An Act to provide rehabilitation, compensation and other entitlements for veterans, members and former members of the Defence Force, and for other purposes
Chapter 1—Introduction
1 Short title
This Act may be cited as the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 2004.
2 Commencement
(1) Each provision of this Act specified in column 1 of the table commences, or is taken to have commenced, in accordance with column 2 of the table. Any other statement in column 2 has effect according to its terms.
Commencement information |
Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
Provision(s) | Commencement | Date/Details |
1. Sections 1 and 2 and anything in this Act not elsewhere covered by this table | The day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent. | 27 April 2004 |
2. Sections 3 to 359 | A single day to be fixed by Proclamation. However, if any of the provision(s) do not commence within the period of 6 months beginning on the day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent, they commence on the first day after the end of that period. | 1 July 2004 (see Gazette 2004, GN22) |
3. Sections 360 to 385 | The day on which this Act receives the Royal Assent. | 27 April 2004 |
4. Sections 386 to 440 | At the same time as the provision(s) covered by table item 2. | 1 July 2004 |
Note: This table relates only to the provisions of this Act as originally passed by the Parliament and assented to. It will not be expanded to deal with provisions inserted in this Act after assent.
(2) Column 3 of the table contains additional information that is not part of this Act. Information in this column may be added to or edited in any published version of this Act.
3 Simplified outline of this Act
This Act provides for compensation and other benefits to be provided for current and former members of the Defence Force who suffer a service injury or disease. The Act also provides for compensation and other benefits to be provided for the dependants of some deceased members.
Before most benefits can be paid or provided, the Commission must accept liability for an injury, disease or death of a current or former member under Chapter 2. Chapters 3 to 6 set out what the benefits are.
The procedure for dealing with claims under this Act is dealt with under Chapters 7 and 8. The Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission and the administration of the Act are dealt with in Chapters 9 to 11.
Provisions in this Act might be affected by the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation (Consequential and Transitional Provisions) Act 2004.
A person who is entitled to a benefit under this Act might also be entitled to a pension, allowance or other benefit under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986. This might include the following:
(a) a service pension under Part III of that Act;
(b) treatment under Part V of that Act;
(c) veterans supplement, a Victoria Cross allowance or Income Support Supplement;
(d) a funeral benefit.
Note: Under section 203 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986, the Minister may enter into an arrangement with a foreign country providing for the making of payments that are, or the provision of treatment or rehabilitation that is, comparable to payments or treatment or rehabilitation under this Act.
4 Extension to external Territories
This Act extends to every external Territory.
4A Secretary may arrange for use of computer programs to make decisions or determinations
(1) The Secretary may arrange for the use, under the Secretary’s control, of computer programs for any purposes for which the Commission may, or must, under this Act or a legislative instrument made for the purposes of this Act:
(a) make a decision or determination; or
(b) exercise any power or comply with any obligation; or
(c) do anything else related to making a decision or determination or exercising a power or complying with an obligation.
(1A) Subsection (1) does not apply to the following:
(a) a decision or determination that the death of a person is not a service death;
(b) a decision or determination that an injury sustained by a person is not a service injury;
(c) a decision or determination that a disease contracted by a person is not a service disease.
(2) For the purposes of this Act or the legislative instrument, the Commission is taken to have:
(a) made a decision or determination; or
(b) exercised a power or complied with an obligation; or
(c) done something else related to the making of a decision or determination or the exercise of a power or the compliance with an obligation;
that was made, exercised, complied with or done by the operation of a computer program under an arrangement made under subsection (1).
Substituted decisions or determinations
(3) The Commission may, under a provision of this Act or of the legislative instrument, make a decision or determination in substitution for a decision or determination the Commission is taken to have made under paragraph (2)(a) if the Commission is satisfied that the decision or determination made by the operation of the computer program is incorrect.
Note: For review of a determination made in substitution, see Chapter 8.
(4) Subsection (3) does not limit Chapter 8 (about reconsideration and review of determinations).
5 Definitions
(1) In this Act:
actual earnings:
(a) in Part 3 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by subsection 89(3); and
(b) in Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by subsection 132(1).
aggravated injury or disease means an injury or disease that is a service injury or disease because of paragraph 27(d), subsection 29(2) or section 30 (aggravations etc.) (and only because of that paragraph, subsection or section).
appointed Commission member means a Commission member described in paragraph 364(1)(b).
approved program provider has the meaning given by section 41.
approved rehabilitation program has the meaning given by section 41.
attendant care services has the meaning given by section 213.
Australian Defence Force Cadets has the meaning given by the Defence Act 1903.
Board means the Veterans’ Review Board constituted under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
cadet means a member of the Australian Defence Force cadets.
child: without limiting who is a child of a person for the purposes of this Act, someone is the child of a person if he or she is a child of the person within the meaning of the Family Law Act 1975.
civilian work means work other than as a member of the Defence Force.
claimant means a person who has made a claim under section 319.
clean energy bonus under an Act or scheme means any of the following that is provided for by the Act or scheme:
(b) a payment known as an energy supplement or a quarterly energy supplement;
(c) an increase that is described using the phrase “energy supplement” and affects the rate of another payment that is provided for by the Act or scheme.
clean energy payment means energy supplement.
clean energy underlying payment means:
(a) compensation under Part 2 of Chapter 4 (whether weekly compensation or a lump sum); or
(b) Special Rate Disability Pension; or
(c) compensation under Division 2 of Part 2 of Chapter 5 (whether weekly compensation or a lump sum).
Comcare means the body corporate established by section 68 of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988.
Commission means the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission established by section 361.
Commission Chair means the Chair of the Commission.
Commission member means a member of the Commission (including the Commission Chair).
Commonwealth superannuation scheme means:
(aa) for the purposes of the following provisions:
(i) sections 89A and 89B;
(ii) Division 7 of Part 3 of Chapter 4;
(iii) sections 416 to 418 (to the extent to which they relate to compensation under Part 3 of Chapter 4);
any superannuation scheme under which or to which, or retirement savings account to which, the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority makes contributions on behalf of employees (other than members of the Defence Force) and includes a superannuation scheme established or maintained by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority and the Australian Defence Force Cover Act 2015; or
(a) if a person’s normal earnings are worked out (or would be worked out if the person had not chosen a Special Rate Disability Pension) under:
(i) Subdivision D of Division 4 of Part 4 of Chapter 4; or
(ii) Division 5 of Part 4 of Chapter 4; or
(iia) sections 126 and 126A;
(iii) Subdivision D of Division 8 of Part 4 of Chapter 4;
any superannuation scheme under which or to which, or retirement savings account to which, the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority makes contributions on behalf of employees (other than members of the Defence Force) and includes a superannuation scheme established or maintained by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority and the Australian Defence Force Cover Act 2015; or
(b) otherwise—any superannuation scheme under which the Commonwealth makes contributions on behalf of members of the Defence Force or the Australian Defence Force Cover Act 2015.
Note: Section 14 affects the operation of paragraph (a) of this definition.
compensable treatment has the meaning given by section 289.
compensation means compensation under this Act, including the following:
(a) alterations provided, or aids and appliances provided or repaired, under section 56;
(b) a Special Rate Disability Pension under Part 6 of Chapter 4;
(c) MRCA supplement under section 221, 245 or 300;
(d) education or training provided under the education scheme mentioned in Division 6 of Part 3 of Chapter 5;
(e) treatment provided under Chapter 6;
(f) clean energy payments.
continuous full‑time Reservist means a member of the Reserves on continuous full‑time service.
continuous full‑time service (CFTS) means defence service of a continuous nature that is rendered by a member of the Reserves.
date of the member’s death for a deceased member means the date determined under section 343 for the member.
deceased member means a person:
(a) who has died; and
(b) who was a member or former member before his or her death.
declared member means a person to whom a determination under section 8 applies.
Defence Department means the Department of State that deals with defence and that is administered by the Defence Minister.
Defence Force means:
(a) the Permanent Forces; and
(b) the Reserves.
Defence Minister means the Minister administering section 1 of the Defence Act 1903.
defence service has the meaning given by paragraph 6(1)(d).
dental practitioner means a person registered or licensed as a dental practitioner or dentist under a law of a State or Territory that provides for the registration or licensing of dental practitioners or dentists.
dependant has the meaning given by section 15.
dependent means dependent for economic support.
disease means:
(a) any physical or mental ailment, disorder, defect or morbid condition (whether of sudden onset or gradual development); or
(b) the recurrence of such an ailment, disorder, defect or morbid condition;
but does not include:
(c) the aggravation of such an ailment, disorder, defect or morbid condition; or
(d) a temporary departure from:
(i) the normal physiological state; or
(ii) the accepted ranges of physiological or biochemical measures;
that results from normal physiological stress (for example, the effect of exercise on blood pressure) or the temporary effect of extraneous agents (for example, alcohol on blood cholesterol levels).
duty, for a cadet or a declared member, has the meaning given by section 9.
Note: Duty has its ordinary meaning for other kinds of members.
eligible young person means:
(a) a person under 16; or
(b) a person who:
(i) is 16 or more but under 25; and
(ii) is receiving full‑time education at a school, college, university or other educational institution; and
(iii) is not in full‑time employment or engaged in work full‑time on his or her own account.
energy supplement means energy supplement payable under section 83A, 209A or 238A.
expense allowance means an allowance paid in respect of any expense incurred, or likely to be incurred, by a person in respect of the person’s work.
former member means a person who has ceased to be a member.
Note: A cadet or a part‑time Reservist who is unlikely to be able to perform his or her duties in the future as a result of an incapacity might be taken to be a former member (see section 10).
full‑time service means defence service as:
(a) a Permanent Forces member; or
(b) a continuous full‑time Reservist.
hospital or other institution includes the following:
(a) a home;
(b) a hostel;
(c) a medical centre;
(d) an out‑patient clinic;
(e) a rehabilitation or training establishment.
household services has the meaning given by section 213.
impairment, in relation to a person, means the loss, the loss of the use, or the damage or malfunction, of any part of the person’s body, of any bodily system or function, or of any part of such a system or function.
impairment points of a person means the points worked out for the person using the guide determined under section 67.
incapacitated person:
(a) in Division 5 of Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 152; and
(b) in Division 6 of Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 160; and
(c) in Division 7 of Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 163; and
(d) in Division 8 of Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 166.
incapacitated Reservist:
(a) in Division 3 of Part 3 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 94; and
(b) in Division 4 of Part 3 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 103; and
(c) in Division 5 of Part 3 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by section 107.
incapacity for service, in relation to a person who has sustained an injury or contracted a disease, means an incapacity of the person to engage in the defence service that he or she was engaged in before the onset of the incapacity, at the same level at which he or she was previously engaged.
Note: For example, a person might be unable to engage in defence service at the same level at which he or she was engaged before the incapacity because the person is unable to perform all of his or her previous duties or is unable to work his or her normal weekly hours.
incapacity for service or work means incapacity for service or incapacity for work.
incapacity for work, in relation to a person who has sustained an injury or contracted a disease, means:
(a) an incapacity of the person to engage in the work that he or she was engaged in before the onset of the incapacity, at the same level at which he or she was previously engaged; or
(b) if the person was not previously engaged in work, an incapacity of the person to engage in any work that it is reasonably likely that he or she would otherwise be engaged in.
Note: For example, a person might be unable to engage in work at the same level at which he or she was engaged before the incapacity because the person is unable to perform all of his or her previous duties or is unable to work his or her normal weekly hours.
indexation year means the financial year commencing on 1 July 2003, and each subsequent financial year.
initial training for a person means:
(a) for an officer (other than a non‑commissioned officer)—training undertaken to become a commissioned officer; and
(b) otherwise—recruit training and initial employment training undertaken to allocate the person to a category of defence work.
injury means any physical or mental injury (including the recurrence of a physical or mental injury) but does not include:
(a) a disease; or
(b) the aggravation of a physical or mental injury.
legal personal representative means:
(a) the executor of the will, or the administrator of the estate, of a deceased person; or
(b) the trustee of the estate of a person under a legal disability; or
(c) a person who holds an enduring power of attorney granted by another person; or
(d) a person who, by order of a court or otherwise, has the legal administration or control of the affairs of another person.
medical aid of a person means an artificial limb or other artificial substitute, or a medical, surgical or other similar aid or appliance, that is used by the person.
medical practitioner means a person registered or licensed as a medical practitioner under a law of a State or Territory that provides for the registration or licensing of medical practitioners.
member means:
(a) a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) a cadet; or
(ba) a person to whom section 7A applies; or
(c) a declared member.
non‑warlike service has the meaning given by paragraph 6(1)(b).
normal earnings:
(a) in Part 3 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by subsection 89(3);
(b) in Part 4 of Chapter 4—has the meaning given by subsection 132(2).
normal weekly hours has the meaning given by subsection 132(2).
onset date, for a person’s incapacity for service or work, means the date determined under section 342 for the person.
overtime includes:
(a) time spent performing duties on shifts or on Saturdays, Sundays or other holidays; and
(b) excess travelling time;
that does not count towards the average number of hours worked.
parent: without limiting who is a parent of a person for the purposes of this Act, someone is the parent of a person if the person is his or her child because of the definition of child in this subsection.
partner of a member means a person in respect of whom at least one of the following applies:
(a) if the member is a member of the Aboriginal race of Australia or a descendant of Indigenous inhabitants of the Torres Strait Islands—the person is recognised as the member’s husband or wife by the custom prevailing in the tribe or group to which the member belongs;
(b) the person is legally married to the member;
(ba) a relationship between the person and the member (whether the person and the member are the same sex or different sexes) is registered under a law of a State or Territory prescribed for the purposes of section 2E of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 as a kind of relationship prescribed for the purposes of that section;
(c) the person (whether of the same sex or a different sex to the member):
(i) is, in the Commission’s opinion (see subsection (2)), in a de facto relationship with the member; and
(ii) is not an ancestor, descendant, brother, sister, half‑brother or half‑sister of the member (see subsection (3)).
Note: This section also applies to former members (see section 20).
part‑time Reservist means a member of the Reserves who is not on continuous full‑time service.
pay‑related allowance means an allowance specified in a determination under section 11.
peacetime service has the meaning given by paragraph 6(1)(c).
pension age has the meaning given by subsection 23(5A), (5B), (5C) or (5D) of the Social Security Act 1991.
Permanent Forces has the same meaning as in the Defence Act 1903.
Permanent Forces member means a member of the Permanent Forces.
pharmaceutical benefits has the same meaning as in section 91 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
pharmaceutical benefits determination: see subsection 286(3).
practising lawyer means a person who is admitted to the legal profession by a federal court or a Supreme Court of a State or Territory and who holds a practising certificate (however described) entitling the person to practise that profession.
practitioner means a person:
(a) who is a medical practitioner; or
(b) who is a dental practitioner.
registered charity means an entity that is registered under the Australian Charities and Not‑for‑profits Commission Act 2012 as the type of entity mentioned in column 1 of item 1 of the table in subsection 25‑5(5) of that Act.
rehabilitation authority has the meaning given by section 39.
rehabilitation program has the meaning given by section 41.
Repatriation Commission means the body corporate continued in existence by section 179 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
Repatriation Medical Authority means the body corporate established under section 196A of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
Reserves has the same meaning as in the Defence Act 1903.
retirement savings account means a retirement savings account within the meaning of the Retirement Savings Accounts Act 1997.
Secretary means Secretary of the Department.
service death has the meaning given by section 28 and subsection 29(3).
service disease has the meaning given by section 27, subsections 29(1) and (2) and section 30.
Note: A reference to a service disease being contracted includes a reference to a disease being aggravated by defence service (see section 7).
service injury has the meaning given by section 27, subsections 29(1) and (2) and section 30.
Note: A reference to a service injury being sustained includes a reference to an injury being aggravated by defence service (see section 7).
service injury, disease or death means a service injury, a service disease or a service death.
service injury or disease means a service injury or a service disease.
Special Rate Disability Pension has the meaning given by section 198.
SRC Minister means the Minister administering Division 3 of Part VII of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988.
Statement of Principles means a Statement of Principles made under section 196B of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
stepchild: without limiting who is a stepchild of a person for the purposes of this Act, someone who is a child of a partner of the person is the stepchild of the person, if he or she would be the person’s stepchild except that the person is not legally married to the partner.
step‑parent: without limiting who is a step‑parent of a person for the purposes of this Act, someone who is a partner of a parent of the person is the step‑parent of the person, if he or she would be the person’s step‑parent except that he or she is not legally married to the person’s parent.
suitable work for a person means work for which the person is suited having regard to the following:
(a) the person’s age, experience, training, language and other skills;
(b) the person’s suitability for rehabilitation or vocational retraining;
(c) if work is available in a place that would require the person to change his or her place of residence—whether it is reasonable to expect the person to change his or her place of residence;
(d) any other relevant matter.
treatment has the meaning given by section 13.
treatment determination: see subsection 286(4).
Tribunal means the Administrative Appeals Tribunal.
trust funds, in respect of a trustee of payments of compensation, means the following:
(a) the amounts of compensation received by the trustee;
(b) interest on those amounts;
(c) investments of the compensation or interest;
(d) returns received on those investments.
Veterans’ Affairs Minister means the Minister administering the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
vocational assessment and rehabilitation has the meaning given by section 41.
warlike service has the meaning given by paragraph 6(1)(a).
wholly dependent partner of a deceased member means a person:
(a) who was the partner of the member immediately before his or her death; and
(b) who was wholly dependent on the member at that time.
Note: A partner who was living with a deceased member immediately before the member’s death is taken to have been wholly dependent on the partner (see section 17).
work means work for financial gain or reward (whether as an employee, a self‑employed person or otherwise).
(2) For the purposes of subparagraph (c)(i) of the definition of partner in subsection (1), section 11A of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 applies to the forming of the Commission’s opinion about whether a person and a member are in a de facto relationship.
(3) For the purposes of subparagraph (c)(ii) of the definition of partner in subsection (1), a child who is, or has ever been, an adopted child of a person is taken to be the natural child of that person and the person is taken to be the natural parent of the child.
6 Kinds of service to which this Act applies
(1) In this Act:
(a) warlike service means service with the Defence Force that is of a kind determined in writing by the Defence Minister to be warlike service for the purposes of this Act; and
(b) non‑warlike service means service with the Defence Force that is of a kind determined in writing by the Defence Minister to be non‑warlike service for the purposes of this Act; and
(c) peacetime service means any other service with the Defence Force; and
(d) defence service means warlike service, non‑warlike service or peacetime service.
Note: The determination may be varied or revoked (see subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), service with the Defence Force means:
(a) for a cadet—participation in the activities of the Australian Defence Force cadets; and
(b) for a declared member—engagement in, or performance of, activities or acts specified in the determination under section 8 that applies to the member.
7 Reference to service injury sustained or service disease contracted includes reference to aggravation etc.
To avoid doubt, a reference to a service injury being sustained, or a service disease being contracted, at a particular time includes a reference to an injury or disease that is aggravated, or materially contributed to, by defence service at such a time.
7A Classes of members
For the purposes of paragraph (ba) of the definition of member in subsection 5(1), this section applies to the following:
(a) a person who holds an honorary rank or appointment in the Defence Force and who performs acts at the request or direction of the Defence Force;
(b) a person who performs acts at the request or direction of the Defence Force as an accredited representative of a registered charity (where the accreditation is by the Defence Force);
(c) a person who is receiving assistance under the Career Transition Assistance Scheme established under a determination under section 58B of the Defence Act 1903 and who performs acts in connection with the scheme.
8 Ministerial determinations that other people are members
(1) The Defence Minister may make a written determination that a person, or a class of persons, who engage, or have engaged, in activities, or who perform, or have performed, acts:
(a) at the request or direction of the Defence Force; or
(b) for the benefit of the Defence Force; or
(c) in relation to the Defence Force, under a requirement made by or under a Commonwealth law;
are taken to be, or to have been, members for the purposes of this Act.
Note: The determination may be varied or revoked (see subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) The determination must specify:
(a) the date (which may be retrospective) from which the determination applies; and
(b) the person, or class of persons, to whom the determination applies; and
(c) the activities or acts, or classes of activities or acts, to which the determination applies.
(3) The date referred to in paragraph (2)(a) must be, or be after, the date on which this section commences.
(4) A determination, or a variation or revocation of a determination, is a legislative instrument.
9 Definition of duty for cadets and declared members
In this Act:
duty:
(a) for a cadet—means participation in an activity mentioned in paragraph 6(2)(a); and
(b) for a declared member—means engagement in or performance of an activity or act specified in the determination that applies to the member, as mentioned in paragraph 6(2)(b).
Note: Duty has its ordinary meaning for other kinds of members.
10 Determinations for part‑time Reservists and cadets who are unlikely to return to defence service
Determination that part‑time Reservist unlikely to return to defence service
(1) If a claim for compensation has been made under section 319 in respect of a part‑time Reservist, the Chief of the Defence Force may advise the Commission in writing if the Reservist is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a part‑time Reservist in the future as a result of his or her incapacity.
Determination that cadet unlikely to return to defence service
(2) If a claim for compensation has been made under section 319 in respect of a cadet, the commanding officer of the cadet’s unit (within the meaning of the Cadet Forces Regulations 1977) may advise the Commission in writing if the cadet is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a cadet in the future as a result of his or her incapacity.
Person taken to have ceased to be a member
(3) If the Commission is given an advice in respect of a person under subsection (1) or (2), the person is taken to have ceased to be a member for the purposes of this Act.
Advice to specify the date
(4) The advice must specify the date (which must not be retrospective) from which the person is taken to have ceased to be a member for the purposes of this Act.
11 Ministerial determination of pay‑related allowances
(1) The Defence Minister must make a written determination specifying which allowances that are paid under a determination made under section 58B or 58H of the Defence Act 1903 are pay‑related allowances for the purposes of this Act.
Note: The determination may be varied or revoked (see subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) A determination, or a variation or revocation of a determination, is a legislative instrument.
12 Deceased members whose dependants are entitled to benefits under this Act
Deceased member whose death was a service death
(1) This section applies in respect of a deceased member if the Commission has accepted liability for the member’s death.
Note: A dependant of a deceased member in respect of whom this section applies might be entitled to compensation under Chapter 5 or 6.
Deceased members eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension
(2) This section applies in respect of a deceased member if the member satisfied the eligibility criteria in section 199 (persons who are eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension) during some period of his or her life.
Deceased members with 80 impairment points
(3) This section applies in respect of a deceased member if the Commission has determined under Part 2 of Chapter 4 that the impairment suffered by the deceased member before the member’s death, as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases, constituted 80 or more impairment points.
13 Definition of treatment
(1) In this Act:
treatment means treatment provided, or action taken, with a view to:
(a) restoring a person to physical or mental health or maintaining a person in physical or mental health; or
(b) alleviating a person’s suffering; or
(c) ensuring a person’s social well‑being.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), treatment includes:
(a) providing accommodation in a hospital or other institution, or providing medical procedures, nursing care, social or domestic assistance or transport; and
(b) supplying, renewing, maintaining and repairing artificial replacements, medical aids and other aids and appliances; and
(c) providing diagnostic and counselling services;
for the purposes of, or in connection with, any treatment.
14 Definition of Commonwealth superannuation scheme for a person who has chosen a Special Rate Disability Pension
For the purposes of paragraph (a) of the definition of Commonwealth superannuation scheme in section 5, the normal earnings of a person who has chosen a Special Rate Disability Pension would be worked out under Subdivision D of Division 4 or 8 of Part 4 of Chapter 4 if the amount worked out under that Subdivision is greater than the amount worked out under Subdivision C of Division 4 or 8 of Part 4 of Chapter 4.
15 Definition of dependant
(1) A dependant of a member means any person mentioned in subsection (2):
(a) who is wholly or partly dependent on the member; or
(b) who would be wholly or partly dependent on the member but for an incapacity of the member that resulted from an injury or disease or an aggravation of an injury or disease.
Note 1: Sections 17 and 18 set out some examples of when a person is wholly dependent on a member.
Note 2: This section also applies to former members (see section 20).
(2) These are the persons who can be a dependant of a member for the purposes of subsection (1):
(a) any of the following persons:
(i) the member’s partner;
(ii) a parent or step‑parent of the member;
(iii) a parent or step‑parent of the member’s partner;
(iv) a grandparent of the member;
(v) a child or stepchild of the member;
(vi) a child or stepchild of the member’s partner;
(vii) a grandchild of the member;
(viii) the member’s brother, sister, half‑brother or half‑sister; or
Note: This paragraph is affected by section 16.
(b) a person in respect of whom the member stands in the position of a parent; or
(c) a person who stands in the position of a parent to the member.
16 Certain relationships
(1) For the purposes of paragraph 15(2)(a), if one person is the child of another person because of:
(a) adoption; or
(b) the definition of child in this Act;
relationships traced to or through the person are to be determined on the basis that the person is the child of the other person.
(2) For the purposes of paragraphs 215(f) and 218(g), the relatives of a person are taken to include the following (without limitation):
(a) a partner of the person;
(b) a stepchild or an adopted child of the person, or someone of whom the person is a stepchild or an adopted child;
(c) someone who is a child of the person, or someone of whom the person is a child, because of the definition of child in this Act;
(d) anyone else who would be a relative of the person if someone mentioned in paragraph (a), (b) or (c) is taken to be a relative of the person.
17 When partners and eligible young persons are wholly dependent on a member
Partners
(1) For the purposes of this Act, the partner of a member is taken to be wholly dependent on the member if:
(a) the partner lives with the member; or
(b) the Commission is of the opinion that the partner would be living with the member but for a temporary absence of the member or partner or but for an absence of the member or partner due to illness or infirmity.
Note: This subsection also applies to former members (see section 20).
Eligible young persons
(2) For the purposes of this Act, an eligible young person is taken to be wholly dependent on a member if:
(a) either:
(i) the young person lives with the member; or
(ii) the Commission is of the opinion that the young person would be living with the member but for a temporary absence of the member or young person or but for an absence of the member or young person due to illness or infirmity; or
(b) the member is liable to provide child support under the Child Support (Assessment) Act 1989 for the young person.
Note: This subsection also applies to former members (see section 20).
18 Child of a member born or adopted after the member’s death
(1) For the purposes of this Act, a child of a deceased member who is born alive after the member’s death:
(a) is taken to have been wholly dependent on the member immediately before the member’s death; and
(b) is taken to have been an eligible young person immediately before the member’s death.
Note: A deceased member may be a member or former member at the time of his or her death (see the definition of deceased member in section 5).
(2) For the purposes of this Act, if, before a deceased member’s death, a member begins adoption proceedings to adopt a child, and the proceedings are finalised after the member’s death, the child:
(a) is taken to have been wholly dependent on the member immediately before the member’s death; and
(b) is taken to have been an eligible young person immediately before the member’s death.
Note: A deceased member may be a member or former member at the time of his or her death (see the definition of deceased member in section 5).
19 Ascertaining whether persons receiving family tax benefits etc. are dependent
For the purposes of ascertaining whether a person is or was dependent on a member, any amount of the following benefits must not be taken into account:
(a) family tax benefit worked out under Part 2 or 3 of Schedule 1 to the A New Tax System (Family Assistance) Act 1999 (an individual’s Part A rate);
(b) carer’s allowance under the Social Security Act 1991;
(c) double orphan pension under the Social Security Act 1991.
Note: This section also applies to former members (see section 20).
20 Some references to members include references to former members
For the purposes of the definition of partner in section 5, and for the purposes of sections 15, 17 and 19, a reference to a member includes a reference to a former member.
Chapter 2—Accepting liability for service injuries, diseases and deaths
Part 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
21 Simplified outline of this Chapter
A condition for most benefits under this Act is that the Commission has accepted liability for an injury, disease or death. The Commission accepts liability if there is some connection between the injury, disease or death and defence service.
The process for deciding whether to accept liability is as follows:
(a) first, a person makes a claim under section 319 for acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death (the rules for making claims are found in Chapter 7);
(b) then, the Commission decides whether the injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death under Part 3;
(c) then, the Commission decides whether it is prevented from accepting liability for the injury, disease or death because of an exclusion under Part 4 (for example, because the injury, disease or death resulted from a serious default or a wilful act).
The Commission must accept liability if the injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death, and none of the exclusions in Part 4 apply.
The effect of this Chapter in respect of cadets and declared members might be modified by the regulations (see section 439).
Part 2—When the Commission must accept liability for service injuries, diseases and deaths
22 Simplified outline of this Part
The Commission accepts liability for an injury, disease or death under this Part.
The Commission must accept liability if a claim for acceptance of liability has been made under section 319, the injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death, and none of the exclusions in Part 4 apply.
There are 2 standards of proof that the Commission applies in deciding matters under this Chapter (and the rest of the Act).
The more beneficial standard of proof (in subsections 335(1) and (2)) applies to some claims that an injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death that relates to warlike or non‑warlike service. The other standard of proof (in subsection 335(3)) applies to all other decisions under this Chapter.
For some claims for acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death the standard of proof can only be met if the injury or disease, or the cause of death, is covered by a Statement of Principles (see sections 338 and 339). (Chapter 7 has more rules about the Statements of Principles.)
A Statement of Principles is an instrument made under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986. The Statement sets out all factors related to defence service that have been found to cause specific injuries, diseases and deaths.
For other claims for acceptance of liability, the Statements of Principles are not relevant.
23 Commission’s acceptance of liability for service injuries and diseases
When Commission must accept liability for service injuries and diseases
(1) The Commission must accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) the person’s injury or disease is a service injury or disease under section 27; and
(b) the Commission is not prevented from accepting liability for the injury or disease by Part 4; and
(c) a claim for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The standard of proof mentioned in subsections 335(1) and (2) applies to claims that the injury or disease is a service injury or disease that relates to warlike or non‑warlike service.
Note 2: The standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) applies to the following:
(a) claims that the injury or disease is a service injury or disease that relates to peacetime service;
(b) all claims when determining whether a person sustained a particular injury or contracted a particular disease;
(c) all claims when determining whether the Commission is prevented from accepting liability for the injury or disease by Part 4.
When Commission must accept liability for service injuries and diseases arising from Commonwealth treatment
(2) The Commission must accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) the person’s injury or disease is a service injury or disease under section 29 (arising from treatment provided by the Commonwealth); and
(b) a claim for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease has been made under section 319.
Note: The standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) applies to all claims:
(a) that an injury or disease is a service injury or disease under section 29; and
(b) when determining whether a person sustained a particular injury or contracted a particular disease.
When Commission must accept liability for service injuries and diseases arising from aggravations of signs and symptoms
(3) The Commission must accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) the person’s injury or disease is a service injury or disease under section 30 (aggravations etc. of signs and symptoms); and
(b) the Commission is not prevented from accepting liability for the injury or disease by Part 4; and
(c) a claim for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The standard of proof mentioned in subsections 335(1) and (2) applies to claims that the injury or disease is a service injury or disease that relates to warlike or non‑warlike service.
Note 2: The standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) applies to the following:
(a) claims that an injury or disease is a service injury or disease that relates to peacetime service; and
(b) all claims when determining whether a sign or symptom was aggravated etc.; and
(c) all claims when determining whether the Commission is prevented from accepting liability for the injury or disease by Part 4.
Acceptance of liability for aggravations etc. of injuries and diseases
(4) A reference in this section to acceptance of liability for an injury or disease is taken to include a reference to acceptance of liability for an aggravation of an injury or disease.
Note: The definitions of injury and disease exclude aggravations (see section 5).
24 Commission’s acceptance of liability for service deaths
When Commission must accept liability for service deaths
(1) The Commission must accept liability for the death of a person if:
(a) the person’s death is a service death under section 28; and
(b) the Commission is not prevented from accepting liability for the death by subsection 34(4) or section 35 or 36; and
(c) a claim for acceptance of liability for the death has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The standard of proof mentioned in subsections 335(1) and (2) applies to claims that the death is a service death that relates to warlike or non‑warlike service.
Note 2: The standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) applies to the following:
(a) claims that the death is a service death that relates to peacetime service;
(b) all claims when determining whether a person sustained or contracted a particular injury or disease;
(c) all claims when determining the cause of a person’s death;
(d) all claims when determining whether the Commission is prevented from accepting liability for the death by subsection 34(4) or section 35 or 36.
When Commission must accept liability for service deaths arising from Commonwealth treatment
(2) The Commission must accept liability for the death of a person if:
(a) the person’s death is a service death under section 29 (service death arising from treatment provided by the Commonwealth); and
(b) a claim for acceptance of liability for the death has been made under section 319.
Note: The standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) applies to all claims:
(a) that a death is a service death under section 29; and
(b) when determining the cause of a person’s death.
Commission must accept liability for deaths after being prevented from accepting liability for the injury or disease that resulted in the death
(3) To avoid doubt, the Commission must accept liability for a service death even if the Commission was prevented by section 32 or 33 from accepting liability for a service injury or disease that resulted in the death.
Note: Sections 32 and 33 only prevent the Commission from accepting liability for a service injury or disease, and not a service death.
25 Limited effect of acceptance of liability
The Commission’s acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death only has effect for the purposes of this Act.
Note: This means that a person cannot rely on the Commission’s acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death in a common law action against the Commonwealth.
Part 3—Definitions of service injury, service disease and service death
26 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part defines service injury, service disease and service death.
An injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death if:
(a) it is related to defence service in the ways mentioned in section 27 or 28; or
(b) it resulted from certain treatment provided by the Commonwealth (see section 29); or
(c) an aggravation of, or a material contribution to, a sign or symptom of the injury or disease relates to defence service (see section 30).
However, even if an injury, disease or death is a service injury or disease under this Part, the Commission might be prevented from accepting liability for the injury, disease or death by an exclusion under Part 4.
27 Main definitions of service injury and service disease
For the purposes of this Act, an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person is a service injury or a service disease if one or more of the following apply:
(a) the injury or disease resulted from an occurrence that happened while the person was a member rendering defence service;
(b) the injury or disease arose out of, or was attributable to, any defence service rendered by the person while a member;
(c) in the opinion of the Commission:
(i) the injury was sustained due to an accident that would not have occurred; or
(ii) the disease would not have been contracted;
but for:
(iii) the person having rendered defence service while a member; or
(iv) changes in the person’s environment consequent upon his or her having rendered defence service while a member;
(d) the injury or disease:
(i) was sustained or contracted while the person was a member rendering defence service, but did not arise out of that service; or
(ii) was sustained or contracted before the commencement of a period of defence service rendered by the person while a member, but not while the person was rendering defence service;
and, in the opinion of the Commission, the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree by, or was aggravated by, any defence service rendered by the person while a member after he or she sustained the injury or contracted the disease;
Note: This paragraph might not cover aggravations of, or material contributions to, signs and symptoms of an injury or disease (see Repatriation Commission v Yates (1995) 38 Administrative Law Decisions 80). This is dealt with in section 30.
(e) the injury or disease resulted from an accident that occurred while the person was travelling, while a member rendering peacetime service but otherwise than in the course of duty, on a journey:
(i) to a place for the purpose of performing duty; or
(ii) away from a place of duty upon having ceased to perform duty.
28 Main definition of service death
Definition of service death
(1) For the purposes of this Act, the death of a person is a service death if one or more of the following apply:
(a) the death resulted from an occurrence that happened while the person was a member rendering defence service;
(b) the death arose out of, or was attributable to, any defence service rendered by the person while a member;
(c) in the opinion of the Commission, the death was due to:
(i) an accident that would not have occurred; or
(ii) a disease that would not have been contracted;
but for:
(iii) the person having rendered defence service while a member; or
(iv) changes in the person’s environment consequent upon his or her having rendered defence service while a member;
(d) the injury or disease from which the person died:
(i) was sustained or contracted while the person was a member rendering defence service, but did not arise out of that service; or
(ii) was sustained or contracted before the commencement of a period of defence service rendered by the person while a member, but not while the person was rendering defence service;
and, in the opinion of the Commission, the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree by, or was aggravated by, any defence service rendered by the person while a member after he or she sustained the injury or contracted the disease;
(e) the injury or disease from which the person died is an injury or disease that has been determined under section 27, 29 or 30 to be a service injury or a service disease, as the case may be;
Note 1: The effect of this paragraph is that, if the person has died from an injury or disease that has already been determined by the Commission to be a service injury or disease, the death is a service death. Accordingly, the Commission is not required to relate the death to defence service rendered by the person and sections 338 and 339 do not apply.
Note 2: This paragraph does not apply to certain aggravations etc. of injuries and diseases (see subsection (2)).
(f) the death resulted from an accident that occurred while the person was travelling, while a member rendering peacetime service but otherwise than in the course of duty, on a journey:
(i) to a place for the purpose of performing duty; or
(ii) away from a place of duty upon having ceased to perform duty.
Aggravations etc. that cease before death
(2) Paragraph (1)(e) does not apply if:
(a) the service injury or disease mentioned in that paragraph is an aggravated injury or disease; and
(b) immediately before the death, the injury or disease was no longer aggravated or contributed to in a material degree.
29 Definitions of service injury, service disease and service death arising from treatment provided by the Commonwealth
Liability for injuries and diseases caused by treatment
(1) For the purposes of this Act, an injury (the relevant injury) sustained, or a disease (the relevant disease) contracted, by a person is a service injury or a service disease if:
(a) all of the following apply:
(i) the person receives treatment for an earlier service injury or service disease;
(ii) the treatment is paid for or provided wholly or partly by the Commonwealth;
(iii) as a consequence of that treatment, the person sustains the relevant injury or contracts the relevant disease; or
(b) the person receives any treatment under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903 for an earlier injury or disease that is not a service injury or service disease and as an unintended consequence of that treatment, the person sustains the relevant injury or contracts the relevant disease.
Liability for injuries and diseases aggravated by treatment
(2) For the purposes of this Act, an injury (the relevant injury) sustained, or a disease (the relevant disease) contracted, by a person is a service injury or a service disease if:
(a) all of the following apply:
(i) the person receives treatment for an earlier service injury or service disease;
(ii) the treatment is paid for or provided wholly or partly by the Commonwealth;
(iii) as a consequence of that treatment, the relevant injury or relevant disease, or a sign or symptom of the relevant injury or relevant disease, is aggravated by the treatment; or
(b) the person receives any treatment under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903 for an earlier injury or disease that is not a service injury or service disease and, as an unintended consequence of that treatment, the relevant injury or relevant disease, or a sign or symptom of the relevant injury or relevant disease, is aggravated by the treatment.
Liability for deaths caused by treatment
(3) For the purposes of this Act, the death of a person is a service death if:
(a) either:
(i) the person receives treatment under this Act for a service injury or disease and the treatment is paid for or provided wholly or partly by the Commonwealth; or
(ii) the person receives any treatment under regulations made under the Defence Act 1903; and
(b) as a consequence of that treatment, the person dies.
30 Definitions of service injury and service disease for aggravations etc. of signs and symptoms
For the purposes of this Act, an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person is a service injury or a service disease if:
(a) the injury or disease:
(i) was sustained or contracted while the person was a member rendering defence service, but did not arise out of that service; or
(ii) was sustained or contracted before the commencement of a period of defence service rendered by the person while a member, but not while the person was rendering defence service; and
(b) in the opinion of the Commission, a sign or symptom of the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree by, or was aggravated by, any defence service rendered by the person while a member after he or she sustained the injury or contracted the disease.
Part 4—When the Commission is prevented from accepting liability for service injuries, diseases and deaths
31 Simplified outline of this Part
Even if the Commission decides that an injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death, the Commission might be prevented from accepting liability for that injury, disease or death because of an exclusion under this Part.
There are 5 kinds of exclusions. They relate to the following:
(a) serious defaults or wilful acts etc.;
(b) reasonable counselling about a person’s performance as a member;
(c) false representations;
(d) travel during peacetime service;
(e) the use of tobacco products.
The Commission applies the standard of proof mentioned in subsection 335(3) in deciding whether the exclusions apply.
32 Exclusions relating to serious defaults or wilful acts etc.
Exclusion of injuries or diseases resulting from serious default or wilful acts etc.
(1) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) the injury or disease resulted from the person’s serious default or wilful act while a member; or
(b) the injury or disease arose from:
(i) a serious breach of discipline committed by the person while a member; or
(ii) an occurrence that happened while the person was committing a serious breach of discipline while a member; or
(c) the injury or disease was intentionally self‑inflicted while the person was a member;
except if the injury or disease results in serious and permanent impairment.
(2) For the purpose of paragraph (1)(a), an injury or disease is taken to have resulted from a person’s serious default or wilful act if:
(a) the person consumed alcohol or took a drug (other than a drug administered by a person legally authorised to administer the drug or a drug legally obtained and taken in accordance with the directions provided with the drug); and
(b) the injury or disease resulted from being under the influence of the alcohol or drug.
This subsection does not otherwise limit paragraph (1)(a).
Exclusion of aggravations etc. resulting from serious default etc.
(3) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) the injury or disease has been contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the material contribution or aggravation:
(i) resulted from the serious default or wilful act of the person while a member; or
(ii) arose from a serious breach of discipline committed by the person while a member; or
(iii) arose from an occurrence that happened while the person was committing a serious breach of discipline while a member; or
(iv) was intentionally self‑inflicted while the person was a member;
except if the aggravation or material contribution results in serious and permanent impairment.
Exclusion of aggravations etc. of signs or symptoms resulting from serious default etc.
(4) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if:
(a) a sign or symptom of the injury or disease has been contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the material contribution or aggravation:
(i) resulted from the serious default or wilful act of the person while a member; or
(ii) arose from a serious breach of discipline committed by the person while a member; or
(iii) arose from an occurrence that happened while the person was committing a serious breach of discipline while a member; or
(iv) was intentionally self‑inflicted while the person was a member;
except if the aggravation or material contribution results in serious and permanent impairment.
(5) For the purpose of subparagraph (3)(b)(i) or (4)(b)(i), a material contribution or aggravation is taken to have resulted from a person’s serious default or wilful act if:
(a) the person consumed alcohol or took a drug (other than a drug administered by a person legally authorised to administer the drug or a drug legally obtained and taken in accordance with the directions provided with the drug); and
(b) the material contribution or aggravation results from being under the influence of the alcohol or drug.
This subsection does not otherwise limit subparagraph (3)(b)(i) or (4)(b)(i).
33 Exclusions relating to reasonable counselling about performance etc.
Injuries or diseases resulting from reasonable counselling about performance etc.
(1) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person if the injury or disease resulted from:
(a) reasonable and appropriate counselling in relation to the person’s performance as a member; or
(b) a failure to obtain a promotion, transfer or benefit in relation to the person’s service as a member.
Aggravations etc. of injuries or diseases resulting from reasonable counselling about performance etc.
(2) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a member if:
(a) the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the material contribution or aggravation resulted from:
(i) reasonable and appropriate counselling in relation to the person’s performance as a member; or
(ii) a failure to obtain a promotion, transfer or benefit in relation to the person’s service as a member.
Aggravations etc. of signs and symptoms of injuries or diseases resulting from reasonable counselling about performance etc.
(3) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a member if:
(a) a sign or symptom of the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the material contribution or aggravation resulted from:
(i) reasonable and appropriate counselling in relation to the person’s performance as a member; or
(ii) a failure to obtain a promotion, transfer or benefit in relation to the person’s service as a member.
34 Exclusions of injuries, diseases and deaths relating to certain false representations
Injuries or diseases
(1) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, if the person made a wilful and false representation, in connection with his or her defence service or proposed defence service, that he or she did not suffer, or had not previously suffered, from that injury or disease.
Aggravations etc. of injuries or diseases
(2) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, if:
(a) the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the person made a wilful and false representation, in connection with his or her defence service or proposed defence service, that he or she did not suffer, or had not previously suffered, from that injury or disease.
Aggravations etc. of signs and symptoms of injuries or diseases
(3) The Commission must not accept liability for an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, if:
(a) a sign or symptom of the injury or disease was contributed to in a material degree, or aggravated, by defence service; and
(b) the person made a wilful and false representation, in connection with his or her defence service or proposed defence service, that he or she did not suffer, or had not previously suffered, from that injury or disease.
Deaths
(4) The Commission must not accept liability for the death of a person if the person made a wilful and false representation, in connection with his or her defence service or proposed defence service, that he or she did not suffer, or had not previously suffered, from the injury or disease that resulted in his or her death.
35 Exclusions relating to travel
Commission not to accept liability for injuries etc. resulting from certain peacetime accidents
(1) This section only applies in respect of an injury, disease or death of a person that relates to peacetime service rendered by the person as a member.
Note: This section applies if the injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death because of the application of any of sections 27, 28 and 30 (not only paragraphs 27(e) and 28(1)(f)).
(2) The Commission must not accept liability for:
(a) an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, or the death of a person; or
(b) an injury or a disease that has been aggravated, or materially contributed to; or
(c) an injury or disease, a sign or symptom of which has been aggravated, or materially contributed to;
if the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution resulted from the kinds of accidents mentioned in subsection (3), (4) or (5).
Substantial delay commencing journey
(3) The Commission must not accept liability if the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution resulted from an accident that occurred while the person was a member travelling on a journey from the person’s place of duty if the person delayed commencing the journey for a substantial time after he or she ceased to perform duty at that place, unless:
(a) the delay was for a reason connected with the performance of the person’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution occurring was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
by that delay or by anything that happened during that delay.
Routes that are not reasonably direct
(4) The Commission must not accept liability if the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution resulted from an accident that occurred while the person was a member travelling on a journey, or a part of a journey, by a route that was not reasonably direct having regard to the means of transport used, unless:
(a) the journey, or that part of the journey, was made by that route for a reason connected with the performance of the person’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution occurring was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
by reason that the journey, or that part of the journey, was made by that route.
Substantial interruptions to journeys
(5) The Commission must not accept liability if the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution resulted from an accident that occurred while the person was a member travelling on a part of a journey made after a substantial interruption of the journey, unless:
(a) the interruption was made for a reason connected with the performance of the person’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution occurring was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
by reason of that interruption.
36 Exclusion relating to use of tobacco products
The Commission must not accept liability for:
(a) an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, or the death of a person; or
(b) an injury or a disease that has been aggravated, or materially contributed to; or
(c) an injury or disease, a sign or symptom of which has been aggravated, or materially contributed to;
if the injury, disease, death, aggravation or material contribution is related to defence service only because of the person’s use of tobacco products.
Chapter 3—Rehabilitation
Part 1—General provisions
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
37 Simplified outline of this Chapter
This Chapter provides for the following for certain current and former members suffering a service injury or disease:
(a) rehabilitation programs;
(b) assistance in finding suitable defence or civilian work;
(c) assistance in moving from defence service to civilian life.
The capacity for rehabilitation of a person with a service injury or disease is assessed under Part 2. If the person is capable of rehabilitation, he or she may be required to undertake a rehabilitation program under that Part.
Part 2 also provides for rehabilitation for certain persons who have made a claim for acceptance of liability by the Commission for a service injury or disease, where the claim has not been determined.
Under Part 3, a person who is undertaking a rehabilitation program, or a person who cannot undertake a program, can have his or her home or place of work etc. altered or an aid or appliance provided.
All members and former members who are incapacitated for service or work are assisted in finding suitable work under Part 4.
A case manager is appointed under Part 5 to assist a Permanent Forces member, a continuous full‑time Reservist or a part‑time Reservist move to civilian life if the person is likely to be discharged from the Defence Force.
Division 2—Aim of rehabilitation
38 Aim of rehabilitation
The aim of rehabilitation is to maximise the potential to restore a person who has an impairment, or an incapacity for service or work, as a result of an injury or disease to at least the same physical and psychological state, and at least the same social, vocational and educational status, as he or she had before the injury or disease.
Division 3—Definitions
39 Definition of rehabilitation authority
(1) The Chief of the Defence Force is a rehabilitation authority for the purposes of this Chapter.
(2) The Commission is a rehabilitation authority for the purposes of this Chapter.
(3) The rehabilitation authority for a person at a time is:
(a) subject to paragraph (aa), the Chief of the Defence Force for a time when the person:
(i) is a Permanent Forces member, a continuous full‑time Reservist or a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) has not been identified by or on behalf of the Chief of the Defence Force as being likely to be discharged from the Defence Force for medical reasons; or
(aa) if the Commission, after considering advice from the Chief of the Defence Force, determines, in writing, that the Commission is to be the rehabilitation authority for a specified person at a specified time—the Commission for that time; or
(b) the Commission for any other time.
(4) A determination made under paragraph (3)(aa) is not a legislative instrument.
40 Rule if rehabilitation authority for a person changes
(1) This section applies if a person’s rehabilitation authority (the original rehabilitation authority) changes to another rehabilitation authority (the new rehabilitation authority) because of section 39.
(2) If:
(a) under subsection 44(2), the person requests the original rehabilitation authority to carry out an assessment of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation; and
(b) the rehabilitation authority changes before the assessment begins;
the person’s request is taken to have been made to the new rehabilitation authority.
(3) A determination of the original rehabilitation authority that is in force immediately before the rehabilitation authority changes has effect as a determination of the new rehabilitation authority. The new rehabilitation authority is responsible for giving effect to the determination.
41 Other definitions
(1) In this Chapter:
approved program provider means:
(a) a person or body that is an approved program provider for the purposes of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988; or
(b) a person nominated in writing by a rehabilitation authority, being a person the rehabilitation authority is satisfied has appropriate skills and expertise to design and provide rehabilitation programs.
approved rehabilitation program means a rehabilitation program determined under section 51 for a person by the person’s rehabilitation authority.
rehabilitation program means a program that consists of or includes any one or more of the following:
(a) medical, dental, psychiatric and hospital services (whether on an in‑patient or out‑patient basis);
(b) physical training and exercise;
(c) physiotherapy;
(d) occupational therapy;
(e) vocational assessment and rehabilitation;
(f) counselling;
(g) psycho‑social training.
vocational assessment and rehabilitation consists of or includes any one or more of the following:
(a) assessment of transferable skills;
(b) functional capacity assessment;
(c) workplace assessment;
(d) vocational counselling and training;
(e) review of medical factors;
(f) training in resume preparation, job‑seeker skills and job placement;
(g) provision of workplace aids and equipment.
Part 2—Rehabilitation programs
Division 1—Application of Part
42 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part applies to a person who is incapacitated for service or work, or who is impaired, as a result of a service injury or disease.
Most decisions under this Part are made by the person’s rehabilitation authority. The rehabilitation authority is either the Chief of the Defence Force or the Commission.
The rehabilitation authority, either on its own initiative or on the person’s request, carries out an initial assessment of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation. The person might be required to undergo an examination (paid for by the Commonwealth) as part of the assessment. (Compensation can be paid for costs incurred in travelling to the examination.)
Once the assessment is done, the rehabilitation authority decides if the person should undertake a rehabilitation program (provided by an approved program provider). In certain cases, the rehabilitation authority can stop or vary the program once it has begun.
A person’s right to compensation can be suspended if the person fails to undergo an examination or fails to undertake the program as required.
This Part also provides for rehabilitation for certain persons who have made a claim for acceptance of liability by the Commission for a service injury or disease, where the claim has not been determined.
43 Persons to whom this Part applies
Commission has accepted liability for service injury or disease
(1) This Part applies to a person at a time if, at that time:
(a) the person is incapacitated for service or work, or has an impairment, as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for the injury or disease.
(2) To avoid doubt, this Part applies to a person who is incapacitated or impaired as a result of an aggravated injury or disease even if the incapacity or impairment resulted from the original injury or disease and not from the aggravation or material contribution.
Claim for acceptance of liability for service injury or disease not determined
(3) This Part also applies to a person if:
(a) the person has made a claim of a kind referred to in paragraph 319(1)(a); and
(b) the Commission has not determined the claim; and
(c) the person is included in a class of persons determined in an instrument under subsection (4); and
(d) the Commission has determined, in writing, that this Part applies to the person.
(4) The Commission may, by legislative instrument, determine a class of persons for the purposes of paragraph (3)(c).
(5) A determination under paragraph (3)(d) is not a legislative instrument.
Division 2—Assessment of a person’s capacity for rehabilitation
44 When an assessment may or must be carried out
Assessments on rehabilitation authority’s initiative
(1) The rehabilitation authority for a person to whom this Part applies may, on its own initiative, carry out an initial assessment or a further assessment of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation.
Requests for assessments
(2) A person to whom this Part applies may request his or her rehabilitation authority to carry out an initial assessment or a further assessment of his or her capacity for rehabilitation.
(3) The rehabilitation authority:
(a) must carry out an initial assessment; and
(b) may carry out a further assessment;
if the person requests the rehabilitation authority to do so.
Requirement to carry out assessment before ceasing or varying a program
(4) The rehabilitation authority must carry out an assessment before ceasing or varying a rehabilitation program under section 53.
45 What may be done as part of an assessment
(1) This section applies if the person’s rehabilitation authority carries out an assessment under section 44 of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation.
(2) The rehabilitation authority may seek the assistance of a person the authority is satisfied has suitable qualifications or expertise to provide assistance.
(3) The rehabilitation authority may take into account any relevant information of which it is aware.
(4) The rehabilitation authority may require the person to undergo an examination under section 46.
46 Requirements for examinations
(1) This section applies if the person’s rehabilitation authority requires the person to undergo an examination.
(2) The examination is to be carried out by an examiner nominated by the rehabilitation authority whom the authority is satisfied has suitable qualifications or expertise to carry out the examination.
(3) The examiner must give a written report of the examination to the rehabilitation authority. The report must include:
(a) an assessment of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation; and
(b) if the person has a capacity for rehabilitation—the kinds of rehabilitation from which the person would benefit; and
(c) any other information relating to the provision of a rehabilitation program for the person that the rehabilitation authority requires.
(4) The Commonwealth is liable to pay the cost of conducting the examination.
47 Compensation for journey and accommodation costs
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred if:
(a) the costs are incurred:
(i) in making a necessary journey in connection with the examination; or
(ii) in remaining, for the purpose of the examination, at a place to which the person has made a journey for that purpose; and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: This section might be affected by section 50 or 52 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program).
48 Amount of compensation for journey and accommodation costs
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 47 is the amount determined by the rehabilitation authority to be the amount reasonably incurred in making the journey or remaining at the place.
(2) In determining the amount, the rehabilitation authority must have regard to:
(a) the means of transport available to the person for the journey; and
(b) the route or routes by which the person could have travelled; and
(c) the accommodation available to the person.
49 Whom the compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 47 for costs reasonably incurred is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who provided services in connection with the journey or accommodation; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of services in connection with the journey or accommodation.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 47 to a person who provided services in connection with the journey or accommodation discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of those services to the extent of the payment.
50 Consequences of failure to undergo an examination
(1) If the rehabilitation authority for a person requires the person to undergo an examination under section 45 and the person:
(a) refuses or fails to undergo the examination; or
(b) in any way obstructs the examination;
the rehabilitation authority may determine that the person’s right to compensation (but not the person’s right to treatment or compensation for treatment under Chapter 6) under this Act is suspended until the examination takes place.
Note: Subsection (6) provides that this section does not apply to a person to whom this Part applies because of subsection 43(3) (claim for acceptance of liability not determined).
(2) A determination under subsection (1) must not be made in relation to a refusal or failure to undergo the examination if, before the time fixed for the examination, the person gives to the rehabilitation authority evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal or failure.
(3) The rehabilitation authority must determine that the suspension under subsection (1) is terminated from a date determined by the rehabilitation authority if, within 14 days after the date fixed for the examination, the person gives to the rehabilitation authority evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal, failure or obstruction.
(4) If a determination under subsection (1) is made by a delegate of the rehabilitation authority, the rehabilitation authority must ensure that any determination terminating the suspension under subsection (3) also made by a delegate of the rehabilitation authority is made by a delegate other than a delegate who was involved in making the determination under subsection (1).
(5) If a person’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (1), compensation is not payable during or in respect of the period of the suspension.
(6) This section does not apply to a person to whom this Part applies because of subsection 43(3) (claim for acceptance of liability not determined).
Division 3—Provision of rehabilitation programs
51 Rehabilitation authority may determine that a person is to undertake a rehabilitation program
(1) The rehabilitation authority for a person to whom this Part applies may determine that the person is to undertake a rehabilitation program specified in the determination if an assessment has been made under section 44 of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation.
(2) In making a determination under subsection (1) in respect of the person, the person’s rehabilitation authority is to have regard to the following:
(a) any written report in respect of the person under subsection 46(3);
(b) any reduction in the future liability of the Commonwealth to pay or provide compensation if the program is undertaken;
(c) the cost of the program;
(d) any improvement in the person’s opportunity to be engaged in work after completing the program;
(e) the person’s attitude to the program;
(f) the relative merits of any alternative and appropriate rehabilitation program;
(g) any other matter the rehabilitation authority considers relevant.
(3) If the rehabilitation authority for a person makes a determination under subsection (1) that a person is to undertake a rehabilitation program, the rehabilitation authority must make arrangements with an approved program provider for the provision of the program for the person.
Note: The person might also be entitled to have his or her home altered or aids or appliances provided under Part 3.
(4) For the purposes of designing or providing a rehabilitation program:
(a) the rehabilitation authority or approved program provider concerned may seek the assistance of persons with suitable qualifications or expertise in the design or provision of rehabilitation programs; and
(b) the rehabilitation authority or approved program provider concerned may take into account any relevant information of which it is aware or that is brought to its attention.
(5) The cost of a rehabilitation program provided for a person under this section is to be paid by the Commonwealth.
52 Consequences of failure to undertake a rehabilitation program
(1) If the rehabilitation authority for a person requires the person to undertake a rehabilitation program under section 51, and the person refuses or fails to undertake the rehabilitation program, the rehabilitation authority may determine that the person’s right to compensation (but not the person’s right to treatment or compensation for treatment under Chapter 6) under this Act is suspended until the person undertakes the rehabilitation program.
Note: Subsection (6) provides that this section does not apply to a person to whom this Part applies because of subsection 43(3) (claim for acceptance of liability not determined).
(2) A determination under subsection (1) must not be made in relation to a refusal or failure to undertake the rehabilitation program if, before the date fixed for starting the rehabilitation program, the person gives to the rehabilitation authority evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal or failure.
(3) The rehabilitation authority must determine that the suspension under subsection (1) is terminated from a date determined by the rehabilitation authority if, within 14 days after the date fixed for starting the rehabilitation program, the person gives to the rehabilitation authority evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal or failure.
(4) If a determination under subsection (1) is made by a delegate of the rehabilitation authority, the rehabilitation authority must ensure that any determination terminating the suspension under subsection (3) also made by a delegate of the rehabilitation authority is made by a delegate other than a delegate who was involved in making the determination under subsection (1).
(5) If a person’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (1), compensation is not payable during or in respect of the period of the suspension.
(6) This section does not apply to a person to whom this Part applies because of subsection 43(3) (claim for acceptance of liability not determined).
53 Cessation or variation of a rehabilitation program
(1) This section applies if:
(a) the rehabilitation authority for a person has made a determination under subsection 51(1) that the person is to undertake a rehabilitation program; and
(b) an approved program provider has commenced providing the rehabilitation program.
(2) The rehabilitation authority may, on its own initiative or on written application by the person, determine that:
(a) the rehabilitation program cease; or
(b) the rehabilitation program be varied.
(3) Before making a determination under subsection (2), the rehabilitation authority must:
(a) undertake an assessment under section 44 of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation; and
(b) consult the person about the proposed determination.
Part 3—Alterations, aids and appliances relating to rehabilitation
Division 1—Preliminary
54 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part applies to a person with an impairment from a service injury or disease who is either undertaking a rehabilitation program or who cannot undertake a program.
If it is reasonably required for the person, the Commission can:
(a) alter the person’s home or work; or
(b) alter articles used by the person; or
(c) repair or provide aids or appliances for the person.
55 Persons to whom Part applies
(1) This Part applies to a person if:
(a) the person has an impairment as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for the injury or disease; and
(c) the person:
(i) is undertaking, or has completed, an approved rehabilitation program in respect of the impairment; or
(ii) has been assessed under section 44 as not having the capacity for rehabilitation.
(2) To avoid doubt, this Part applies to a person who has an impairment as a result of an aggravated injury or disease even if the impairment resulted from the original injury or disease and not from the aggravation or material contribution.
Division 2—Alterations, aids and appliances relating to rehabilitation
56 Alterations, aids and appliances relating to rehabilitation
(1) The Commission may do the following for a person to whom this Part applies:
(a) alter the person’s place of residence, education, work or service, or articles used by the person;
(b) provide aids or appliances for use by the person; or
(c) repair or replace any aids or appliances for use by the person;
if the alterations, aids or appliances are reasonably required by the person.
Note: Section 58 sets out the matters that the Commission must consider in determining if an alteration, aid or appliance is reasonably required by the person.
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred by a person to whom this Part applies if the costs are incurred in respect of alterations, aids or appliances of a kind mentioned in subsection (1).
(3) A claim for compensation in respect of the person must have been made under section 319.
Note: This section might be affected by section 50 or 52 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program).
57 Amount of compensation for alterations, aids and appliances
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under subsection 56(2) is the amount determined by the Commission to be the amount reasonably incurred in respect of the alterations, aids or appliances.
Note: Section 58 sets out the matters that the Commission must consider in determining the amount of compensation.
58 Matters to be considered in determining matters relating to alterations, aids and appliances
(1) This section applies for the purposes of:
(a) determining whether an alteration, aid or appliance is reasonably required by a person under section 56; and
(b) the amount of compensation under section 57.
(2) The Commission must have regard to:
(a) the likely period during which the alteration, article, aid or appliance will be required; and
(b) any difficulties faced by the person in gaining access to, or enjoying reasonable freedom of movement in, his or her place of residence, education, work or service; and
(c) whether arrangements can be made for hiring the article, aid or appliance concerned; and
(d) if the person has previously received compensation under this section in respect of an alteration of his or her place of residence and has later disposed of that place of residence—whether the value of that place of residence was increased as a result of the alteration; and
(e) if the person is a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist:
(i) the length of time that the person is likely to continue to serve as a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(ii) whether the provision of an alteration, article, aid or appliance would increase that length of time.
59 Whom compensation for alterations etc. is payable to
(1) Compensation under subsection 56(2) for costs reasonably incurred is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who provided services in connection with the alteration, aids or appliances; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of services in connection with the alteration, aids or appliances.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under subsection 56(2) to a person who provided services in connection with the alteration, aids or appliances discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the services to the extent of the payment.
Part 4—Assistance in finding suitable work
60 Simplified outline of this Part
All members and former members who are incapacitated for service or work from a service injury or disease are assisted in finding suitable work under this Part.
The work might be work in the Defence Force or civilian work.
The employers providing civilian work may be entitled to payments under a scheme determined by the Commission.
61 Assistance in finding suitable work for full‑time members
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person is a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for service or work as a result of a service injury or disease for which the Commission has accepted liability.
(2) To avoid doubt, this section applies to a person who is incapacitated as a result of an aggravated injury or disease even if the incapacity resulted from the original injury or disease and not from the aggravation or material contribution.
(3) The person’s rehabilitation authority must take all reasonable steps to:
(a) if the person is a Permanent Forces member who has not been identified by or on behalf of the Chief of the Defence Force as being likely to be discharged from the Permanent Forces for medical reasons—assist the person to find suitable work within the Permanent Forces; or
(b) if the person is a continuous full‑time Reservist who has not been identified by or on behalf of the Chief of the Defence Force as being likely to be discharged from the Reserves for medical reasons—assist the person to find suitable work as a continuous full‑time Reservist; or
(c) if the person has been identified by or on behalf of the Chief of the Defence Force as being likely to be discharged from the Defence Force for medical reasons—assist the person to find suitable civilian work.
Note: A person who has been identified as being likely to be discharged from the Defence Force is entitled to a case manager (see section 64).
62 Assistance in finding suitable work for other members and former members
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person:
(i) is a part‑time Reservist, a cadet or a declared member; or
(ii) is a former member; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for service or work as a result of a service injury or disease for which the Commission has accepted liability.
(2) To avoid doubt, this section applies to a person who is incapacitated as a result of an aggravated injury or disease even if the incapacity resulted from the original injury or disease and not from the aggravation or material contribution.
(3) The person’s rehabilitation authority must take all reasonable steps to assist the person to find suitable civilian work.
62A Scheme may provide for payments to employers
(1) The Commission may, in writing, determine a scheme for and in relation to the making of payments to employers in respect of the provision by the employers of suitable civilian work to persons as mentioned in paragraph 61(3)(c) and subsection 62(3).
Scheme must be approved by the Minister
(2) The scheme has no effect unless the Minister has approved it in writing.
Variation or revocation of scheme
(3) The Commission may, by written determination, vary or revoke the scheme that is in force under this section.
(4) A determination under subsection (3) has no effect unless the Minister has approved it in writing.
Legislative instruments
(5) A determination under subsection (1) or (3) made by the Commission and approved by the Minister is a legislative instrument made by the Minister on the day on which the determination is approved.
Part 5—Transition management
63 Simplified outline of this Part
Under this Part, a case manager is appointed to assist a Permanent Forces member, a continuous full‑time Reservist or a part‑time Reservist move from the Defence Force to civilian life if the member or Reservist is likely to be discharged from the Defence Force for medical reasons (whether or not as a result of a service injury or disease).
64 Transition management
(1) This section applies to a person if:
(a) the person is a Permanent Forces member, a continuous full‑time Reservist or a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person has been identified by or on behalf of the Chief of the Defence Force as being likely to be discharged from the Defence Force for medical reasons.
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must appoint a case manager for the person.
(3) The role of the case manager is to assist the person in the transition to civilian life, including by advising the person about entitlements and services for which the person may be eligible as a member or former member, and about how to obtain access to such entitlements and services.
Chapter 4—Compensation for members and former members
Part 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
65 Simplified outline of this Chapter
This Chapter provides for compensation and other benefits to be provided for current and former members who suffer a service injury or disease.
Part 2 provides for compensation to be provided for current and former members who have suffered a permanent impairment.
Part 3 provides for compensation to be provided for current members who are incapacitated for service from a service injury or disease. Current part‑time Reservists, cadets and declared members who are incapacitated for work can also be paid compensation under that Part.
Part 4 provides for compensation to be provided for former members who are incapacitated for work from a service injury or disease.
Part 5 contains rules for adjusting the amount of compensation the Commonwealth is liable to pay under Parts 3 and 4.
Some former members who have suffered a serious impairment from an injury or disease can choose to be paid a Special Rate Disability Pension under Part 6 instead of compensation under Part 4.
Part 7 provides for additional compensation and benefits to be provided, such as compensation to modify vehicles, and compensation for household and attendant care services and damage to a member’s medical aid. Part 7 also provides for the payment of MRCA supplement.
Part 2—Permanent impairment
66 Simplified outline of this Part
Compensation is payable for permanent impairment that occurs as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases if the degree of that impairment is above a certain level.
The level of impairment is measured in impairment points according to a guide prepared by the Commission.
Interim compensation can be payable to a person whose condition has not stabilised.
The compensation is payable weekly unless the person chooses to convert some or all of the weekly amount to a lump sum.
A severely impaired person who has a dependent child is entitled to an additional lump sum.
67 Guide to determining impairment and compensation
(1) The Commission may determine, in writing, a guide setting out:
(a) criteria to be used in deciding the degree of impairment of a person resulting from a service injury or disease; and
(b) methods by which the degree of that impairment can be expressed in impairment points on a scale from 0 to 100; and
(c) criteria to be used in assessing the effect of a service injury or disease on a person’s lifestyle; and
(d) methods by which the effect of a service injury or disease on a person’s lifestyle can be expressed as a numerical rating; and
(e) methods by which the impairment points of a person, and the effect on a person’s lifestyle, from a service injury or disease can be used to determine the compensation payable to the person under this Part by reference to the maximum compensation that can be payable to a person under this Part.
(2) The guide must:
(a) specify different methods under paragraph (1)(e) for:
(i) service injuries or diseases that relate to warlike service or non‑warlike service; and
(ii) other service injuries or diseases; and
(b) specify a method for determining the compensation payable to a person who has both:
(i) a service injury or disease that relates to warlike service or non‑warlike service; and
(ii) another service injury or disease.
(3) The Commission may, from time to time, repeal or amend the guide in writing.
(4) The guide, and any repeal or amendment of the guide, is a legislative instrument.
(5) Despite subsection 14(2) of the Legislation Act 2003, the guide, or an amendment of the guide, may make provision in relation to a matter by applying, adopting or incorporating, with or without modification, any matter contained in an instrument or other writing as in force or existing from time to time.
68 Entitlement to compensation for permanent impairment
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for one or more service injuries or diseases (the compensable condition) of the person; and
(b) the Commission is satisfied that:
(i) as a result of the compensable condition, the person has suffered an impairment; and
(ii) the impairment is likely to continue indefinitely; and
(iii) the person’s compensable condition has stabilised; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The impairment must constitute a minimum number of impairment points for compensation to be payable (see sections 69 and 70). However, the impairment points from more than one service injury or disease can be combined to make up that minimum number.
Note 2: This subsection might also be affected by sections 73 (indefinite impairments) and 389 (choice to institute action for damages).
(2) The Commission must determine:
(a) the degree of impairment suffered by the person as a result of the compensable condition; and
(b) the date on which the person became entitled to compensation under this section by satisfying paragraph (1)(b) and sections 69 and 70 (if applicable).
69 No compensation for less than the threshold impairment points
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person under section 68 only if:
(a) for an impairment resulting from a single service injury or disease consisting of:
(i) hearing loss; or
(ii) the loss, or the loss of the use, of a finger or toe; or
(iii) the loss of the sense of taste or smell;
the impairment suffered by the person constitutes at least 5 impairment points; and
(b) otherwise—the impairment suffered by the person from the compensable condition constitutes at least 10 impairment points.
Note: This section might be affected by section 70 (aggravations etc.).
70 Compensation for aggravations etc.
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation under section 68 in respect of a single aggravated injury or disease only if:
(a) for an aggravation of, or a material contribution to:
(i) hearing loss; or
(ii) the loss, or the loss of the use, of a finger or toe; or
(iii) the loss of the sense of taste or smell;
the impairment suffered by the person as a result of the aggravation or material contribution constitutes at least 5 impairment points; and
(b) otherwise—the impairment suffered by the person as a result of the aggravation or material contribution constitutes at least 10 impairment points.
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay in respect of the person’s aggravated injury or disease is the amount payable in respect of the impairment points of the person, and the effect on the person’s lifestyle, from the aggravation or material contribution.
71 Additional compensation
Additional compensation for impairment from another service injury or disease
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay additional compensation to a person who has been paid, or is entitled to be paid, compensation under this Part (including interim compensation under section 75) if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for one or more additional service injuries or diseases of the person (other than the original compensable condition in respect of which the person is entitled to be paid compensation); and
(b) the Commission is satisfied that:
(i) as a result of the additional injuries or diseases, the person suffers additional impairment; and
(ii) the additional impairment is likely to continue indefinitely; and
(iii) the increase in the person’s overall impairment constitutes at least 5 impairment points; and
(iv) each of the person’s additional injuries or diseases have stabilised; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The impairment points from more than one service injury or disease can be combined to make up the 5 impairment points needed for compensation to be payable.
Note 2: This subsection might also be affected by sections 72 (aggravations), 73 (indefinite impairments) and 389 (choice to institute action for damages).
Additional compensation for deterioration of original condition
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay additional compensation to a person who has been paid, or is entitled to be paid, compensation under this Part (including interim compensation under section 75) for the compensable condition if:
(a) the Commission is satisfied that:
(i) the person has suffered additional impairment as a result of a deterioration in the person’s compensable condition; and
(ii) the additional impairment is likely to continue indefinitely; and
(iii) the deterioration is directly related to the natural progression of the compensable condition; and
(iv) the increase in the person’s overall impairment constitutes at least 5 impairment points; and
(v) the person’s compensable condition has stabilised; and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: This subsection might be affected by sections 72 (aggravations etc.) and 73 (indefinite impairments).
Note 2: The Commission must be notified of the deterioration (see paragraph 77(3)(a)).
Determination of date
(3) The Commission must determine the date on which:
(a) for additional compensation under subsection (1)—the person became entitled to compensation under this section by satisfying paragraph (1)(b) and section 72 (if applicable); and
(b) for additional compensation under subsection (2)—the person became entitled to compensation under this section by satisfying paragraph (2)(a).
72 Additional compensation for aggravations etc.
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay additional compensation under subsection 71(1) in respect of a single aggravated injury or disease only if the increase in the person’s overall impairment resulting from the aggravation or material contribution constitutes at least 5 impairment points.
(2) The amount of additional compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under subsection 71(1) in respect of the aggravated injury or disease of a person is the amount payable in respect of the impairment points of the person, and the effect on the person’s lifestyle, from the aggravation or material contribution.
73 Deciding whether an impairment is likely to continue indefinitely
For the purposes of subparagraph 68(1)(b)(ii) and subparagraphs 71(1)(b)(ii) and (2)(a)(ii), in deciding whether an impairment suffered by a person is likely to continue indefinitely, the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the duration of the impairment; and
(b) the likelihood of improvement in the one or more service injuries or diseases concerned; and
(c) whether the person has undertaken all reasonable rehabilitative treatment for the impairment; and
(d) any other relevant matters.
74 Amount of compensation
(1) The maximum weekly amount of compensation payable to a person under this Part (including additional compensation under section 71) is $233.07.
Note: The amount of $233.07 is indexed under section 404.
(2) The Commission must, as soon as practicable after the Commonwealth becomes liable to pay compensation under section 68 or 71 to a person for an impairment resulting from one or more service injuries or diseases:
(a) assess the effect of the injuries or diseases on the person’s lifestyle; and
(b) determine the weekly amount of compensation to which the person is entitled under that section.
75 Interim compensation
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay interim compensation to a person if:
(a) the Commission is satisfied that the person will be entitled to compensation under section 68 or 71; and
(b) the Commission is not able to determine the degree of impairment suffered by the person because the one or more service injuries or diseases concerned have not stabilised; and
(c) the Commission is satisfied that the impairment suffered by the person as a result of the injuries or diseases constitutes at least the number of impairment points required for the person to become entitled to compensation under section 68 or 71; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: The impairment points from more than one service injury or disease can be combined to make up the impairment points needed for compensation to be payable.
Note 2: Compensation is not payable under this section if the person chooses under section 389 to institute a common law action.
(2) The weekly amount of the interim compensation is the amount the Commission determines to be reasonable having regard to the Commission’s estimate of the final degree of impairment that will be suffered by the person and after assessing the effect of the injuries or diseases on the person’s lifestyle.
(3) The Commission must determine the date on which the impairment suffered by the person constituted at least the number of impairment points required for the person to become entitled to compensation under section 68 or 71.
(4) The Commission must, when the Commission becomes satisfied that the one or more injuries or diseases concerned have all stabilised:
(a) determine the degree of impairment suffered by the person; and
(b) assess the effect of the injuries or diseases on the person’s lifestyle; and
(c) determine the weekly amount of compensation to which the person is entitled.
(5) If the weekly amount determined under subsection (4) is more than the weekly amount determined under subsection (2), the person is entitled to an additional weekly amount equal to the difference between those amounts.
76 Notifying the claimant
(1) If the Commission determines, under section 74, the weekly amount of compensation that is payable to a person under section 68 or 71, or determines the weekly amount of interim compensation payable to a person under subsection 75(2), the Commission must give the person a written notice:
(a) specifying that weekly amount; and
(b) specifying what percentage that weekly amount is of the maximum weekly amount of compensation that could be payable to a person under this Part; and
(c) advising the person that the person can choose, under section 78, to convert some or all of the weekly amount to a lump sum in accordance with that section.
Note 1: Section 74 sets the maximum weekly amount of compensation that could be payable to a person under this Part. That amount is indexed under section 404.
Note 2: If the Commission determines that no compensation is payable under this Part, the Commission is required to notify the person of that determination (see section 346).
(2) If the Commission determines under subsection 75(4) a weekly amount of compensation payable to a person that is more than the weekly amount determined for the person under subsection 75(2), the Commission must give the person a written notice:
(a) specifying the difference between those weekly amounts; and
(b) advising the person that the person can choose, under section 78, to receive a lump sum instead of the difference between those weekly amounts (whether or not the person has made a choice under that section in respect of the amount determined for the person under subsection 75(2)).
Note: The amount of the lump sum is worked out under subsection 78(5).
(3) The notice must specify the date on which it is given.
(4) The notice may be included in the notice given under section 346.
77 When weekly compensation becomes payable
(1) Weekly compensation payable to a person under section 68, to the extent the compensation is in respect of a service injury or disease, is payable from the later of:
(a) the date on which a claim was made under section 319 for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease; and
(b) the date determined by the Commission under paragraph 68(2)(b).
(2) Additional weekly compensation payable to a person under subsection 71(1), to the extent that the compensation is in respect of a service injury or disease, is payable from the later of:
(a) the date on which a claim was made under section 319 for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease; and
(b) the date determined by the Commission under paragraph 71(3)(a).
(3) Additional weekly compensation payable to a person under subsection 71(2), to the extent the compensation is in respect of a deterioration in a service injury or disease, is payable from the later of:
(a) the date on which the Commission was notified of the deterioration in the service injury or disease; and
(b) the date determined by the Commission under paragraph 71(3)(b).
(4) Interim weekly compensation payable to a person under section 75, to the extent the compensation is in respect of a service injury or disease, is payable from the later of:
(a) the date on which a claim was made under section 319 for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease; and
(b) the date determined by the Commission under subsection 75(3).
(5) An additional weekly amount to which a person is entitled under subsection 75(5) is payable from the date on which the Commission becomes satisfied that all of the person’s service injuries or diseases have stabilised.
78 Choice to take lump sum
(1) A person who receives a notice under section 76 about a weekly amount payable to the person under section 68 or 71 or subsection 75(2) (the convertible amount) may choose:
(a) to convert 100% of the convertible amount to a lump sum; or
(b) if the convertible amount is at least 10%, but not more than 20%, of the maximum weekly amount of compensation that could be payable to a person under this Part—to convert 50% of the convertible amount to a lump sum; or
(c) if the convertible amount is more than 20% of the maximum weekly amount of compensation that could be payable to a person under this Part—to convert 25%, 50% or 75% of the convertible amount to a lump sum.
Note: Section 74 sets the maximum weekly amount of compensation that could be payable to a person under this Part. That amount is indexed under section 404.
(2) A person who makes the choice cannot change it.
(3) The choice must be made in writing and must be given to the Commission within 6 months after the date on which the person received the notice.
(4) The Commission may, either before or after the end of that period, extend the period within which the choice must be made if it considers there are special circumstances for doing so.
(5) The amount of the lump sum is worked out using the following formula:

where:
appropriate percentage means the percentage chosen by the person under subsection (1).
notice date means the date specified in the notice given to the person under section 76.
weekly amount converted to a lump sum means the appropriate percentage of the weekly amount payable to the person, as at the date of the notice given to the person under section 76, converted to a lump sum in accordance with advice from the Australian Government Actuary by reference to the person’s age at that date.
Note: Arrears of compensation are payable for the period between the date when compensation became payable and the notice date. These are not subtracted from the weekly amount converted to a lump sum.
(6) However, a lump sum that can be payable to a person must not exceed that worked out by reference to the conversion to a lump sum of a periodic payment payable to a male aged 30.
(7) The legal personal representative of a deceased person is not entitled to choose to convert any percentage of a weekly amount that was payable to the deceased person to a lump sum.
79 When lump sum is payable
(1) The lump sum is payable to the person within 30 days after the date on which the Commission became aware of the choice under section 78.
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay interest to the person on the amount of the lump sum if the lump sum is not paid to the person before the end of that period. The interest is payable in respect of the period starting at the end of that period of 30 days and ending on the day on which the lump sum is paid.
(3) The interest is payable at the rate from time to time determined by the Minister by legislative instrument.
80 Additional amounts payable if maximum compensation paid
(1) This section applies to a person (the impaired person) who has been paid, or is entitled to be paid, compensation under this Part if the Commission has determined that the degree of impairment suffered by the person as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases constitutes at least 80 impairment points.
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay the impaired person $60,000 for each person who is both a dependant of the impaired person and an eligible young person at the later of:
(a) the date determined by the Commission to be the date on which the impairment suffered by the impaired person constitutes at least 80 impairment points; or
(b) either:
(i) if the person has a single service injury or disease—the date on which a claim was made under section 319 for acceptance of liability for the injury or disease; or
(ii) otherwise—the date on which the most recent claim was made under section 319 for acceptance of liability for one of the service injuries or diseases concerned.
Note: The amount of $60,000 is indexed under section 404.
(3) The amount specified in subsection (2) is also payable in respect of a child of the impaired person:
(a) who was born alive on or after the later of those times but who was conceived before that time; or
(b) who was adopted on or after the later of those times but in respect of whom adoption proceedings were begun before that time.
81 Compensation for cost of financial advice and legal advice
Financial advice
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of financial advice obtained by a person if:
(a) the Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to the person under section 68, 71 or 75; and
(b) the Commission determines that the impairment suffered by the person as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases constitutes at least 50 impairment points; and
(c) the financial advice was obtained from a suitably qualified financial adviser after the Commission had made the determination; and
(ca) the financial advice was obtained in respect of the choice the person may make under subsection 78(1); and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Legal advice
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of legal advice obtained by a person if:
(a) the Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to the person under section 68, 71 or 75; and
(b) the Commission determines that the impairment suffered by the person as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases constitutes at least 50 impairment points; and
(c) the legal advice was obtained from a practising lawyer after the Commission had made the determination; and
(d) the legal advice was obtained in respect of the choice the person may make under subsection 78(1); and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
82 Amount of financial advice and legal advice compensation
Financial advice
(1) The Commission must determine an amount of compensation under subsection 81(1) for the cost of the financial advice that it considers reasonable.
Legal advice
(2) The Commission must determine an amount of compensation under subsection 81(2) for the cost of the legal advice that it considers reasonable.
Limit
(3) The sum of the total amount of compensation under subsections 81(1) and (2) in respect of the person must not exceed $2,400.
Note: The amount of $2,400 is indexed under section 404.
(4) The amount of $2,400 applies both to financial advice and legal advice under this Part for the person and financial advice and legal advice under Part 6 (Special Rate Disability Pension) for the person if the date specified in the first notice given to the person under section 76, and the date on which the offer under Part 6 was made, are the same.
83 Whom the compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 81 for the cost of financial advice or legal advice is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who gave the advice; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of the advice.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) An amount paid to the person who gave the advice discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the advice to the extent of the payment.
83A Energy supplement for compensation under this Part
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay an energy supplement to a person for a day if:
(a) the condition in subsection (2) is met for the day; and
(b) the person is residing in Australia on the day; and
(c) on the day the person either:
(i) is in Australia; or
(ii) is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so for a continuous period not exceeding 6 weeks.
Note: Section 424L may affect the person’s entitlement to the energy supplement.
Condition—receipt of compensation under this Part
(2) The condition is that either or both of the following apply:
(a) weekly compensation under this Part (except this section):
(i) is payable to the person for the day; or
(ii) would be payable to the person for the day apart from paragraph 398(3)(b) (of this Act) and offsetting described in subsection 13(4) of the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation (Consequential and Transitional Provisions) Act 2004;
(b) before the day the person received lump sum compensation under this Part.
Rate of energy supplement
(3) The daily rate of the supplement is 1/7 of $3.80.
Part 3—Compensation for incapacity for service or work for members
Division 1—Entitlement to compensation
84 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides for compensation to be provided for current members who are incapacitated for service as a result of a service injury or disease. The Part also provides for compensation for some current part‑time Reservists, cadets and declared members who are incapacitated for work as a result of a service injury or disease.
The Commission must have accepted liability for the injury or disease, and a claim must have been made in respect of the member, to be entitled to the compensation.
The amount of compensation a member receives for a week depends on the difference between the member’s normal and actual earnings for the week. The member’s normal earnings are a notional amount. The member’s actual earnings are based on how much the member actually earns for the week.
Normal earnings are worked out under Divisions 2 to 6, depending on the member’s current status (for example, as a Permanent Forces member or a Reservist) and their status at the time the service injury or disease occurred.
Division 7 deals with how to work out the amount of compensation a member receives for a week if the member receives or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme. (However, the amount of compensation the member receives for a week might be worked out under Divisions 2 to 6 if the member has applied for the benefit, but has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (see section 89B).)
Part 5 of this Chapter contains other important rules that apply in working out normal earnings, actual earnings and the amount of compensation generally.
85 Compensation for incapacitated full‑time members
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person for a week if:
(a) the person is a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist for the week; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(c) the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for service for the week; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) section 88 (aggravations etc.);
(c) section 196 (compensation for part weeks).
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay is worked out under section 89 or 89A.
Note: The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation if the amount of compensation is nil or a negative amount.
86 Compensation for incapacitated part‑time Reservists
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person for a week if:
(a) the person is a part‑time Reservist for the week; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(c) either or both of the following applies:
(i) the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for service for the week;
(ii) the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for work for the week; and
(d) the Chief of the Defence Force has not advised the Commission under section 10 that the person is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a part‑time Reservist in the future; and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) section 88 (aggravations etc.);
(c) section 196 (compensation for part weeks).
Note 2: If the Chief of the Defence Force has advised the Commission under section 10 that a person is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a part‑time Reservist in the future, the person might be entitled to compensation under Part 4.
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay is worked out under section 89 or 89A.
Note: The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation if the amount of compensation is nil or a negative amount.
87 Compensation for incapacitated cadets and declared members
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person for a week if:
(a) the person is a cadet or a declared member for the week; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(c) the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for work for the week; and
(d) if the person is a cadet—the commanding officer of the cadet’s unit (within the meaning of the Cadet Forces Regulations 1977) has not advised the Commission under section 10 that the person is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a cadet in the future; and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) section 88 (aggravations etc.);
(c) section 196 (compensation for part weeks).
Note 2: A person whose commanding officer has advised the Commission under section 10 that the person is unlikely to be able to perform the duties of a cadet in the future might be entitled to compensation under Part 4.
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay is worked out under section 89 or 89A.
Note: The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation if the amount of compensation is nil or a negative amount.
88 No compensation in certain cases relating to aggravations etc. of injuries or diseases
The Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation under section 85, 86 or 87 in respect of an aggravated injury or disease if it is because of the aggravation or material contribution (whether wholly or partly) that the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for service or work for the week.
89 Amount of compensation for current members
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 85, 86, or 87, to pay to a member for a week is worked out using the following formula:

