entitled, in the absence of the member who appointed him or her from a meeting of the Authority, to attend that meeting and, when so attending, is taken to be a member.
(4) A deputy may resign the office of deputy by delivering to the member who appointed him or her a signed notice of resignation.
(5) Anything done by or in relation to a deputy purporting to act under this section is not invalid merely because:
(a) there is a defect or irregularity in connection with the appointment; or
(b) the appointment had ceased to have effect; or
(c) the occasion for the deputy to act had not arisen or had ceased.
Persons acting as Chairperson or Deputy Chairperson
113.(1) The Minister may appoint a person to act as the Chairperson or the Deputy Chairperson:
(a) during a vacancy in the office of Chairperson or Deputy
Chairperson, whether or not an appointment has previously been made to the office; or
(b) during any period or during all periods when the Chairperson or the Deputy Chairperson is absent from duty or from Australia or is, for any other reason, unable to perform the duties of the office.
(2) Anything done by or in relation to a person purporting to act under an appointment under subsection (1) is not invalid merely because:
(a) the occasion for the appointment had not arisen; or
(b) there was a defect or irregularity in connection with the appointment; or
(c) the appointment had ceased to have effect; or
(d) the occasion to act had not arisen or had ceased.
Remuneration and allowances
114.(1) The Chairperson and Deputy Chairperson are to be paid such remuneration as is determined by the Remuneration Tribunal, but, if no such determination is in operation, the Chairperson and Deputy Chairperson are to be paid such remuneration as is prescribed.
(2) A member and the deputy of a member are to be paid such allowances as are prescribed.
(3) This section has effect subject to the Remuneration Tribunal Act 1973.
Leave of absence
115.(1) The Minister may grant the Chairperson leave to be absent from a meeting or meetings to the Authority.
(2) The Chairperson may grant another member leave to be absent from a meeting or meetings of the Authority.
Disclosure of interests
116.(1) A member who has a direct or indirect pecuniary interest in a matter being considered or about to be considered by the Authority must, as soon as possible after the relevant facts have come to his or her knowledge, disclose the nature of the interest at a meeting of the Authority.
(2) A disclosure must be recorded in the minutes of the meeting of the Authority and the member must not, unless the Minister or the Authority otherwise determines:
(a) be present during any deliberation of the Authority with respect to that matter; or
(b) take part in any decision of the Authority with respect to that matter.
(3) For the purpose of making a determination by the Authority under subsection (2) in relation to a member who has made a disclosure, a member who has a direct or indirect pecuniary interest in the matter to which the disclosure relates must not:
(a) be present during any deliberation of the Authority for the purpose of making the determination; or
(b) take part in the making by the Authority of the determination.
(4) In this section:
“member” includes a person who is acting in the office of a member.
Resignation
117. A member may resign by delivering to the Minister a signed notice of resignation.
Termination of appointment
118.(1) The Minister may terminate a member’s appointment for misbehaviour or physical or mental incapacity.
(2) If a member:
(a) becomes bankrupt, applies to take the benefit of any law for the relief of bankrupt or insolvent debtors, compounds with his or her creditors for their benefit or makes an assignment of his or her remuneration for their benefit; or
(b) contravenes section 116 without reasonable excuse; or
(c) is absent from 3 consecutive meetings of the Authority, except on leave of absence; or
(d) is a member referred to in paragraph 109(c) or (d) and the organisation that nominated the member requests, in writing, that the appointment be terminated;
the Minister may terminate the member’s appointment.
Meetings
119.(1) The Authority must meet as often as is necessary for the efficient performance of its functions but must meet at least once in the period of 3 months beginning on the day on which the Authority is established and at least once in each successive period of 3 months.
(2) A member may convene a meeting of the Authority.
(3) At a meeting of the Authority, 3 members form a quorum if:
(a) one of them is a member referred to in paragraph 109(a) or (b); and
(b) one of them is a member referred to in paragraph 109(c); and
(c) one of them is a member referred to in paragraph 109(d).
(4) Questions arising at a meeting of the Authority must be determined by the majority of the votes of the members present and voting at the meeting.
(5) If the Authority so determines, a resolution is taken to have been passed at a meeting of the Authority if, without meeting, a majority of the members who would, if present at a meeting and entitled to vote on the resolution at that meeting, have formed a quorum indicate agreement with the resolution in accordance with a method determined by the Authority.
(6) The Chairperson is to preside at all meetings of the Authority at which he or she is present.
(7) If the Chairperson is not present at a meeting of the Authority and the Deputy Chairperson is present at the meeting, the Deputy Chairperson is to preside at the meeting.
(8) If the Chairperson and Deputy Chairperson are not present at a meeting of the Authority, the members present must elect one of their number to preside.
(9) The member presiding at a meeting of the Authority has a deliberative vote and, if necessary, also has a casting vote.
(10) Subject to this section, the Authority may determine the procedure to be followed at its meetings.
Division 3—Finance
Application of Division 3 of Part XI of the Audit Act
120.(1) The Authority is hereby declared to be a public authority to which Division 3 of Part XI of the Audit Act 1901 applies.
(2) Subsection 63M(1) of the Audit Act 1901 applies in relation to the Authority as if:
(a) the reference in that subsection to 30 June in each year were a reference to 30 June 1993 and each following 30 June; and
(b) it required that the report prepared and submitted as soon as practicable after 30 June 1993 be a report of the Authority’s operations during the period commencing on the commencement of this Part and ending on the expiration of 30 June 1993.
(3) The Authority must, in each report prepared under section 63M of the Audit Act 1901 (as that section applies to the Authority because of this section) include particulars of each direction given by the Minister under section 107 during the period to which the report relates.
Money of Authority
121.(1) There is payable to the Authority such money as is appropriated by the Parliament for the purposes of the Authority.
(2) The Minister for Finance may give directions as to the amounts in which, and at the times at which, money referred to in subsection (1) is to be paid to the Authority.
(3) The money of the Authority is to be applied only:
(a) in payment or discharge of the expenses, charges, obligations and liabilities incurred or undertaken by the Authority in the performance of its functions and the exercise of its powers; and
(b) in payment of remuneration and allowances payable under this Act; and
(c) in making any other payments required or permitted to be made by the Authority.
(4) Money of the Authority not immediately required for the purposes of the Authority may be invested:
(a) on deposit with a bank that is an approved bank within the meaning of section 63J of the Audit Act 1901; or
(b) in securities of the Commonwealth; or
(c) in any other manner approved by the Treasurer.
Estimates of receipts and expenditure
122.(1) The Authority must prepare estimates, in such form as the Minister directs, of the receipts and expenditure of the Authority for each financial year and, if the Minister so directs, for any other period specified by the Minister, and submit those estimates to the Minister not later than such date as the Minister directs.
(2) The money of the Authority must not be expended otherwise than in accordance with estimates of expenditure approved by the Minister.
(3) A reference in this section to the receipts and expenditure of the Authority is taken not to include a reference to amounts of compensation paid or payable to, or in accordance with the directions of, the Authority under this Act.
Exemption from taxation
123. The Authority is not subject to taxation under any law of the Commonwealth or of a State or a Territory.
Borrowings
124.(1) The Authority may borrow money from the Commonwealth.
(2) The Treasurer must determine in writing the terms and conditions of loans made to the Authority under subsection (1).
(3) The Authority must not borrow money, except under this section, or otherwise raise money.
Division 4—Miscellaneous
Delegation by Authority
125.(1) The Authority may, by resolution, delegate its powers and functions to a person in the Department who holds, or performs the duties of:
(a) a Senior Executive office; or
(b) a Senior Officer Grade A, B or C.
(2) A delegation under this section:
(a) continues in force in spite of a change in the membership of the Authority; and
(b) may be varied or revoked by resolution of the Authority (whether or not constituted by the persons constituting the Authority at the time when the power or function was delegated).
(3) A certificate signed by the Chairperson stating any matter with respect to a delegation of a power or function under this section is prima facie evidence of that matter.
(4) A document purporting to be a certificate under subsection (3) is, unless the contrary is established, taken to be a certificate and to have been duly signed.
PART 9—MISCELLANEOUS
Employee to give information about prior employers
126.(1) An employer who has been given a claim under section 63 may, by written notice to the claimant, ask the claimant to give that employer within 28 days any information or document in the employee’s possession or control as to:
(a) the name; and
(b) the address;
of each employer by whom the employee was employed before the day on which the injury happened.
(2) If a claimant, without reasonable excuse, does not comply with a notice under subsection (1), the employer may refuse to deal with the claim until the claimant gives the employer the information, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice.
Determinations to be in writing
127.(1) A determination under this Act must be in writing.
(2) A determination is taken to be in writing if it is recorded with the use of a computer.
Shared liability
128. If:
(a) an injury suffered by an employee arises out of, or in the course of, the employee’s employment with more than one employer; and
(b) one of the employers has paid compensation to the employee in respect of the injury;
the employer who paid the compensation may, by an action in a court of competent jurisdiction, recover from the other employer or employers an amount equal to the compensation paid multiplied by the proportion of the contribution to the injury made by the employment of the other employer or employers.
Subrogation of rights of actual employer to Fund
129.(1) If:
(a) the Fund has become the employer of an employee because of subsection 4(3); and
(b) the Fund has paid an amount of money in respect of an employee in accordance with this Act; and
(c) the actual employer of the employee had a policy of insurance or indemnity with an insurer under section 93;
then:
(d) the Fund is subrogated to all of the actual employer’s rights and remedies in relation to the policy or insurance or indemnity, as the case may be; and
(e) the actual employer is not entitled to, and may not enforce payment of, the amount.
(2) If:
(a) the Fund has become the employer of an employee because of subsection 4(3); and
(b) the Fund has paid an amount of money in respect of an employee in accordance with this Act; and
(c) the actual employer of the employee was a member of a protection and indemnity association under section 93;
then:
(d) the Fund is subrogated to all of the actual employer’s rights and remedies in relation to the association.
Payment of compensation
130.(1) Subject to this section, an amount of compensation payable to a claimant under section 29, 39, 40 or 41, must be paid to the claimant within 30 days after the date of the determination of the amount.
Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(2) If an amount of compensation is not paid to a claimant in accordance with subsection (1), interest is payable to the claimant on that amount in respect of the period beginning at the end of the period of 30 days referred to in that subsection and ending on the day the amount is paid.
(3) Interest payable under subsection (2) must be paid at such rate as is from time to time specified by the Minister for the purposes of this section by notice in writing.
(4) This section does not apply if:
(a) an employer has been requested under Part 6 to reconsider a determination under section 78; or
(b) the Administrative Appeals Tribunal has been requested under Part 6 to review a determination under section 88; or
(c) a proceeding in respect of such a determination has been instituted under Part 6.
Employee to notify other employers that compensation has been paid
131. If an employer pays the full amount of compensation payable under this Act to an employee in respect of an injury the employee must notify all other employers against whom a claim was made that the employee has received compensation in respect of the injury.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
Recovery of compensation payments
132. If an amount of compensation is due and payable under this Act, the claimant may recover the amount from the employer as a debt.
Money paid for benefit of person
133.(1) Any money payable under this Act to a person under a legal disability must be paid to, or in accordance with the directions of, the Authority for the benefit of the person and, when so paid, is taken to have been paid to the person.
(2) If money is held by the Authority for the benefit of a person, the Authority must, subject to subsections (4) and (5), invest the money in any manner for the time being allowed for the investment of trust money by an Act, or by a State or Territory enactment.
(3) Income resulting for an investment of money under subsection (2) is taken to form part of that money.
(4) The Authority may pay any money held by it for the benefit of a person to, or in accordance with the directions of, the person or apply the money in such manner as it thinks fit, for the benefit of the person.
(5) If money is held by the Authority for the benefit of a person under a legal disability, the Authority must, when the person stops being under a legal disability, pay the money to, or in accordance with the directions of, the person or, if the money has been invested, deal with the investments in accordance with the directions of the person.
Provisions applicable on death of beneficiary
134.(1) Subject to subsection (3), if:
(a) a determination is made that an amount of compensation is payable under this Act to a person; and
(b) the person dies before the amount is paid; the amount forms part of the person’s estate.
(2) Subject to subsection (4), if the Authority holds any money or investments for the benefit of a person under this Act and that person dies, that money or those investments form part of the person’s estate.
(3) If a person referred to in subsection (1) dies intestate and nobody is apparently entitled to claim the person’s estate (including that amount of compensation):
(a) subsection (1) does not apply; and
(b) subject to subsection (5), the compensation will not be paid.
(4) If a person referred to in subsection (2) dies intestate and nobody is apparently entitled to claim the person’s estate (including that money or those investments):
(a) subsection (2) does not apply; and
(b) subject to subsection (5), the Authority must pay the money, or realise the investments and pay the proceeds of the realisation, as the case may be, to the Commonwealth.
(5) Any provision of this section may be made inoperative, in a particular case, as a result of a decision made on a review of a determination under this Act.
Assignment, set-off or attachment of compensation
135.(1) An assignment of any compensation payable under this Act is void as against the employer or the Authority.
(2) Except as provided by this Act, an amount payable by an employee or a dependant of a deceased employee to an employer or the Fund must not be set-off against the amount of any compensation payable under this Act to the employee or for the benefit of the dependant.
(3) Except as provided by the Child Support Act 1988 or by regulations under the Family Law Act 1975, compensation payable under this Act is not subject to attachment.
Recovery of overpayments
136.(1) If:
(a) an amount of compensation under this Act has been paid to a person by an employer as a result of a false or misleading statement or representation, or in consequence of a failure to comply with a provision of this Act; or
(b) an amount of compensation that has been paid to a person by an employer under this Act should not have been paid; or
(c) a person is liable to pay an amount to an employer under this Act;
the amount concerned is recoverable from the person by the employer as a debt.
(2) If:
(a) an amount is recoverable from a person under subsection (1); and
(b) an amount is payable under this Act to, or for the benefit of, that person;
the recoverable amount may be deducted from the amount so payable.
Employees on compensation leave
137. Despite any other Act, or any award, an employee is not entitled to be granted any kind of leave with pay (other than maternity leave with pay) during, or in respect of, any period when the employee is or was on compensation leave, but long service leave entitlements continue to accrue in relation to the employee in accordance with the applicable award, determination or certified agreement.
Double benefits
138.(1) If State workers’ compensation is paid to, or for the benefit of, anyone for:
(a) an injury suffered by an employee or deceased employee; or
(b) for the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee; compensation is not payable under this Act for that injury, loss or damage.
(2) If:
(a) an employer has paid compensation to, or for the benefit of, anyone under this Act for an injury suffered by an employee or a deceased employee, or for the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee; and
(b) State workers’ compensation is paid to, or for the benefit of, that person for the injury, loss or damage;
the employer may recover an amount equal to that compensation mentioned in paragraph (a) from the person to whom it was paid as a debt.
(3) A person who has been given a claim may ask the claimant to give the person a statutory declaration stating whether any State workers’ compensation has been paid to the claimant, or to anyone else, for the injury, loss or damage to which the claim relates.
(4) If a claimant, without reasonable excuse, does not give a statutory declaration under subsection (3), the claimant’s rights to compensation
under this Act for the injury, loss or damage to which the claim relates, and to institute or continue any proceedings under this Act in relation to that compensation, are suspended until the declaration is given.
(5) If a claimant’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (4), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
(6) In this section:
“State workers’ compensation” means compensation recoverable under a law of a State or a Territory relating to workers’ compensation.
Compensation where State compensation payable
139.(1) If State compensation is paid to, or for the benefit of, anyone for:
(a) an injury suffered by an employee or a deceased employee; or
(b) the loss of, or damage to, property used by an employee;
the compensation payable under this Act to, or for the benefit of, that person for the injury, loss or damage is the amount (if any) worked out using the formula:
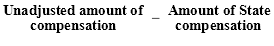
where:
“Unadjusted amount of compensation” means the amount of compensation that would, apart from this subsection, be payable under this Act to, or for the benefit of, the person for the injury, loss or damage;
“Amount of State compensation” means the amount of State compensation paid to, or for the benefit of, the person.
(2) If:
(a) an employer pays compensation under this Act to, or for the benefit of, anyone for an injury suffered by an employee, or a deceased employee, or for the loss of, or damage to, property used by the employee; and
(b) State compensation is later paid to, or for the benefit of, the same person for that injury, loss or damage;
the person is liable to pay to the employer an amount equal to:
(c) the amount of the compensation paid under this Act; or
(d) the amount of the State compensation;
whichever is less.
(3) If:
(a) a person (“the debtor”) is liable to pay an amount to a employer under this section; and
(b) the employer, or anyone else, holds on behalf of the debtor:
(i) an amount of compensation payable under this Act for the benefit of the debtor; or
(ii) an amount of State compensation payable to the debtor; or
(iii) investments acquired out of such compensation;
the employer or other person must:
(c) deduct from the amount so held, or realise those investments so held and deduct from the proceeds of the realisation, an amount that is not more than the amount referred to in paragraph (a); and
(d) pay the amount so deducted to the employer.
(4) The payment of an amount to an employer under subsection (3) is, to the extent of the amount paid, a discharge of:
(a) the liability of the debtor to the employer; and
(b) the liability of the other person to the debtor.
(5) A reference in subsection (2) to compensation under this Act that was paid for the benefit of a person does not include a reference to compensation paid under subsection 29(5).
(6) If the whole or part of the State compensation referred to in subsection (1) received by, or on behalf of, a person did not relate to an injury, loss or damage, for which compensation is payable under this Act, this section has effect in relation to that person as if the person had received, by way of State compensation, an amount equal to so much (if any) of the amount of compensation the person actually received as did relate to such an injury, loss or damage.
(7) In this section:
“specified law” means a law of a State or a Territory that provides for the payment of compensation, other than workers’ compensation, and is declared by the Minister, by written notice, to be a specified law for the purposes of this section;
“State compensation” means compensation recoverable under a specified law.
Notice of departure from Australia etc.
140.(1) This section applies to a person to whom payments of compensation under section 31 are being made, and have been made for a period of 3 months or longer, by a employer.
(2) If the person proposes to leave Australia (whether or not he or she intends to return), the person may give the employer a written notice:
(a) stating that the person proposes to leave Australia; and
(b) specifying the day on which the person proposes to leave.
(3) If the person has left Australia (whether or not he or she proposes to return) without giving a notice under subsection (2), the person must, within 7 days after the day on which he or she left Australia, send the employer a written notice:
(a) stating that the person has left Australia; and
(b) specifying the day on which the person did so.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
(4) If the person is absent from Australia for longer than 3 months, the person must:
(a) within 7 days after the end of the period of 3 months starting on the day on which the person left Australia; and
(b) within 7 days after the end of each successive period of 3 months (if any) that ends while the person is still absent from Australia;
give the employer, as the case requires, a written notice setting out particulars of the person’s residential address on the day on which the notice is given.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
Comcare may charge for officer’s services provided to employer
141.(1) Comcare may charge an employer the prescribed fee for the provision of a Comcare officer’s services for the purposes of section 78.
(2) The regulations may make provision for the recovery of such fees as are prescribed for the provision of a Comcare officer’s services for the purposes of section 78.
Disallowable instruments
142. A notice in writing under paragraph 10(1)(b), subsection 44(3), 66(6), 130(3) or 139(7) is a disallowable instrument for the purposes of section 46A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Regulations
143. The Governor-General may make regulations, not inconsistent with this Act, prescribing all matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed; or
 (b) necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
(b) necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.
[Minister’s second reading speech made in—
House of Representatives on 14 October 1992
Senate on 5 November 1992]