Note: See subsection (4) for an exception.
(2) However, if an amount of compensation worked out using the formula is nil or a negative amount, then the Commonwealth is not liable to pay the compensation for the week.
(3) Use this table to work out a member’s actual earnings and normal earnings:
Definitions of actual earnings and normal earnings |
Item | For this type of member | actual earnings has the meaning given by... | normal earnings has the meaning given by... |
1 | A Permanent Forces member | section 92 | subsection 91(1) |
2 | A continuous full‑time Reservist | section 92 | subsection 91(1) |
3 | A part‑time Reservist to whom Division 3 applies | section 101 | subsection 95(1) |
4 | A part‑time Reservist to whom Division 4 applies | section 105 | subsection 104(1) |
5 | A part‑time Reservist to whom Division 5 applies | section 115 | subsection 108(1) |
6 | A cadet or a declared member | the regulations (see Division 6) | the regulations (see Division 6) |
Note 1: If a member’s normal earnings are less than the relevant minimum wage set by a national minimum wage order, then the member’s normal earnings are instead the relevant minimum wage (see section 179).
Note 2: Certain amounts (such as bonuses) are excluded from the calculation of normal and actual earnings under section 180.
(4) Subsection (1) does not apply if section 89A applies.
89A Amount of compensation for persons receiving a Commonwealth superannuation benefit
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 85, 86 or 87, to pay for a week to a person who receives either or both a pension or lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme is worked out in accordance with the following sections:
(a) if the person is receiving only a pension—section 116B;
(b) if the person has received only a lump sum—section 116C;
(c) if the person is receiving a pension and has received a lump sum—section 116D.
Note: The Commission may determine that this section does not apply if a person has applied for a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme, but has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (see section 89B).
89B Payments before a person receives a Commonwealth superannuation benefit
(1) The Commission may, in writing, determine that section 89A does not apply to a person if:
(a) the person has applied for a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme on the basis of the person’s incapacity for service or work, and the application has not been withdrawn; and
(b) the person has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (as the case requires); and
(c) the person has been notified, in writing:
(i) of the effect of section 89A and this section; and
(ii) that the person may be overpaid while section 89A does not apply to the person; and
(iii) that the overpayments may be recovered under Part 3 of Chapter 11; and
(d) the person has agreed, in writing:
(i) for section 89A not to apply; and
(ii) to notify the Commission if the person withdraws the application for the benefit; and
(iii) to notify the Commission if the person begins to receive or receives the benefit.
(2) The determination has effect according to its terms.
Revocation of determination
(3) The Commission may, in writing, revoke the determination if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) the person has withdrawn the application for the benefit; or
(b) the person has begun to receive or has received the benefit; or
(c) the person has not complied with a requirement to provide information, or take any further action, in relation to the application for the benefit.
(4) After a determination is revoked in relation to a person who has begun to receive or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme, section 89A is taken always to have applied to the person.
Status of instruments
(5) A determination under subsection (1), or a revocation under subsection (3), is not a legislative instrument.
Division 2—Working out normal and actual earnings for full‑time members
90 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal and actual earnings for a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist who is incapacitated for service.
The normal earnings are based on how much the member would have earned for the week if the member were not incapacitated. Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Section 92 tells you how to work out actual earnings.
91 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for a week for a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, who is incapacitated for service means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The member’s normal ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the member would have earned for the week as a member of the Defence Force if the member were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The member’s normal ADF pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The member’s normal pay‑related allowances for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the member for the week if the member were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The member’s normal pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the member if the member were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for a member means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the member immediately before the onset date for the member’s incapacity for service; or
(b) that would be paid to the member because the member is promoted, as mentioned in paragraph 186(2)(b); or
(c) that the member would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
92 Working out actual earnings
(1) The actual earnings for a week for a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, who is incapacitated for service means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The member’s actual ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the member earns for the week as a member of the Defence Force.
(3) The member’s actual pay‑related allowances for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances (as defined in subsection 91(5)) that are paid to the member for the week.
Division 3—Working out normal and actual earnings for part‑time Reservists
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
93 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal and actual earnings for a person who is currently a part‑time Reservist and who was a part‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred. (For example, this Division would apply to a person who has always been a part‑time Reservist.)
The Reservist’s normal earnings are made up of an ADF component and a civilian component. For a Reservist who is incapacitated for both service and work:
(a) the ADF component is based on how much the Reservist would have earned as a part‑time Reservist if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service; and
(b) the civilian component is based on how much the Reservist earned from civilian work during an example period taken from before the onset of the incapacity for work.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Subdivision E tells you how to work out actual earnings.
Subdivision B—Working out normal earnings for part‑time Reservists
94 Application of this Division to part‑time Reservists
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person is a part‑time Reservist for the week; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for either or both service or work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was also a part‑time Reservist when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted.
The person is called an incapacitated Reservist in this Division.
95 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for an incapacitated Reservist for a week is the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
ADF component for a week:
(a) for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for service—means the amount worked out under section 96; and
(b) for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for service—means the amount worked out under section 97.
civilian component for a week:
(a) for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for work—means the amount worked out under section 98; and
(b) for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for work—means the amount worked out under section 100.
Subdivision C—Working out the ADF component of normal earnings
96 Working out the ADF component for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for service
(1) The ADF component for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for service is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (3).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of:
(a) the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the Reservist; and
(b) the number of days (if any) in each week that the Reservist would have been paid as a Reservist; and
(c) the number of days (if any) in each week that the Reservist would have been paid an amount of pay‑related allowances;
if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
(3) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for an incapacitated Reservist for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the Reservist as a part‑time Reservist for the day if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to an incapacitated Reservist immediately before the onset date for the Reservist’s incapacity for service; or
(b) that would be paid to an incapacitated Reservist because the Reservist is promoted, as mentioned in paragraph 186(2)(b); or
(c) that an incapacitated Reservist would have been paid after the Reservist completed his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
pay‑related allowance days for an incapacitated Reservist for a week means the number of days advised by the Chief of the Defence Force under paragraph (2)(c).
rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist for a day means the amount of pay that the Reservist would have earned for the day as a part‑time Reservist if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
reserve days for an incapacitated Reservist for a week means the number of days advised by the Chief of the Defence Force under paragraph (2)(b).
97 Working out the ADF component for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for service
(1) The ADF component for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for service means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: An incapacitated Reservist might only be incapacitated for work and not incapacitated for service (see paragraph 86(1)(c)).
(2) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance has the same meaning as in subsection 96(3).
Subdivision D—Working out the civilian component of normal earnings
98 Working out the civilian component for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for work
Working out the civilian component of normal earnings
(1) The civilian component for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for work is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The civilian component for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for work is worked out under section 100.
Civilian daily earnings for those working before the onset of the incapacity
(2) The following formula sets out how to work out the civilian daily earnings for an incapacitated Reservist who was engaged in civilian work before the onset date for the incapacity:

Note 1: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (5).
Note 2: The Reservist’s civilian daily earnings might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) If the incapacitated Reservist was required to work overtime on a regular basis in that work, the civilian daily earnings also include the amount worked out using the following formula:
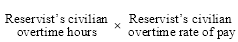
Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (5).
Civilian daily earnings for those not working
(4) The civilian daily earnings for an incapacitated Reservist who was not engaged in civilian work before the onset date for the incapacity is nil.
Definitions
(5) In this section:
allowances for an incapacitated Reservist for a day means the average amount of allowances (other than expense allowances) paid to the Reservist for a day for his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian daily hours for an incapacitated Reservist means the average number of hours worked each day by the Reservist in his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian overtime hours for an incapacitated Reservist means the average number of hours of overtime worked each day by the Reservist in his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian overtime rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist means the average hourly overtime rate of pay for the Reservist’s overtime in civilian work during the example period.
civilian rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist means the average hourly ordinary time rate of pay for the Reservist’s civilian work during the example period.
example period has the meaning given by section 99.
99 Definition of example period for the civilian component of normal earnings
(1) For the purposes of section 98, the example period for an incapacitated Reservist who is incapacitated for work is the latest period of 2 weeks:
(a) during which the Reservist was continuously engaged in civilian work; and
(b) ending before the onset date for the incapacity.
(2) However, the Commission may determine as the example period:
(a) a different 2 week period that it considers reasonable; or
(b) a period of a different length that it considers reasonable;
if the civilian daily earnings for the example period under subsection (1) would not fairly represent the daily rate at which the Reservist was being paid for his or her civilian work before the onset date for the incapacity.
100 Working out the civilian component for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for work
The civilian component for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who is not incapacitated for work is the amount the Reservist earns (including from allowances other than expense allowances) for the week from civilian work that he or she undertakes for the week.
Note: An incapacitated Reservist might only be incapacitated for service and not incapacitated for work (see paragraph 86(1)(c)).
Subdivision E—Working out actual earnings
101 Working out actual earnings
(1) The actual earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The Reservist’s actual ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the Reservist earns for the week as a part‑time Reservist.
(3) The Reservist’s actual pay‑related allowances for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances (as defined in subsection 96(3)) that are paid to the Reservist for the week.
(4) The Reservist’s actual civilian earnings means the greater of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount (if any) that the Reservist is able to earn in suitable work;
(b) the amount the Reservist earns (including from allowances other than expense allowances) for the week from civilian work that he or she undertakes for the week.
Note: Section 181 sets out some matters the Commission must have regard to in determining how much the person is able to earn under paragraph (4)(a).
Division 4—Working out normal and actual earnings for part‑time Reservists who were previously Permanent Forces members
102 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal and actual earnings for a person:
(a) who is currently a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) who was a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(c) whose last period of full‑time service was as a Permanent Forces member.
The normal earnings are based on the amount the person would have earned if the person were still a Permanent Forces member.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Section 105 tells you how to work out actual earnings.
103 Application of this Division to part‑time Reservists who were previously Permanent Forces members
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person is a part‑time Reservist for the week; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for either or both service or work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, when the service injury was sustained or the service disease contracted; and
(d) the person was a Permanent Forces member immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service.
The person is called an incapacitated Reservist in this Division.
104 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The Reservist’s full‑time ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the Reservist would have earned for the week as a Permanent Forces member if:
(a) the Reservist were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s full‑time ADF pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The Reservist’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the Reservist for the week if:
(a) the Reservist were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s allowance component might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the Reservist if:
(a) the Reservist were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated Reservist means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the Reservist immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service; or
(b) that the Reservist would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
105 Working out actual earnings
(1) The actual earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The Reservist’s actual ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the Reservist earns for the week as a part‑time Reservist.
(3) The Reservist’s actual pay‑related allowances for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances (as defined in subsection 104(5)) that are paid to the Reservist for the week.
(4) The Reservist’s actual civilian earnings means the greater of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount (if any) that the Reservist is able to earn in suitable work;
(b) the amount the Reservist earns (including from allowances other than expense allowances) for the week from civilian work that he or she undertakes for the week.
Note: Section 181 sets out some matters the Commission must have regard to in determining how much the person is able to earn under paragraph (4)(a).
Division 5—Working out normal and actual earnings for part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
106 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal and actual earnings for a person:
(a) who is currently a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) who was a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(c) whose last period of full‑time service was as a continuous full‑time Reservist.
The Reservist has a one‑off choice between 2 ways of working out normal earnings. Normal earnings can be based on the amount the person would have earned if the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist. (This amount is called the full‑time ADF earnings.) Alternatively, normal earnings can be based on the Reservist’s earnings from other work engaged in before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. (This amount is called the pre‑CFTS earnings.)
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Subdivision B—Working out normal earnings for part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
107 Application of this Division to part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person is a part‑time Reservist for the week; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for either or both service or work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted; and
(d) the person was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service.
The person is called an incapacitated Reservist in this Division.
108 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for the week for an incapacitated Reservist means whichever of the following amounts is chosen by the Reservist:
(a) the amount of the Reservist’s full‑time ADF earnings for a week (see Subdivision C);
(b) the amount of the Reservist’s pre‑CFTS earnings for a week (see Subdivision D).
(2) The Reservist must inform the Commission in writing of his or her choice between the full‑time ADF earnings and the pre‑CFTS earnings.
(3) The Reservist is only entitled to make one choice for all weeks in respect of which this Division applies. The Reservist cannot change his or her choice once it has been made.
Subdivision C—Working out full‑time ADF earnings
109 Working out full‑time ADF earnings
(1) The full‑time ADF earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The Reservist’s full‑time ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the Reservist would have earned for the week as a continuous full‑time Reservist if:
(a) the Reservist were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s full‑time ADF pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The Reservist’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the Reservist for the week if:
(a) the Reservist were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s allowance component might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the Reservist if:
(a) the Reservist were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated Reservist means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the Reservist immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service; or
(b) that the Reservist would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
Subdivision D—Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
110 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
The pre‑CFTS earnings are worked out by looking back at the period before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. During this period, the Reservist might have been a part‑time Reservist as well as being engaged in other work.
The Reservist’s pre‑CFTS earnings have 2 components: pre‑CFTS pay and reserve pay. The Reservist’s pre‑CFTS pay is based on earnings from work the Reservist was engaged in before beginning the last period of continuous full‑time service. The work engaged in might be civilian work or defence work (as some people become continuous full‑time Reservists after being Permanent Forces members). The Reservist’s reserve pay is based on earnings from service as a part‑time Reservist.
However, for a Reservist whose service injury or disease occurred while a continuous full‑time Reservist, the Commission may determine pre‑CFTS earnings by looking back at the period before the onset date for the Reservist’s incapacity instead of the period before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
111 Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
(1) The pre‑CFTS earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:
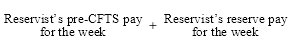
(2) In this section:
pre‑CFTS pay for a person for a week is worked out under section 112.
reserve pay for a person for a week is worked out under section 114.
112 Working out pre‑CFTS pay
Pre‑CFTS pay for those engaged in work before beginning last period of full‑time service
(1) The following formula sets out how to work out the pre‑CFTS pay for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who was engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service:

Note 1: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Note 2: The Reservist’s pre‑CFTS pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(2) If the incapacitated Reservist was required to work overtime on a regular basis in that work, the pre‑CFTS pay for a week also includes the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Pre‑CFTS pay for those not working
(3) The pre‑CFTS pay for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who was not engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
allowances for an incapacitated Reservist for a week is the average amount of allowances (other than expense allowances) paid to the Reservist for a week for his or her work during the example period.
example period has the meaning given by section 113.
pre‑CFTS overtime hours for an incapacitated Reservist means the average number of hours of overtime worked each week by the Reservist in his or her work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS overtime rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist means the average hourly overtime rate of pay for the Reservist’s overtime in work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist means the Reservist’s average hourly ordinary time rate of pay for the Reservist’s work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS weekly hours for an incapacitated Reservist means the average number of hours worked in each week by the Reservist in his or her work during the example period.
work includes work as a member of the Defence Force (other than as a part‑time Reservist).
Note: A person might have been a Permanent Forces member before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. This work is taken into account in working out pre‑CFTS pay. However, work as a part‑time Reservist is taken into account in working out reserve pay.
113 Definition of example period for pre‑CFTS pay
(1) For the purposes of section 112, the example period for an incapacitated Reservist is the latest period of 2 weeks:
(a) during which the Reservist was continuously engaged in work (as defined in subsection 112(4)); and
(b) ending before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
(2) However, the Commission may determine as the example period:
(a) a different 2 week period that it considers reasonable; or
(b) a period of a different length that it considers reasonable;
if the pre‑CFTS pay for the example period under subsection (1) would not fairly represent the weekly rate at which the Reservist was being paid for his or her work before beginning the continuous full‑time service.
114 Working out reserve pay
Reserve pay for persons who were part‑time Reservists
(1) The reserve pay for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who was a part‑time Reservist before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the Reservist if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Reserve pay for persons who were not part‑time Reservists
(3) The reserve pay for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who was not a part‑time Reservist before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for an incapacitated Reservist for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the Reservist for the day if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated Reservist means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the Reservist immediately before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service; or
(b) that would be paid to the Reservist because the Reservist is promoted, as mentioned in paragraph 186(2)(b).
example period for an incapacitated Reservist means:
(a) the latest period of one year:
(i) during which the Reservist was a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) ending before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service; or
(b) such other period that the Commission determines is reasonable.
pay‑related allowance days for an incapacitated Reservist for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the Reservist was paid a pay‑related allowance.
rate of pay for an incapacitated Reservist for a day means the amount of pay that the Reservist would have been paid for the day as a part‑time Reservist if the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The Reservist’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
reserve days for an incapacitated Reservist for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the Reservist was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
114A Example periods for those injured as continuous full‑time Reservists
(1) For the purposes of the definition of example period in sections 113 and 114 for an incapacitated Reservist who was a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury was sustained, or the service disease was contracted, the Commission may determine, as the end of the example period, a time before the onset date for the Reservist’s incapacity for service or work (instead of a time before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service).
(2) If the Commission does so, a reference in sections 112, 113 and 114 to a time before the Reservist began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is taken instead to be a reference to a time before the onset date for the Reservist’s incapacity.
Subdivision E—Working out actual earnings
115 Working out actual earnings
(1) The actual earnings for a week for an incapacitated Reservist means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The Reservist’s actual ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the Reservist earns for the week as a part‑time Reservist.
(3) The Reservist’s actual pay‑related allowances for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances (as defined in subsection 114(4)) that are paid to the Reservist for the week.
(4) The Reservist’s actual civilian earnings means the greater of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount (if any) that the Reservist is able to earn in suitable work;
(b) the amount the Reservist earns (including from allowances other than expense allowances) for the week from civilian work that he or she undertakes for the week.
Note: Section 181 sets out some matters the Commission must have regard to in determining how much the person is able to earn under paragraph (4)(a).
Division 6—Working out normal and actual earnings for cadets and declared members
116 Regulations may prescribe methods for working out normal and actual earnings for cadets and declared members
The regulations may prescribe one or more methods of working out the normal earnings and actual earnings for persons who are cadets or declared members.
Note: The regulations may also modify the application of this Part in respect of cadets and declared members (see section 439).
Division 7—Amount of compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received
116A Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the amount of compensation a member receives for a week if the member receives or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme. (However, this Division might not apply if the member has applied for the benefit, but has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (see section 89B).)
The method of working out the amount of compensation depends on whether the member:
(a) is receiving only a Commonwealth superannuation pension (see section 116B); or
(b) has received only a Commonwealth superannuation lump sum (see section 116C); or
(c) has received a lump sum and is receiving a pension (see section 116D).
Basically, the amount of compensation paid is the amount worked out under Division 1 reduced by the amount of superannuation received.
116B Amount of compensation for person receiving only Commonwealth superannuation pension
(1) If paragraph 89A(a) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 85, 86 or 87, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this Division:
Division 1 compensation amount for a person for a week means the amount of compensation the person would have been paid for the week if subsection 89(1) had applied.
superannuation pension amount for a person who receives a pension for a week under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means:
(a) if the scheme identifies a part of the pension as attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority—the amount of that part; or
(b) in any other case, either:
(i) the amount assessed by the Commission to be the part of the pension that is attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority; or
(ii) if such an assessment cannot be made—the amount of the pension received by the person for the week.
116C Amount of compensation for person who has received only Commonwealth superannuation lump sum
(1) If paragraph 89A(b) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 85, 86 or 87, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this Division:
superannuation age‑based number for a person who receives a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means the number that is advised by the Australian Government Actuary by reference to the person’s age on the day on which the lump sum is paid.
superannuation lump sum amount for a person who receives a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means:
(a) if the scheme identifies a part of the lump sum as attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority—the amount of that part; or
(b) in any other case, either:
(i) the amount assessed by the Commission to be the part of the lump sum that is attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority; or
(ii) if such an assessment cannot be made—the amount of the lump sum.
Note: Subsection 116B(2) defines Division 1 compensation amount.
116D Amount of compensation for person receiving both superannuation pension and lump sum
If paragraph 89A(c) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 85, 86 or 87, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

Note: Subsection 116B(2) defines Division 1 compensation amount and superannuation pension amount. Subsection 116C(2) defines superannuation age‑based number and superannuation lump sum amount.
116E No compensation if amount worked out is nil or a negative amount
If an amount of compensation worked out under this Division is nil or a negative amount, then the Commonwealth is not liable to pay the compensation for the week.
Part 4—Compensation for incapacity for work for former members
Division 1—Entitlement to compensation
117 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides for compensation to be provided for former members who are incapacitated for work as a result of a service injury or disease. The Commission must have accepted liability for the injury or disease, and a claim must have been made in respect of the former member, to be entitled to the compensation.
The amount of compensation a person receives for a week depends on the difference between the person’s normal and actual earnings for the week. The person’s normal earnings are a notional amount. The person’s actual earnings are based on how much the person actually earns for the week.
Normal earnings are worked out under Divisions 3 to 8.
Division 3 applies to a person who left the Defence Force as a Permanent Forces member. Division 4 applies to a person who left the Defence Force as a continuous full‑time Reservist.
Divisions 5 to 8 apply to a person who left the Defence Force as a part‑time Reservist. The Division that applies depends on the person’s status (for example, as a Permanent Forces member or a Reservist) when the service injury or disease occurred and on leaving the Defence Force.
Division 9 applies to a person who was a cadet or declared member.
Part 5 of this Chapter contains other important rules that apply in working out normal earnings, actual earnings and the amount of compensation generally.
118 Compensation for incapacitated former members
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to a person for a week if:
(a) the person is a former member; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(c) the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for work for the week; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) section 119 (aggravations etc.);
(c) sections 120 and 121 (persons who are the age that is 2 years before pension age or older);
(d) section 122 (imprisonment of persons);
(e) section 138 (small amounts of compensation);
(f) section 196 (compensation for part weeks).
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay is:
(a) if a person has chosen to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension under Part 6—the amount worked out under Part 6; or
(b) otherwise—the amount worked out under Division 2 of this Part.
Note: The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation if the amount worked out under Division 2 is nil or a negative amount.
119 No compensation in certain cases relating to aggravations etc. of injuries or diseases
The Commonwealth is only liable, under section 118, to pay compensation in respect of an aggravated injury or disease if it is because of the aggravation or material contribution (whether wholly or partly) that the service injury or disease results in the person’s incapacity for work for the week.
120 Compensation for those over pension age
Other than as provided in section 121, the Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation to a person to whom paragraph 118(2)(b) applies if the person is pension age or older.
121 Compensation for those over the age that is 2 years before pension age
(1) This section applies to a person if:
(a) paragraph 118(2)(b) applies to the person; and
(b) the person’s service injury is sustained, or service disease is contracted, when the person is the age that is 2 years before pension age or older.
(2) The Commonwealth is only liable, under section 118, to pay compensation to the person for a maximum of 104 weeks (whether consecutive or not) during which the person is incapacitated for work.
122 Persons who are imprisoned
The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for a week to a person to whom section 118 applies if the person is imprisoned for the week in connection with his or her conviction of an offence.
Division 2—Amount of compensation (other than for those who have chosen to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension)
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
123 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the amount of compensation a former member receives for a week during which he or she is incapacitated for work (other than for a person who has chosen to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension).
Subdivision B—Amount of compensation generally
124 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
Different methods for working out the amount of compensation apply in different situations (such as where a person is receiving or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme). This Subdivision gives an overview of where these different methods are found in this Division.
The normal rule for working out the amount of compensation is found in Subdivision C.
Special rules apply in the following cases:
(a) retired persons who are receiving or have received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme (although the amount of compensation the persons receive might be worked out under Subdivision C if the persons have applied for the benefit, but have not begun to receive or have not received the benefit) (see sections 126 and 126A);
(b) those maintained in hospitals etc. (see section 127);
(c) those receiving small amounts of compensation (see Subdivision E);
(d) those who choose to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension (see Part 6).
125 Amount of compensation for former members
Amount of compensation generally
(1) Generally, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to a person for a week is worked out under Subdivision C.
Amount of compensation for others
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply if any of the following provisions apply instead:
(a) section 126 (retired persons receiving a Commonwealth superannuation benefit);
(b) section 127 (those maintained in hospitals etc.);
(c) Subdivision E (small amounts of compensation);
(d) Part 6 (those who choose to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension).
No compensation if amount worked out is nil or a negative amount
(3) If an amount of compensation worked out under this Division is nil or a negative amount, then the Commonwealth is not liable to pay the compensation for the week.
126 Amount of compensation for retired persons receiving a Commonwealth superannuation benefit
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay for a week to a person who:
(a) has retired voluntarily, or is compulsorily retired, from his or her work; and
(b) receives either or both a pension or lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme as a result of the retirement;
is worked out in accordance with the following sections:
(c) if the person is receiving only a pension—section 134;
(d) if the person has received only a lump sum—section 135;
(e) if the person is receiving a pension and has received a lump sum—section 136.
Note: The Commission may determine that this section does not apply if a person has applied for a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme, but has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (see section 126A).
126A Payments before a retired person receives a Commonwealth superannuation benefit
(1) The Commission may, in writing, determine that section 126 does not apply to a person if:
(a) the person has applied for a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme on the basis of the person’s incapacity for service or work, and the application has not been withdrawn; and
(b) the person has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (as the case requires); and
(c) the person has been notified, in writing:
(i) of the effect of section 126 and this section; and
(ii) that the person may be overpaid while section 126 does not apply to the person; and
(iii) that the overpayments may be recovered under Part 3 of Chapter 11; and
(d) the person has agreed, in writing:
(i) for section 126 not to apply; and
(ii) to notify the Commission if the person withdraws the application for the benefit; and
(iii) to notify the Commission if the person begins to receive or receives the benefit.
(2) The determination has effect according to its terms.
Revocation of determination
(3) The Commission may, in writing, revoke the determination if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) the person has withdrawn the application for the benefit; or
(b) the person has begun to receive or has received the benefit; or
(c) the person has not complied with a requirement to provide information, or take any further action, in relation to the application for the benefit.
(4) After a determination is revoked in relation to a person who has begun to receive or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme, section 126 is taken always to have applied to the person.
Status of instruments
(5) A determination under subsection (1), or a revocation under subsection (3), is not a legislative instrument.
127 Amount of compensation for former members who are maintained in hospital etc.
Application of section
(1) This section applies to a person (the patient) if:
(a) the patient has been continuously maintained in a hospital or other institution as a result of a service injury or disease for at least one year; and
(b) the patient is still being maintained as such a patient; and
(c) the patient has:
(i) no dependants; and
(ii) no dependent young persons (see subsection (4)); and
(iii) no carer for a dependent young person (see subsection (4)); and
(d) subsection 125(1) would apply to the patient but for the operation of this section.
Amount of compensation
(2) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation that it considers reasonable that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the patient for each week during which he or she is so maintained. However, the amount must be at least one‑half of, and not more than, the amount of compensation that would otherwise have been payable to the patient for a week if subsection 125(1) had applied.
Matters to be considered
(3) In determining the amount, the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the present and probable future needs and expenses of the patient; and
(b) the period during which the patient is likely to remain a patient in the hospital or the other institution.
The Commission must not have regard to any other matter.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
carer for a dependent young person means a person:
(a) who is wholly or mainly maintained by the patient; and
(b) who has the care of a dependent young person (other than a person who has that care only because the patient remunerates that person for caring for the young person).
dependent young person means an eligible young person who is dependent on the patient.
Subdivision C—Amount of compensation where no Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received
128 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
This Subdivision tells you the normal rule for working out the amount of compensation for a former member.
The person is paid a full amount of compensation for at least the first 45 weeks of the incapacity. A reduced rate of compensation might be paid after that depending on how many hours a week the person is working.
129 Amount of compensation for maximum rate weeks
(1) If subsection 125(1) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the person for a week that is a maximum rate week is worked out using the following formula:

Note: Section 132 defines normal earnings and actual earnings.
(2) In this Subdivision, a week is a maximum rate week for a person who is incapacitated for work if:
(a) it is a week during which:
(i) the person’s incapacity prevents the person from working his or her normal weekly hours; or
(ii) if the person is working his or her normal weekly hours, the person’s incapacity prevents the person from working at the level at which he or she worked before the incapacity; and
(b) the total number of hours in that week, and in all previous maximum rate weeks (if any), during which the incapacity has prevented the person from so working, does not exceed 45 times the person’s normal weekly hours.
Note: Section 132 defines normal weekly hours.
130 Amount of compensation for the week whose hours exceed 45 times the normal weekly hours
(1) If during, but before the end of, a particular week the total number of hours worked out in accordance with paragraph 129(2)(b) exceeds 45 times the normal weekly hours for a person, then:
(a) subsection (2) applies in respect of the hours that elapse before that number is exceeded (the maximum rate hours as defined in subsection (2)); and
(b) subsection (3) applies in respect of the remaining hours in the week (the reduced rate hours as defined in subsection (3)).
Note: Section 132 defines normal weekly hours.
Amount of compensation in respect of maximum rate hours
(2) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to a person in respect of the maximum rate hours is worked out using the following formula:

where:
maximum rate hours for a person means the total number of hours in the week:
(a) that would have counted towards the person’s normal weekly hours (whether those hours are worked or not); and
(b) that elapse before the total number of hours worked out in accordance with paragraph 129(2)(b) exceeds 45 times the person’s normal weekly hours.
Note: Section 132 defines normal weekly hours, normal earnings and actual earnings.
Amount of compensation in respect of reduced rate hours
(3) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to a person in respect of the reduced rate hours is worked out using the following formula:

where:
reduced compensation amount for a person means the amount of compensation worked out in accordance with section 131 if that section had applied for the whole week.
reduced rate hours for a person means the total number of hours worked out using the following formula:
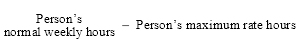
Note: Section 132 defines normal weekly hours. Subsection (2) defines maximum rate hours.
131 Amount of compensation after 45 weeks
(1) If subsection 125(1) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the person for a week (other than a week in respect of which section 129 or 130 applies) is worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
adjustment percentage for a person for a week means the following percentage:
(a) if the person is not working during that week—75%;
(b) if the person is working for 25% or less of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—80%;
(c) if the person is working for more than 25% but not more than 50% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—85%;
(d) if the person is working for more than 50% but not more than 75% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—90%;
(e) if the person is working for more than 75% but less than 100% of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—95%;
(f) if the person is working for 100% or more of his or her normal weekly hours during that week—100%.
Note: Section 132 defines normal weekly hours, normal earnings and actual earnings.
132 Definitions of actual earnings, normal earnings and normal weekly hours
(1) In this Part:
actual earnings for a person for a week means the greater of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount (if any) that the person is able to earn in suitable work;
(b) the amount (if any) that the person earns for the week (including from allowances other than expense allowances) from any work that is undertaken by the person during the week.
Note 1: Bonuses are excluded from the calculation of actual earnings under section 180.
Note 2: Section 181 sets out some matters that the Commission must have regard to in determining the amount that the person is able to earn under paragraph (a).
(2) Use this table to work out the normal earnings and the normal weekly hours for a person:
Definitions of normal earnings and normal weekly hours |
Item | For this type of person | normal earnings has the meaning given by... | normal weekly hours means... |
1 | A person who was a Permanent Forces member immediately before last ceasing to be a member | Division 3 | 37.5 hours |
2 | A person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member | Division 4 | (a) if the person has chosen pre‑CFTS earnings under section 143—the number of hours worked out under section 150; or (b) otherwise—37.5 hours |
3 | A person who is or was a part‑time Reservist to whom section 152 applies | Division 5 | the number of hours worked out under section 158 |
4 | A person who is or was a part‑time Reservist to whom section 160 applies | Division 6 | 37.5 hours |
5 | A person who is or was a part‑time Reservist to whom section 163 applies | Division 7 | 37.5 hours |
6 | A person who is or was a part‑time Reservist to whom section 166 applies | Division 8 | (a) if the person has chosen pre‑CFTS earnings under section 167—the number of hours worked out under section 174; or (b) otherwise—37.5 hours |
7 | A former cadet or declared member | the regulations (see Division 9) | the number of hours worked out under the regulations (see Division 9) |
Note 1: If a person’s normal earnings are less than the relevant minimum wage set by a national minimum wage order, then the person’s normal earnings are instead the relevant minimum wage (see section 179).
Note 2: Certain amounts (such as bonuses) are excluded from the calculation of normal earnings under section 180.
Subdivision D—Amount of compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received
133 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
This Subdivision tells you how to work out the amount of compensation a person receives for a week if the person receives or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme. (However, this Subdivision might not apply if the person has applied for the benefit, but has not begun to receive or has not received the benefit (see section 126A).)
The method of working out the amount of compensation depends on whether the person:
(a) is receiving only a Commonwealth superannuation pension (see section 134); or
(b) has received only a Commonwealth superannuation lump sum (see section 135); or
(c) has received a lump sum and is receiving a pension (see section 136).
Basically, the amount of compensation paid is the amount worked out under Subdivision C reduced by the amount of superannuation received.
134 Amount of compensation for retired person receiving only Commonwealth superannuation pension
(1) If paragraph 126(c) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this Subdivision:
Subdivision C compensation amount for a person for a week means the amount of compensation the person would have been paid for the week if Subdivision C had applied.
superannuation pension amount for a person who receives a pension for a week under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means:
(a) if the scheme identifies a part of the pension as attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority—the amount of that part; or
(b) in any other case, either:
(i) the amount assessed by the Commission to be the part of the pension that is attributable to the contribution made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority; or
(ii) if such an assessment cannot be made—the amount of the pension received by the person for the week.
135 Amount of compensation for retired person who has received only Commonwealth superannuation lump sum
(1) If paragraph 126(d) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this Subdivision:
superannuation age‑based number for a person who receives a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means the number that is advised by the Australian Government Actuary by reference to the person’s age on the day on which the lump sum is paid.
superannuation lump sum amount for a person who receives a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme means:
(a) if the scheme identifies a part of the lump sum as attributable to the contributions made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority—the amount of that part; or
(b) in any other case, either:
(i) the amount assessed by the Commission to be the part of the lump sum that is attributable to the contribution made under or to the scheme by the Commonwealth or a Commonwealth authority; or
(ii) if such an assessment cannot be made—the amount of the lump sum.
Note: Subsection 134(2) defines Subdivision C compensation amount.
136 Amount of compensation for retired person receiving both superannuation pension and lump sum
If paragraph 126(e) applies to a person, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable, under section 118, to pay to the person for a week is worked out using the following formula:

Note: Subsection 134(2) defines Subdivision C compensation amount and superannuation pension amount. Subsection 135(2) defines superannuation age‑based number and superannuation lump sum amount.
Subdivision E—Small amounts of compensation
137 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
Under this Subdivision, a person who receives weekly compensation of $150 or less is entitled to convert that amount into a lump sum if the person is still working or is receiving or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme.
If the person later stops working because the person’s condition deteriorates, or the person stops receiving the superannuation, then the person can be paid compensation on a weekly basis again.
138 Converting small amounts of weekly compensation into lump sum compensation
(1) This section applies if:
(a) apart from this section, the Commonwealth would be liable to pay an amount of compensation, worked out in accordance with subsection 125(1) or section 126, of $150 or less for a person’s incapacity for work for a week; and
(b) the person:
(i) is engaged in work; or
(ii) is receiving a pension under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme; or
(iii) has received a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme; and
(c) the Commission is satisfied that the degree of the person’s incapacity is unlikely to change; and
(d) the person advises the Commission in writing that he or she chooses to receive a lump sum under this Division rather than weekly payments.
Note 1: The Commonwealth might later be liable for weekly compensation if the person becomes unable to engage in work or stops receiving superannuation (see section 139).
Note 2: The amount of $150 is indexed under section 404.
(2) Instead of being liable to pay compensation for that week and future weeks, the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay is the amount of the lump sum worked out using the following formula:

Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) section 122 (persons who are imprisoned);
(c) subsection 125(3) (nil and negative amounts).
(3) In this section:
n means the number worked out using the formula:

where:
number of days means the number of days in the period beginning on the day after the day on which the person advises the Commission of his or her choice under paragraph (1)(d) and ending:
(a) if the person’s service injury is sustained, or service disease is contracted, before the person turns the age that is 2 years before pension age—on the day before the person turns pension age; and
(b) if the person’s service injury is sustained, or service disease is contracted, on or after the day on which the person turns the age that is 2 years before pension age—on the day before the person is no longer entitled to compensation under this Part.
specified number means the number specified in writing (in decimal notation) by the Commission for the purposes of this definition.
weekly amount means the amount payable to the person under section 118 for the week in which the person advises the Commission of his or her choice under paragraph (1)(d).
139 Weekly compensation following conversion of weekly amounts to a lump sum
(1) This section applies if:
(a) the Commonwealth has paid a lump sum to a person under section 138 in respect of the person’s incapacity for work; and
(b) either:
(i) subparagraph 138(1)(b)(i) applied and the person’s condition later deteriorates to the extent that the person is no longer able to engage in work; or
(ii) subparagraph 138(1)(b)(ii) applied and the person stops receiving the pension under the Commonwealth superannuation scheme; and
(c) the Commission is satisfied that the person’s incapacity is likely to continue indefinitely.
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation under section 118 for each week during which the person continues to be incapacitated for work.
Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) sections 50, 52 and 329 (failure to undergo examination or rehabilitation program);
(b) sections 120 and 121 (persons who are the age that is 2 years before pension age or older);
(c) section 122 (imprisonment of persons);
(d) section 196 (compensation for part weeks).
(3) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay for a week is worked out using the following formula:

Note: The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation if the amount worked out is nil or a negative amount (see subsection 125(3)).
(4) In subsection (3):
Subdivision C or D compensation amount for a person for a week means the amount of compensation the person would have been paid for the week if Subdivision C or D had applied.
weekly amount has the same meaning as in subsection 138(3).
Division 3—Working out normal earnings for certain former Permanent Forces members
140 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person who left the Defence Force as a Permanent Forces member.
The normal earnings are based on how much the person would have earned for the week if the person were still a Permanent Forces member.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
141 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for a week for a person who was a Permanent Forces member immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The person’s ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the person would have earned for the week as a Permanent Forces member if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s ADF pay for a week might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The person’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the week if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s allowance component for a week might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for a person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
Division 4—Working out normal earnings and normal weekly hours for certain former continuous full‑time Reservists
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
142 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person who left the Defence Force as a continuous full‑time Reservist.
The person has a one‑off choice between 2 ways of working out normal earnings. Normal earnings can be based on the amount the person would have earned if the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist. (This amount is called the ADF earnings.) Alternatively, normal earnings can be based on the person’s earnings from other work engaged in before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. (This amount is called the pre‑CFTS earnings.)
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Subdivision E tells you how to work out the normal weekly hours for a person who chooses the pre‑CFTS earnings. (Normal weekly hours for a person who chooses the ADF earnings are 37.5 hours (see subsection 132(2).)
Subdivision B—Working out normal earnings
143 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for a week for a person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force means whichever of the following amounts is chosen by the person:
(a) the amount of the person’s ADF earnings for a week (see Subdivision C);
(b) the amount of the person’s pre‑CFTS earnings for a week (see Subdivision D).
(2) The person must inform the Commission in writing of his or her choice between the ADF earnings and the pre‑CFTS earnings.
(3) The person is only entitled to make one choice for all weeks in respect of which subsection (1) applies. The person cannot change his or her choice once it has been made.
Subdivision C—Working out ADF earnings
144 Working out ADF earnings
(1) The ADF earnings for a week for a person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The person’s ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the person would have earned for the week as a continuous full‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s ADF pay for a week might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The person’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the week if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s allowance component for a week might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for a person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
Subdivision D—Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
145 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
The pre‑CFTS earnings are worked out by looking back at the period before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. During this period, the person might have been a part‑time Reservist as well as being engaged in work.
The person’s pre‑CFTS earnings has 2 components: pre‑CFTS pay and reserve pay.
The person’s pre‑CFTS pay is based on earnings from work the person was engaged in before beginning the last period of continuous full‑time service. The work engaged in might be civilian work or defence work (as some people become continuous full‑time Reservists after being Permanent Forces members).
The person’s reserve pay is based on earnings from service as a part‑time Reservist.
146 Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
(1) The pre‑CFTS earnings for a week for a person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
pre‑CFTS pay for a person for a week means the amount worked out under section 147.
reserve pay for a person for a week means the amount worked under section 149.
147 Working out pre‑CFTS pay
Pre‑CFTS pay for those engaged in work before beginning last period of full‑time service
(1) The following formula sets out how to work out the pre‑CFTS pay for a week for a person who was engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service:

Note 1: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Note 2: The person’s pre‑CFTS pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(2) If the person was required to work overtime on a regular basis in that work, the pre‑CFTS pay for a week also includes the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Pre‑CFTS pay for those not working
(3) The pre‑CFTS pay for a week for a person who was not engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
allowances for a person for a week is the average amount of allowances (other than expense allowances) paid to the person for a week for his or her work during the example period.
example period has the meaning given by section 148.
pre‑CFTS overtime hours for a person means the average number of hours of overtime worked each week by the person in his or her work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS overtime rate of pay for a person means the average hourly overtime rate of pay for the person’s overtime in his or her work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS rate of pay for a person means the person’s average hourly ordinary time rate of pay for the person’s work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS weekly hours for a person means the average number of hours worked in each week by the person in his or her work during the example period.
work includes work as a member of the Defence Force (other than as a part‑time Reservist).
Note: A person might have been a Permanent Forces member before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. This work is taken into account in the pre‑CFTS pay. However, work as a part‑time Reservist is taken into account in working out the reserve pay.
148 Definition of example period for former continuous full‑time Reservists
(1) For the purposes of section 147, the example period for a person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force is the latest period of 2 weeks:
(a) during which the person was continuously engaged in work (as defined in subsection 147(4)); and
(b) ending before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
(2) However, the Commission may determine as the example period:
(a) a different 2 week period that it considers reasonable; or
(b) a period of a different length that it considers reasonable;
if the pre‑CFTS pay for the example period under subsection (1) would not fairly represent the weekly rate at which the person was being paid for his or her work before beginning the continuous full‑time service.
149 Working out reserve pay
Reserve pay for persons who were part‑time Reservists
(1) The reserve pay for a week for a person who was a part‑time Reservist immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this subsection are defined in subsection (4).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the Reservist were not incapacitated for service.
Reserve pay for persons who were not part‑time Reservists
(3) The reserve pay for a week for a person who was not a part‑time Reservist immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for a person for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the day if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance for a person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service; or
(b) that would be paid to the person because the person is promoted, as mentioned in section 186.
example period for a person who was a part‑time Reservist immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is:
(a) the latest period of one year:
(i) during which the person was a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) ending before the person began that continuous full‑time service; or
(b) such other period that the Commission determines is reasonable.
pay‑related allowance days for a person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid an amount of pay‑related allowances.
rate of pay for a person for a day means the amount of pay that the person would have been paid for the day as a part‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
reserve days for a person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
Subdivision E—Working out normal weekly hours for persons who have chosen pre‑CFTS earnings
150 Working out normal weekly hours for persons who have chosen pre‑CFTS earnings
(1) The normal weekly hours for a person who has chosen the pre‑CFTS earnings under section 143 are worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
ADF hours for a person means the average number of hours per week (if any) during the example period (as defined in subsection 149(4)) for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
pre‑CFTS overtime hours has the meaning given by subsection 147(4).
pre‑CFTS weekly hours has the meaning given by subsection 147(4).
Division 5—Working out normal earnings and normal weekly hours for former part‑time Reservists who were engaged in civilian work
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
151 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person who:
(a) was a part‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(b) was still a part‑time Reservist when he or she left the Defence Force; and
(c) was working in civilian work before leaving the Defence Force.
The person’s normal earnings are made up of an ADF component and a civilian component. The ADF component is based on how much the person would have earned as a part‑time Reservist if the person were still a part‑time Reservist. The civilian component is based on how much the person earned from civilian work during an example period taken before the person left the Defence Force.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Subdivision E tells you how to work out the normal weekly hours for the person.
Subdivision B—Working out normal earnings of former part‑time Reservists who were engaged in civilian work
152 Application of this Division to former part‑time Reservists who were engaged in civilian work
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person was a part‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was also a part‑time Reservist when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted; and
(d) the person was engaged in civilian work before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force.
The person is called an incapacitated person in this Division.
153 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for an incapacitated person for a week is the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
ADF component for an incapacitated person for a week means the amount worked out under Subdivision C.
civilian component for an incapacitated person for a week means the amount worked out under Subdivision D.
Subdivision C—Working out the ADF component of normal earnings
154 Working out the ADF component of normal earnings
(1) The ADF component for a week for an incapacitated person is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this subsection are defined in subsection (3).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(3) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for an incapacitated person for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the day as a part‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
example period has the meaning given by section 155.
pay‑related allowance days for an incapacitated person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid an amount of pay‑related allowances.
rate of pay for an incapacitated person for a day means the amount of pay that the person would have been paid for the day as a part‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
reserve days for an incapacitated person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
155 Definition of example period for ADF component of normal earnings
For the purposes of section 154 and the definitions of defence days and defence hours in section 158, the example period for an incapacitated person is:
(a) the latest period of one year:
(i) during which the person was a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) ending before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) such other period that the Commission determines is reasonable.
Subdivision D—Working out the civilian component of normal earnings
156 Working out the civilian component of normal earnings
(1) The civilian component for a week for an incapacitated person is the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) The following formula sets out how to work out the civilian daily earnings for an incapacitated person:

Note 1: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Note 2: The person’s civilian daily earnings might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) If the incapacitated person was required to work overtime on a regular basis in his or her work, the civilian daily earnings also include the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
(4) In this section:
allowances for an incapacitated person for a day means the average amount of allowances (other than expense allowances) paid to the person for a day for his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian daily hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours worked each day by the person in his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian overtime hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours of overtime worked each day by the person in his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian overtime rate of pay for an incapacitated person means the person’s average hourly overtime rate of pay for the person’s overtime in his or her civilian work during the example period.
civilian rate of pay for an incapacitated person means the average hourly ordinary time rate of pay for the person’s civilian work during the example period.
example period has the meaning given by section 157.
157 Definition of example period for the civilian component of normal earnings
(1) For the purposes of this section 156 and the definition of civilian days in section 158, the example period for an incapacitated person is the latest period of 2 weeks:
(a) during which the person was continuously engaged in civilian work; and
(b) ending before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force.
(2) However, the Commission may determine as the example period:
(a) a different 2 week period that it considers reasonable; or
(b) a period of a different length that it considers reasonable;
if the civilian daily earnings for the example period under subsection (1) would not fairly represent the daily rate at which the person was being paid for his or her civilian work before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force.
Subdivision E—Working out normal weekly hours
158 Working out normal weekly hours
(1) The normal weekly hours for an incapacitated person means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
civilian daily hours has the meaning given by subsection 156(4).
civilian days for an incapacitated person means the average number of days (if any) per week during the example period for which the person was paid civilian daily earnings.
civilian overtime hours has the meaning given by subsection 156(4).
defence days for an incapacitated person means the average number of days (if any) per week during the example period for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
defence hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours per day during the example period for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
example period:
(a) for the purposes of the definition of defence days and defence hours—has the meaning given by section 155; and
(b) for the purposes of the definition of civilian days—has the meaning given by section 157.
Division 6—Working out normal earnings for former part‑time Reservists who were not engaged in civilian work
159 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person who:
(a) was a part‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(b) was still a part‑time Reservist when he or she left the Defence Force; and
(c) was not working in civilian work before leaving the Defence Force.
Basically, the person’s normal earnings are 7 times the daily rate that the person would be paid if the person were still a part‑time Reservist.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
160 Application of this Division to former part‑time Reservists who were not engaged in civilian work
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person was a part‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was a part‑time Reservist when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted; and
(d) the person was not engaged in civilian work before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force.
The person is called an incapacitated person in this Division.
161 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for an incapacitated person for a week means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (3).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(3) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for an incapacitated person for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the day as a part‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s pay‑related allowances might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
example period for an incapacitated person is:
(a) the latest period of one year:
(i) during which the person was a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) ending before the person ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; or
(b) such other period that the Commission determines is reasonable.
pay‑related allowance days for an incapacitated person for a week means the average number of days per week (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid an amount of pay‑related allowances.
rate of pay for an incapacitated person for a day means the rate of pay that the person would have been paid for the day as a part‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
Division 7—Working out normal earnings for former part‑time Reservists who were previously Permanent Forces members
162 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person:
(a) who was a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(b) who was a part‑time Reservist when he or she left the Defence Force; and
(c) whose last period of full‑time service was as a Permanent Forces member.
The normal earnings are based on how much the person would have earned if the person were still a Permanent Forces member.
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
163 Application of this Division to former part‑time Reservists who were previously Permanent Forces members
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person was a part‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted; and
(d) the person was a Permanent Forces member immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service.
The person is called an incapacitated person in this Division.
164 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for a week for an incapacitated person means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The person’s full‑time ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the person would have earned for the week as a Permanent Forces member if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s full‑time ADF pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The person’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the week if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s allowance component might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a Permanent Forces member; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
Division 8—Working out normal earnings and normal weekly hours for former part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
Subdivision A—Simplified outline of this Division
165 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division tells you how to work out the normal earnings for a person:
(a) who was a Permanent Forces member or a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury or disease occurred; and
(b) who was a part‑time Reservist when he or she left the Defence Force; and
(c) whose last period of full‑time service was as a continuous full‑time Reservist.
The person has a one‑off choice between 2 ways of working out normal earnings. Normal earnings can be based on the amount the person would have earned if the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist. (This amount is called the full‑time ADF earnings.) Alternatively, normal earnings can be based on the person’s earnings from other work engaged in before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. (This amount is called the pre‑CFTS earnings.)
Normal earnings worked out under this Division might be adjusted under Part 5.
Subdivision D tells you how to work out the normal weekly hours for a person who chooses the pre‑CFTS earnings. (Normal weekly hours for a person who chooses the ADF earnings are 37.5 hours (see subsection 132(2).)
Subdivision B—Working out normal earnings for former part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
166 Application of this Division to former part‑time Reservists who were previously continuous full‑time Reservists
This Division applies to a person in respect of a week if:
(a) the person was a part‑time Reservist immediately before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(b) the person is incapacitated for work for the week as a result of a service injury or disease; and
(c) the person was a Permanent Forces member, or a continuous full‑time Reservist, when the service injury was sustained or the service disease was contracted; and
(d) the person was a continuous full‑time Reservist immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service.
The person is called an incapacitated person in this Division.
167 Working out normal earnings
(1) The normal earnings for an incapacitated person for a week means whichever of the following amounts is chosen by the person:
(a) the amount of the person’s full‑time ADF earnings for a week (see Subdivision C);
(b) the amount of the person’s pre‑CFTS earnings for a week (see Subdivision D).
(2) The person must inform the Commission in writing of his or her choice between the full‑time ADF earnings and the pre‑CFTS earnings.
(3) The person is only entitled to make one choice for all weeks in respect of which subsection (1) applies. The person cannot change his or her choice once it has been made.
Subdivision C—Working out full‑time ADF earnings
168 Working out full‑time ADF earnings
(1) The full‑time ADF earnings for a week for an incapacitated person means the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The amount of $100 is indexed under section 183.
(2) The person’s full‑time ADF pay for a week means the amount of pay that the person would have earned for the week as a continuous full‑time Reservist if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s full‑time ADF pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(3) The person’s allowance component for a week means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the week if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s allowance component might be adjusted under Part 5.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a continuous full‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
(5) In this section:
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated person means a pay‑related allowance:
(a) that was being paid to the person immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service; or
(b) that the person would have been paid after completing his or her initial training, as mentioned in section 189.
Subdivision D—Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
169 Simplified outline of this Subdivision
The pre‑CFTS earnings are worked out by looking back at the period before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. During this period, the person might have been a part‑time Reservist as well as being engaged in work.
The person’s pre‑CFTS earnings have 2 components: pre‑CFTS pay and reserve pay.
The person’s pre‑CFTS pay is based on earnings from work the person was engaged in before beginning the last period of continuous full‑time service. The work engaged in might be civilian work or defence work (as some people become continuous full‑time Reservists after being Permanent Forces members).
The person’s reserve pay is based on earnings from service as a part‑time Reservist.
However, for a person whose service injury or disease occurred while a continuous full‑time Reservist, the Commission may determine pre‑CFTS earnings by looking back at the period before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force instead of the period before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
170 Working out pre‑CFTS earnings
(1) The pre‑CFTS earnings for a week for an incapacitated person means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
pre‑CFTS pay for an incapacitated person for a week means the amount worked out under section 171.
reserve pay for an incapacitated person for a week means the amount worked out under section 173.
171 Working out pre‑CFTS pay
Pre‑CFTS pay for those engaged in work before beginning last period of full‑time service
(1) The following formula sets out how to work out the pre‑CFTS pay for a week for an incapacitated person who was engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service:

Note 1: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Note 2: The person’s pre‑CFTS pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
(2) If the incapacitated person was required to work overtime on a regular basis in that work, the pre‑CFTS pay for the week also includes the amount worked out using the following formula:
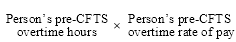
Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
Pre‑CFTS pay for those not working
(3) The pre‑CFTS pay for a week for an incapacitated person who was not engaged in work before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
allowances for an incapacitated person for a week is the average amount of allowances (other than expense allowances) paid to the person for a week for his or her work during the example period.
example period has the meaning given by section 172.
pre‑CFTS overtime hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours of overtime worked each week by the person in his or her work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS overtime rate of pay for an incapacitated person means the average hourly overtime rate of pay for the person’s overtime in his or her work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS rate of pay for an incapacitated person means the average hourly ordinary time rate of pay for the person’s work during the example period.
pre‑CFTS weekly hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours worked in each week by the person in his or her work during the example period.
work includes work as a member of the Defence Force (other than as a part‑time Reservist).
Note: A person might have been a Permanent Forces member before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service. This work is taken into account in the pre‑CFTS pay. However, work as a part‑time Reservist is taken into account in the reserve pay.
172 Definition of example period for the pre‑CFTS pay
(1) For the purposes of this section 171, the example period for an incapacitated person is the latest period of 2 weeks:
(a) during which the person was continuously engaged in work (as defined in subsection 171(4)); and
(b) ending before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
(2) However, the Commission may determine as the example period:
(a) a different 2 week period that it considers reasonable; or
(b) a period of a different length that it considers reasonable;
if the pre‑CFTS pay for the example period under subsection (1) would not fairly represent the weekly rate at which the person was being paid for his or her work before beginning the continuous full‑time service.
173 Working out reserve pay
Reserve pay for persons who were part‑time Reservists
(1) The reserve pay for a week for an incapacitated person who was a part‑time Reservist immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note: The expressions used in this formula are defined in subsection (4).
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the date on which each compensable pay‑related allowance would normally have ceased to be paid to the person if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Reserve pay for persons who did not serve as part‑time Reservists
(3) The reserve pay for a week for an incapacitated Reservist who was not serving as a part‑time Reservist immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is nil.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
amount of pay‑related allowances for an incapacitated person for a day means the total amount of compensable pay‑related allowances that would have been paid to the person for the day if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s pay‑related allowance might be adjusted under Part 5.
compensable pay‑related allowance for an incapacitated person means a pay‑related allowance that was being paid to the person immediately before beginning his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
example period for an incapacitated person is:
(a) the latest period of one year:
(i) during which the person was a part‑time Reservist; and
(ii) ending before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service; or
(b) such other period that the Commission determines is reasonable.
pay‑related allowance days for an incapacitated person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid a pay‑related allowance.
rate of pay for a person for a day means the amount of pay that the person would have been paid for the day as a member of the Reserves if:
(a) the person were still a part‑time Reservist; and
(b) the person were not incapacitated for service.
Note: The person’s rate of pay might be adjusted under Part 5.
reserve days for an incapacitated person for a week means the average number of days (if any) served each week during the example period for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
173A Example periods for those injured as continuous full‑time Reservists
(1) For the purposes of the definition of example period in sections 172 and 173 for an incapacitated person who was a continuous full‑time Reservist when the service injury was sustained, or the service disease was contracted, the Commission may determine, as the end of the example period, a time before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force (instead of a time before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service).
(2) If the Commission does so, a reference in sections 171, 172 and 173 to a time before the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service is taken instead to be a reference to a time before the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force.
Subdivision E—Working out normal weekly hours for persons who have chosen pre‑CFTS earnings
174 Working out normal weekly hours for persons who have chosen pre‑CFTS earnings
(1) The normal weekly hours for an incapacitated person who has chosen the pre‑CFTS earnings under section 167 means the amount worked out using the following formula:

(2) In this section:
ADF hours for an incapacitated person means the average number of hours per week (if any) during the example period (as defined in subsection 173(4)) for which the person was paid as a part‑time Reservist.
pre‑CFTS overtime hours has the meaning given by subsection 171(4).
pre‑CFTS weekly hours has the meaning given by subsection 171(4).
Division 9—Working out normal and actual earnings and normal weekly hours for persons who were cadets or declared members
175 Regulations may prescribe methods for working out normal and actual earnings and normal weekly hours for cadets and declared members
The regulations may prescribe one or more methods of working out normal earnings, actual earnings and normal weekly hours for persons who were cadets and declared members.
Note: The regulations may also modify the application of this Part in respect of cadets and declared members (see section 439).
Part 5—Adjusting the amount of compensation for incapacity for service or work
Division 1—Introduction
176 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part sets out some important rules relating to a person’s normal earnings, actual earnings and the amount of compensation paid under Part 3 or 4.
Division 2 has some general rules that apply when working out normal and actual earnings.
Division 3 adjusts normal earnings for persons whose normal earnings relate to ADF pay.
Division 4 adjusts normal earnings for persons whose normal earnings relate to civilian pay.
Division 5 sets out how to work out compensation for part of a week.
177 Definitions of normal earnings and actual earnings
In this Part:
actual earnings has the meaning given by subsection 89(3) or 132(1) (as the case requires).
normal earnings has the meaning given by subsection 89(3) or 132(2) (as the case requires).
Division 2—General rules relating to normal and actual earnings etc.
178 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division deals with the following matters:
(a) the amount of a person’s normal earnings if his or her normal earnings are less than the relevant minimum wage set by a national minimum wage order;
(b) amounts to be excluded in working out normal and actual earnings;
(c) matters to be considered when determining actual earnings;
(d) indexation.
179 Normal earnings that are less than the minimum wage
If a person’s normal earnings for a week are less than an amount calculated by multiplying the relevant minimum wage set by a national minimum wage order (under section 294 of the Fair Work Act 2009) by 38 hours per week, then the person’s normal earnings for the week are instead the amount calculated by multiplying the relevant minimum wage set by a national minimum wage order (under section 294 of the Fair Work Act 2009) by 38 hours per week.
180 Amounts that are excluded when working out normal and actual earnings
(1) In working out normal earnings, do not include:
(a) any amount of a bonus that is earned by the person (whether paid as a lump sum or periodically); or
(b) the amount of any expected increase due to:
(i) the reasonable expectation of a bonus; or
(ii) the reasonable expectation of a promotion; or
(iii) the reasonable expectation of a posting.
(2) In working out actual earnings, do not include any amount of a bonus that is earned by the person (whether paid as a lump sum or periodically).
181 Matters to be considered in determining actual earnings
(1) This section sets out those matters that the Commission must have regard to in determining the weekly amount that a person is able to earn in suitable work for the purposes of:
(a) paragraphs 101(4)(a), 105(4)(a) and 115(4)(a) (definition of actual civilian earnings); and
(b) paragraph (a) of the definition of actual earnings in subsection 132(1).
In addition, the Commission may have regard to any other matter it considers relevant.
(2) If the person is working in suitable work, the Commission must have regard to the weekly amount that the person is earning in that work.
(3) If any of the following applies after the person becomes incapacitated for work, the Commission must have regard to the matters set out in subsection (4):
(a) the person fails to accept an offer of suitable work that is made to the person;
(b) an offer of suitable work is made to the person and accepted but the person fails to begin, or fails to continue, the work;
(c) an offer of suitable work is made to the person on the condition that the person complete a reasonable rehabilitation or vocational retraining program but the person fails to do so.
(4) If subsection (3) applies, the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the weekly amount that the person would be earning in that work if the person had not failed as described in subsection (3); and
(b) whether that failure was reasonable in all the circumstances.
(5) If the person has failed to seek suitable work after becoming incapacitated for work, the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the weekly amount that the person could reasonably be expected to earn in suitable work, having regard to the state of the labour market at the relevant time; and
(b) whether that failure was reasonable in all the circumstances.
182 Indexation of pre‑CFTS pay and civilian daily earnings
(1) The regulations may specify:
(a) an index for the purposes of this section; and
(b) the manner of working out an increase in the amount of a person’s pre‑CFTS pay or civilian daily earnings (as the case requires) by reference to the movement of that index over the year ending each 31 December.
(2) The amount of a person’s pre‑CFTS pay or civilian daily earnings, for an indexation year in which there is an increase in the prescribed index, is increased in the manner prescribed by the regulations.
(3) In this section:
civilian daily earnings means the amount worked out under the following provisions:
(a) subsections 98(2) and (3);
(b) subsections 156(2) and (3).
pre‑CFTS pay means the amount worked out under the following provisions:
(a) section 112;
(b) section 147;
(c) section 171.
183 Indexation of $100 in ADF pay
(1) The regulations may specify:
(a) an index for the purposes of this section; and
(b) the manner of working out an increase in the amount of $100 mentioned in subsections 104(1), 109(1), 141(1), 144(1), 164(1) and 168(1) by reference to the movement of that index over the year ending each 31 December.
(2) The amount of $100, for an indexation year in which there is an increase in the prescribed index, is increased in the manner prescribed by the regulations.
Division 3—Adjusting ADF pay and pay‑related allowances
184 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division adjusts the amount of a person’s normal earnings worked out under Part 3 or 4 if the normal earnings relate to ADF pay.
The normal earnings are adjusted in the following situations:
(a) if a person’s pay would increase (because of an increment increase, a pay rise or a promotion);
(b) if a pay‑related allowance, or the category of defence work that is used to determine the person’s normal earnings, is abolished;
(c) if the person is injured during initial training.
Once a person’s normal earnings have been worked out under Part 3 or 4, the earnings can only be adjusted under this Division.
185 Increases in pay and allowances
(1) This section applies for the purposes of the following sections:
(a) section 91;
(b) section 96;
(c) section 104;
(d) section 109;
(e) section 114;
(f) section 141;
(g) section 144;
(h) section 149;
(i) section 154;
(j) section 161;
(k) section 164;
(l) section 168;
(m) section 173.
(2) The amount of pay that a person would have earned for a period as a member of the Defence Force, and the amount of a pay‑related allowance that a person would have been paid for a period, include the following amounts that would have applied for the period:
(a) the amount of any increase in the person’s pay by way of an increment in a range of pay;
(b) the amount of any increase in the person’s pay or a pay‑related allowance as a result of:
(i) the operation of a law of the Commonwealth, a State or a Territory; or
(ii) the making, alteration or operation of a national minimum wage order (within the meaning given by the Fair Work Act 2009), or an award, order, determination or industrial agreement, or the doing of any other act or thing, under such a law.
186 Increases in pay and allowances due to actual promotions
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 91, 96, 114 and 149 if a person is promoted.
(2) The amount of pay that the person would have earned for a period as a member of the Defence Force, and the amount of a pay‑related allowance that the person would have been paid for a period, include:
(a) the amount of any actual increase in the person’s pay or a pay‑related allowance; or
(b) the amount of an additional pay‑related allowance the person would be paid;
for the period because the person is promoted.
Note: A person must actually be promoted in order to receive an increase under this subsection.
187 Commission must determine category of defence work when defence work abolished
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 104, 109, 114, 141, 144, 149, 154, 161, 164, 168 and 173 if the category of defence work that is used to determine a person’s normal earnings ceases to exist.
Note: For example, the category of defence work that is used to determine the normal earnings of a person to whom section 104 applies is the category of defence work that the person was engaged in immediately before completing his or her last period of full‑time service.
(2) The Commission must determine which of the current categories of defence work should be used to determine a person’s normal earnings instead.
(3) The amount of pay that the person would have earned for a period is the amount that the person would have earned for the period if the person performed the category of defence work determined under subsection (2).
Note: The amount of pay mentioned in subsection (3) might include increases mentioned in section 185.
188 Commission may determine pay‑related allowances when defence work abolished
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 91, 96, 104, 109, 114, 141, 144, 149, 154, 161, 164, 168 and 173 if a person’s compensable pay‑related allowance (the old allowance) ceases to exist before the allowance’s cessation date.
Note: Subsection (6) defines cessation date and compensable pay‑related allowance.
(2) The Commission may determine which of the current pay‑related allowances (if any) the person would have been paid instead.
(3) The amount of the old allowance that the person would have been paid for a period is the amount (if any) for the period of the pay‑related allowance determined under subsection (2).
Note: The amount of the pay‑related allowance mentioned in subsection (3) might include increases mentioned in section 185.
(4) The pay‑related allowance determined under subsection (2) is taken to be a compensable pay‑related allowance.
(5) The cessation date for the new allowance is taken to be the old allowance’s cessation date.
(6) In this section:
cessation date for a person’s pay‑related allowance means the date advised by the Chief of the Defence Force under the following provisions (as the case requires):
(a) subsection 91(4);
(b) subsection 96(2);
(c) subsection 104(4);
(d) subsection 109(4);
(e) subsection 114(2);
(f) subsection 141(4);
(g) subsection 144(4);
(h) subsection 149(2);
(i) subsection 154(2);
(j) subsection 161(2);
(k) subsection 164(4);
(l) subsection 168(4);
(m) subsection 173(2).
compensable pay‑related allowance has the meaning given by the following provisions (as the case requires):
(a) subsection 91(5);
(b) subsection 96(3);
(c) subsection 104(5);
(d) subsection 109(5);
(e) subsection 114(4);
(f) subsection 141(5);
(g) subsection 144(5);
(h) subsection 149(4);
(i) subsection 154(3);
(j) subsection 161(3);
(k) subsection 164(5);
(l) subsection 168(5);
(m) subsection 173(4).
189 Amount of pay and allowances for those undergoing initial training
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 91, 96, 104, 109, 141, 144, 154, 161, 164 and 168:
(a) in respect of a person who was undergoing initial training immediately before:
(ia) if section 91 or 96 applies—the onset date for the person’s incapacity for service; and
(i) if section 104, 109, 164 or 168 applies—completing his or her last period of full‑time service; and
(ii) if section 141, 144, 154 or 161 applies—last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(b) for each week that occurs after the person would have completed the initial training if the person had completed the training.
(2) The amount of pay that the person would have earned, and the amount of pay‑related allowances that the person would have been paid, for each such week is the amount advised under subsection (3).
Note: An amount advised under this section might later include increases mentioned in section 185.
(3) The Chief of the Defence Force must advise the Commission in writing of the following:
(a) the rank that the Chief of the Defence Force considers the person would have held after completing the initial training;
(b) the amount of pay for a week for that rank that the Chief of the Defence Force considers the person would have earned as a member of the Defence Force after completing the training;
(c) any pay‑related allowance that the Chief of the Defence Force considers the person would have been paid after completing the training;
(d) the amount of that pay‑related allowance for a week that the Chief of the Defence Force considers the person would have been paid after completing the training.
190 No other adjustments to be taken into account
The only adjustments of the amount of a person’s pay or a pay‑related allowance to be taken into account in determining the person’s normal earnings are the adjustments mentioned in this Division.
Division 4—Adjusting other pay
191 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division adjusts the amount of a person’s civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay if:
(a) the amount is varied during the example period; or
(b) it is impracticable to work it out for the person.
192 Definitions of civilian daily earnings, example period and pre‑CFTS pay
In this Division:
civilian daily earnings has the meaning given by section 98 or 156 (as the case requires).
example period has the meaning given by section 99, 113, 148, 157 or 172 (as the case requires).
pre‑CFTS pay has the meaning given by section 112, 147 or 171 (as the case requires).
193 Variations during the example period
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 98, 112, 147, 156 and 171 if a person’s civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay varies during the example period.
(2) If the variation occurs as a result of:
(a) the operation of a law of the Commonwealth, a State or a Territory; or
(b) the making, alteration or operation of a national minimum wage order (within the meaning given by the Fair Work Act 2009), or an award, order, determination or industrial agreement, or the doing of any other act or thing, under such a law;
then the amount of the civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay for the person is instead the amount that would have been his or her civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay if the variation had taken effect at the beginning of the example period.
194 Civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay if working them out is impracticable
(1) This section applies for the purposes of sections 98, 112, 147, 156 and 171 if it is impracticable to work out the civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay for a person.
(2) The civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay for a person before the relevant date is the civilian daily earnings or pre‑CFTS pay before that date of another person performing comparable work.
(3) In this section:
relevant date for a person means:
(a) if section 98 applies—the onset date for the person’s incapacity; and
(b) if section 156 applies—the date the person last ceased to be a member of the Defence Force; and
(c) if section 112, 147 or 171 applies—the date the person began his or her last period of continuous full‑time service.
Division 5—Working out compensation for parts of weeks
195 Simplified outline of this Division
This Division sets out how to work out the amount of compensation the Commonwealth is liable to pay under Part 3 or 4 of this Chapter if a person is only entitled to compensation for part of a week and not a whole week.
196 Working out compensation for parts of weeks
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation under section 85, 86, 87 or 118 for a part of a week rather than a whole week if a person satisfies subsection 85(1), 86(1), 87(1) or 118(1) for the part of the week.
(2) The following formula sets out how to work out the amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay to a person for a part of a week rather than a whole week:

(3) In this section:
number of days means:
(a) if the person is entitled to compensation under section 118 and Division 6 of Part 4 applies to the person—7; and
(b) if the person is entitled to compensation under section 87—the number of days prescribed by the regulations in respect of the person; and
(c) otherwise:
(i) 5; or
(ii) if the Commission determines another number as the number of days that the person would normally work in the part of the week—that other number.
Note 1: Division 6 of Part 4 applies to former part‑time Reservists who are incapacitated for work but who did not engage in civilian work before last ceasing to be a member of the Defence Force.
Note 2: Section 87 applies to incapacitated cadets and declared members.
Part 6—Choice to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension
197 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides a choice for severely impaired people (at least 50 impairment points) who are unable to work more than 10 hours per week to receive a pension under this Part instead of compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4.
The rate of the pension is the same as the rate applicable under section 24 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986. However, the rate may be reduced for a recipient who receives an amount under Part 2 (permanent impairment) or who receives or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme.
A person who works more than 10 hours per week stops receiving the Special Rate Disability Pension. However, the person might still be eligible for assistance under the Return to Work Scheme determined by the Commission under section 210, or compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4.
198 What is a Special Rate Disability Pension?
(1) A Special Rate Disability Pension is an ongoing weekly payment (other than a payment under the Return to Work Scheme in section 210) that can be paid to certain persons instead of compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4.
(2) The maximum weekly amount of a Special Rate Disability Pension is one half of the fortnightly rate at which a pension is payable from time to time under section 24 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
199 Persons who are eligible to make a choice under this Part
(1) A person is eligible to make a choice under this Part if the Commission is satisfied that the person meets the following criteria (the eligibility criteria):
(a) at least one of the following applies:
(i) the person is receiving compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4 as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases;
(ii) the amount, under section 126, of the person’s compensation for a week, as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases, is nil or a negative amount;
(iii) the person has been paid a lump sum under section 138 in respect of the person’s incapacity for work as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases;
(b) as a result of the injuries or diseases, the person has suffered an impairment that is likely to continue indefinitely;
(c) the Commission has determined under Part 2 that the person’s impairment constitutes at least 50 impairment points;
(d) the person is unable to undertake remunerative work for more than 10 hours per week, and rehabilitation is unlikely to increase the person’s capacity to undertake remunerative work.
(2) The Commission must, as soon as practicable after becoming satisfied that a person meets the eligibility criteria, make the person a written offer of a choice under this Part. The offer must specify the date on which the offer is made.
200 Choice to receive Special Rate Disability Pension
(1) A person who is offered the choice under this Division can choose to receive a Special Rate Disability Pension instead of compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4.
(2) A person who makes the choice cannot change it.
(3) However, a person to whom the Commonwealth is no longer liable to pay a Special Rate Disability Pension under section 209 is taken not to have chosen to receive the Pension.
Note: This means that the person might still be entitled to compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4 or under the Return to Work Scheme in section 210.
201 When the choice is to be made
(1) A person who is offered the choice under this Part and who wishes to make the choice must do so within 12 months after the date on which the offer was made.
(2) The Commission may, either before or after the end of that period, extend the period within which the person must make the choice if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) there was a delay in the person receiving the offer under subsection 199(2); or
(b) the person did not receive the offer.
202 Other requirements for the choice
(1) The Commission may, in writing, approve a form for the purposes of this section.
(2) A person must make the choice in writing in accordance with the form.
(3) Before making the choice, the person must obtain financial advice from a suitably qualified financial adviser in respect of the choice.
Note: The person might be entitled to compensation for the cost of the financial advice under section 205.
203 Determinations by Commission
(1) The Commission must determine that the Commonwealth is liable to pay a Special Rate Disability Pension to a person instead of compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4 if:
(a) the person is offered the choice under this Part; and
(b) the person makes the choice to receive the pension within the period applicable under section 201 and in accordance with section 202; and
(c) the Commission is satisfied that the person meets the eligibility criteria on the day on which the person makes the choice.
(2) The Commission must determine that a person is to continue to receive compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4 if:
(a) the person is offered a choice under this Part; and
(b) either:
(i) the person does not make the choice within the period applicable under section 201 and in accordance with section 202; or
(ii) the Commission is satisfied that the person does not meet the eligibility criteria on the day on which the person makes the choice.
(3) If the Commission makes a determination under subsection (1) in relation to a person, a Special Rate Disability Pension is payable to the person instead of compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4 from the day on which the Commission becomes aware of the person’s choice.
204 Offsets
(1) The maximum weekly amount of a Special Rate Disability Pension that could be payable to a person is reduced in accordance with this section.
Permanent impairment compensation
(2) There is a reduction that is made by reference to amounts payable or paid to the person under Part 2 (permanent impairment). However, a payment received for eligible young persons, financial advice, legal advice or energy supplement under that Part does not reduce the maximum weekly amount of Special Rate Disability Pension that could be payable to the person.
(3) The maximum weekly amount of a Special Rate Disability Pension that could be payable to a person is reduced by the sum of:
(a) any weekly amounts that are being paid to the person under Part 2; and
(b) if the person has chosen to convert all or part of one or more weekly amounts that were payable to the person under that Part to lump sums—those weekly amounts or those parts of those weekly amounts.
(4) Subsection (3) applies to a person to whom section 389 or 402 applies as if the person were being paid the weekly amounts under Part 2 that the person would be paid if that section did not apply to the person.
Note: Section 389 provides that compensation under Part 2 is not payable to a person who chooses to institute proceedings for damages against the Commonwealth. Under section 402, compensation under this Act is not payable to a person who recovers damages from a third party.
Commonwealth superannuation
(5) There is a reduction if the person:
(a) has retired voluntarily, or has been compulsorily retired, from his or her work; and
(b) receives either or both a pension or lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme as a result of the retirement.
(6) The amount of the reduction under subsection (5) is 60% of the reduction that would apply to the person under section 134, 135 or 136 if the person were receiving compensation worked out under Division 2 of Part 4.
Relationship with subsection 415(4)
(7) This section does not limit the application of subsection 415(4) in relation to a Special Rate Disability Pension.
Note: Subsection (7) has the effect that if the maximum weekly amount of a Special Rate Disability Pension is reduced in accordance with this section, that amount may be further reduced in accordance with subsection 415(4).
204A Overpayment if payment of lump sum under section 138
(1) This section applies if the Commission makes a determination under subsection 203(1) in relation to a person where subparagraph 199(1)(a)(iii) applies.
(2) An amount, equal to so much of the lump sum under section 138 as is worked out in accordance with a legislative instrument made by the Commission under this subsection, is taken to be an amount of compensation that should not have been paid to the person.
Note 1: Section 415 allows the Commission to recover that amount as a debt due to the Commonwealth and allows that amount to be deducted from an amount that is payable under this Act.
Note 2: Section 1228 of the Social Security Act 1991 provides that amount is recoverable under that Act by means of deductions from payments under that Act.
Note 3: Section 205 of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 provides that amount is recoverable under that Act by means of deductions from payments under that Act.
205 Compensation for cost of financial advice and legal advice
Financial advice
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of financial advice obtained by a person if:
(a) the person obtains financial advice from a suitably qualified financial adviser as mentioned in subsection 202(3); and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Legal advice
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of legal advice obtained by a person if:
(a) the legal advice was obtained from a practising lawyer; and
(b) the legal advice was obtained in respect of the choice the person may make under this Part; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
206 Amount of financial advice and legal advice compensation
Financial advice
(1) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation under subsection 205(1) for the cost of the financial advice that it considers reasonable.
Legal advice
(2) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation under subsection 205(2) for the cost of the legal advice that it considers reasonable.
Limit
(3) The sum of the total amount of compensation under subsections 205(1) and (2) in respect of the person must not exceed $2,400.
Note: The amount of $2,400 is indexed under section 404.
(4) The amount of $2,400 applies both to financial advice and legal advice under this Part and financial advice and legal advice under Part 2 if the day on which the offer under this Part was made, and the day specified in the first notice given to the person under section 76, are the same.
207 Whom the compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 205 for the cost of financial advice or legal advice is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who gave the advice; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of the advice.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) An amount paid to the person who gave the advice discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the advice to the extent of the payment.
208 Persons who are imprisoned
The Commonwealth is not liable to pay a Special Rate Disability Pension to a person for any period during which the person is imprisoned in connection with his or her conviction of an offence.
209 Ceasing to meet certain criteria
The Commonwealth is no longer liable to pay a Special Rate Disability Pension to a person if the Commission is satisfied that:
(a) the person’s impairment as a result of all of the service injuries or diseases from which the person suffers constitutes fewer than 50 impairment points; or
(b) the person is able to undertake remunerative work for more than 10 hours per week.
209A Energy supplement for Special Rate Disability Pension
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay an energy supplement to a person for a day if:
(a) Special Rate Disability Pension:
(i) is payable to the person for the day; or
(ii) would be payable to the person for the day apart from section 204 and paragraph 398(3)(b); and
(b) the person resides in Australia on the day; and
(c) on the day the person either:
(i) is in Australia; or
(ii) is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so for a continuous period not exceeding 6 weeks.
Note: Section 424L may affect the person’s entitlement to the energy supplement.
(2) The daily rate of the supplement is 1/7 of $10.75.
210 Return to work scheme
(1) The Commission may determine, in writing, a scheme, called the Return to Work Scheme, under which the Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation of a kind mentioned in subsection (2) to a person in circumstances identified in the Return to Work Scheme if:
(a) the person:
(i) was receiving a Special Rate Disability Pension; and
(ii) becomes able to undertake remunerative work for more than 10 hours per week; and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: The person would no longer be entitled to Special Rate Disability Pension because of paragraph 209(b).
(2) The compensation is a weekly payment of an amount:
(a) worked out under the Return to Work Scheme; and
(b) worked out, at least in part, by reference to the number of hours per week of remunerative work that the person is able to undertake.
(3) The Commission may, from time to time, repeal or amend the Return to Work Scheme in writing.
(4) The Return to Work Scheme, and any repeal or amendment of the Return to Work Scheme, is a legislative instrument.
Part 7—Other types of compensation for members and former members
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
211 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides other types of compensation for current and former members who have suffered a service injury or disease.
A person who, because of an impairment resulting from a service injury or disease, has special requirements for his or her car can obtain compensation under Division 2.
Compensation is provided under Division 3 for household and attendant care services that are required because of a service injury or disease.
MRCA supplement is provided under Division 4.
Compensation for loss or damage to a member’s medical aid might be provided under Division 5 (but only if the member has not claimed compensation for a related service injury or disease).
Division 2—Motor Vehicle Compensation Scheme
212 Motor Vehicle Compensation Scheme
(1) The Commission may determine, in writing, a scheme, called the Motor Vehicle Compensation Scheme (the MVCS), under which the Commonwealth is liable to provide compensation of a kind mentioned in subsection (2) to a person in circumstances identified in the MVCS if:
(a) the person has suffered an impairment as a result of a service injury or disease for which the Commission has accepted liability; and
(b) because of that impairment, the person has a need for compensation of that kind; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
(2) The kinds of compensation are:
(a) modifying a motor vehicle for a person; and
(b) maintaining or repairing modifications to a motor vehicle; and
(c) subsidising the purchase of a motor vehicle by a person; and
(d) purchasing a motor vehicle for a person; and
(e) other kinds of compensation relating to motor vehicles specified in the MVCS.
(3) The Commission may, from time to time, repeal or amend the MVCS in writing.
(4) The MVCS, and any repeal or amendment of the MVCS, is a legislative instrument.
(5) The Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation under the MVCS in respect of an aggravated injury or disease if it is because of the aggravation or material contribution (whether wholly or partly) that the person suffered the impairment.
Division 3—Compensation for household and attendant care services
213 Definitions of attendant care services and household services
In this Division:
attendant care services for a person means services (other than household services, medical or surgical services or nursing care) that are required for the essential and regular personal care of the person.
household services for a person means services of a domestic nature (including cooking, house cleaning, laundry and gardening services) that are required for the proper running and maintenance of the person’s household.
214 Compensation for household services
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay weekly compensation for household services provided to a person if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(b) the person obtains household services that he or she reasonably requires because of the injury or disease; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
(2) However, the Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation in respect of an aggravated injury or disease if it is because of the aggravation or material contribution (whether wholly or partly) that the person reasonably requires the household services.
215 Matters to be considered in household services compensation claims
In determining whether household services are reasonably required for a person, the Commission must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the extent to which household services were provided by the person before the service injury or disease;
(b) the extent to which he or she is able to provide those services after the service injury or disease;
(c) the number of other persons (household members) living with that person as members of his or her household;
(d) the age of the household members and their need for household services;
(e) the extent to which household services were provided by household members before the service injury or disease;
(f) the extent to which household members, or any other relatives of the person, might reasonably be expected to provide household services for themselves and for the person after the service injury or disease;
(g) the need to avoid substantial disruption to the work or other activities of the household members;
(h) any other matter that the Commission considers relevant.
216 Amount of household compensation
The weekly amount of compensation under section 214 that the Commonwealth is liable to pay for household services is the lesser of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount paid or payable for those services;
(b) $330.
Note: The amount of $330 is indexed under section 404.
217 Compensation for attendant care services
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay weekly compensation for attendant care services provided to a person if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for a service injury or disease of the person; and
(b) the person obtains attendant care services that he or she reasonably requires because of the injury or disease; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
(2) However, the Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation in respect of an aggravated injury or disease if it is because of the aggravation or material contribution (whether wholly or partly) that the person reasonably requires the attendant care services.
218 Matters to be considered in attendant care compensation claims
In determining whether attendant care services are reasonably required for a person, the Commission must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the nature of the person’s injury or disease;
(b) the degree to which that injury or disease impairs the person’s ability to provide for his or her personal care;
(c) the extent to which any medical service or nursing care received by the person provides for his or her essential and regular personal care;
(d) the extent to which the attendant care services are necessary to meet any reasonable wish by the person to live outside an institution;
(e) the extent to which attendant care services are necessary to enable the person to undertake or continue defence service or any other work;
(f) any assessment made in relation to the rehabilitation of the person;
(g) the extent to which a relative of the person might reasonably be expected to provide attendant care services;
(h) any other matter that the Commission considers relevant.
219 Amount of compensation for attendant care services
The weekly amount of compensation under section 217 that the Commonwealth is liable to pay for attendant care services is the lesser of the following amounts:
(a) the weekly amount paid or payable for those services;
(b) $330.
Note: The amount of $330 is indexed under section 404.
220 Whom household and attendant care compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 214 or 217 for household services or attendant care services is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who provided, or will provide, the services; or
(ii) any other person who incurred, or will incur, the cost of the services.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 214 or 217 to a person who provided, or will provide, the services discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the services to the extent of the payment.
Division 4—MRCA supplement for members and former members
221 Eligibility for MRCA supplement
Persons eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension
(1) A person is eligible for MRCA supplement under this section if:
(a) the person satisfies the eligibility criteria in section 199 (persons who are eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension), or has satisfied those criteria during some period of his or her life; and
(b) the person is an Australian resident (within the meaning of section 5G of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986).
Note: Section 222 sets out some circumstances in which MRCA supplement is not payable.
Persons with 80 or more impairment points
(2) A person is eligible for MRCA supplement under this section if:
(a) the Commission has determined under Part 2 that an impairment suffered by the person as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases constitutes 80 or more impairment points; and
(b) the person is an Australian resident (within the meaning of section 5G of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986).
Note: Section 222 sets out some circumstances in which MRCA supplement is not payable.
222 MRCA supplement not payable in some circumstances
Persons leaving Australia otherwise than temporarily
(1) A person who leaves Australia otherwise than temporarily is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 221 after the day on which he or she left Australia.
Temporary absence from Australia
(2) A person who is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so absent for more than 26 weeks is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 221 after the first 26 weeks of the absence.
When a person becomes eligible for MRCA supplement after leaving Australia
(3) A person mentioned in subsection (1) or (2) again becomes eligible to receive MRCA supplement under section 221 on the later of the following days:
(a) the day on which the person returns to Australia;
(b) the day on which the person notifies the Commission of his or her return to Australia.
Persons receiving other payments
(4) Even though a person is eligible for MRCA supplement under subsection 221(2), the supplement is not payable to the person if he or she is receiving MRCA supplement under subsection 221(1).
(5) Even though a person is eligible for MRCA supplement under section 221, the supplement is not payable to the person if he or she is receiving:
(a) veterans supplement under section 118B of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(b) a telephone allowance under the Social Security Act 1991; or
(c) MRCA supplement under Division 5 of Part 2 of Chapter 5; or
(d) energy supplement under Part 2.25B of the Social Security Act 1991 or Part VIIAD of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(e) a social security payment (within the meaning of the Social Security Act 1991) for which a pension supplement amount (within the meaning of that Act) is used to work out the rate of the payment; or
(f) a service pension (within the meaning of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986).
223 Rate of MRCA supplement
The rate of MRCA supplement that is payable under section 221 is the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
224 Payment of MRCA supplement
MRCA supplement generally payable fortnightly
(1) Unless a determination under subsection (2) is in force in relation to the person, a person’s MRCA supplement under section 221 is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986) on which:
(a) the person is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(b) the MRCA supplement is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
MRCA supplement may be payable weekly
(2) The Commission may determine, in writing, that a person’s MRCA supplement under section 221 is payable in 2 payments (the part payments) if the person is a member of a class specified under subsection (4).
(3) A determination made under subsection (2) is not a legislative instrument.
(4) The Commission may, by legislative instrument, specify a class of persons for the purposes of subsection (2).
(5) The first of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable on each Thursday that is not a pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of that Act) on which:
(i) the person is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(ii) the MRCA supplement is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(6) The other of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable 7 days after the first of the part payments is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(7) If a person’s MRCA supplement under section 221 is payable in part payments, it is taken for the purposes of this Act that:
(a) a single supplement is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986); and
(b) that supplement is payable when the last of the part payments is, or is to be, made; and
(c) the amount of that supplement is equal to the total of the part payments.
(8) However, sections 426 and 431 (about deductions of amounts) apply as if each of the part payments were a separate supplement.
Division 5—Compensation for loss of, or damage to, medical aids
226 Compensation for loss of, or damage to, medical aids
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid if:
(a) the loss or damage results from an occurrence that happened while the member was rendering defence service; and
(b) the loss or damage requires the medical aid to be repaired or replaced; and
(c) a claim for acceptance of liability for the loss or damage, and a claim for compensation in respect of the member, has been made under section 319.
Exclusions
(2) However, the Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss or damage if:
(a) a claim for the Commission to accept liability for a service injury, disease or death resulting from the occurrence has been made under section 319; or
(b) one or more of the exclusions in sections 227 and 228 applies in respect of the loss or damage, or in respect of the occurrence that resulted in the loss or damage.
(3) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss or damage to the extent that the medical aid is repaired or replaced by the Commonwealth (other than under this section).
227 Exclusions relating to serious defaults etc.
(1) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid if:
(a) the occurrence that results in the loss or damage:
(i) resulted from the member’s serious default or wilful act; or
(ii) happened while the member was committing a serious breach of discipline; or
(iii) resulted from reasonable and appropriate counselling in relation to the member’s performance as a member; or
(b) the loss or damage was intentionally caused by the member.
(2) For the purpose of subparagraph (1)(a)(i), an occurrence is taken to have resulted from a member’s serious default or wilful act if:
(a) the member consumed alcohol or took a drug (other than a drug administered by a person legally authorised to administer the drug or a drug legally obtained and taken in accordance with the directions provided with the drug); and
(b) the occurrence resulted from the member being under the influence of the alcohol or drug.
This subsection does not otherwise limit subparagraph (1)(a)(i).
228 Exclusions relating to travel
Substantial delay commencing journey
(1) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid that resulted from an accident that occurred while the member was travelling on a journey from the member’s place of duty if the member delayed commencing the journey for a substantial time after he or she ceased to perform duty at that place, unless:
(a) the delay was for a reason connected with the performance of the member’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of having the accident was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
by that delay or by anything that happened during that delay.
Routes that are not reasonably direct
(2) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid that resulted from an accident that occurred while the member was travelling on a journey, or a part of a journey, by a route that was not reasonably direct having regard to the means of transport used, unless:
(a) the journey, or that part of the journey, was made by that route for a reason connected with the performance of the member’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of having the accident was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
because the journey, or that part of the journey, was made by that route.
Substantial interruptions to journeys
(3) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid that resulted from an accident that occurred while the member was travelling on a part of a journey made after a substantial interruption of the journey, unless:
(a) the interruption was made for a reason connected with the performance of the member’s duties; or
(b) in the circumstances of the particular case:
(i) the nature of the risk of having the accident was not substantially changed; and
(ii) the extent of that risk was not substantially increased;
because of that interruption.
229 Amount of medical aid compensation
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 226 for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid is the amount reasonably incurred by the member (whether paid or payable) in the necessary replacement or repair of the medical aid. This may include any reasonable fees or charges of a practitioner, or other qualified person, for a consultation, examination, prescription, or other service that is reasonably rendered in connection with the replacement or repair.
230 Whom medical aid compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 226 for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who provided any goods or services in connection with the replacement or repair of the medical aid; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of goods or services in connection with the replacement or repair.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 226 to a person who provided the goods or services discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the goods or services to the extent of the payment.
Chapter 5—Compensation for dependants of certain deceased members, members and former members
Part 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
231 Simplified outline of this Chapter
This Chapter provides for compensation and other benefits for dependants of certain deceased, current and former members.
Most of the benefits are provided to dependants of deceased members to whom section 12 applies. That section applies to a deceased member who died from a service death or who suffered a serious impairment from a service injury or disease before his or her death.
Part 2 provides compensation for the partners of these members if the partners were wholly dependent on the member before the member’s death.
Part 3 provides compensation for the children of these members. Other young people who were dependent on a deceased member before the member’s death might also be entitled to compensation.
The Commission can set up a scheme under Part 3 to provide education and training for the children and young dependants of deceased members, as well as for the children and young dependants of some current and former members.
Part 4 provides compensation for other dependants who were wholly or partly dependent on a deceased member to whom section 12 applies.
Part 5 provides compensation for the cost of such a deceased member’s funeral.
Part 2—Compensation for member’s death for wholly dependent partners
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
232 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides compensation for the partners of deceased members in respect of whom section 12 applies if the partner was wholly dependent on the member before his or her death.
Division 2 provides that compensation is payable weekly, but that the partner may choose to convert 25%, 50%, 75% or 100% of the weekly amount to a lump sum. Division 2 also provides additional lump sum compensation for a partner if the deceased member died from a service death.
Division 3 provides compensation for the cost of financial advice and legal advice obtained for a partner who is entitled to compensation under Division 2.
Division 4 provides a partner with a further lump sum if the deceased member received some types of compensation under Chapter 4.
The partner might be entitled to MRCA supplement under Division 5.
A partner who is entitled to compensation under this Chapter might also be entitled to have free treatment, or compensation for treatment, provided under Chapter 6.
Division 2—Compensation for member’s death for wholly dependent partners
233 Compensation for member’s death for wholly dependent partners
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member if:
(a) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the partner has been made under section 319.
234 Amount of compensation for wholly dependent partners
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 233 is:
(a) if the Commission has accepted liability for the member’s death—the amount of the lump sum mentioned in subsection (2); and
(b) in any case—subject to section 236, the weekly amount mentioned in subsection (5) of this section.
Note: Section 236 allows the partner to choose to convert 25%, 50%, 75% or 100% of the weekly amount to a lump sum.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(a), the amount of the lump sum is the amount worked out using the following formula:

Note 1: Subsection (7) defines partner’s age‑based number.
Note 2: The amount of $100,000 is indexed under section 404.
(5) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), the weekly amount is:
(a) one half of the fortnightly rate at which a pension is payable from time to time under paragraphs 30(1)(a), (b) and (c) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) payable from the date of the member’s death until the partner’s death.
(7) In this section:
partner’s age‑based number, in respect of a lump sum under paragraph (1)(a), means the number that is advised by the Australian Government Actuary by reference to the partner’s age at the date of the member’s death.
235 Notifying the partner
(1) The Commission must give the partner a written notice as soon as practicable:
(b) specifying the weekly amount mentioned in paragraph 234(1)(b) that is currently payable; and
(c) advising the partner that he or she can choose, under section 236, to convert 25%, 50%, 75% or 100% of the weekly amount to a lump sum in accordance with that section; and
(ca) advising the partner of the amount of the lump sum that would be payable to the partner in each of those cases; and
(d) specifying the date on which the notice is given.
(2) The notice may be included in the notice given under section 346.
236 Choice to take lump sum
(1) A partner who receives a notice under section 235 may choose to convert 25%, 50%, 75% or 100% of the weekly amount to a lump sum.
(2) A partner who makes a choice cannot change it.
(3) The choice must be made in writing and must be given to the Commission within 6 months after the date on which the partner received the notice.
(4) The Commission may, either before or after the end of that period, extend the period within which the choice must be made if it considers there are special circumstances for doing so.
Amount of lump sum
(5) The amount of the lump sum is worked out using the following formula:

where:
appropriate percentage means the percentage chosen by the partner under subsection (1).
partner’s age‑based number, in respect of a lump sum, means the number that is advised by the Australian Government Actuary by reference to the partner’s age at the date of the member’s death.
No lump sum for legal personal representative of a deceased partner
(6) The legal personal representative of a deceased partner is not entitled to choose to convert any percentage of the weekly amount that was payable to the deceased partner to a lump sum.
Effect on weekly payment of choosing a lump sum
(7) If a partner who receives a notice under section 235 chooses to convert 100% of the weekly amount to a lump sum, then, as soon as practicable after the choice is made, the weekly amount ceases to be payable to the partner.
(8) If a partner who receives a notice under section 235 chooses to convert 25%, 50% or 75% of the weekly amount to a lump sum, then, as soon as practicable after the choice is made, the weekly amount must be reduced accordingly.
238 Whom the compensation is payable to
Compensation under section 233 is payable to the partner.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
238A Energy supplement for compensation for wholly dependent partners of deceased members
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay an energy supplement to a person for a day if:
(a) the condition in subsection (2) is met for the day; and
(b) the person is residing in Australia on the day; and
(c) on the day the person either:
(i) is in Australia; or
(ii) is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so for a continuous period not exceeding 6 weeks.
Note: Section 424L may affect the person’s entitlement to the energy supplement.
Condition—receipt of compensation under this Division
(2) The condition is that either or both of the following apply:
(a) weekly compensation under this Division (except this section) either:
(i) is payable to the person for the day; or
(ii) would be payable to the person for the day apart from paragraph 398(3)(b);
(b) before the day the person received lump sum compensation under this Division and subsection 388(6) has not applied to the person before the day.
Rate of energy supplement
(3) The daily rate of the supplement is 1/7 of $7.10.
Division 3—Compensation for cost of financial advice and legal advice for wholly dependent partners
239 Compensation for cost of financial advice and legal advice
Financial advice
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of financial advice obtained by a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member if:
(a) the partner is entitled to compensation under section 233; and
(b) the financial advice was obtained from a suitably qualified financial adviser after the member’s death; and
(ba) the financial advice was obtained in respect of the choice the partner may make under subsection 236(1); and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the partner has been made under section 319.
Legal advice
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of legal advice obtained by a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member if:
(a) the partner is entitled to compensation under section 233; and
(b) the legal advice was obtained from a practising lawyer after the member’s death; and
(c) the legal advice was obtained in respect of the choice the partner may make under subsection 236(1); and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the partner has been made under section 319.
240 Amount of financial advice and legal advice compensation
Financial advice
(1) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation under subsection 239(1) for the cost of the financial advice that it considers reasonable.
Legal advice
(2) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation under subsection 239(2) for the cost of the legal advice that it considers reasonable.
Limit
(3) The sum of the total amount of compensation under subsections 239(1) and (2) in respect of the partner must not exceed $2,400.
Note: The amount of $2,400 is indexed under section 404.
241 Whom the compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 239 for the cost of the financial advice or legal advice is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who gave the advice; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of the advice.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) An amount paid to the person who gave the advice discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the advice to the extent of the payment.
Division 4—Continuing permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation for wholly dependent partners
242 Continuing permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation for wholly dependent partners
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member if:
(a) the member was paid compensation for the week before the week in which the member died under one or more of the following provisions:
(i) section 68, 71 or 75 (permanent impairment);
(ii) Part 3 or 4 of Chapter 4 (incapacity for service or work);
(iii) Part 6 of Chapter 4 (Special Rate Disability Pension); and
(b) a claim for compensation in respect of the partner has been made under section 319.
(2) In subsection (1):
(a) a reference to compensation paid for a week does not include a reference to compensation paid as a lump sum; and
(b) a reference to compensation paid includes a reference to compensation that the member was entitled to be paid.
243 Amount of permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 242 is the amount that is 12 times:
(a) the total amount of compensation that the member was paid under the provisions mentioned in paragraph 242(1)(a) for the week before the week in which the member died; or
(b) the total amount of compensation that the member was entitled to have been paid under those provisions for that week;
(as the case requires).
(2) The amount mentioned in subsection (1) is the total amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 242, even if more than one person is entitled to compensation under that section because of the same deceased member’s death.
244 Whom permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation for the partner under section 242 is payable to the partner.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) If 2 or more partners are entitled to compensation under section 242 because of the same deceased member’s death, then the compensation is payable in accordance with the directions of the Commission.
(3) In making directions under subsection (2), the Commission must have regard to any loss of financial support suffered by the partners as a result of the member’s death. The Commission must not have regard to any other matter.
Division 5—MRCA supplement for wholly dependent partners
245 Eligibility for MRCA supplement
A wholly dependent partner of a deceased member is eligible for MRCA supplement under this section if:
(a) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(b) the partner is an Australian resident (within the meaning of section 5G of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986).
Note: Section 246 sets out some circumstances when MRCA supplement is not payable.
246 MRCA supplement not payable in some circumstances
People leaving Australia otherwise than temporarily
(1) A wholly dependent partner who leaves Australia otherwise than temporarily is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 245 after the day on which he or she left Australia.
Temporary absence from Australia
(2) A wholly dependent partner who is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so absent for more than 26 weeks is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 245 after the first 26 weeks of the absence.
When a person becomes eligible for MRCA supplement after leaving Australia
(3) The wholly dependent partner mentioned in subsections (1) and (2) again becomes eligible to receive MRCA supplement under section 245 on the later of the following days:
(a) the day on which the partner returns to Australia; or
(b) the day on which the partner notifies the Commission of his or her return to Australia.
Persons receiving other payments
(4) Even though a wholly dependent partner is eligible for MRCA supplement under section 245, the supplement is not payable to the partner if he or she is receiving:
(a) veterans supplement under section 118B of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(b) a telephone allowance under the Social Security Act 1991; or
(c) MRCA supplement under Division 4 of Part 7 of Chapter 4; or
(d) energy supplement under Part 2.25B of the Social Security Act 1991 or Part VIIAD of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(e) a social security payment (within the meaning of the Social Security Act 1991) for which a pension supplement amount (within the meaning of that Act) is used to work out the rate of the payment; or
(f) a service pension (within the meaning of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986).
247 Rate of MRCA supplement
The rate of MRCA supplement that is payable under section 245 is the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
248 Payment of MRCA supplement
MRCA supplement generally payable fortnightly
(1) Unless a determination under subsection (2) is in force in relation to the partner, a wholly dependent partner’s MRCA supplement under section 245 is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986) on which:
(a) the partner is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(b) the MRCA supplement is payable to the partner.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
MRCA supplement may be payable weekly
(2) The Commission may determine, in writing, that a partner’s MRCA supplement under section 245 is payable in 2 payments (the part payments) if the partner is a member of a class specified under subsection (4).
(3) A determination made under subsection (2) is not a legislative instrument.
(4) The Commission may, by legislative instrument, specify a class of wholly dependent partner for the purposes of subsection (2).
(5) The first of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable on each Thursday that is not a pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of that Act) on which:
(i) the partner is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(ii) the MRCA supplement is payable to the partner.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(6) The other of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118D of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable 7 days after the first of the part payments is payable to the partner.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(7) If a partner’s MRCA supplement under section 245 is payable in part payments, it is taken for the purposes of this Act that:
(a) a single supplement is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986); and
(b) that supplement is payable when the last of the part payments is, or is to be, made; and
(c) the amount of that supplement is equal to the total of the part payments.
(8) However, sections 426 and 431 (about deductions of amounts) apply as if each of the part payments were a separate supplement.
Part 3—Compensation for eligible young persons dependent on certain deceased members, members or former members
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
250 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides compensation and other benefits for the children of certain deceased, current and former members. Young dependants under 25 might also be entitled to compensation or benefits even though they are not the child of a deceased, current or former member.
Divisions 2 to 4 provide compensation to children and young people who were dependants of deceased members to whom section 12 applies.
Division 2 provides lump sum compensation for most children and young people. Divisions 3 and 4 provide an additional weekly amount and lump sum for certain children and young people who were wholly or mainly dependent on deceased members.
Under Division 6, the Commission can set up a scheme to provide education and training for children and young people who are the dependants of certain deceased, current and former members.
A child or young person who is entitled to compensation under this Chapter might also be entitled to have free treatment, or compensation for treatment, provided under Chapter 6.
Division 2—Lump sum compensation for member’s death for certain eligible young persons
251 Lump sum compensation for member’s death for certain eligible young persons
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a person if:
(a) the person:
(i) was an eligible young person; and
(ii) was a dependant of a deceased member;
immediately before the member’s death; and
(b) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 257 sets out who the compensation is payable to.
Note 2: This Part does not apply to an eligible young person who was also the wholly dependent partner of the deceased member (see section 260).
252 Amount of compensation for dependent eligible young persons
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 251 for the eligible young person is $60,000.
Note: The amount of $60,000 is indexed under section 404.
Division 3—Weekly compensation for certain eligible young persons
253 Weekly compensation for certain eligible young persons
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a person for a week if:
(a) the person is an eligible young person for the week or a part of the week; and
(b) the person was a dependant of a deceased member immediately before the member’s death; and
(c) either:
(i) the young person was wholly or mainly dependent on the member immediately before the member’s death; or
(ii) the young person would have been wholly or mainly dependent on the member for the week or the part of the week if the member had not died; and
(d) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 257 sets out who the compensation is payable to.
Note 2: This Part does not apply to an eligible young person who was also the wholly dependent partner of the deceased member (see section 260).
(2) The Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation for an eligible young person who is born alive after the deceased member’s death from the week in which the young person is born.
254 Amount of weekly compensation
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 253 for the eligible young person for a week is $135.34.
Note: The amount of $135.34 is indexed under section 404.
Division 4—Continuing permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation for certain eligible young persons
255 Continuing permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation for certain eligible young persons
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a person if:
(a) the person:
(i) was an eligible young person; and
(ii) was a dependant of a deceased member;
immediately before the member’s death; and
(b) the person was wholly or mainly dependent on the member immediately before the member’s death; and
(c) the member was paid compensation for the week before the week in which the member died under one or more of the following provisions:
(i) section 68, 71 or 75 (permanent impairment);
(ii) Part 3 or 4 of Chapter 4 (incapacity for service or work);
(iii) Part 6 of Chapter 4 (Special Rate Disability Pension); and
(d) there is no wholly dependent partner of the member:
(i) who is entitled to compensation under section 242; or
(ii) who would be entitled to compensation under that section if a claim for compensation in respect of the partner were made; and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 257 sets out who the compensation is payable to.
Note 2: This Part does not apply to an eligible young person who was also the wholly dependent partner of the deceased member (see section 260).
(2) In paragraph (1)(c):
(a) a reference to compensation paid for a week does not include a reference to compensation paid as a lump sum; and
(b) a reference to compensation paid includes a reference to compensation that the member was entitled to be paid.
256 Amount of permanent impairment and incapacity etc. compensation
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 255 is the amount that is 12 times:
(a) the total amount of compensation that the member was paid under the provisions mentioned in paragraph 255(1)(c) for the week before the week in which the member died; or
(b) the total amount of compensation that the member was entitled to be paid under those provisions for that week;
(as the case requires).
(2) The amount mentioned in subsection (1) is the total amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 255, even if more than one person is entitled to compensation under that section because of the same deceased member’s death.
Note: If more than one person is entitled to compensation under section 255, the amount mentioned in subsection (1) is payable in accordance with the directions of the Commission (see section 257).
Division 5—Whom compensation under Divisions 2 to 4 is payable to
257 Whom the compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under Divisions 2 to 4 is payable to:
(a) if the eligible young person is less than 18 years old—the person who has primary responsibility for the daily care of the young person; or
(b) otherwise—the eligible young person.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) If 2 or more eligible young persons are entitled to compensation under section 255 because of the same deceased member’s death, then compensation under that section is payable in accordance with the directions of the Commission.
(3) In making directions under subsection (2), the Commission must have regard to any loss of financial support suffered by the eligible young persons as a result of the member’s death. The Commission must not have regard to any other matter.
Division 6—Education scheme for certain eligible young persons dependent on members, former members and deceased members
258 Education scheme for certain eligible young persons
(1) The Commission may determine, in writing, a scheme to provide education and training for:
(a) an eligible young person who is a dependant of the following member or former member:
(i) a member or former member who satisfies the eligibility criteria in section 199 (persons who are eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension), or who has satisfied those criteria during some period of his or her life;
(iii) a member or former member who suffers an impairment, as a result of one or more service injuries or diseases, that the Commission has determined under Part 2 of Chapter 4 constitutes 80 or more impairment points; and
(b) an eligible young person who, immediately before a deceased member’s death, was a dependant of the member in respect of whom section 12 applies.
Note: This Part does not apply to an eligible young person who was also the wholly dependent partner of the deceased member (see section 260).
(2) A claim under section 319 must be made in respect of the eligible young person in order to be provided with education and training under the scheme.
(3) The scheme may provide for the following:
(a) the payment of maintenance allowances for eligible young persons who are being provided with education or training under the scheme;
(aa) the payment of scholarships for eligible young persons who are being provided with education or training under the scheme;
(b) how applications for education or training for eligible young persons are made under the scheme;
(c) investigating and determining those applications;
(d) the establishment, membership and operation of any body to perform the functions, and exercise the powers, that are conferred on the body by or under the scheme in respect of the operation of the scheme;
(e) guidance and counselling services in respect of the education or training of eligible young persons under the scheme.
(4) The Commission may, by written determination, vary or revoke a determination under subsection (1).
(5) A determination, and any variation or revocation of a determination, under this section has no effect unless the Minister has approved the determination, variation or revocation in writing.
(6) A determination, and any variation or revocation of a determination, under this section prepared by the Commission and approved by the Minister is a legislative instrument made by the Minister on the day on which the determination, variation or revocation is approved.
259 Completing courses begun before turning 25 years old
This Division, and the scheme established under section 258, continue to apply to a person after he or she turns 25 if:
(a) before turning 25, the person began a course of education or training provided under the scheme; and
(b) the person turns 25 before finishing the course; and
(c) after turning 25, the person continues the course in order to finish it.
Division 7—Exclusion of Part for wholly dependent partners
260 Exclusion of Part for wholly dependent partners
This Part does not apply to an eligible young person who was dependent on a deceased member immediately before the member’s death if the eligible young person was also the wholly dependent partner of the member at that time.
Note: A wholly dependent partner of a deceased member is entitled to compensation under Part 2.
Part 4—Compensation for dependants other than wholly dependent partners and eligible young persons
261 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides compensation for dependants of deceased members to whom section 12 applies (other than partners and children of those members).
Each dependant can be paid a lump sum determined by the Commission.
262 Compensation for dependants other than wholly dependent partners and eligible young persons
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for a person if:
(a) the person was a dependant of a deceased member immediately before the member’s death; and
(b) the dependant was neither:
(i) a wholly dependent partner of the member; nor
(ii) an eligible young person who was a dependant of the member;
immediately before the member’s death; and
(c) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
263 Amount of compensation for other dependants
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 262 in respect of a dependant is the amount that the Commission determines is reasonable. However:
(a) that amount must not exceed $60,000; and
(b) the total amount paid under section 262 in respect of all dependants of a particular deceased member must not exceed $190,000.
Note: The amounts of $60,000 and $190,000 are indexed under section 404.
(2) In making a determination under subsection (1), the Commission must have regard to:
(a) any financial loss suffered by the dependant as a result of the member’s death (other than compensation paid or payable under this Act); and
(b) the degree to which the dependant was dependent on the deceased member; and
(c) the length of time that the dependant would have been dependent on the member.
The Commission must not have regard to any other matter (in particular, any amount of compensation paid or payable under this Act before the member died).
264 Whom the compensation is payable to
Compensation for a dependant under section 262 is payable to:
(a) if the dependant is less than 18 years old—the person who has primary responsibility for the daily care of the dependant; or
(b) otherwise—the dependant.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
Part 5—Compensation for funeral expenses
265 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides compensation to pay for the cost of the funeral of a deceased member in respect of whom section 12 applies.
266 Compensation for cost of funeral
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of a deceased member’s funeral if:
(a) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(b) a claim for compensation has been made under section 319.
(2) The claim under section 319 may only be made:
(a) in respect of a dependant of the deceased member if the dependant incurred the cost of the funeral; or
(b) by the deceased member’s legal personal representative.
267 Amount of funeral compensation
(1) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation under section 266 that it considers reasonable for the cost of the deceased member’s funeral. The amount must not exceed the amount determined in accordance with subsection (3).
(2) In determining the amount, the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the charges ordinarily made for funerals in the place where the funeral was carried out; and
(b) any amount paid or payable in respect of the cost of the funeral under any other law of the Commonwealth.
The Commission must not have regard to any other matter.
(3) The maximum amount of compensation under subsection (1) is:
(a) $9,000; or
(b) if the regulations prescribe a higher amount—that amount.
Note: The amount of $9,000 is indexed under section 404.
268 Whom funeral compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 266 for the cost of a deceased member’s funeral is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who carried out the funeral; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of the funeral.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 266 to a person who carried out the funeral discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the funeral to the extent of the payment.
Chapter 6—Treatment for injuries and diseases
Part 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
269 Simplified outline of this Chapter
This Chapter deals with the provision of treatment for injuries and diseases for certain current and former members and dependants of deceased members.
Compensation for the cost of treatment is provided for under Part 2, while treatment itself is provided for under Part 3.
Some people are entitled to treatment, or compensation for the cost of treatment, for any injury or disease. Other people are only entitled to treatment, or compensation for treatment, for a service injury or disease.
Additional compensation for costs incurred in travelling to obtain treatment and MRCA supplement are provided for under Part 4.
Generally, a claim for compensation must be made under section 319 to be entitled to treatment or compensation under this Chapter.
Part 5 contains offence provisions relating to treatment compensated or provided for under this Chapter. The offences relate to conduct by those claiming compensation or treatment under this Chapter, as well as conduct by practitioners and providers of pathology services.
Part 2—Compensation for treatment costs
270 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides compensation for the cost of treatment for injuries or diseases of certain current and former members and dependants of deceased members.
Under this Part, the Commission can provide current and former members with compensation for the cost of treatment for service injuries or diseases instead of providing the treatment under Part 3 or under the Defence Force Regulations 1952.
Treatment can be compensated under this Part even if the person obtains the treatment before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to the treatment under Part 3 or if the person dies after receiving the treatment.
A claim for compensation must be made under section 319 in respect of a person to be entitled to the compensation.
A person who is entitled to compensation under this Part might also be entitled to compensation under Part 4 for costs incurred in travelling to obtain the treatment.
Compensation for costs incurred in treating an aggravated injury or disease might not be paid if the aggravation or material contribution ceases.
271 Compensation for treatment for service injuries and diseases etc.
Compensation for treatment for service injuries and diseases
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for a person’s service injury or disease if:
(a) the person is a former member, or a current part‑time Reservist, cadet or declared member; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for the service injury or disease; and
(c) it was reasonable for the person to obtain the treatment in the circumstances; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319; and
(e) the Commission determines under section 327 that this section applies to the person.
Note 1: Treatment for current members of the Defence Force (other than part‑time Reservists) is provided under the Defence Force Regulations 1952. However, compensation or treatment for such a member might also be provided under section 272 or under Part 3.
Note 2: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 274 (relationship with other compensation provisions);
(b) section 275 (no compensation if aggravation etc. ceases);
(c) section 276 (amount of compensation);
(d) section 277 (whom compensation is payable to).
Compensation for treatment prior to a service death
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for a person’s injury or disease if:
(a) the person later dies from the injury or disease; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for the service death; and
(c) it was reasonable for the person to obtain the treatment in the circumstances; and
(d) a claim for compensation has been made under section 319 by the person’s legal personal representative.
Note: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 274 (relationship with other compensation provisions);
(b) section 275 (no compensation if aggravation etc. ceases);
(c) section 276 (amount of compensation);
(d) section 277 (whom compensation is payable to).
272 Compensation for members entitled to treatment under the Defence Force Regulations
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for a member’s service injury or disease if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for the injury or disease; and
(b) it was reasonable for the member to obtain the treatment in the circumstances; and
(c) the member is entitled to medical and dental treatment under the Defence Force Regulations 1952; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the member has been made under section 319; and
(e) the Commission, after considering any advice from the Chief of the Defence Force, determines that it is more appropriate to provide compensation for the treatment under this section even though the treatment could have been provided under the Defence Force Regulations 1952.
Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 274 (relationship with other compensation provisions);
(b) section 275 (no compensation if aggravation etc. ceases);
(c) section 276 (amount of compensation);
(d) section 277 (whom compensation is payable to).
273 Compensation for those entitled to treatment under Part 3
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for a person’s injury or disease if:
(a) the person is entitled to treatment under Part 3 in respect of the injury or disease; and
(b) the person obtains the treatment before any determination by the Commission that the person is entitled to the treatment under that Part; and
(c) it was reasonable for the person to obtain the treatment in the circumstances; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: This section might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 274 (relationship with other compensation provisions);
(b) section 275 (no compensation if aggravation etc. ceases);
(c) section 276 (amount of compensation);
(d) section 277 (whom compensation is payable to).
274 Relationship of this Part with other compensation provisions
(1) The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation under section 271, 272 or 273 for the cost of treatment if the Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation in respect of the treatment under a section in another Chapter of this Act.
(2) If a person would be entitled to compensation for the cost of treatment under more than one section in this Part, then the Commonwealth is only liable to pay compensation in respect of the treatment under one of those sections.
275 No compensation if aggravated injury or disease ceases to be aggravated etc.
The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for an aggravated injury or disease if, at the time of the treatment, the aggravation or material contribution had ceased.
276 Amount of treatment compensation
(1) The Commission must determine the amount of compensation payable under section 271, 272 or 273. The amount must be the amount the Commission considers reasonable for the cost of the treatment for a person’s injury or disease. However, the amount must not be more than the amount actually incurred in obtaining the treatment.
Note 1: The amount determined by the Commission must not take into account increases in the cost of a particular treatment after that treatment has been obtained.
Note 2: Compensation for costs incurred in respect of journeys etc. made for the purposes of obtaining treatment is paid under Part 4.
(2) The amount of compensation for treatment includes the amount reasonably incurred (whether paid or payable) in the necessary replacement or repair of a medical aid used by the person. This may include any reasonable fees or charges of a practitioner, or other qualified person, for a consultation, examination, prescription, or other service that is reasonably rendered in connection with the replacement or repair.
277 Whom treatment compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 271, 272 or 273 for the cost of the treatment is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) the person who provided the treatment; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of the treatment.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 271, 272 or 273 to a person who provided the treatment discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of the treatment to the extent of the payment.
Part 3—Entitlement to provision of treatment
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
278 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part provides for treatment to be provided for the injuries and diseases of certain current and former members and dependants of deceased members.
Current and former members might be entitled to treatment for a service injury or disease rather than compensation under Part 2 or treatment under the Defence Force Regulations 1952.
Current and former members who have suffered a serious impairment from a service injury or disease are entitled to treatment for any injury or disease.
Some partners and young dependants (such as children) of deceased members in respect of whom section 12 applies are also entitled to treatment for any injury or disease.
Generally, a claim for compensation in respect of the person must be made under section 319 to be entitled to the treatment.
Treatment might not be provided for an aggravated injury or disease if the aggravation or material contribution ceases.
Former members might be entitled to treatment for an injury or disease under this Part rather than receiving compensation for medical expenses under the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988. The Commission accepts liability for such an injury or disease under that Act and not this Act.
The Commission can arrange for treatment under this Part in accordance with arrangements it has with hospitals and doctors etc. or in accordance with a determination it makes under Division 4 of this Part.
A person who is entitled to treatment under this Part might also be entitled to compensation for costs incurred in travelling to obtain the treatment and MRCA supplement under Part 4.
Division 2—Treatment for some members and former members
279 Treatment for members entitled to treatment under the Defence Force Regulations
A member is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for a service injury or disease of the member if:
(a) the Commission has accepted liability for the injury or disease; and
(b) the member is entitled to medical and dental treatment under the Defence Force Regulations 1952; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the member has been made under section 319; and
(d) the Commission, after considering any advice from the Chief of the Defence Force, determines that it is more appropriate to provide treatment for the injury or disease under this Part than to provide such treatment under the Defence Force Regulations 1952.
Note 1: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Note 2: A person is not entitled to treatment for an aggravated injury or disease if the aggravation ceases (see section 283).
280 Treatment for service injuries and diseases of former members and part‑time Reservists etc.
A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for a service injury or disease of the person if:
(a) the person is a former member or a current part‑time Reservist, cadet or declared member; and
(b) the Commission has accepted liability for the service injury or disease; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319; and
(d) the Commission determines under section 327 that this section applies to the person.
Note 1: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Note 2: A person is not entitled to treatment for an aggravated injury or disease if the aggravation ceases (see section 283).
280A Treatment for certain injuries covered by the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988
Person not otherwise entitled to be provided with treatment under this Act
(1) A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for an injury (within the meaning of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988) if, as a result of table item 1 of the table in subsection 144B(3) of that Act, this section applies to the person and the injury.
Note 1: Table item 1 applies to persons who are not entitled to be provided with treatment under this Act or the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 for any other injury.
Note 2: The treatment is paid for with money appropriated under subsection 160(2) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988.
Person entitled to be provided with treatment under this Act for another injury or disease
(2) A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for an injury (within the meaning of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988) if, as a result of table item 2 of the table in subsection 144B(3) of that Act, this section applies to the person and the injury.
Note 1: Table item 2 applies to persons who are entitled to be provided with treatment under section 279 or 280 of this Act for another injury.
Note 2: The treatment is paid for with money appropriated under section 423 of this Act.
281 Treatment for persons with 60 impairment points
(1) A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for any injury or disease of the person if:
(a) the Commission has determined under Part 2 of Chapter 4 (permanent impairment) that an impairment resulting from one or more service injuries or diseases suffered by the person constitutes 60 or more impairment points; and
(b) the person’s impairment continues to constitute 60 or more impairment points; and
(c) the treatment is provided to the person after the determination under Part 2 of Chapter 4 is made.
Note 1: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Note 2: A person who ceases to be entitled to treatment under this section might still be entitled to treatment under section 282.
(2) However, if the person is only suffering from a single aggravated injury or disease, then the person is only entitled to be provided with the treatment if the impairment resulting from the aggravation or material contribution constitutes, and continues to constitute, 60 or more impairment points.
282 Treatment for persons who are eligible for a Special Rate Disability Pension
A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for any injury or disease of the person if:
(a) the person satisfies the eligibility criteria in section 199 (persons who are eligible for Special Rate Disability Pension), or has satisfied those criteria during some period of his or her life; and
(b) the treatment is provided to the person after paragraph (a) begins to apply to the person.
Note 1: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Note 2: A person who ceases to be entitled to treatment under this section might still be entitled to treatment under section 281.
283 No treatment for aggravated injury or disease if aggravation ceases
A person is not entitled to be provided with treatment under section 279 or 280 for an aggravated injury or disease if the aggravation or material contribution ceases.
Division 3—Treatment for certain dependants of deceased members
284 Treatment for certain wholly dependent partners and eligible young persons
Treatment for certain wholly dependent partners
(1) A wholly dependent partner of a deceased member is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for any injury or disease of the partner if:
(a) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(b) the treatment is provided to the partner after the member’s death; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the partner has been made under section 319.
Note: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Treatment for certain eligible young persons
(2) A person is entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part for any injury or disease of the person if:
(a) the person is an eligible young person; and
(b) the person was an eligible young person who was wholly or mainly dependent on a deceased member immediately before the member’s death; and
(c) section 12 applies in respect of the member; and
(d) the treatment is provided to the person after the member’s death; and
(e) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note: Compensation might be payable in respect of treatment obtained before the Commission determines that the person is entitled to treatment (see section 273).
Division 4—Administration of the provision of treatment
285 Treatment at hospitals and other institutions etc.
(1) For the purposes of this Part, the Commission may:
(a) enter into arrangements with the appropriate authority of the Commonwealth, a State or a Territory for the provision of care and welfare at a public hospital or other institution for persons entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part; and
(b) enter into arrangements with any other body operating a hospital or other institution for the provision of care and welfare at that hospital or institution for persons entitled to be provided with treatment under this Part; and
(c) enter into arrangements with any practitioner or other person qualified to provide treatment.
(2) In this section:
public hospital or other institution means a hospital or other institution that is operated by the Commonwealth, a State or a Territory.
286 Determination for providing treatment or pharmaceutical benefits
Commission may make determination
(1) The Commission may make a written determination of any one or more of the following:
(a) the places at which, the circumstances in which, and the conditions subject to which, a particular kind or class of treatment may be provided under this Part;
(b) the places at which, the circumstances in which, and the conditions subject to which, treatment may be provided under this Part to persons as private patients;
(c) the places at which, the circumstances in which, and the conditions subject to which, pharmaceutical benefits may be provided under this Part;
(d) the kinds or classes of treatment that will not be provided under this Part;
(e) the places at which, the circumstances in which, and the conditions subject to which, treatment will not be provided under this Part;
(f) whether the Commission’s prior approval of a particular kind or class of treatment is required;
(g) if the Commission’s prior approval is required:
(i) the circumstances in which the Commission may exercise its power to give prior approval; and
(ii) the circumstances in which the Commission may exercise its power to give approval if the treatment was obtained without prior approval;
(h) both:
(i) kinds of treatment for the purposes of paragraph 287(2A)(b); and
(ii) the circumstances in which, and the extent to which, the Commission may accept financial responsibility for particular costs relating to that treatment (including amounts of subsidy payable under Chapter 3 of the Aged Care Act 1997 or of the Aged Care (Transitional Provisions) Act 1997).
Determination must be approved by the Minister
(2) A determination under subsection (1) has no effect unless the Minister has approved it in writing.
(3) A determination under subsection (1), so far as it relates to paragraph (1)(c), approved by the Minister and as in force from time to time is a pharmaceutical benefits determination.
(4) Any other determination under subsection (1) approved by the Minister and as in force from time to time is a treatment determination.
Variation or revocation of determinations
(5) The Commission may, by written determination, vary or revoke a pharmaceutical benefits determination or treatment determination.
(6) A determination under subsection (5) has no effect unless the Minister has approved it in writing.
Legislative instruments
(6A) A determination under subsection (1) or (5) made by the Commission and approved by the Minister is a legislative instrument made by the Minister on the day on which the determination is approved.
Incorporation of other instruments
(6B) Despite subsection 14(2) of the Legislation Act 2003:
(a) a determination under subsection (1); or
(b) a determination under subsection (5) varying a pharmaceutical benefits determination or treatment determination;
may make provision in relation to a matter by applying, adopting or incorporating, with or without modification, any matter contained in an instrument or other writing as in force or existing from time to time.
When treatment is provided as a private patient
(7) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), treatment is taken to be provided to a person as a private patient if:
(a) the treatment is provided to the person as a person who is a private patient of a hospital, for the purposes of the Health Insurance Act 1973; or
(b) the treatment is provided to the person by a medical specialist to whom the person has been referred but is not provided at a hospital.
287 Provision of treatment
(1) The Commission may arrange for treatment to be provided to a person who is entitled to treatment under this Part:
(a) in accordance with the arrangements made under section 285; or
(b) in accordance with a treatment determination under section 286; or
(c) in accordance with the arrangements and the determination.
(2) However, if a person who is entitled to treatment under this Part requires a particular kind or class of treatment that is not dealt with in the arrangements or the determination, then the person’s entitlement is subject to the Commission’s approval of the treatment (whether that approval is given before or after the treatment is provided).
(2A) If:
(a) the Commission is satisfied that an entity, other than the Commission, has arranged for the provision of treatment for a person who is entitled to treatment under this Part; and
(b) the treatment is of a kind mentioned in subparagraph 286(1)(h)(i) and specified in a treatment determination;
then the Commission may, in accordance with the treatment determination as it relates to subparagraph 286(1)(h)(ii), accept financial responsibility for particular costs in relation to that treatment (including amounts of subsidy payable under Chapter 3 of the Aged Care Act 1997 or of the Aged Care (Transitional Provisions) Act 1997).
(3) Nothing in this Part:
(a) imposes a duty on the Commission to arrange for treatment to be provided to a person outside Australia; or
(b) confers a right on a person to be provided with treatment outside Australia.
Part 4—Other compensation relating to treatment
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
288 Simplified outline of this Part
Division 2 of this Part provides for compensation for costs incurred in some travel taken by a patient to obtain treatment. The Commission can also approve an attendant to accompany the patient and pay the attendant’s travel costs. The costs of the patient’s or attendant’s accommodation can be paid if they have to stay at a place to obtain the treatment.
Division 3 of this Part provides for compensation for costs incurred by certain persons in transporting another person to a hospital etc. or a mortuary.
Division 4 provides for MRCA supplement for those who are entitled to treatment under Part 3 of this Chapter.
Division 2—Compensation for patients’ and attendants’ journey and accommodation costs
289 Definition of compensable treatment
In this Division:
compensable treatment means:
(a) treatment in respect of which compensation is payable under Part 2; or
(b) treatment to which a person is entitled under Part 3 (other than under section 280A (treatment for certain injuries covered by the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988)).
Note: Compensation for travel expenses incurred in relation to treatment to which a person is entitled under section 280A may be payable under section 16 of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988.
290 Compensation for journey costs relating to treatment
Compensation for costs of a patient’s journey
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred if:
(a) the costs are incurred in respect of a journey that is made by a person that is necessary for the person to obtain compensable treatment for an injury or disease of the person; and
(b) any one or more of the following applies:
(i) if the journey is by ambulance services—the person’s injury or disease reasonably requires using those services; or
(ii) the journey is by public transport; or
(iii) if the journey is by means other than public transport or ambulance services—it is unreasonable for the person to use public transport having regard to the nature of the person’s injury or disease, or public transport is unavailable; or
(iv) the reasonable length of the journey (including the return part of the journey) exceeds 50 kilometres; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 289 defines compensable treatment.
Note 2: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 292 (journeys etc. outside Australia);
(b) section 293 (amount of compensation).
Compensation for costs of an attendant’s journey
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred if:
(a) the Commission approves a person (the attendant) to accompany another person (the patient) on a journey that is necessary for the patient to obtain compensable treatment for an injury or disease of the patient; and
(b) the costs are incurred in respect of the attendant’s journey; and
(c) any one or more of the following applies:
(i) if the journey is by ambulance services—the person’s injury or disease reasonably requires using those services; or
(ii) the journey is by public transport; or
(iii) if the journey is by means other than public transport or ambulance services—it is unreasonable for the person to use public transport having regard to the nature of the person’s injury or disease, or public transport is unavailable; or
(iv) the reasonable length of the journey (including the return part of the journey) exceeds 50 kilometres; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the attendant has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 289 defines compensable treatment.
Note 2: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 292 (journeys etc. outside Australia);
(b) section 293 (amount of compensation).
291 Compensation for accommodation relating to treatment
Compensation for the costs of a patient’s accommodation
(1) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred if:
(a) a person makes a journey that is necessary for the person to obtain compensable treatment for an injury or disease of the person; and
(b) it is necessary for the person to remain at the place to which the journey was made to obtain the treatment; and
(c) the costs are incurred in respect of the person’s accommodation at that place; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the person has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 289 defines compensable treatment.
Note 2: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 292 (journeys etc. outside Australia);
(b) section 294 (amount of compensation).
Compensation for the costs of an attendant’s accommodation
(2) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred if:
(a) the Commission approves a person (the attendant) to accompany another person (the patient) on a journey that is necessary for the patient to obtain compensable treatment for an injury or disease of the patient; and
(b) it is necessary for the patient and the attendant to remain at the place to which the journey was made to obtain that treatment; and
(c) the costs are incurred in respect of the attendant’s accommodation at that place; and
(d) a claim for compensation in respect of the attendant has been made under section 319.
Note 1: Section 289 defines compensable treatment.
Note 2: This subsection might be affected by the following provisions:
(a) section 292 (journeys etc. outside Australia);
(b) section 294 (amount of compensation).
292 No compensation for journeys or accommodation outside Australia
The Commonwealth is not liable to pay compensation under section 290 or 291 for:
(a) costs incurred in respect of a journey that is made outside Australia for the main purpose of obtaining treatment; or
(b) costs incurred in respect of accommodation required during such a journey.
293 Amount of compensation for journeys
(1) The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 290 (compensation for journeys) is the amount determined by the Commission to be the amount reasonably incurred in respect of the journey.
(2) In determining an amount under subsection (1), the Commission may determine the amount of compensation using the following formula:

Note: For example, the Commission might use the formula if a person used a private vehicle to make a journey, but not if a person flew on a commercial airline.
(3) In this section:
length of the journey in kilometres means:
(a) if only subparagraph 290(1)(b)(iv) or (2)(c)(iv) applies—the number of whole kilometres the Commission determines to be the reasonable length of the journey that it was necessary to make; and
(b) otherwise—the length of the journey in kilometres.
specified rate per kilometre means the rate per kilometre that the Minister, by legislative instrument, determines for the purposes of this section.
Note: The determination may be varied or revoked (see subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
294 Amount of compensation for accommodation
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 291 (compensation for accommodation) is the amount reasonably incurred in respect of the accommodation.
295 Matters to be considered in journey and accommodation compensation claims
In determining issues arising under this Division, the Commission must have regard to the following matters:
(a) the places where appropriate treatment was available to the person;
(b) the means of transport available to the person for the journey;
(c) the means of transport appropriate for the person to take for the journey;
(d) the routes by which the person could have travelled;
(e) the accommodation available to the person at the place to which the journey was made;
(f) any other relevant matters.
296 Whom compensation is payable to
(1) Compensation under section 290 or 291 for costs reasonably incurred is payable to:
(a) the person who made the claim for compensation; or
(b) if that person so directs:
(i) a person who provided services in connection with the journey or accommodation; or
(ii) any other person who incurred the cost of services in connection with the journey or accommodation.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
(2) A payment under section 290 or 291 to a person who provided services in connection with the journey or accommodation discharges any liability of any other person for the cost of those services to the extent of the payment.
Division 3—Compensation for transportation costs
297 Compensation for other person’s transportation costs
The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation for any costs reasonably incurred by a person (the first person) if:
(a) the first person reasonably incurred those costs in connection with transporting another person to:
(i) a hospital or other institution; or
(ii) a mortuary;
from a place where that other person had sustained an injury, contracted a disease or died; and
(b) either:
(i) that injury, disease or death is a service injury, disease or death in respect of which the Commission has accepted liability; or
(ii) the other person is entitled to treatment under section 284 in respect of the injury or disease; and
(c) a claim for compensation in respect of the first person has been made under section 319.
298 Amount of transportation costs
The amount of compensation that the Commonwealth is liable to pay under section 297 is the amount reasonably incurred by the person.
299 Whom compensation is payable to
Compensation under section 297 is payable to the person.
Note: A special rule applies if a trustee is appointed under section 432.
Division 4—MRCA supplement for members, former members and dependants
300 Eligibility for MRCA supplement
A person is eligible for MRCA supplement under this section if the person is entitled to treatment under Part 3 of this Chapter.
Note 1: Section 301 sets out some circumstances when MRCA supplement is not payable.
Note 2: MRCA supplement that is payable in relation to treatment provided under subsection 280A(1) is paid for with money appropriated under subsection 160(2) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988.
301 MRCA supplement not payable in some circumstances
People leaving Australia otherwise than temporarily
(1) A person who leaves Australia otherwise than temporarily is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 300 after the day on which he or she left Australia.
Temporary absence from Australia
(2) A person who is temporarily absent from Australia and has been so absent for more than 26 weeks is not eligible for MRCA supplement under section 300 after the first 26 weeks of the absence.
When a person becomes eligible for MRCA supplement after leaving Australia
(3) The person mentioned in subsections (1) and (2) again becomes eligible to receive MRCA supplement under section 300 on the later of the following days:
(a) the day on which the person returns to Australia; or
(b) the day on which the person notifies the Commission of his or her return to Australia.
When MRCA supplement is not payable
(4) Even though a person is eligible for MRCA supplement under section 300, the supplement is not payable to the person if:
(a) he or she is receiving veterans supplement under section 118A of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(b) he or she is receiving a pharmaceutical allowance under the Social Security Act 1991; or
(c) he or she is a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member; or
(d) he or she is receiving a social security payment (within the meaning of the Social Security Act 1991) for which a pension supplement amount (within the meaning of that Act) is used to work out the rate of the payment; or
(e) he or she is receiving a service pension (within the meaning of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986); or
(f) he or she is receiving pharmaceutical supplement under Part 3A of the Australian Participants in British Nuclear Tests and British Commonwealth Occupation Force (Treatment) Act 2006.
(5) Paragraph (4)(c) does not apply to a person who is a wholly dependent partner of a deceased member if:
(a) the member died before 20 September 2009; and
(b) at any time and in respect of the member’s death, the person chose under section 236 to convert a percentage of the weekly amount mentioned in paragraph 234(1)(b) to a lump sum.
302 Rate of MRCA supplement
The rate of MRCA supplement that is payable under section 300 is the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118C of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
303 Payment of MRCA supplement
MRCA supplement generally payable fortnightly
(1) Unless a determination under subsection (2) is in force in relation to the person, a person’s MRCA supplement under section 300 is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986) on which:
(a) the person is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(b) the MRCA supplement is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
MRCA supplement may be payable weekly
(2) The Commission may determine, in writing, that a person’s MRCA supplement under section 300 is payable in 2 payments (the part payments) if the person is a member of a class specified under subsection (4).
(3) A determination made under subsection (2) is not a legislative instrument.
(4) The Commission may, by legislative instrument, specify a class of persons for the purposes of subsection (2).
(5) The first of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118C of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable on each Thursday that is not a pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of that Act) on which:
(i) the person is eligible for the MRCA supplement; and
(ii) the MRCA supplement is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(6) The other of the part payments:
(a) is an amount equal to one half of the rate of veterans supplement that is payable from time to time under section 118C of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; and
(b) is payable 7 days after the first of the part payments is payable to the person.
Note: If a trustee is appointed under section 432, then the MRCA supplement would be payable to the trustee.
(7) If a person’s MRCA supplement under section 300 is payable in part payments, it is taken for the purposes of this Act that:
(a) a single supplement is payable on each pension payday (within the meaning of subsection 5Q(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986); and
(b) that supplement is payable when the last of the part payments is, or is to be, made; and
(c) the amount of that supplement is equal to the total of the part payments.
(8) However, sections 426 and 431 (about deductions of amounts) apply as if each of the part payments were a separate supplement.
Part 5—Offences relating to treatment under this Chapter
304 Simplified outline of this Part
This Part contains offences relating to treatment provided or compensated under this Chapter.
The offences relate to:
(a) false or misleading statements or documents given in respect of treatment; and
(b) medical service providers who cause or threaten detriment to others; and
(c) medical service providers who bribe practitioners in respect of treatment; and
(d) practitioners who accept bribes in respect of treatment; and
(e) pathology practitioners who provide payments or services to other practitioners with whom they have arrangements.
There are other offence provisions in the Criminal Code that might also apply (such as in Parts 7.3 (fraudulent conduct), 7.4 (false or misleading statements) and 7.7 (forgery)).
The Criminal Code and the Crimes Act 1914 also contain provisions that are relevant to offences generally.
305 Definitions
(1) In this Part:
medical service provider means a person:
(a) who is a pathology practitioner; or
(b) who is a proprietor of premises at which pathology services are rendered; or
(c) who is a proprietor of a hospital or other institution that is not operated by the Commonwealth, a State or a Territory; or
(d) who is acting on behalf of a proprietor of such a hospital or other institution.
pathology practitioner means a person in respect of whom there is in force an undertaking given by the person, and accepted by the Minister, under section 23DC of the Health Insurance Act 1973.
pathology service has the meaning given by subsection 3(1) of the Health Insurance Act 1973.
proprietor means:
(a) in relation to premises—the person, authority or body of persons having effective control of the premises (whether or not that person, authority or body is the holder of an estate or interest in the premises); and
(b) in relation to a hospital or other institution—the proprietor (within the meaning of paragraph (a)) of the premises occupied by the hospital or other institution.
treatment under this Chapter includes treatment in respect of which compensation is paid under Part 2 of this Chapter.
(2) In this Part, a person engages in conduct dishonestly if:
(a) the person engages in conduct; and
(b) the conduct is dishonest according to the standards of ordinary people; and
(c) the defendant knows the conduct is dishonest according to the standards of ordinary people.
306 Offence for false or misleading statements or documents relating to treatment
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) any of the following applies:
(i) the person makes a statement (whether oral or in writing);
(ii) the person issues or presents a document;
(iii) the person authorises a statement to be made or a document to be issued or presented; and
(b) the statement or document is false or misleading in a material particular; and
(c) the statement or document is capable of being used in connection with:
(i) a claim for compensation under Part 2 or 4; or
(ii) a claim by a person for payment for treatment provided by the person under Part 3.
Penalty: 20 penalty units.
(2) Subsection (1) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply if:
(a) the person did not know, and could not reasonably be expected to have known, that the statement or document was false or misleading in a material particular; or
(b) the person did not know, and could not reasonably be expected to have known, that the statement or document was capable of being used in connection with:
(i) a claim for compensation under Part 2 or 4; or
(ii) a claim by a person for payment for treatment provided by the person under Part 3.
Note: A defendant bears an evidential burden in relation to the matter in subsection (3) (see subsection 13.3(3) of the Criminal Code).
(4) Section 9.2 of the Criminal Code (mistake of fact) does not apply in relation to the matters mentioned in subsection (3).
(5) Despite section 15B of the Crimes Act 1914, a prosecution for an offence under this section can be commenced at any time within 3 years after the offence is committed.
307 Offence for medical service providers causing detriment to others
A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a medical service provider; and
(b) the person engages in conduct or omits to engage in conduct; and
(c) the conduct or omission causes detriment to another person; and
(d) the person engages in the conduct or omits to engage in the conduct intending:
(i) the conduct or omission to cause detriment to the other person; and
(ii) to encourage the other person to request a pathology service in respect of treatment provided under this Chapter; and
(e) the other person does not consent to the conduct or omission.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
308 Offence for medical service providers threatening detriment
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a medical service provider; and
(b) the medical service provider makes a threat to another person to cause detriment to the other person or a third person; and
(c) the medical service provider is reckless as to causing the other person or the third person to fear that the threat will be carried out; and
(d) the medical service provider makes the threat intending to encourage the other person to request a pathology service in respect of treatment provided under this Chapter.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), a threat may be:
(a) express or implied; or
(b) conditional or unconditional.
(3) In a prosecution for an offence against subsection (1), it is not necessary to prove that the person actually feared that the threat would be carried out.
309 Offence for bribery by medical service providers
A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a medical service provider; and
(b) the person dishonestly:
(i) provides a benefit to another person; or
(ii) causes a benefit to be provided to another person; or
(iii) offers or promises to provide a benefit to another person; or
(iv) causes an offer or a promise to provide a benefit to be made to another person; and
(c) the person does so intending to encourage the other person to request a pathology service in respect of treatment provided under this Chapter.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
310 Offence for practitioners receiving bribes etc.
A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a practitioner; and
(b) the person dishonestly:
(i) asks for a benefit for himself or herself, or for another person; or
(ii) receives or obtains a benefit for himself or herself, or for another person; or
(iii) agrees to receive or obtain a benefit for himself or herself, or for another person; and
(c) the person does so intending:
(i) that treatment provided by him or her under this Chapter will be influenced; or
(ii) to induce, foster or sustain a belief that such treatment will be influenced.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
311 Offence for pathology practitioners making payments to requesting practitioners
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a pathology practitioner; and
(b) another practitioner (the requesting practitioner) requests the pathology practitioner to provide pathology services to a person (the patient); and
(c) the patient is entitled to treatment under this Chapter; and
(d) the pathology practitioner provides those services; and
(e) the pathology practitioner makes a payment (either directly or indirectly) to the requesting practitioner either:
(i) in respect of other services provided by the requesting practitioner to the patient in connection with the request; or
(ii) in respect of the use of the requesting practitioner’s staff in connection with taking pathology specimens from the patient.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
(2) Strict liability applies to paragraph (1)(c).
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
312 Offence for pathology practitioners providing pathology services to persons with whom they have arrangements
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a pathology practitioner; and
(b) the person has entered an arrangement with another practitioner to share the cost of:
(i) employing staff; or
(ii) buying, renting or maintaining items of equipment;
(whether or not the arrangement involves paying money or providing other consideration); and
(c) the other practitioner requests the person to provide pathology services in respect of treatment under this Chapter; and
(d) the person provides those services while the arrangement is in force.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
(2) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a pathology practitioner; and
(b) the pathology practitioner has entered an arrangement with a practitioner:
(i) to share a particular space in a building; or
(ii) for one of them to provide space in a building for the other to use or occupy; or
(iii) for one of them to permit the other to use or occupy the building; and
(c) the charges payable under the arrangement are not charges fixed at normal commercial rates; and
(d) the practitioner requests the pathology practitioner to provide pathology services in respect of treatment under this Chapter; and
(e) the pathology practitioner provides those services while the arrangement is in force.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
313 Offence for providing staff to be used in pathology services
A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is a pathology practitioner; and
(b) the person provides nursing or other staff at the premises of another practitioner (whether the staff are present full‑time, part‑time or from time to time); and
(c) the person intends the staff to be used in taking pathology specimens in respect of treatment under this Chapter.
Penalty: 120 penalty units or imprisonment for 2 years.
314 Counselling statements inadmissible as evidence
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person (the treatment provider) has provided treatment under this Chapter; and
(b) the treatment provider has been counselled by a staff member assisting the Commission with respect to providing treatment under this Chapter; and
(c) the treatment provider makes a statement during the counselling.
(2) The statement is inadmissible as evidence against the treatment provider in proceedings prosecuting him or her for an offence mentioned in subsection (3) unless:
(a) the treatment provider consents to the statement being admitted as evidence in the proceedings; or
(b) both of the following apply:
(i) evidence of another statement made by the treatment provider during such counselling is admitted on behalf of the provider;
(ii) evidence of the statement mentioned in paragraph (1)(c) is adduced to refute evidence of that other statement.
(3) For the purposes of subsection (2), these are the offences:
(a) an offence under this Part;
(b) an offence against:
(i) section 6 of the Crimes Act 1914 (accessory after the fact); or
(ii) section 11.1, 11.4 or 11.5 of the Criminal Code (attempt, incitement or conspiracy);
that relates to an offence under this Part.
315 Recovery of amounts paid because of false or misleading statements
(1) This section applies if:
(a) an amount is paid under this Chapter purportedly by way of compensation or payment to a person for treatment provided by the person; and
(b) as a result of making a false or misleading statement, the amount paid exceeds the amount (if any) that should have been paid.
(2) The amount of the excess is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from:
(a) the person by or on behalf of whom the statement was made; or
(b) the estate of that person.
(3) Subsection (2) applies whether or not:
(a) the amount was paid to the person by or on behalf of whom the statement was made; and
(b) any person has been convicted of an offence in relation to the making of the statement.
316 Interest payable on amounts paid because of false or misleading statements
(1) This section applies if:
(a) an amount (the principal sum) is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from a person or estate under section 315; and
(b) the Commission has served a notice on the person or estate (as the case requires) claiming the amount as a debt due to the Commonwealth; and
(c) an arrangement has been entered into between the Commission and the person or estate (as the case requires) to repay the principal sum within the following period (the relevant period):
(i) the period of 3 months from the day the notice is served;
(ii) such longer period as the Commission allows; and
(d) there has been a default (whether before or after the end of that period) in repaying all or part of the principal sum as required by the arrangement.
(2) This section applies if:
(a) an amount (the principal sum) is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from a person or estate under section 315; and
(b) the Commission has served a notice on the person or estate (as the case requires) claiming the amount as a debt due to the Commonwealth; and
(c) an arrangement to repay the principal sum has not been entered into within the following period (the relevant period):
(i) the period of 3 months from the day the notice is served;
(ii) such longer period as the Commission allows; and
(d) all or part of the principal sum remains unpaid.
(3) Interest is payable on the amount of the principal sum that remains unpaid from time to time.
(4) The interest is payable from:
(a) the day after the end of the relevant period; or
(b) such other later day ordered by a court in any proceedings instituted by the Commonwealth to recover an amount due under this section.
(5) The interest is payable at the rate prescribed from time to time for the purposes of subsection 129AC(2) of the Health Insurance Act 1973.
(6) The interest is recoverable as a debt due to the Commonwealth from the person or estate (as the case requires).
317 Reduction in payments because of previous overpayments
(1) The Commission may reduce the amount of any payment that becomes payable to a person if:
(a) an amount has previously been paid under this Chapter to the person purportedly by way of compensation or payment for treatment provided; and
(b) the amount paid exceeds the amount (if any) that should have been paid; and
(c) the person agrees to the reduction.
(2) The amount of the reduction must not exceed:
(a) if the Commission has not previously reduced a payment under this section—the amount of the excess; and
(b) otherwise—the amount by which the sum of all amounts of excess under subsection (1) exceeds the sum of all amounts recovered under this section.
Chapter 7—Claims
Part 1—Making a claim
Division 1—Simplified outline of this Part
318 Simplified outline of this Part
Most benefits under this Act require a claim to have been made under section 319 in respect of a person. This Part sets out the rules that apply in making claims.
A claim can be made for:
(a) acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death; or
(b) acceptance of liability for the loss of or damage to a member’s medical aid;
(c) compensation.
The claim can be made by a current or former member who suffered a service injury or disease, a dependant of a deceased member, or a person who is entitled to compensation. A claim can also be made on behalf of such a person.
Once a claim is made, the Commission must investigate the claim. As part of this investigation, the Commission can assess the needs of a person who has made a claim for acceptance of liability for a service injury or disease (including by requiring the person to undergo an examination). The Commission decides under section 327 whether the person should be paid compensation for treatment under Part 2 of Chapter 6 or whether the person should be provided with treatment under Part 3 of Chapter 6.
The Commission can require information or documents that are relevant to a claim to be provided. The Chief of the Defence Force or a person who has made a claim can require the Commission to provide information or documents that are relevant to a claim.
Division 2—Making a claim
319 Making a claim
(1) A claim may be made under this section for one or more of the following:
(a) acceptance of liability by the Commission for a service injury sustained by a person or a service disease contracted by a person;
(b) acceptance of liability by the Commission for the service death of a person;
(c) acceptance of liability by the Commission for the loss of, or damage to, a member’s medical aid;
(d) compensation.
Note: Section 320 sets out who may make the claim.
(2) A claim must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) be given to the Commission; and
(c) satisfy the requirements (if any):
(i) prescribed by the regulations; or
(ii) determined in writing by the Commission;
as to the form and content of claims, or claims of that kind.
Note: Section 323 sets out when a claim is taken to have been given to the Commission.
(3) The Commission must give a copy of a claim that has been made in respect of a person to the Chief of the Defence Force if:
(a) the claim is for the acceptance of liability by the Commission for a service injury sustained by the person, a service disease contracted by the person or the person’s service death; and
(b) the person was a member of the Defence Force:
(i) for a claim relating to a service injury or disease—at the time the claim was made; or
(ii) for a claim relating to a service death—at the time of death.
(4) The Commission must give a copy of a claim that has been made in respect of a person to the Chief of the Defence Force if:
(a) the claim is for compensation under Part 2 of Chapter 4 (permanent impairment); and
(b) the person was a member of the Defence Force at the time the claim was made.
320 Who may make a claim
(1) A claim under subsection 319(1) may be made by:
(a) if paragraph 319(1)(a) applies—the person who sustained the injury or contracted the disease; or
(b) if paragraph 319(1)(b) applies—a person who is a dependant of the person who died; or
(c) if paragraph 319(1)(c) applies—the member whose medical aid is lost or damaged; or
(d) if paragraph 319(1)(d) applies—the person who is entitled to the compensation.
Note: A special rule applies in respect of claims for the cost of funerals and compensation for treatment for members who later die (see section 266 and subsection 271(2)).
(2) Alternatively, a claim may be made on behalf of such a person:
(a) with the person’s approval; or
(b) by the person’s legal personal representative; or
(c) if the person is unable, because of physical or mental incapacity, to approve someone to make the claim on his or her behalf—by another person approved by the Commission; or
(d) if the person is under the age of 18 years:
(i) by a parent or guardian of the person; or
(ii) by someone approved by a parent or guardian of the person; or
(iii) if there is not a parent or guardian of the person alive, or willing and able to make, or approve someone to make such a claim on behalf of the person—by another person approved by the Commission.
(3) The Commission may approve another person to make a claim on a person’s behalf as mentioned in paragraph (2)(c) or subparagraph (2)(d)(iii) only if:
(a) the person has no legal personal representative; or
(b) the Commission is satisfied that:
(i) the person’s legal personal representative has been notified that the legal personal representative has, or may have, a right to make a claim; and
(ii) the person’s legal personal representative has refused, or failed within a reasonable time after having been so notified, to make the claim.
321 Survival of claims and of right to claim
Claim made before death
(1) A claim made before the death of the person who made the claim (including a claim made by a dependant of a deceased member) continues to have effect after the death of that person.
(2) If a person makes a claim under section 319 before the person’s death, the person’s legal personal representative can make a claim for any compensation (including compensation under Part 2 of Chapter 4 (permanent impairment)) that could have been payable to the person up to the date of death.
Note 1: The legal personal representative cannot convert compensation for permanent impairment to a lump sum (see section 78).
Note 2: The legal personal representative of a deceased partner cannot convert compensation for a member’s death to a lump sum (see section 236).
No claim made before death
(3) If a person who is entitled to make a claim under this Act dies before making the claim, the claim may be made on the person’s behalf by the person’s legal personal representative.
(4) The person’s legal personal representative can make a claim for any compensation that could have been payable to the person up to the date of death, except compensation under Part 2 of Chapter 4 (permanent impairment).
Note: A payment of compensation in respect of a deceased person normally forms part of the estate of the person (see section 436).
322 No new claim before earlier claim finally determined
Claim for acceptance of liability
(1) A claim for acceptance of liability for a service injury, disease or death, or the loss of or damage to a medical aid, must not be made if another claim for acceptance of liability for that injury, disease, death, loss or damage has not yet been finally determined.
(3) Another claim for acceptance of liability for that service injury, disease or death, or loss of or damage to a medical aid, must be supported by additional evidence.
Claim for compensation
(4) A claim for compensation must not be made if another claim for compensation for the same matter has not yet been finally determined.
(5) Another claim for compensation for the same matter must be supported by additional evidence.
When a claim is finally determined
(6) For the purposes of this section, a claim is finally determined when either:
(a) a decision that has been made in respect of the claim is not subject to any form of reconsideration or review; or
(b) a decision that has been made in respect of the claim was subject to some form of reconsideration or review, but the period within which such a reconsideration or review could be instituted has ended without a reconsideration or review having been instituted.
323 Giving claims and documents to the Commission
(1) This section regulates the lodgment of claims and other documents under this Act.
(2) A claim or other document (other than a claim or other document that is approved by the Commission for electronic lodgment and that is transmitted electronically):
(a) is taken to have been given to the Commission only if the claim or other document is:
(i) lodged at a place within or outside Australia approved by the Commission for the purposes of this subsection; or
(ii) delivered to a person approved by the Commission for the purposes of this subsection; and
(b) is taken to have been so given on the day on which it is received at that place or delivered to that person.
(3) A claim or other document that is approved by the Commission for electronic lodgment and that is transmitted electronically:
(a) is taken to have been given to the Commission only if the claim or document is transmitted electronically in a manner, and to an electronic address, approved by the Commission for the purposes of this subsection in relation to claims or documents of that kind; and
(b) is taken to have been so given on the day on which it is received at that electronic address.
(4) Claims and other documents transmitted electronically other than in a manner approved by the Commission, or to an electronic address other than an electronic address approved by the Commission, are treated as not having been given to the Commission.
(5) A claim is taken to have been made on the day on which, under subsection (2) or (3), it is taken to have been given to the Commission.
(6) If a provision of this Act requires any material to be lodged in support of a claim or other document, that supporting material:
(a) unless paragraph (b) applies—may be lodged in accordance with this section in the same manner as the claim or other document to which it relates; and
(b) if the supporting material is not appropriate to be lodged in the same manner as the claim or other document to which it relates—may be lodged in such other manner contemplated by this section as the Commission approves.
Division 3—What happens after a claim is made
Subdivision A—Investigation of claims
324 Investigation by the Commission
If a claim is given to the Commission in accordance with section 323, the Commission must investigate the matters to which the claim relates.
Subdivision B—Needs assessments
325 When the Commission may or must carry out a needs assessment
(1) The Commission may carry out an assessment of a person’s needs at any time after the Commission accepts liability for a service injury or disease of the person.
Note: Section 326 sets out some matters that are considered in an assessment of a person’s needs.
(2) However, the Commission must carry out an assessment of a person’s needs before determining a claim for compensation in respect of the person’s injury or disease.
326 Assessment of a person’s needs
For the purposes of section 325, an assessment of a person’s needs may include, but is not limited to, an assessment of any or all of the following:
(a) whether an assessment of the person’s capacity for rehabilitation should be conducted under section 44;
(b) whether the person would be entitled to any compensation or treatment under this Act;
(c) the person’s medical needs, including but not limited to:
(i) any treatment (including ongoing treatment) that the person needs or is likely to need; and
(ii) whether Part 2 or 3 of Chapter 6 (treatment or compensation for treatment) should apply to the person.
327 Treatment path
(1) Subject to subsections (2) and (3), if the Commission conducts an assessment of a person’s needs under section 325 in relation to a claim for compensation, the Commission must make a written determination specifying that either section 271 or 280 applies to the person.
Note: A person is paid compensation for treatment of a service injury or disease under section 271. A person is provided with treatment for a service injury or disease under section 280.
(2) The Commission is only required to make a written determination under subsection (1) specifying that section 271 applies to a person who is a current member if the Commonwealth is liable, under section 272, to pay compensation for the cost of treatment obtained for the person’s service injury or disease.
(3) The Commission is only required to make a written determination under subsection (1) specifying that section 280 applies to a person if:
(a) for a person who is a current member—the person is, because of section 279, entitled to be provided with treatment under Part 3 of Chapter 6 but is not entitled to be provided with treatment under section 281 or 282; or
(b) for a person who is a former member—the person is not entitled to be provided with treatment under section 281 or 282.
Subdivision C—Medical examinations
328 Power to require medical examination
(1) This section applies if a claim is made under section 319 by or on behalf of a person who is member or a former member.
(2) The Commission may, at any time after the claim is made, require the person to undergo an examination by one medical practitioner nominated by the Commission.
(3) The Commonwealth is liable to pay the cost of conducting the examination.
(4) The Commonwealth is liable to pay compensation to the person for any costs the Commission determines are reasonably incurred by the person:
(a) in making a necessary journey in connection with the examination; or
(b) in remaining, for the purpose of the examination, at a place to which the person has made a journey for that purpose.
(5) In making a determination under subsection (4), the Commission must have regard to:
(a) the means of transport available to the person for the journey; and
(b) the route or routes by which the person could have travelled; and
(c) the accommodation available to the person.
(6) A person must not be required to undergo an examination under this section at more frequent intervals than are specified by the Minister by legislative instrument.
329 Consequences of failure to undergo an examination
(1) If the Commission requires a person to undergo an examination under subsection 328(2), and the person:
(a) refuses or fails to undergo the examination; or
(b) in any way obstructs the examination;
the Commission may determine that the person’s right to compensation (but not to treatment or compensation for treatment under Chapter 6) under this Act is suspended until the examination takes place.
(2) A determination under subsection (1) must not be made in relation to a refusal or failure to undergo the examination if, before the time fixed for the examination, the person gives to the Commission evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal or failure.
(3) The Commission must determine that the suspension under subsection (1) is terminated from a date determined by the Commission if, within 14 days after the date fixed for the examination, the person gives to the Commission evidence of a reasonable excuse for the refusal, failure or obstruction.
(4) If a determination under subsection (1) is made by a delegate of the Commission, the Commission must ensure that any determination terminating the suspension under subsection (3) also made by a delegate of the Commission is made by a delegate other than a delegate who was involved in making the determination under subsection (1).
(5) If a person’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (1), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
Subdivision D—Obligations of claimants and Commission
330 Power to request the provision of information
(1) This section applies if the Commission is satisfied that a person who has made a claim:
(a) has information or a document (including information or a document relating to costs incurred by the person, such as a receipt) that is relevant to the claim; or
(b) may obtain any such information or a copy of such a document without unreasonable expense or inconvenience.
(2) The Commission may, by notice in writing given to the person, request the person to give:
(a) specified information or a specified document; or
(b) information or a document in a specified class of information or documents;
to the Commission within 28 days after the date of the notice or within such further period (if any) as the Commission, on the request of the person, allows.
(3) If the person refuses or fails, without reasonable excuse, to comply with a notice under subsection (2), the Commission may refuse to deal with the claim until the person gives the Commission the information, or a copy of the document, specified in the notice.
331 Certain documents to be supplied on request
(1) Any of the following persons may request the Commission to give him or her any document held by the Commission that relates to the claim:
(a) if the claim is made in respect of a member or former member—the Chief of the Defence Force;
(b) if the claim is made in respect of a dependant of a deceased member—the Chief of the Defence Force;
(c) in any case—a person who has made a claim under section 319.
(2) The Commission must comply with the request.
Part 2—Determination of claims
332 Simplified outline of this Part
The Commission must decide all claims under this Act in accordance with this Part. In deciding claims, the usual technicalities and rules that apply to courts do not apply to the Commission. The standards of proof that apply in determining issues under this Act are found in section 335.
There are 2 standards of proof that the Commission applies in deciding matters under this Part (and the rest of the Act).
The more beneficial standard of proof (in subsections 335(1) and (2)) only applies to some claims that relate to warlike or non‑warlike service. The other standard of proof (in subsection 335(3)) applies to all other decisions under this Act.
This Part also introduces the Statements of Principles regime under sections 338 and 339. For some claims for acceptance of liability for an injury, disease or death the standard of proof can only be met if the injury or disease, or the cause of death, is covered by a Statement of Principles.
A Statement of Principles is an instrument made under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 (VEA). The Statement sets out all factors related to defence service that have been found to cause specific injuries, diseases and deaths.
The process for making Statements of Principles is found in Part XIA of the VEA. A person who is entitled to a benefit under this Act can apply under the VEA to the Repatriation Medical Authority (RMA) to investigate a particular injury, disease or death or review one of its previous decisions about a Statement of Principles.
Under Part XIB of the VEA, the Specialist Medical Review Council can review decisions of the RMA about Statements of Principles. The Commission can also override an RMA decision about a Statement of Principles under section 340 of this Act.
333 Determination of claims
After the Commission has investigated a claim under section 324, the Commission must:
(a) consider all matters that, in the Commission’s opinion, are relevant to the claim; and
(b) determine the claim in writing in accordance with this Act.
Note: The Commission is required to give notice of determinations to claimants (see section 346).
334 Commission not bound by technicalities
(1) In considering, hearing or determining a claim or request mentioned in subsection (2) and in making a decision in relation to such a claim or request, the Commission:
(a) is not bound to act in a formal manner and is not bound by any rules of evidence, but may inform itself on any matter in such manner as it thinks just; and
(b) must act according to substantial justice and the substantial merits of the case, without regard to legal form and technicalities; and
(c) without limiting paragraphs (a) and (b), must take into account any difficulties that, for any reason, lie in the way of ascertaining the existence of any fact, matter, cause or circumstance, including any reason attributable to:
(i) the effects of the passage of time, including the effect of the passage of time on the availability of witnesses; and
(ii) the absence of, or a deficiency in, relevant official records, including an absence or deficiency resulting from the fact that an occurrence that happened during the defence service of a member was not reported to the appropriate authorities.
(2) Subsection (1) applies to:
(a) a claim under section 319; and
(b) a request under section 349 for reconsideration of a determination.
335 Standard of proof for Commission and Chief of the Defence Force
Standard of proof for claims relating to warlike or non‑warlike service
(1) If a claim in respect of subsection 23(1) or (3) or 24(1) for acceptance of liability for a person’s injury, disease or death relates to warlike or non‑warlike service rendered by the person while a member, the Commission must determine that the injury is a service injury, that the disease is a service disease, or that the death is a service death, as the case may be, unless it is satisfied, beyond reasonable doubt, that there is no sufficient ground for making that determination.
Note: This subsection, to the extent that it relates to subsections 23(1) and 24(1), is affected by section 338.
When there is no sufficient ground for making a determination
(2) In applying subsection (1) in respect of a person’s injury, disease or death, related to service rendered by the person while a member, the Commission must be satisfied, beyond reasonable doubt, that there is no sufficient ground for determining:
(a) that the injury is a service injury; or
(b) that the disease is a service disease; or
(c) that the death is a service death;
as the case may be, if the Commission, after consideration of the whole of the material before it, is of the opinion that the material before it does not raise a reasonable hypothesis connecting the injury, disease or death with the circumstances of the particular service rendered by the person while a member.
Note: This subsection, to the extent that it relates to subsections 23(1) and 24(1), is affected by section 338.
Other determinations to be made to its reasonable satisfaction
(3) Except in making a determination to which subsection (1) applies, the Chief of the Defence Force or the Commission must, in making any determination or decision in respect of a matter arising under this Act, the regulations, or any other instrument made under this Act or the regulations, decide the matter to his, her or its reasonable satisfaction.
Note: This subsection, to the extent that it relates to subsections 23(1) and 24(1), is affected by section 339.
336 Commission not entitled to make certain presumptions
Nothing in section 335, or in any other provision of this Act, entitles the Commission to presume that:
(a) an injury sustained by a person is a service injury; or
(b) a disease contracted by a person is a service disease; or
(c) the death of a person is a service death; or
(d) a person is entitled to be granted compensation.
337 No onus of proof
Nothing in section 335, or in any other provision of this Act, imposes on:
(a) a person claiming compensation or claiming for the acceptance of liability; or
(b) the Commission, the Commonwealth, the Department or any other person in relation to such a claim;
any onus of proving any matter that is, or might be, relevant to the determination of the claim.
338 Reasonableness of hypothesis to be assessed by reference to Statement of Principles
(1) This section applies to a claim under section 319 for acceptance of liability under subsection 23(1) or 24(1) for an injury, disease or death that relates to warlike or non‑warlike service.
Note: Subsections 335(1) and (2) are relevant to these claims.
(2) If the Repatriation Medical Authority has given notice under section 196G of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 that it intends to carry out an investigation in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death:
(a) the Commission is not to determine a claim for acceptance of liability for a person’s injury, disease or death of that kind; and
(b) the Commission, the Board or the Tribunal is not to make a decision on the reconsideration or review of:
(i) a determination by the Commission on such a claim; or
(ii) such a determination as previously affirmed or varied; or
(iii) a decision made on a previous review in substitution for a determination referred to in subparagraph (i) or (ii);
unless or until the Authority:
(c) has determined a Statement of Principles under subsection 196B(2) of that Act in respect of that kind of injury, disease or death; or
(d) has declared that it does not propose to determine such a Statement of Principles.
(3) For the purposes of subsection 335(2), a hypothesis connecting an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, or the death of a person, with the circumstances of any particular service rendered by the person while a member, is reasonable only if there is in force:
(a) a Statement of Principles determined under subsection 196B(2) or (11) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(b) a determination of the Commission under subsection 340(2) of this Act;
that upholds the hypothesis.
Note: See subsection (4) about the application of this subsection.
(4) Subsection (3) does not apply in relation to a claim for acceptance of liability for a person’s injury, disease or death if the Repatriation Medical Authority has neither determined a Statement of Principles under subsection 196B(2) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986, nor declared that it does not propose to make such a Statement of Principles, in respect of:
(a) the kind of injury sustained by the person; or
(b) the kind of disease contracted by the person; or
(c) the kind of death met by the person;
as the case may be.
339 Reasonable satisfaction to be assessed in certain cases by reference to Statement of Principles
(1) This section applies to a claim under section 319 for acceptance of liability under subsection 23(1) or 24(1) for an injury, disease or death that relates to peacetime service.
Note: Subsection 335(3) is relevant to these claims.
(2) If the Repatriation Medical Authority has given notice under section 196G of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 that it intends to carry out an investigation in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death:
(a) the Commission is not to determine a claim for acceptance of liability for a person’s injury, disease or death of that kind; and
(b) the Commission, the Board or the Tribunal is not to make a decision on the review of:
(i) a determination by the Commission on such a claim; or
(ii) such a determination as previously affirmed or varied; or
(iii) a decision made on a previous review in substitution for a determination referred to in subparagraph (i) or (ii);
unless or until the Authority:
(c) has determined a Statement of Principles under subsection 196B(3) of that Act in respect of that kind of injury, disease or death; or
(d) has declared that it does not propose to make such a Statement of Principles.
(3) In applying subsection 335(3) to determine a claim, the Commission is to be reasonably satisfied that an injury sustained, or a disease contracted, by a person, or the death of a person, is a service injury, a service disease, or a service death, only if:
(a) the material before the Commission raises a connection between the injury, disease or death of the person and some particular defence service rendered by the person while a member; and
(b) there is in force:
(i) a Statement of Principles determined under subsection 196B(3) or (12) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(ii) a determination of the Commission under subsection 340(3) of this Act; and
(c) the material, and the Statement of Principles or the determination (as the case may be), upholds the contention that the injury, disease or death of the person is, on the balance of probabilities, connected with that service.
(4) Subsection (3) does not apply in relation to a claim for acceptance of liability for a person’s injury, disease or death if the Repatriation Medical Authority has neither determined a Statement of Principles under subsection 196B(3) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986, nor declared that it does not propose to make such a Statement of Principles, in respect of:
(a) the kind of injury sustained by the person; or
(b) the kind of disease contracted by the person; or
(c) the kind of death met by the person;
as the case may be.
340 Determination by Commission overriding Authority’s decision in relation to Statements of Principles
Commission may make determinations
(1) If:
(a) the Repatriation Medical Authority has determined, or has declared that it does not propose to make or amend, a Statement of Principles in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death (see section 196B of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986); and
(b) the Commission is of the opinion that, because the Statement of Principles is in force, or because of the decision by the Authority not to make or amend the Statement of Principles:
(i) claims for acceptance of liability for injuries or diseases of that kind made by members or former members of a particular class; or
(ii) claims for acceptance of liability for the deaths of such members or former members made by dependants of those members or former members;
cannot succeed; and
(c) the Commission is also of the opinion that, in all the circumstances of the case, those persons or their dependants should be entitled to receive compensation under this Act;
the Commission may, in its discretion, make a determination in respect of that kind of injury, disease or death under either or both subsections (2) and (3).
Requirements for a reasonable hypothesis determination
(2) A determination under this subsection in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) state that it has effect only in relation to the specified class of members; and
(c) state that it applies only in respect of claims relating to:
(i) warlike service; or
(ii) non‑warlike service; and
(d) set out:
(i) the factors that must as a minimum exist; and
(ii) which of those factors must be related to service rendered by a member;
before it can be said that a reasonable hypothesis has been raised connecting an injury, disease or death of that kind with the circumstances of that service.
Requirements for a reasonable satisfaction determination
(3) A determination under this subsection in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) state that it has effect only in relation to the specified class of members; and
(c) state that it applies only in respect of claims relating to peacetime service; and
(d) set out:
(i) the factors that must exist; and
(ii) which of those factors must be related to service rendered by a member;
before it can be said, on the balance of probabilities, that an injury, disease or death of that kind is connected with the circumstances of that service.
Determination is a legislative instrument
(4) A determination under subsection (2) or (3) is a legislative instrument.
Effect of reasonable hypothesis determination
(5) While there is in force under subsection (2) a determination in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death, any Statement of Principles in force under subsection 196B(2) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 in respect of that kind of injury, disease or death does not apply in respect of any person in relation to whom the determination has effect.
Effect of reasonable satisfaction determination
(6) While there is in force under subsection (3) a determination in respect of a particular kind of injury, disease or death, any Statement of Principles in force under subsection 196B(3) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 in respect of that kind of injury, disease or death does not apply in respect of any person in relation to whom the determination has effect.
Definition of related to service
(7) A factor causing, or contributing to, an injury, disease or death is related to service rendered by a member if:
(a) it resulted from an occurrence that happened while the member was rendering that service; or
(b) it arose out of, or was attributable to, that service; or
(c) it was contributed to in a material degree by, or was aggravated by, that service; or
(d) in the case of a factor causing, or contributing to, an injury—it resulted from an accident that would not have occurred:
(i) but for the rendering of that service by the member; or
(ii) but for changes in the member’s environment consequent upon his or her having rendered that service; or
(e) in the case of a factor causing, or contributing to, a disease—it would not have occurred:
(i) but for the rendering of that service by the member; or
(ii) but for changes in the member’s environment consequent upon his or her having rendered that service; or
(f) in the case of a factor causing, or contributing to, the death of a member—it was due to an accident that would not have occurred, or to a disease that would not have been contracted:
(i) but for the rendering of that service by the member; or
(ii) but for changes in the member’s environment consequent upon his or her having rendered that service; or
(g) it resulted from an accident that occurred while the member was travelling, while rendering that service but otherwise than in the course of duty, on a journey:
(i) to a place for the purpose of performing duty; or
(ii) away from a place of duty upon having ceased to perform duty.
341 Current Statement of Principles to be applied on review of a decision
(1) This section applies if:
(a) the Commission, the Board or the Tribunal is reconsidering or reviewing a determination in relation to a claim to which section 338 or 339 applies; and
(b) at the time of the making of the decision on the review, there is in force a Statement of Principles (the current Statement of Principles) determined under section 196B of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 in respect of:
(i) the kind of injury sustained by the person in respect of whom the claim is made; or
(ii) the kind of disease contracted by the person in respect of whom the claim is made; or
(iii) the kind of death suffered by the person in respect of whom the claim is made.
(2) Subject to section 340, the Commission, the Board or the Tribunal is to apply the current Statement of Principles when making its decision on the reconsideration or review.
(3) To avoid doubt, it is declared that no right, privilege, obligation or liability is acquired, accrued or incurred that would permit the Commission, the Board or the Tribunal, in making a decision on the reconsideration or review, to apply any Statement of Principles that is no longer in force.
342 Determination of the onset date for an incapacity for service or work
The Commission must determine in writing the date of onset of an incapacity for service or work of a member if the member is entitled to compensation under Part 3 of Chapter 4.
343 Determination of the date of death
The Commission must determine in writing the date of a deceased member’s death if a dependant of the member is entitled to compensation under Chapter 5 or 6.
Chapter 8—Reconsideration and review of determinations
Part 1—Preliminary
344 Simplified outline of this Chapter
Most determinations made by the Commission (the original determinations) can be reconsidered and reviewed. This also applies to decisions of the Chief of the Defence Force about rehabilitation.
The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force must give notice of an original determination to the claimant. The notice must set out the terms of and the reasons for the determination and the claimant’s right to apply for review.
A claimant who has received notice of an original determination can ask the Veterans’ Review Board to review it. If dissatisfied with the determination on review (the reviewable determination), the claimant can apply to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for review of the reviewable determination.
The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force can also initiate reconsideration of original determinations made by the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force.
345 Definitions
(1) In this Chapter:
original determination means:
(a) a determination of the Commission under this Act (including a determination under subsection 347(3) or 347A(2) or (4)) that is not specified in subsection (2); or
(b) a determination of the Chief of the Defence Force under this Act (including a determination under subsection 347(3)) that relates to rehabilitation for a person if the Chief of the Defence Force is the rehabilitation authority of the person.
reviewable determination means:
(a) a determination under subsection 350(2) revoking, confirming or varying an original determination; or
(b) a determination that has been varied under subsection 348(1); or
(c) a determination under Part 4 by the Board on review of an original determination (except a determination that has been varied under subsection 348(1)).
(2) These determinations of the Commission are not original determinations:
(a) a determination under section 50, 52, 329 or 397 (suspending compensation);
(b) a determination under section 67 (guide to determining impairment and compensation);
(ba) a determination or revocation under section 89B or 126A (payments before a person receives a Commonwealth superannuation benefit);
(c) a determination under section 210 (Return to Work Scheme);
(d) a determination under section 212 (Motor Vehicle Compensation Scheme);
(e) a determination under section 258 (education scheme for certain eligible young persons);
(f) a determination about the compensation to be provided under that education scheme;
(g) a determination under section 272 (compensation for members entitled to treatment under the Defence Force Regulations 1952);
(h) a determination under Part 3 of Chapter 6 (entitlement to provision of treatment);
(i) a determination under section 315 or 415 to recover an overpayment (but not as to the amount that should be recovered);
(j) a determination under section 316 to recover interest (but not as to the amount that should be recovered);
(k) a determination under section 327 that section 271 or 280 applies to a person (treatment path under Chapter 6);
(l) a determination under section 428 to write off a debt (but not as to the amount that should be written off);
(m) a determination under section 429 to waive a debt (but not as to the amount that should be waived);
(n) a determination that has been varied under subsection 348(1);
(o) a determination under subsection 349(6) (extending the period within which a request for reconsideration must be made).
345A Application of this Chapter to decisions about clean energy payments
(1) This section modifies the way this Chapter applies in relation to a decision by the Commission that is only about a person’s entitlement to a clean energy payment.
(2) This Chapter applies to the person in the same way as it applies to a claimant. However, this does not affect the following provisions:
(a) subsection 346(3);
(b) section 348;
(d) Part 4;
(e) subsections 356(2) and (3);
(f) subsection 357(6);
(g) subsections 358(2) and (3).
Part 2—Notifying original determinations
346 Notifying original determinations
(1) As soon as practicable after the Commission makes an original determination in relation to a claim, the Commission must give the claimant a written notice setting out:
(a) the terms of the original determination; and
(b) the reasons for the original determination.
(2) The Commission must also give a copy of the notice to the Chief of the Defence Force if the original determination relates to liability for a service injury, disease or death, or the permanent impairment, of a person who was a member of the Defence Force:
(a) for a service injury or disease or permanent impairment—at the time when the original determination was made; or
(b) for a service death—at the time of death.
(3) As soon as practicable after the Chief of the Defence Force makes an original determination in relation to a claim, the Chief of the Defence Force must give the claimant a written notice setting out:
(a) the terms of the original determination; and
(b) the reasons for the original determination.
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force must also give a copy of the notice to the Commission.
(5) A notice under subsection (1) or (3) must include a statement to the effect that the claimant may, if dissatisfied with the original determination, make an application to the Board under Part 4 for review of the determination.
(6) A failure to comply with this section does not affect the validity of the determination.
Part 3—Reconsideration of determinations
347 Commission or Chief of the Defence Force initiating reconsideration of original determinations
(1) The Commission may, on its own initiative, reconsider an original determination made by the Commission.
(2) The Chief of the Defence Force may, on his or her own initiative, reconsider an original determination made by the Chief of the Defence Force.
(3) If the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force reconsiders an original determination under subsection (1) or (2), the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force may make a determination revoking, confirming or varying the original determination.
(4) The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force must ensure that, if the original determination was made by a delegate and reconsideration of the determination is also to be made by a delegate, the reconsideration is done by a delegate who was not involved in making the original determination.
(5) The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force must not reconsider an original determination under subsection (1) or (2) if the Tribunal has made a determination in proceedings under Part 5 for review of a reviewable determination made in relation to that original determination.
(6) The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force must not reconsider an original determination under subsection (1) or (2) if the Board has made a determination in proceedings under Part 4 for review of that determination.
347A Reconsideration of permanent impairment compensation
(1) If:
(a) an amount of compensation paid or payable under Part 2 of Chapter 4 has been worked out using Chapter 25 of the guide referred to in section 67, being the guide as in force before 1 July 2013; and
(b) a reviewable determination has been made, or the Tribunal has made a decision in a review under Part 5 of this Chapter, in relation to that compensation;
then the Commission may, on its own initiative, review the amount of that compensation using Chapter 25 of that guide, being that guide as in force when the review is conducted.
Note: The Commission’s powers under this section are in addition to its powers under section 347 to reconsider original determinations it makes in relation to compensation under Part 2 of Chapter 4.
Increase in compensation
(2) If, after that review, the Commission is satisfied that the amount of that compensation is less than it should be, the Commission may make a determination increasing the amount of that compensation.
(3) A determination under subsection (2) takes effect on the day specified in the determination (which may be earlier than the day on which the determination is made).
No change in compensation
(4) If, after that review, the Commission is satisfied that the amount of that compensation should not be increased, the Commission may make a determination confirming the amount of that compensation.
(5) A determination under subsection (4) takes effect on the day on which the determination is made.
348 Varying determinations made by the Board
(1) The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force may, with the consent of the claimant, vary:
(a) an original determination made by the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force that has been affirmed by the Board under Part 4; or
(b) a determination made by the Board under Part 4 in substitution for an original determination made by the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force;
if the claimant has made an application to the Tribunal under Part 5 for review of the affirmed determination or the determination made by the Board and the review has not been determined.
(2) The Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force may, for the purpose only of correcting a manifest error, vary the date approved by the Board as the date from which a determination of the Board made in substitution for a determination of the Commission or of the Chief of the Defence Force is to operate.
349 Chief of the Defence Force initiating reconsideration of determinations
(4) The Chief of the Defence Force may request the Commission to reconsider an original determination made by the Commission that relates to liability for a service injury, disease or death of a person who is or was a member of the Defence Force.
(5) A request must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) set out the reasons for the request; and
(c) be given to the Commission within 30 days after the day on which notice of the determination was given to the person making the request.
(6) The Commission may, either before or after the end of that period, extend the period within which the request must be made.
Note: A determination under subsection (6) is not an original determination.
350 Reconsideration
(1) The Commission must, as soon as practicable after receiving a request to reconsider an original determination under section 349, reconsider the original determination.
(2) The Commission may make a determination revoking, confirming or varying the original determination.
(3) The Commission must ensure that, if the original determination was made by a delegate and reconsideration of the determination is also to be made by a delegate, the reconsideration is done by a delegate who was not involved in making the original determination.
351 Notifying reviewable determinations
(1) The Commission must, as soon as practicable after it makes a reviewable determination, give the claimant a written notice setting out:
(a) the terms of the reviewable determination; and
(b) the reasons for the reviewable determination.
(2) The notice must include a statement to the effect that, subject to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975, an application may be made to the Tribunal under Part 5 for review of the reviewable determination.
(3) The Commission must also give a copy of the notice to the Chief of the Defence Force if the reviewable determination relates to liability for a service injury, disease or death, or the permanent impairment, of a person who was a member of the Defence Force:
(a) for a service injury or disease or permanent impairment—at the time when the reviewable determination was made; or
(b) for a service death—at the time of death.
(4) A failure to comply with this section does not affect the validity of the determination.
Part 4—Review by the Board of original determinations
352 Applications to the Board for review
(1) The claimant may make an application to the Board for review of an original determination.
(3) An application for review must:
(a) be in writing; and
(b) set out the reasons for the application; and
(c) be given to the Commission within 12 months after the day on which notice of the determination was given to the person making the application.
353 Application of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986
(1) Subsections 132(5), (6), (9), (10), (11), (11A), (11B) and (11C), sections 133, 133A, 137, 137A, 138, 138A, 139, 140 and 140A, and Divisions 4, 4A, 5, 6 and 8 of Part IX (except sections 154 and 157), of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 apply for the purposes of a review by the Board under this Part.
(2) Those provisions (the applied provisions) apply subject to the modifications set out in this table.
Modifications of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 |
Item | Provision | Modification |
1 | The applied provisions | References to the Repatriation Commission have effect as references to the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission |
2 | The applied provisions | References to the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 have effect as references to this Act |
3 | The applied provisions | References to Part IX of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 have effect as references to this Chapter |
4 | The applied provisions | References to a pension or allowance under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 have effect as references to compensation under this Act |
5 | The applied provisions | References to the rate of a pension or allowance have effect as references to an amount of compensation |
6 | The applied provisions | References to a decision, where the decision is a decision of the Repatriation Commission, have effect as references to an original determination |
7 | The applied provisions | References to a veteran have effect as references to a claimant |
7A | Subsection 132(5) | The reference to section 135 has effect as a reference to section 352 of this Act |
7B | Subsections 132(5), (6) and (9) | Regulations made for the purposes of those subsections apply in working out amounts of travelling expenses for the purposes of attending a hearing of a review by the Board under this Part of this Act. However, regulations may be made under this table item for the purposes of working out the amounts of travelling expenses and, if such regulations are made, those regulations apply instead. |
7C | Subsection 132(9) | The reference to a claim for a pension has effect as a reference to a claim that is made under section 319 of this Act by a person who, under subsection 320(2) of this Act, is entitled to make the claim. The subsection has effect as if paragraphs (a), (b) and (c) of that subsection were omitted |
7D | Subsections 132(11A) and (11C) | A reference to an office of the Department in Australia has effect as a reference to a place approved by the Commission under subsection 323(2) of this Act |
8 | Section 137 | References to the Secretary have effect as references to the Commission. The report under that section is to be prepared within 6 weeks after an application for review by the Board under this Chapter is received by the Commission |
8A | Section 137A | The reference to section 135 has effect as a reference to section 352 of this Act |
9 | Paragraph 138(1)(b) | Instead of the reason attributable to a thing described in subparagraph 138(1)(b)(ii), the Board is to have regard to a reason attributable to the absence of, or a deficiency in, relevant official records, including one resulting from the fact that something that happened during warlike service or non‑warlike service rendered by a person was not reported to the appropriate authorities |
10 | Paragraph 138(2)(a) | The paragraph does not apply |
11 | Subsection 140(6) | The reference to subsection 175(1) has effect as a reference to subsection 354(1) of this Act |
12 | Subsection 147(1) | The parties to a review by the Board are: (a) the claimant; and (b) the Commission. The Chief of the Defence Force may also choose to be a party to the review |
13 | Subsection 148(2) | The reference to either party to the review has effect as a reference to each party to the review |
14 | Subsection 148(6A) | References to the Secretary have effect as references to the Commission |
15 | Section 152 | References to the Secretary have effect as references to the Commission |
16 | Subsection 153(1) | The reference to the other party to the review has effect as a reference to each other party to the review |
19 | Subsection 156(1) | The subsection has effect as if “, being a date fixed in accordance with section 157” were omitted |
20 | Subsection 170A(2) | The subsection has effect as if “referred to in section 135” were omitted |
21 | Subsections 170B(1) and 171(1) | Regulations made for the purposes of those subsections apply in working out amounts of travelling allowance, and fees and expenses for witnesses, for the purposes of a review by the Board under this Part of this Act |
22 | Subsections 170A(5) and 170B(5) | A reference to an office of the Department in Australia has effect as a reference to a place approved by the Commission under subsection 323(2) of this Act |
Part 5—Review by the Tribunal
354 Applications to the Tribunal for review
(1) An application may be made to the Tribunal for review of a reviewable determination.
Note: Item 2 of the table in section 355 sets out who may make the application.
(1A) The Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies to an application for review of a reviewable determination by the Board under Part 4 as if references in section 37 of that Act to the person who made the decision the subject of the application were instead references to whichever of the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force made the original determination.
Note: Section 37 of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies normally in respect of other kinds of reviewable determinations.
(1B) If:
(a) a person applies to the Tribunal for review of a decision (the reviewable decision) that is a reviewable determination made by the Board; and
(b) that reviewable determination is a determination affirming an original determination made by the Commission; and
(c) in the course of the review by the Tribunal, the person provides to the Tribunal a document relevant to the review; and
(d) the Tribunal is satisfied that, at the time when the Board made the reviewable determination, the Board did not have the document and the person could have provided the document to the Board without unreasonable expense or inconvenience; and
(e) the Tribunal is satisfied that, if the Board had the document at the time when the Board made the reviewable determination, the Board would have made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable determination;
then section 42D of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies in relation to the review by the Tribunal of the reviewable decision as if references in that section to the person who made the decision were instead references to the Commission.
(1C) If, under subsection 42D(1) of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 (as modified by subsection (1B) of this section), the Tribunal remits the reviewable decision to the Commission for reconsideration of that decision by the Commission:
(a) subsections 42D(2), (5), (6) and (7) of that Act do not apply in relation to that remittal; and
(b) the Commission must reconsider that decision, and do one of the following things, within the period of 28 days beginning on the day on which that decision was remitted to the Commission:
(i) affirm that decision;
(ii) vary that decision;
(iii) set aside that decision and make a new decision in substitution for the decision set aside; and
(c) if the Commission has not reconsidered that decision, and done one of those things, within that 28‑day period, the Commission is taken to have affirmed that decision; and
(d) subsections 42D(3), (4) and (8) of that Act apply in relation to that remittal.
Note: Section 42D of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 applies normally in respect of other kinds of reviewable determinations.
(2) An application may be made to the Tribunal for review of:
(a) a determination under subsection 50(1), 52(1), 329(1) or 397; or
(b) a failure to make a determination under subsection 50(3), 52(3), 329(3) or 397.
355 Modifications of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975
For the purposes of a review by the Tribunal under this Part, the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 has effect subject to the modifications set out in this table.
Modifications of the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 |
Item | Provision | Modification |
1 | Section 18C | Sittings of the Tribunal for the purposes of a review under this Part may be held at any place, whether within or outside Australia |
2 | Section 27 | An application may be made only by: (a) the claimant; or (b) the Chief of the Defence Force; or (c) the Commission. |
3 | Subsection 29(2) | The period within which an application may be made to the Tribunal is: (a) for a review of a determination by the Board, or a determination that has been varied under subsection 348(1)—3 months after the day on which the notice of the Board’s determination or variation was given to the applicant; or (b) otherwise—60 days after the day on which notice of the determination was given to the applicant |
4 | Subsection 29(7) | For a review of a determination by the Board on review of an original determination, or a determination that has been varied under subsection 348(1), the Tribunal cannot extend the time for making an application beyond the period of 12 months after the day on which notice of the Board’s determination or variation was given to the applicant |
5 | Paragraph 30(1)(b) | The Commission rather than the Board is a party to a proceeding before the Tribunal for review of a determination by the Board |
356 Evidence
(1) Evidence of a matter is not, without the leave of the Tribunal, admissible in proceedings under this Part if:
(a) the person who instituted the proceedings seeks to adduce the evidence before the Tribunal; and
(b) the person had not disclosed that matter to the Tribunal at least 28 days before the day fixed for the hearing of those proceedings.
(2) Information or a document is not, without the leave of the Tribunal, admissible in evidence in proceedings under this Part if:
(a) the Commission has determined a claim and, before doing so, gave the claimant a notice under section 330 requesting the claimant to give the Commission the information or document specified in the notice; and
(b) the claimant failed to comply with the notice; and
(c) the claimant had the information or document, or could have obtained it without unreasonable expense or inconvenience, before the determination was made.
(3) The Tribunal must not give leave under subsection (2) unless:
(a) the claimant provides a statement of reasons why he or she failed to comply with the notice; and
(b) the Tribunal is satisfied that there are special circumstances justifying the admission of the information or document in evidence.
357 Costs of proceedings before the Tribunal
(1) Subject to this section and to subsection 358(1), the costs incurred by a party to proceedings instituted under this Part in respect of a determination are to be borne by that party.
(2) If, in proceedings instituted by a claimant, the Tribunal makes a determination:
(a) varying a determination in a manner favourable to the claimant; or
(b) setting aside a determination and making a determination in substitution for the first‑mentioned determination that is more favourable to the claimant than the first‑mentioned determination;
the Tribunal may order that the costs of those proceedings incurred by the claimant, or a part of those costs, are to be paid by the Commonwealth.
(3) The Tribunal may order that the costs incurred by the claimant of proceedings instituted by the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force be paid by the Commonwealth.
(4) If the Tribunal makes a determination setting aside a determination and remitting the case for re‑determination by the Commission or the Chief of the Defence Force, the Tribunal must order that the costs of the proceedings before it incurred by the claimant are to be paid by the Commonwealth.
(5) This section does not authorise the Tribunal to order the Commonwealth to pay any costs incurred by a claimant in relation to an application for an extension of time for applying to the Tribunal for a review of a determination.
(6) If, in any proceedings, the Tribunal varies or sets aside a determination, the Tribunal must not make an order under subsection (2) or (4) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings if:
(a) the Commission, before making the determination, gave the claimant a notice under section 330 requesting the claimant to give the Commission information or a document specified in the notice; and
(b) the Tribunal is satisfied that:
(i) the claimant failed to comply with that notice; and
(ii) at the time when the Commission made the reviewable determination, it did not have the information or document, nor was the information or document reasonably available to it; and
(iii) if the Commission had the information or document at the time when it made the determination, it would have made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable determination.
(6A) If, in any proceedings, the Tribunal varies or sets aside a reviewable determination made by the Board, the Tribunal must not make an order under subsection (2) or (4) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings if:
(a) in the course of the review by the Tribunal, the claimant provided to the Tribunal a document relevant to the review; and
(b) the Tribunal is satisfied that, at the time when the Board made the reviewable determination, the Board did not have the document and the claimant could have provided the document to the Board without unreasonable expense or inconvenience; and
(c) the Tribunal is satisfied that, if the Board had the document at the time when the Board made the reviewable determination, the Board would have made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the reviewable determination.
(6B) If, in any proceedings, the Tribunal varies or sets aside a reviewable determination made by the Board, the Tribunal must not make an order under subsection (2) or (4) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings if the Tribunal is satisfied that:
(a) in connection with the review by the Tribunal or Board, the claimant was granted legal aid under a Commonwealth, State or Territory legal aid scheme or service; or
(b) the claimant failed, without reasonable excuse, to appear at the hearing of the review by the Board; or
(c) in connection with the review by the Board, the claimant failed to comply with a direction under subsection 148(4B) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(d) the claimant failed to comply with a notice under section 330 before the Commission made the original determination in relation to which the reviewable determination was made.
(6C) If, in any proceedings, the Tribunal remits a reviewable determination made by the Board to the Commission as mentioned in subsection 354(1C), the Tribunal must not make an order under subsection (2) or (4) in favour of a claimant in relation to the costs of those proceedings.
(7) If the Tribunal orders the Commonwealth to pay costs incurred by a claimant, the Tribunal may, in the absence of agreement between the parties as to the amount of the costs, tax or settle the amount of the costs or order that the costs be taxed by the Registrar or an officer of the Tribunal.
358 Costs where proceedings rendered abortive
(1) Subject to this section, if a proceeding instituted under this Part in respect of a reviewable determination is rendered abortive because a determination has been made, following a reconsideration under subsection 347(1) or (2), varying or revoking the reviewable determination, the Commonwealth is liable to reimburse the claimant for costs reasonably incurred by the claimant in connection with that proceeding.
(2) The Commission may determine, in writing, that subsection (1) does not apply to costs if:
(a) a determination (the first determination) of a claim has been made; and
(b) the Commission, before the first determination was made, gave the claimant a notice under section 330 requesting the claimant to give it information or a document specified in the notice; and
(c) the claimant failed to comply with the notice; and
(d) when the first determination was made, the Commission did not have the information or document nor was the information or document reasonably available to it; and
(e) after the first determination was made, the claimant disclosed the information or document to the Commission or to the Tribunal; and
(f) the Commission reconsidered the first determination under subsection 347(1) and made a determination more favourable to the claimant than the first determination; and
(g) the Commission is satisfied that, if it had the information or document when the first determination was made, a determination more favourable to the claimant than the first determination would have been made; and
(h) the Commonwealth would, apart from this subsection, be liable under subsection (1) to reimburse the claimant for costs reasonably incurred by the claimant.
(3) The Commission must give a copy of a determination made by it under subsection (2) to the claimant.
(4) Application may be made to the Tribunal for review of a determination of the Commission to make a determination under subsection (2).
359 Certain provisions not to apply to review of determinations of the Board
Section 356 does not apply to a review by the Tribunal of a determination of the Board.
Chapter 9—The Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission
Part 1—Simplified outline of this Chapter
360 Simplified outline of this Chapter
The Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission is established under Part 2 of this Chapter.
The Commission’s functions are set out in Part 3.
Parts 4, 5 and 6 deal with the administration of the Commission, and include provisions relating to members, acting members and meetings of the Commission.
Part 7 deals with staff, consultants, delegations of the Commission and the Commission’s annual report.
Part 7 of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 also has provisions that are relevant to members and acting members of the Commission.
Part 2—Establishment of the Commission
361 Establishment
The Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Commission is established by this section.
Part 3—Functions
362 Functions
(1) The functions of the Commission are as follows:
(a) to make determinations under this Act relating to:
(i) acceptance of liability; and
(ii) the payment or provision of compensation; and
(iii) the provision of services for treatment and rehabilitation;
(b) to minimise the duration and severity of service injuries and service diseases by arranging quickly under this Act for the rehabilitation of members and former members who suffered those injuries and diseases;
(c) to promote the return to suitable work (defence or civilian) by persons who suffered a service injury or disease;
(d) to promote research into:
(i) the health of members and former members; and
(ii) the prevention of injury and disease; and
(iii) the rehabilitation of persons from injury and/or disease;
(e) to provide advice and information relating to the operation of this Act to:
(i) the Minister; and
(ii) the Defence Minister; and
(iii) the Secretary of the Department; and
(iv) the Secretary of the Defence Department; and
(v) the Chief of the Defence Force;
either on request or on the Commission’s own initiative;
(f) such other functions as are conferred on the Commission by other provisions of this Act or by another Act.
(2) The Commission has power to do all things necessary or convenient to be done for or in connection with the performance of its functions.
Part 4—Constitution of the Commission
363 Constitution
(1) The Commission:
(a) is a body corporate with perpetual succession; and
(b) must have a seal; and
(c) may sue and be sued in its corporate name.
(2) All courts, judges and persons acting judicially must:
(a) take judicial notice of the imprint of the seal of the Commission appearing on a document; and
(b) presume that the document was duly sealed.
(3) Despite paragraph 10(1)(d) of the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013 and the definition of Department of State in section 8 of that Act, the Commission:
(a) is not a Commonwealth entity for the purposes of that Act; and
(b) is taken to be part of the Department administered by the Minister administering this Chapter for those purposes.
Note: This means that the Commission members are officials of the Department for the purposes of the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013.
Part 5—Membership
364 Membership
(1) The Commission consists of the following members:
(a) the persons who, from time to time, hold the following offices:
(i) President of the Repatriation Commission;
(ii) Deputy President of the Repatriation Commission;
(b) the following persons appointed under section 365:
(i) a member of the Repatriation Commission (other than the President or Deputy President) nominated by the Veterans’ Affairs Minister;
(ii) a person who is nominated by the SRC Minister and is the Chief Executive Officer of Comcare, a person described in subsection 89E(1) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988 or a person engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Department of State administered by the SRC Minister;
(iii) 2 persons who are nominated by the Defence Minister, each of whom is either a Permanent Forces member or engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Defence Department.
Note: The performance of the Commission’s functions or the exercise of its powers is not affected merely because of a vacancy in the Commission’s membership (see subsection 33(2B) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) If, when the Veterans’ Affairs Minister is nominating a member under subparagraph (1)(b)(i), there is no member of the Commission who is a member of the Repatriation Commission appointed in accordance with subsection 182(4) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986, then the Minister must nominate the member of the Repatriation Commission appointed in accordance with that subsection.
Note 1: Subsection 182(4) requires one member of the Repatriation Commission to be a person chosen from a list provided by organisations representing veterans.
Note 2: This subsection does not need to be complied with during a temporary vacancy in the office (see subsection 366(5)).
(3) The member described in subparagraph (1)(a)(i) is the Chair of the Commission.
(4) The members of the Commission hold office on a part‑time basis.
365 Appointment of Commission members
(1) The members of the Commission described in paragraph 364(1)(b) are to be appointed by the Governor‑General by written instrument.
(2) An appointed Commission member holds office for the period specified in the instrument of appointment. The period must not exceed 5 years.
(3) The appointment of a person as an appointed Commission member is not invalid merely because there was a defect or irregularity in connection with the appointment.
(4) An appointed Commission member holds office on the terms and conditions (if any) in relation to matters not covered by this Act that are determined by the Governor‑General.
366 Acting appointments for the member described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(i)
Application of section
(1) This section applies:
(a) during a vacancy in the office of a Commission member described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(i), whether or not an appointment has previously been made to the office; or
(b) during any period, or during all periods, when such a Commission member is absent from duty or from Australia, or is, for any reason, unable to perform the duties of the office.
Minister may appoint person to act
(2) The Minister may appoint a person to act in the office of the Commission member in accordance with this section.
Note: For rules that apply to acting appointments, see section 33A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
Appointment if Repatriation Commissioner available
(3) If there is present in Australia a member of the Repatriation Commission who:
(a) is able to perform the duties of the office of the Commission member; and
(b) is not a Commission member under section 364; and
(c) is not absent from duty as a member of the Repatriation Commission;
then the person appointed must be the member of the Repatriation Commission.
Appointment if no Repatriation Commissioner available
(4) Otherwise, the person appointed may be any person.
Person not required to be a person chosen from a list provided by veterans’ organisations
(5) The person appointed is not required to be a person whose name is on a list mentioned in subsection 182(3) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
367 Acting appointment for the members described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(ii) or (iii)
Application of section
(1) This section applies:
(a) during a vacancy in the office of a Commission member described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(ii) or (iii), whether or not an appointment has previously been made to the office; or
(b) during any period, or during all periods, when such a Commission member is absent from duty or from Australia, or is, for any reason, unable to perform the duties of the office.
Minister may appoint person to act
(2) The Minister may appoint the following persons to act in the office of the Commission member:
(a) if the vacant office is of the member described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(ii)—a person who is nominated by the SRC Minister and is the Chief Executive Officer of Comcare, a person described in subsection 89E(1) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988 or a person engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Department of State administered by the SRC Minister; or
(b) if the vacant office is of a member described in subparagraph 364(1)(b)(iii)—a person who is nominated by the Defence Minister and is either a Permanent Forces member or engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Defence Department.
Note: For rules that apply to acting appointments, see section 33A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901.
369 Remuneration and allowances
(1) A Commission member is to be paid the remuneration that is determined by the Remuneration Tribunal. If no determination of that remuneration by the Tribunal is in operation, the member is to be paid the remuneration that is prescribed by the regulations.
(2) A Commission member is to be paid the allowances that are prescribed by the regulations.
(3) This section has effect subject to the Remuneration Tribunal Act 1973.
Note: Subsection 7(11) of the Remuneration Tribunal Act 1973 significantly limits the entitlement of a Commission member to remuneration under this section, because it provides that generally a person who holds a Commonwealth office, or is employed by the Commonwealth, on a full‑time basis is not entitled to remuneration for a part‑time office.
370 Commission members may be granted leave of absence
The Commission Chair may grant leave of absence to an appointed Commission member on the terms and conditions that the Commission Chair determines.
371 Resignation of appointed Commission members
An appointed Commission member may resign his or her appointment by giving the Governor‑General a written resignation.
372 Termination of appointment of appointed Commission members
(1) The Governor‑General may terminate the appointment of an appointed Commission member for misbehaviour or physical or mental incapacity.
(2) The Governor‑General must terminate the appointment of an appointed Commission member if:
(a) the member:
(i) becomes bankrupt; or
(ii) applies to take the benefit of any law for the relief of bankrupt or insolvent debtors; or
(iii) compounds with his or her creditors; or
(iv) assigns his or her remuneration for the benefit of his or her creditors; or
(b) the member is absent, except on leave of absence, from 3 consecutive meetings of the Commission; or
(c) the member fails, without reasonable excuse, to comply with:
(i) section 379 or 380; or
(ii) section 29 of the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013 (which deals with the duty to disclose interests) or rules made for the purposes of that section; or
(d) the member is described in a subparagraph mentioned in an item of the table and the circumstances described in that item exist.
Extra grounds for mandatory termination of appointment |
Item | Subparagraph | Circumstances in which termination is required |
1 | 364(1)(b)(i) | The member ceases to be a member of the Repatriation Commission |
2 | 364(1)(b)(ii) | Either: (a) the member is none of the following: (i) the Chief Executive Officer of Comcare; (ii) a person described in subsection 89E(1) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation Act 1988; (iii) a person engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 performing duties in the Department of State administered by the SRC Minister; or (b) the Minister is asked by the SRC Minister to terminate the member’s appointment (as a Commission member) |
3 | 364(1)(b)(iii) | Either: (a) the member is neither a Permanent Forces member nor a person engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 performing duties in the Defence Department; or (b) the Minister is asked by the Defence Minister to terminate the member’s appointment (as a Commission member) |
Part 6—Meetings and resolutions
373 Convening meetings
(1) The Commission Chair must convene such meetings of the Commission as the Chair considers are necessary for the efficient performance of the Commission’s functions.
(2) The Commission Chair must convene a meeting of the Commission within 4 weeks after receiving a written request signed by at least 3 Commission members.
374 Presiding at meetings
(1) The Commission Chair is to preside at meetings of the Commission at which he or she is present.
(2) If the Commission Chair is absent, then the Commission member described in subparagraph 364(1)(a)(ii) (the Deputy President of the Repatriation Commission) is to preside at the meeting.
375 Quorum
At a meeting of the Commission, 4 Commission members constitute a quorum.
376 Voting at meetings
(1) A question arising at a meeting of the Commission is to be determined by a majority of the votes of Commission members present and voting.
(2) The Commission member presiding at the meeting:
(a) has a deliberative vote; and
(b) if necessary, also a casting vote.
377 Commission resolutions without meetings
A resolution is taken to have been passed at a meeting of the Commission if:
(a) the Commission has determined:
(i) that resolutions may be passed in accordance with this section; and
(ii) the method of indicating agreement with a resolution proposed to be passed in accordance with this section; and
(b) without meeting, a majority of the Commission members indicate agreement with the proposed resolution in accordance with the method determined by the Commission; and
(c) all Commission members were informed of the proposed resolution, or reasonable efforts were made to inform all Commission members of the proposed resolution.
378 Conduct of meetings
(1) The Commission may regulate proceedings at its meetings as it considers appropriate. However, proceedings must not be inconsistent with the other provisions of this Chapter.
Note: Section 33B of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901 lets the Commission permit participation in meetings by various means of communication (for example, by telephone).
(2) The Commission may invite a person to attend a meeting for the purpose of advising or informing the Commission on any matter.
(3) The Commission must ensure that minutes of its meetings are kept.
379 Commission member to disclose any interest in claims etc.
(1) This section applies to a Commission member who has an interest (pecuniary or otherwise) that could conflict with the proper performance of his or her functions in relation to the following matters:
(a) a claim for acceptance of liability or for compensation that the Commission is considering or is to consider;
(b) a claim for acceptance of liability or for compensation that the Commission is reviewing or is to review;
(c) a decision relating to:
(i) compensation or acceptance of liability; or
(ii) a claim for compensation or acceptance of liability;
that the Commission is reviewing, is to review or is considering whether to review.
Note: This section also applies to acting Commission members (see section 33A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) The Commission member must disclose the interest to:
(a) the person making the claim; and
(b) the Minister;
as soon as possible after becoming aware of the relevant facts.
(3) The Commission member must not take part in the Commission’s consideration or review of the matter, except with the consent of the person making the claim and the Minister.
380 Minister may direct Commission member not to take part in consideration or review
(1) This section applies if the Minister becomes aware that:
(a) the Commission is considering or reviewing, or is to consider or review, a matter mentioned in subsection 379(1); and
(b) a Commission member has an interest (pecuniary or otherwise) that could conflict with the proper performance of his or her functions in relation to the matter.
Note: This section also applies to acting Commission members (see section 33A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(2) The Minister must cause the Commission member’s interest to be disclosed to the person making the claim.
(3) The Commission member must not take part in the Commission’s consideration or review of the matter, except with the consent of the person making the claim and the Minister.
Part 7—Other matters
382 Staff
The staff required to assist the Commission are to be persons engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and made available for the purpose by the Secretary of the Department.
383 Consultants
(1) The Commission may engage persons having suitable qualifications and experience as consultants to the Commission.
(2) The consultants are to be engaged on the terms and conditions that the Commission determines.
384 Delegation
The Commission may, by resolution, delegate any of its functions or powers under this Act, under the regulations or under any other legislative instrument made under this Act (other than this power of delegation) to:
(a) a member of the Commission; or
(b) a member of the staff assisting the Commission; or
(c) a consultant to, or an employee of a consultant to, the Commission; or
(d) a person who is engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Department that deals with the matters to which the provision relates and is administered by the Minister administering the provision; or
(e) a member of the Defence Force whose duties relate to matters to which the provision relates.
385 Annual report
As soon as possible after each 30 June, the Commission Chair must give the Minister, for presentation to the Parliament, a report of the Commission’s activities during the financial year that ended on that day.
Chapter 10—Liabilities arising apart from this Act etc.
Part 1—Preliminary
386 Simplified outline of this Chapter
This Chapter deals with the situation where a person who is entitled to compensation under this Act for an injury, disease, death or loss (the compensable loss) has, or may have, a right to recover damages apart from this Act for the compensable loss.
Part 2 prohibits actions against the Commonwealth for the compensable loss. However, it allows the person a choice to take action against the Commonwealth to recover limited damages for non‑economic loss.
Part 3 deals with payment or recovery of compensation under this Act if damages are recovered from a third party. It also allows the Commission to make or take over claims in certain cases.
387 Interpretation
(1) In this Chapter:
potentially liable member, in relation to an action or other proceeding, means a person who was, when the cause of action arose, acting in the capacity of a member.
(2) Unless the contrary intention appears, a reference in this Chapter to a person is, if the person has died, a reference to his or her legal personal representative.
Part 2—Liability of the Commonwealth to other actions
388 Action for damages not to lie against Commonwealth etc. in certain cases
(1) Subject to section 389, an action or other proceeding for damages does not lie against the Commonwealth, or a potentially liable member, in respect of:
(a) a service injury sustained, or a service disease contracted, by another member or a former member; or
(b) the loss of, or damage to, a medical aid used by another member.
Note: However, a person may choose to institute an action for damages for non‑economic loss against the Commonwealth or the potentially liable member under section 389.
(2) Subsection (1) applies whether that injury, disease, loss or damage occurred before or after this section commences. However, subsection (1) does not apply if an action or proceeding in respect of the injury, disease, loss or damage is instituted before this section commences.
(3) Subsection (1) does not prevent a dependant of a deceased member from bringing an action in respect of a service death of the deceased member (whether or not the deceased member had chosen to institute an action under section 389 before his or her death).
(4) However, if such a dependant recovers damages (including damages payable as a result of the settlement of a claim) from the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member in respect of the service death, subsections (5) and (6) have effect.
(5) If the dependant has received compensation under this Act in respect of the service death before recovery of the damages, the dependant is liable to pay to the Commonwealth the lesser of:
(a) the total of all amounts of compensation paid to the person under this Act in respect of the service death before the recovery of the damages (except MRCA supplement under section 245 and compensation for dependants under section 242, 253 or 255); and
(b) the amount of the damages.
(6) Compensation under this Act in respect of the service death is not payable to the dependant after the recovery of the damages.
389 Choice to institute action for damages against the Commonwealth etc. for non‑economic loss
(1) A person may choose to institute an action or proceeding against the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member for damages for non‑economic loss suffered by the person if:
(a) compensation is payable under section 68, 71 or 75 in respect of a service injury or disease of the person but the compensation has not yet been paid; and
(b) the Commonwealth or the potentially liable member would, apart from subsection 388(1), be liable for damages for that loss.
(2) A choice must be in writing and must be given to the Commission.
(3) A choice is irrevocable.
(4) If the person chooses to institute the action or proceeding:
(a) subsection 388(1) does not apply to the action or proceeding; and
(b) compensation under section 68, 71 or 75 in respect of the injury or disease is not payable after the date of the choice.
(5) In any action or proceeding instituted as a result of the person’s choice, the court must not award the person damages of more than $110,000 for non‑economic loss suffered by the person.
(6) The person’s choice to institute an action or proceeding against the Commonwealth or the potentially liable member does not prevent the person from doing any other thing that constitutes an action for non‑economic loss before, or instead of, formally instituting such an action or proceeding.
390 Notice of common law claims against the Commonwealth etc.
(1) This section applies if:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act in respect of a service injury, disease or death of a person; and
(b) the person or a dependant of the person makes a claim for damages in respect of the injury, disease or death against the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member.
(2) The person or dependant must notify the Commission in writing of the claim as soon as practicable, but not later than 7 days after the day on which he or she makes the claim.
(3) A person commits an offence if the person contravenes subsection (2).
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
(4) Subsection (3) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
Part 3—Liability of third parties
Division 1—Notice of common law claims against third parties
391 Notice of common law claims against third parties
(1) This section applies if:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act in respect of:
(i) a service injury, disease or death of a person (the cause of action); or
(ii) the loss of, or damage to, a medical aid used by a person (the cause of action); and
(b) the person or a dependant of the person makes a claim for damages in respect of the cause of action against a person other than the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member.
(2) The person or dependant must notify the Commission in writing of the claim as soon as practicable, but not later than 7 days after the day on which he or she makes the claim.
(3) A person commits an offence if the person contravenes subsection (2).
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
(4) Subsection (3) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
Division 2—Commission may institute proceedings or take over claims against third parties
392 Application of this Division to common law claims against third parties
(1) This Division applies if:
(a) compensation is paid under this Act in respect of:
(i) a service injury, disease or death of a person (the cause of action); or
(ii) the loss of, or damage to, a medical aid used by a person (the cause of action); and
(b) the cause of action occurred in circumstances that appear to create a legal liability of another person (the defendant) other than the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member to pay damages in respect of the cause of action; and
(c) the person or a dependant of the person (as the case may be) (the plaintiff):
(i) has not made a claim for damages against the defendant in respect of the cause of action; or
(ii) has made such a claim, but has not prosecuted it.
(2) In paragraph (1)(c), a reference to a claim having been made or not having been made by the plaintiff includes a reference to a claim having been made or not having been made on behalf of the plaintiff.
393 Commission may make the claim or take over the claim
The Commission may:
(a) make a claim or a fresh claim in the name of the plaintiff against the defendant for the recovery of damages in respect of the cause of action; or
(b) take over the conduct of the existing claim.
394 Commonwealth liable to pay costs of claim
If the Commission takes over the conduct of a claim, the Commonwealth becomes liable to pay the costs of or incidental to the claim that would otherwise be payable by the plaintiff. However, the Commonwealth is not liable for costs unreasonably incurred by the plaintiff.
395 Commission may conclude claim
If the Commission makes, or takes over the conduct of, the claim, the Commission may do any one or more of the following:
(a) take whatever steps are appropriate to bring the claim to a conclusion;
(b) if the claim is before a court—settle the proceedings either with or without obtaining judgment;
(c) if judgment has been obtained in favour of the plaintiff—take such steps as are necessary to enforce the judgment.
396 Plaintiff must sign documents as required
(1) If the Commission makes, or takes over the conduct of, the claim, the plaintiff must sign any document relevant to the claim (including the settlement of the claim or of any proceedings arising out of the claim) that the Commission requires the plaintiff to sign.
(2) If the plaintiff does not do so:
(a) the Commission may apply to:
(i) if the claim is not before a court or tribunal at the time of the failure—the Federal Court of Australia; or
(ii) otherwise—the court or tribunal in which proceedings relating to the claim are being heard;
for a direction that the document be signed on the plaintiff’s behalf by a person appointed by the Commission; and
(b) the court or tribunal may make the direction.
(3) If the Commission proposes to make an application under subsection (2):
(a) the Commission must notify the plaintiff that it is proposing to do so; and
(b) the plaintiff has a right of representation in the hearing of the application.
397 Plaintiff must do as the Commission requires
(1) If the Commission makes, or takes over the conduct of, the claim:
(a) the plaintiff must comply with any reasonable requirement of the Commission for the purposes of the claim; and
(b) if the plaintiff fails to comply, the Commission may determine that the person’s right to compensation (but not to treatment or compensation for treatment under Chapter 6) under this Act in respect of the cause of action to which the claim relates is suspended until the plaintiff does so.
(2) A determination under subsection (1) must not be made in relation to a failure to comply with a requirement if, before the date fixed for complying with the requirement, the person gives to the Commission evidence of a reasonable excuse for the failure.
(3) The Commission must determine that the suspension under subsection (1) is terminated from a date determined by the Commission if, within 14 days after the date fixed for complying with the requirement, the person gives to the Commission evidence of a reasonable excuse for the failure.
(4) If a determination under subsection (1) is made by a delegate of the Commission, the Commission must ensure that any determination terminating the suspension under subsection (3) also made by a delegate of the Commission is made by a delegate other than a delegate who was involved in making the determination under subsection (1).
(5) If a person’s right to compensation is suspended under subsection (1), compensation is not payable in respect of the period of the suspension.
398 What happens when damages are awarded
(1) Any damages payable as a result of a claim made or taken over by the Commission (including damages payable as a result of the settlement of such a claim) must be paid to the Commonwealth.
(2) The Commonwealth must deduct from the amount of those damages:
(a) an amount equal to the total of all amounts of compensation paid to the plaintiff under this Act before the payment of the damages (except MRCA supplement under section 221 or 245 and compensation for dependants under section 242, 253 or 255) in respect of the cause of action to which the claim relates; and
(b) the amount of any costs incidental to the claim paid by the Commonwealth.
(3) If a balance remains after the deductions have been made:
(a) the Commonwealth must pay the balance to the plaintiff; and
(b) the plaintiff is not entitled to any further compensation under this Act in respect of the cause of action to which the claim related until the amount of compensation that would have been payable for the period after payment of the balance (apart from this paragraph) equals the amount paid under paragraph (a).
Division 3—Effect of recovering damages on entitlements under this Act
399 When Division applies
This Division applies if:
(a) compensation is payable under this Act in respect of:
(i) a service injury, disease or death of a person (the cause of action); or
(ii) the loss of, or damage to, a medical aid used by a person (the cause of action); and
(b) the person or a dependant of the person recovers damages (including damages payable as a result of the settlement of a claim) in respect of the cause of action from a person other than the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member.
400 Notifying damages
(1) The person or dependant must, not later than 28 days after the day on which the damages are recovered, notify the Commission in writing of the recovery of the damages, the date of recovery and the amount of the damages.
(2) A person commits an offence if the person contravenes subsection (1).
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
(3) Subsection (2) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
401 Repaying compensation paid under this Act after damages recovered
(1) This section applies if:
(a) compensation under this Act in respect of the cause of action is paid to or for the benefit of a person; and
(b) the person later recovers damages in respect of that cause of action.
(2) The person is liable to pay to the Commonwealth the lesser of:
(a) the total of all amounts of compensation paid to the person under this Act before the recovery of the damages (except MRCA supplement under section 221 or 245 and compensation for dependants under section 242, 253 or 255) in respect of the cause of action; and
(b) the amount of the damages.
(3) If the Commission is satisfied that a part of the damages does not relate to an injury, disease or death, or a loss of, or damage to, a medical aid, in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act, this section only applies to so much of the damages as relates to an injury, disease, death, loss or damage in respect of which compensation is payable under this Act.
402 No compensation under this Act after damages recovered
(1) This section applies if a person recovers damages in respect of the cause of action (whether or not compensation in respect of the cause of action has been paid under this Act to or for the benefit of the person).
(2) Compensation under this Act (except MRCA supplement under section 221 or 245 and compensation for dependants under section 242, 253 or 255) is not payable to the person in respect of the cause of action after the day on which the damages were recovered.
(3) However, subsection (2) does not apply if the damages were recovered as a result of:
(a) a claim, or a fresh claim, made by the Commission under Division 2; or
(b) the Commission’s taking over, under Division 2, the conduct of a claim.
Division 4—Payment of damages by persons to the Commonwealth
403 Payment of damages by persons to the Commonwealth
(1) This section applies if a person other than the Commonwealth or a potentially liable member (the defendant):
(a) appears to the Commission to be liable to pay damages:
(i) to a person (the plaintiff) in respect of a service injury or disease of the plaintiff; or
(ii) to a person (the plaintiff) in respect of the loss of, or damage to, a medical aid of the plaintiff; or
(iii) to a dependant (the plaintiff) of a person in respect of a service death of the person;
in respect of which compensation has been paid under this Act; or
(b) has agreed to pay damages of that kind to the plaintiff; or
(c) has had damages of that kind awarded against him or her in proceedings arising out of a claim made by or on behalf of the plaintiff.
(2) The Commission may give the defendant a written notice requiring him or her to pay to the Commonwealth the damages (if any) that he or she agrees to pay or that are awarded against him or her.
(3) If the defendant is given a notice, the defendant must pay the Commonwealth the lesser of:
(a) the amount of the damages; and
(b) the total amount of compensation paid to the plaintiff under this Act in respect of the injury, disease, death, loss or damage (except MRCA supplement under section 221 or 245 and compensation for dependants under section 242, 253 or 255).
(4) If the defendant is given a notice after paying to or for the benefit of the plaintiff all of the damages to which the notice relates, the notice has no effect.
(5) If the defendant is given a notice after paying to or for the benefit of the plaintiff part of the damages to which the notice relates, the reference in subsection (3) to the amount of the damages has effect as a reference to so much of that amount as has not been paid.
(6) If the defendant fails to pay an amount to the Commonwealth in accordance with the notice, the Commission may recover that amount from the defendant in a court of competent jurisdiction as a debt due to the Commonwealth.
(7) The payment of an amount to the Commonwealth by the defendant in accordance with the notice discharges, to the extent of the amount paid:
(a) the liability of the defendant to the plaintiff; and
(b) the liability (if any) of the plaintiff to the Commonwealth under Division 3.
Chapter 11—Miscellaneous
Part 1—Indexation
404 Indexation of amounts
(1) This section applies to dollar amounts mentioned in the following provisions:
(a) subsection 74(1);
(b) subsection 80(2);
(c) subsection 82(3);
(d) paragraph 138(1)(a);
(e) subsection 206(3);
(f) paragraph 216(b);
(g) paragraph 219(b);
(h) subsection 234(2);
(i) subsection 240(3);
(j) section 252;
(k) section 254;
(l) paragraphs 263(1)(a) and (b);
(m) paragraph 267(3)(a).
(2) The dollar amount mentioned in the provision, for an indexation year in which the indexation factor is greater than 1, is replaced by the amount worked out using the formula:

(3) The indexation factor for an indexation year is the number worked out using the following formula:

(4) The indexation factor is to be calculated to 3 decimal places, but increased by .001 if the fourth decimal place is more than 4.
(5) Calculations under subsection (3):
(a) are to be made using only the December index numbers published in terms of the most recently published index reference period for the Consumer Price Index; and
(b) are to be made disregarding December index numbers that are published in substitution for previously published December index numbers (except where the substituted numbers are published to take account of changes in the index reference period).
(5A) For the purposes of replacing the dollar amount mentioned in subsection 74(1) for an indexation year starting on or after 1 July 2013, the indexation factor is reduced by the brought‑forward CPI indexation amount for the year, but not below 1.
(6) In this section:
brought‑forward CPI indexation amount for an indexation year starting on or after 1 July 2013 means 0.007 less any reduction made under subsection (5A) for an earlier indexation year.
December index number means the All Groups Consumer Price Index number, being the weighted average of the 8 capital cities, published by the Australian Statistician in respect of the 3 months ending on 31 December.
Part 2—Obtaining and giving information etc.
405 Power to obtain information
(1) This section applies to a person who has made a claim under section 319 for:
(a) acceptance of liability for a service injury, disease or death or for the loss of or damage to a medical aid; or
(b) compensation under this Act.
(2) The Commission may give the person a written notice:
(a) requiring the person to notify the Commission (or a specified staff member assisting the Commission) if:
(i) a specified event or change of circumstance occurs; or
(ii) the person becomes aware that such an event or change is likely to occur; or
(b) requiring that person to give the Commission (or a specified staff member assisting the Commission) a statement relating to a specified matter.
(3) The event, change of circumstances or matter:
(a) must be an event, change or matter that might affect or have affected:
(i) the acceptance of liability for the service injury, disease or death or for the loss of or damage to the medical aid; or
(ii) the payment or provision of compensation; and
(b) must be specified in either:
(i) the notice; or
(ii) any other document mentioned in the notice that is also given to the person with the notice.
(4) The notice or other document must specify the period within which the person must comply with the notice. The period must be:
(a) if paragraph (2)(a) applies—at least 14 days after the occurrence of the event or change or after the person becomes aware of the likelihood of the event or change; or
(b) if paragraph (2)(b) applies—at least 14 days after the notice is given.
(5) The notice or other document must:
(a) if paragraph (2)(a) applies—specify the manner in which the person must comply with the notice; or
(b) if paragraph (2)(b) applies—specify the form of the statement.
(6) This section does not require a person to give information to the extent that, in doing so, the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (not being a law of a Territory).
Note: A law of a State or Territory cannot prevent a person from giving information, producing documents or giving evidence for the purposes of this Act (see section 409).
(7) A person commits an offence if the person fails to comply with a notice under this section.
Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(8) An offence under subsection (7) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
(9) Subsection (7) does not apply to the extent that the person is not capable of complying with the notice.
Note: The defendant bears an evidential burden in relation to the matter in subsection (9) (see subsection 13.3(3) of the Criminal Code).
406 Commission may obtain information etc.
(1) The Commission may give a written notice to any person requiring the person, for the purposes of this Act:
(a) to provide the Commission (or a specified staff member assisting the Commission) such information as the Commission requires; or
(b) to produce to the Commission (or a specified staff member assisting the Commission) any documents in the custody or under the control of the person; or
(c) to appear before a specified staff member assisting the Commission to answer questions.
(2) To avoid doubt, the person given the notice may be a person employed:
(a) in or in connection with a Department of the Commonwealth, a State or Territory; or
(b) by any authority of the Commonwealth, a State or Territory.
(3) The notice must specify:
(a) if paragraph (1)(a) or (b) applies:
(i) the period within which the person must comply with the notice; and
(ii) the manner in which the person must comply with the notice; or
(b) if paragraph (1)(c) applies:
(i) the time at which the person must appear before the staff member; and
(ii) the place at which the person must appear before the staff member.
(4) The specified period or the specified time mentioned in subsection (3) must be at least 14 days after the notice is given.
(5) The Commission may require the information or answers provided under paragraph (1)(c) to be verified by, or given on, oath or affirmation and either orally or in writing.
(6) A staff member to whom information or answers are verified or given may administer the oath or affirmation.
(7) This section does not require a person to give information, produce a document or give evidence to the extent that, in doing so, the person would contravene a law of the Commonwealth (not being a law of a Territory).
Note: A law of a State or Territory cannot prevent a person from giving information, producing documents or giving evidence for the purposes of this Act (see section 409).
(8) This section binds the Crown in each of its capacities, but does not make the Crown liable to be prosecuted for an offence.
(9) A person commits an offence if the person fails to comply with a notice under this section.
Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(10) An offence under subsection (9) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
(11) Subsection (9) does not apply to the extent that the person is not capable of complying with the notice.
Note: The defendant bears an evidential burden in relation to the matter in subsection (11) (see subsection 13.3(3) of the Criminal Code).
407 Self‑incrimination
(1) An individual is not excused from giving information or evidence, or producing a document or a copy of a document, under section 406 on the ground that the information or evidence, or the production of the document or copy, might tend to incriminate the individual or expose the individual to a penalty.
(2) However:
(a) giving the information or evidence, or producing the document or copy; or
(b) any information, document or thing obtained as a direct or indirect consequence of giving the information or evidence, or producing the document or copy;
is not admissible in evidence against the individual in any proceedings, other than proceedings for an offence under section 137.1 or 137.2 of the Criminal Code that relates to this Act.
408 Offence for selling etc. goods provided under this Act without consent
(1) A person commits an offence if:
(a) the person is provided with goods under this Act for any purpose; and
(b) the person sells the goods or otherwise disposes of, pledges, mortgages, or deposits by way of security, the goods; and
(c) the person does so without the consent of the Commission.
Penalty: 10 penalty units.
(2) An offence under subsection (1) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
408A Manner of giving notice or other document
(1) If a provision of this Act requires or permits a notice or other document to be given to a person by:
(a) the Commission; or
(b) the Board; or
(c) the Chief of the Defence Force;
then the notice or other document must be given:
(d) in accordance with section 28A of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901; or
(e) in a manner approved in writing by:
(i) in relation to paragraph (a)—the Commission; or
(ii) in relation to paragraph (b)—the Principal Member of the Board; or
(iii) in relation to paragraph (c)—the Chief of the Defence Force.
(2) This section does not limit the Electronic Transactions Act 1999.
409 Giving information
(1) Nothing in a law of a State or of a Territory may operate to prevent a person from giving information, producing documents or giving evidence for the purposes of this Act.
(2) The Commission (or a staff member assisting the Commission) may provide any information obtained in the performance of his or her duties under this Act to a person or agency specified in this table for the purpose specified in the table:
Giving information |
Item | Person or agency | Purpose |
1 | An employee of the Defence Department | A purpose relating to litigation involving a service injury, disease or death in relation to which a claim has been made under section 319 |
2 | The Chief of the Defence Force | A purpose relating to reconsideration or review under Chapter 8 of a determination made under Chapter 2 about acceptance of liability for a service injury, disease or death |
2A | The Commonwealth Superannuation Corporation | A purpose relating to the performance of a function, or the exercise of a power, by that Corporation under: (a) an Act administered by CSC; or (b) an instrument under an Act administered by CSC |
3 | A person or agency specified in the regulations | A purpose specified in the regulations in relation to that person or agency |
(3) The person or agency must not:
(a) use the information for a purpose other than the specified purpose; or
(b) further disclose the information for a purpose other than the specified purpose.
(4) To avoid doubt, if information is disclosed or used in accordance with this section, the disclosure or use is taken, for the purposes of the Australian Privacy Principles, to be authorised by this Act.
(5) In this section:
Act administered by CSC has the meaning given by the Governance of Australian Government Superannuation Schemes Act 2011.
410 Judicial notice to be taken of certain matters
Judicial notice of signature
(1) All courts must take judicial notice of a signature that purports to be attached or appended to any official document if it is the signature of a person who:
(a) holds or has held the office of member of the Commission; or
(b) is or was a staff member assisting the Commission.
Judicial notice that person holds office
(2) If the signature of a person mentioned in subsection (1) purports to be attached or appended to any official document, all courts must take judicial notice of the fact that the person:
(a) holds or has held the office of member of the Commission; or
(b) is or was a staff member assisting the Commission.
411 Evidence
(1) A statement in writing signed by a person who:
(a) holds or has held the office of member of the Commission; or
(b) is or was a staff member assisting the Commission;
that a person is or was receiving compensation, or compensation of a particular kind, under this Act on a certain date or of a certain amount must be received in all courts as prima facie evidence that the person is or was receiving the compensation, or compensation of that kind, on the date or of the amount stated.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a document purporting to be a statement referred to in subsection (1) is, unless the contrary is established, taken to be such a statement and to have been duly given.
Statement not to be admitted unless copy given to defendant 14 days before statement to be admitted in evidence
(3) A statement must not be admitted in evidence under subsection (1) in proceedings for an offence unless the person charged with the offence or a solicitor who has appeared for the person in those proceedings has, at least 14 days before the statement is sought to be so admitted, been given a copy of the statement together with reasonable evidence of the intention to produce the statement as evidence in the proceedings.
Person giving statement may be called to give evidence
(4) Subject to subsection (5), if, under subsection (1), a statement is admitted in evidence in proceedings for an offence, the person charged with the offence may require the person giving the statement to be called as a witness for the prosecution and cross‑examined as if he or she had given evidence of the matters stated in the statement.
(5) Subsection (4) does not entitle the person charged to require the person giving a statement to be called as a witness for the prosecution unless the Court, by order, allows the person charged to require the person giving the statement to be so called.
Evidence in support of rebuttal of matters in statement to be considered on its merits
(6) Any evidence given in support, or in rebuttal, of a matter stated in a statement given under subsection (1) must be considered on its merits and the credibility and probative value of such evidence must be neither increased nor diminished by reason of this section.
412 Providing tax file numbers
Application of section
(1) This section applies to a person who is being paid compensation for incapacity for service or work under Part 3 or 4 of Chapter 4.
Commission may request person’s TFN
(2) If the person is in Australia, the Commission may request (but not compel) the person:
(a) if the person has a tax file number—to give the Commission a written statement of the person’s tax file number; or
(b) if the person does not have a tax file number:
(i) to apply to the Commissioner of Taxation for a tax file number; and
(ii) to give the Commission a written statement of the person’s tax file number after the Commissioner of Taxation has issued it.
Note: Section 413 sets out how to satisfy the request.
Certain compensation not to be paid if request not complied with
(3) The person must not be paid any compensation under Part 3 or 4 of Chapter 4 that the person is otherwise entitled to receive if the request under subsection (2) is not satisfied.
Note: Section 414 allows back pay if the request is satisfied within 3 months.
413 How to satisfy the request under section 412
(1) This section sets out how to satisfy a request under section 412 in respect of a person’s tax file number.
Compliance by giving a TFN declaration
(2) If the person is entitled to compensation for incapacity for service or work and the compensation is assessable income for the purposes of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936 or the Income Tax Assessment Act 1997, the request is complied with if the person gives the Commission a TFN (within the meaning of Part VA of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1936).
Compliance if a person has a TFN but does not know it
(3) If the person has a tax file number but the person does not know what it is, the request is complied with if:
(a) the person gives the Commission a declaration:
(i) that the person has a tax file number but does not know what it is; and
(ii) that the person has asked the Commissioner of Taxation to inform him or her of the number; and
(b) the person gives the Commission a document authorising the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Commission:
(i) whether the person has a tax file number; and
(ii) if so—the tax file number; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Commission that the person has no tax file number.
Compliance if a person has applied for a TFN
(4) If the person has applied for a tax file number, the request is complied with if:
(a) the person gives the Commission a declaration that he or she has applied for a tax file number; and
(b) the person gives the Commission a document authorising the Commissioner of Taxation to tell the Commission:
(i) if a tax file number is issued to the person—the tax file number; or
(ii) if the application is refused—that the application has been refused; or
(iii) if the application is withdrawn—that the application has been withdrawn; and
(c) the Commissioner of Taxation has not told the Commission:
(i) that the person has not applied for a tax file number; or
(ii) that an application by the person for a tax file number has been refused; or
(iii) that the application for a tax file number has been withdrawn.
Declaration to be in approved form
(5) A declaration under this section must be in a form approved by the Commission.
414 Compensation when request is not satisfied initially
Back pay for those who comply within 3 months
(1) If:
(a) a person’s compensation for incapacity for service or work under Part 3 or 4 of Chapter 4 ceases to be paid under subsection 412(3) because the request under subsection 412(2) is not satisfied by a particular day; and
(b) the request is satisfied within the period of 3 months from that day;
then the compensation that would have been paid to the person during that period if the request had been satisfied is to be paid to the person.
No back pay for those who do not comply within 3 months
(2) If the request is satisfied after that period of 3 months, the person’s compensation is to be paid from the day on which the request is satisfied.
Part 3—Recovering overpayments
Division 1—Recovery generally
415 Recovery of overpayments
(1) This section applies if:
(a) an amount of compensation is paid under this Act to a person as a result of a false or misleading statement or representation, or a failure or omission to comply with this Act; or
(b) an amount of compensation (other than an amount that the Commonwealth is entitled to recover under Division 2) that has been paid to a person under this Act should not have been paid; or
(c) a person is liable to pay an amount under this Act to the Commonwealth.
(2) However, this section does not apply in respect of a person if one or more of sections 315, 316 and 317 apply in respect of the person.
Note: Chapter 6 has its own recovery provisions (see sections 315, 316 and 317).
(3) The amount is recoverable by the Commission from the person in a court of competent jurisdiction as a debt due to the Commonwealth.
(4) The recoverable amount may be deducted from an amount that is payable to or for the benefit of the person under this Act.
Division 2—Recovery of overpayments to persons receiving a Commonwealth superannuation benefit
416 Notice to Commission of retirement of person
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person who is or was a member is receiving, or is entitled to receive, compensation under this Act; and
(b) the person retires from his or her employment; and
(c) the person was a member of a Commonwealth superannuation scheme immediately before retiring.
(2) The person must, within 14 days after the person retires from his or her employment, give a written notice to the Commission:
(a) stating that the person has retired; and
(b) specifying the date of the retirement; and
(c) identifying the Commonwealth superannuation scheme of which the person was a member immediately before his or her retirement.
Penalty: 5 penalty units.
(3) An offence under subsection (2) is an offence of strict liability.
Note: For strict liability, see section 6.1 of the Criminal Code.
417 Application of section 418
(1) Section 418 applies if:
(a) a person (the incapacitated person) ceases his or her employment; and
(b) the incapacitated person is or might be entitled to either or both a pension or a lump sum under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme; and
(c) subsection (2) applies to the incapacitated person.
(2) This subsection applies to the incapacitated person if:
(a) without limiting paragraph (b):
(i) the Commission made a determination in relation to the incapacitated person under section 89B or 126A; and
(ii) the determination has been revoked; and
(iii) the incapacitated person has begun to receive or has received a benefit under a Commonwealth superannuation scheme; or
(b) the Commission is of the opinion that it might pay, or might have paid, more compensation under Part 3, 4 or 5 of Chapter 4 to the incapacitated person than he or she is entitled to receive because of:
(i) Division 7 of Part 3 of Chapter 4 (compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received); or
(ii) Subdivision D of Division 2 of Part 4 of Chapter 4 (compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received); or
(iii) section 204 (reduction in rate of Special Rate Disability Pension).
418 Commission may give a notice to the administrator of the scheme
(1) The Commission may give a written notice to the administrator of the Commonwealth superannuation scheme (the administrator):
(a) stating that the Commission might make, or might have made, an overpayment of compensation to the incapacitated person; and
(b) requiring the administrator to tell the Commission whether:
(i) the incapacitated person has received any payment in respect of his or her entitlement mentioned in paragraph 417(1)(b); and
(ii) all the incapacitated person’s benefits under the scheme have been deferred; and
(c) if the incapacitated person has not received such payment and the incapacitated person’s benefits have not been deferred—requiring the administrator to do the things mentioned in subsection (2).
(2) The notice may require the administrator:
(a) not to pay any pension or lump sum to the incapacitated person until the administrator receives a notice from the Commission under subsection 420(2); and
(b) as soon as practicable, to give the Commission details of the following amount that is payable to the incapacitated person under the Commonwealth superannuation scheme:
(i) the amount of the pension;
(ii) the amount of the lump sum worked out as at the date of the incapacitated person’s cessation of employment;
(iii) the amount of the pension and the lump sum as so worked out;
(as the case requires).
419 Commission to give notice to incapacitated person
The Commission must give a written notice to the incapacitated person stating that it has given a notice to the administrator under section 418 and explaining how this Division works.
420 What happens if the incapacitated person has not received any Commonwealth superannuation benefit in respect of his or her cessation of employment
(1) This section applies if:
(a) the incapacitated person has not received any payment in respect of his or her entitlement mentioned in paragraph 417(1)(b); and
(b) the incapacitated person’s benefits under the scheme have not been deferred; and
(c) the Commission has received the details mentioned in paragraph 418(2)(b).
Note: Under paragraph 418(2)(b), the administrator is required to give the Commission details of either or both the amount of the pension or lump sum that is payable to the incapacitated person.
(2) The Commission must do the following within 2 working days after receiving the details:
(a) determine whether an overpayment of compensation to the incapacitated person has occurred;
(b) if it determines that no overpayment has occurred—give a written notice to the administrator stating that fact;
(c) otherwise—give a written notice to the administrator:
(i) stating the amount of the overpayment; and
(ii) requiring the administrator to pay that amount to the Commonwealth in accordance with section 421.
(3) The Commission must not reduce the rate or amount of compensation payable to the incapacitated person under this Act until it has given the notice mentioned in paragraph (2)(b) or (c) to the administrator.
(4) For the purposes of subparagraph (2)(c)(i), the amount of the overpayment is the difference between:
(a) the total amount of compensation paid under Part 3, 4 or 5 of Chapter 4 after the incapacitated person ceased his or her employment; and
(b) the total amount of compensation that should have been paid to the incapacitated person under that Part having regard to:
(ia) Division 7 of Part 3 of Chapter 4 (compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received); or
(i) Subdivision D of Division 2 of Part 4 of Chapter 4 (compensation where a Commonwealth superannuation benefit is received); or
(ii) section 204 (reduction in rate of Special Rate Disability Pension).
421 Administrator must pay the amount of overpayment to the Commonwealth
(1) If section 420 applies in respect of an incapacitated person, the administrator must pay the amount mentioned in subsection (2) to the Commonwealth out of the payments of pension or lump sum that the administrator would otherwise have made to the incapacitated person.
(2) The administrator must pay on a particular day the lesser of the following amounts:
(a) the amount of the payment of pension or lump sum (or both) that the administrator would otherwise have made to the incapacitated person on the day;
(b) the amount of the original overpayment less any amounts that the administrator has paid to the Commonwealth before that day to reduce the original overpayment.
(3) The payment of an amount by the administrator to the Commonwealth discharges, to the extent of that amount:
(a) the liability of the administrator to pay that amount to the incapacitated person; and
(b) the liability of the incapacitated person to pay that amount to the Commonwealth.
422 Compliance by the administrator
(1) The administrator must comply with a requirement made of the administrator under this Division by the Commission. However, a failure to comply with a requirement is not an offence.
(2) This section has effect despite:
(a) sections 143 and 143A of the Superannuation Act 1922; and
(b) sections 85 and 85A of the Defence Forces Retirement Benefits Act 1948; and
(c) sections 129 and 130 of the Defence Force Retirement and Death Benefits Act 1973; and
(d) sections 118 and 119 of the Superannuation Act 1976.
Part 4—Appropriation
423 Appropriation
The Consolidated Revenue Fund is appropriated for the purposes of paying the following:
(a) compensation under this Act (other than compensation under section 212 or 258, or 300 in relation to treatment provided under subsection 280A(1));
(b) costs incurred in respect of assessments, examinations, rehabilitation and finding suitable work under Parts 1 to 4 of Chapter 3 but only to the extent that the rehabilitation authority is the Commission;
(ba) payments under the scheme referred to in section 62A;
(c) treatment and other services provided under Chapter 6 (other than under subsection 280A(1) (treatment for certain injuries covered by the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988));
(caa) costs the Commission has accepted financial responsibility for as mentioned in subsection 287(2A);
(ca) travelling expenses payable under section 353 because of the application of subsections 132(5), (6), (9), (10), (11), (11A), (11B) and (11C) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986;
(d) assistance or benefits granted under section 424 that are of a similar nature to:
(i) compensation mentioned in paragraph (a); or
(ii) costs mentioned in paragraph (b); or
(iii) services mentioned in paragraph (c).
Note 1: The appropriation for compensation and other costs incurred under sections 212 and 258, and for most other costs incurred under this Act that are not mentioned in this section, is included in annual Appropriation Acts.
Note 2: The appropriation in relation to treatment provided under subsection 280A(1) is in subsection 160(2) of the Safety, Rehabilitation and Compensation (Defence‑related Claims) Act 1988.
Part 5—Special assistance
424 Special assistance
(1) The Commission may, in the circumstances and subject to the conditions (if any) prescribed in a legislative instrument made by the Commission for the purposes of this subsection, grant assistance or benefits of the kind, and the amount or value, that it considers reasonable to a person:
(a) who is a member or former member; or
(b) who is or was a dependant of a member, former member or deceased member.
(2) However, the Commission must not grant assistance or benefits in circumstances in which a person:
(a) is entitled to compensation or another benefit under this Act or the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986; or
(b) would be entitled to such compensation or benefit if a claim was made in respect of the person.
Part 5A—Clean energy payments
Division 6—Multiple entitlement exclusions
424L Multiple entitlement exclusions
(1) The Commission may by legislative instrument determine that persons in circumstances specified in the instrument are not entitled to a clean energy bonus under this Act that is specified in the instrument.
Note: For clean energy bonus see subsection 5(1).
(2) Those circumstances must relate to persons’ entitlement to or receipt of one or more of the following:
(a) another clean energy bonus under this Act;
(b) a clean energy bonus under the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986;
(c) a clean energy bonus under the Social Security Act 1991;
(d) a clean energy bonus under a scheme (however described), whether or not the scheme is provided for by or under an Act.
(3) An instrument under subsection (1) has effect according to its terms, despite any other provision of this Act.
Part 6—General
425 Assignment, set‑off or attachment of compensation
(1) An assignment of any compensation payable under this Act is void as against the Commonwealth.
Note: Some provisions of this Act allow a person to whom compensation is payable to direct that the compensation be paid to another person who provided services for the person (see, for example, section 220).
(2) Except as provided by this Act, an amount payable by a member or former member, or a dependant of a deceased member, to the Commonwealth must not be set off against the amount of any compensation payable under this Act to the member or former member or for the benefit of the dependant.
(3) Except as provided by the Maintenance Orders (Commonwealth Officers) Act 1966, the Child Support (Registration and Collection) Act 1988 or the Social Security Act 1991, or by regulations under the Family Law Act 1975, any compensation under this Act is not subject to attachment.
426 Payments to Commissioner of Taxation
(1) This section applies if the Commonwealth is given a notice under Subdivision 260‑A in Schedule 1 to the Taxation Administration Act 1953 in respect of a person who is entitled to compensation under this Act.
Note: This means that the Commonwealth is the third party referred to in section 260‑5 of that Schedule and the person who is entitled to compensation is the debtor referred to in that section.
(2) The Commonwealth must:
(a) deduct amounts from the compensation payable to or for the benefit of the person (except compensation for costs incurred by the person); and
(b) pay the amounts deducted to the Commissioner of Taxation;
in accordance with that Subdivision.
427 Jurisdiction of courts with respect to extraterritorial offences
(1) The several courts of the States are invested with federal jurisdiction, and jurisdiction is conferred on the several courts of the external Territories, with respect to external offences.
(2) The jurisdiction invested in, or conferred on, courts by subsection (1) is invested or conferred within the limits of their several jurisdictions (other than limits based on the places at which offences are committed), whether those limits are as to subject‑matter or otherwise.
(3) Jurisdiction with respect to an external offence is not conferred on a court of an external Territory unless the offence was committed in that Territory.
(4) Subject to this section, the Judiciary Act 1903 applies in relation to offences in relation to which this section applies.
(5) In this section:
external offence means an offence against this Act committed outside Australia.
428 Commission may write off a debt
(1) The Commission may decide, in writing, to write off a debt due to the Commonwealth under this Act.
Note: If the Commission writes off a debt, this means an administrative decision has been made that, in the circumstances, there is no point in trying to recover the debt. In law, however, the debt still exists and may later be pursued.
(2) The decision takes effect:
(a) on the day set out in the decision (which may be before, on or after the day the decision is made); or
(b) if no day is set out in the decision—on the day the decision is made.
429 Commission may waive a debt
(1) The Commission may decide, in writing, to waive the Commonwealth’s right to recover from a person the whole or a part of a debt due to the Commonwealth under this Act.
Note: If the Commission waives the Commonwealth’s rights to recover, this is a permanent bar to recovery of the debt—the debt effectively ceases to exist.
(2) The decision takes effect:
(a) on the day set out in the decision (which may be before, on or after the day the decision is made); or
(b) if no day is set out in the decision—on the day the decision is made.
430 Payment into bank account etc.
(1) The Commission may direct that the whole or a part of a person’s compensation is to be paid, at the intervals that the Commission specifies, to the credit of an account with:
(a) a bank; or
(b) if the person is physically outside Australia—a foreign corporation that takes money on deposit.
This subsection is subject to subsection (3A).
(3) The compensation:
(a) must not be paid into an account until the person has nominated an account; and
(b) must be paid in accordance with the Commission’s direction.
Note: For rules about nomination of accounts, see subsections (3D) to (3F).
(3AA) In specifying intervals in a direction under subsection (1), the Commission may take account of a person’s choice, notified to the Commission, to be paid energy supplement quarterly. This does not limit the Commission’s powers under that subsection.
Compensation must be paid into an account
(3A) A person’s compensation must be paid to the credit of an account with a bank, or a foreign corporation that takes money on deposit, in the circumstances specified under subsection (3C).
Note: Sections 432 and 433 deal with payments to trustees.
(3C) The Commission may, by legislative instrument, specify circumstances for the purposes of subsection (3A).
Nomination of accounts
(3D) The account referred to in subsection (1) or (3A) must be one that is:
(a) nominated, at any time by the person, for the purposes of this section; and
(b) maintained by the person (including an account maintained jointly or in common with another person).
(3E) However, if:
(a) there is no nomination of an account by the person in force for the purposes of this section; and
(b) there is a nomination of an account (the existing account) by the person in force for the purposes of subsection 122A(1) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986;
the existing account is taken to be an account nominated by the person for the purposes of this section.
(3F) Subsection (3E) ceases to apply in relation to the person if, in accordance with subsection (3D), the person nominates an account for the purposes of this section.
Definitions
(4) In this section:
account means an account, maintained by a person, to which money received on deposit by a bank, or a foreign corporation, from that person is credited.
bank includes a body corporate that is an ADI (authorised deposit‑taking institution) for the purposes of the Banking Act 1959.
430A Use and disclosure of account details
Use
(1) The Commission, a member of the Commission or a staff member assisting the Commission may use the details of an account referred to in paragraph 430(3E)(b) for the purposes of section 430.
(2) A person to whom the details of an account are disclosed under subsection 122AA(3) of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986 may use those details for the purposes of section 430 of this Act.
Disclosure
(3) The Commission, a member of the Commission or a staff member assisting the Commission may disclose the details of an account obtained for the purposes of section 430 to the Repatriation Commission, a commissioner of the Repatriation Commission or a staff member assisting the Repatriation Commission for the purposes of section 122A of the Veterans’ Entitlements Act 1986.
Interaction with Privacy Act 1988
(4) For the purposes of the Privacy Act 1988:
(a) the use of the details of an account in accordance with subsection (1) or (2) is taken to be a use that is authorised by this Act; and
(b) the disclosure of the details of an account in accordance with subsection (3) is taken to be a disclosure that is authorised by this Act.
431 Payments at person’s request
(1) A person who is entitled to weekly compensation may request, in writing, the Commission to deduct a specified amount from the compensation:
(a) to pay the Commissioner of Taxation; or
(b) for the purpose of making payments included in a class of payments approved by the Minister.
(2) If such a request is made, the Commission may deduct the amount and, if it does so, is to pay the amount deducted in accordance with the request.
(3) The Minister may, by writing, approve classes of payments for the purposes of paragraph (1)(b).
Note: The approval may be varied or revoked (see subsection 33(3) of the Acts Interpretation Act 1901).
(4) An approval, and any variation or revocation of an approval, is a legislative instrument.
432 Trustees for persons entitled to compensation
(1) This section applies if:
(a) a person who is entitled to be paid compensation under Chapter 3, 4, 5 or 6 is under a legal disability; or
(b) if such a person is under 18—there is no person who has the primary responsibility for the daily care of that person.
(2) The Commission may, in writing, appoint the Commonwealth or any other person to be the trustee of the payments of compensation under this Act.
Note: Section 433 sets out the powers of the trustee.
(3) The Commission may, in writing, revoke the appointment.
(4) If the Commission revokes the appointment:
(a) the Commission may appoint a new trustee in writing; and
(b) the trust funds vest in the new trustee.
Note: Section 433 sets out the powers of the new trustee.
(5) If the Commission revokes the appointment and does not appoint a new trustee in writing, the trust is terminated.
433 Powers of the trustee generally
(1) If a trustee is appointed under section 432 in respect of payments of compensation under this Act, the compensation is payable to the trustee.
(2) A trustee may invest those payments and interest on those payments in accordance with section 434 or 435.
(3) The trust funds may be dealt with in the following ways:
(a) the funds may be applied for the benefit of the person who is entitled to the compensation, a member of that person’s family, or a dependant of that person, as the trustee sees fit;
(b) if the trust is terminated during the life of that person—the trust funds must be transferred to that person;
(c) if that person dies before the trust is terminated—the trust funds must be paid or transferred to:
(i) the legal personal representative of the deceased person as part of the estate of the deceased person; or
(ii) if there is no legal personal representative and the Commission is satisfied that no application will be made for probate of the will or letters of administration of the estate of the deceased person—the person who the Commission determines is best entitled to them.
(4) For the purposes of paragraph (3)(a), the members of a person’s family are taken to include the following (without limitation):
(a) a partner of the person;
(b) a stepchild or an adopted child of the person, or someone of whom the person is a stepchild or an adopted child;
(c) someone who is a child of the person, or someone of whom the person is a child, because of the definition of child in this Act;
(d) anyone else who would be a relative of the person if someone mentioned in paragraph (a), (b) or (c) is taken to be a member of the person’s family.
434 Powers of Commonwealth etc. trustee to invest trust funds
(1) This section applies if a trustee appointed in respect of payments of compensation under section 432 is the Commonwealth or an employee of the Australian Public Service.
(2) A trustee may invest any trust funds not applied for the benefit of a person in any manner prescribed by the regulations.
(3) If a trustee is a trustee in respect of 2 or more persons who are entitled to compensation under this Act, then the trustee may pool those persons’ trust funds for the purposes of investing the funds.
(4) However, a trustee must not pool trust funds or invest pooled trust funds in a way that prevents the trust funds from being identified sufficiently to allow paragraph 433(3)(a) to be complied with.
(5) A trustee in respect of payments of compensation may:
(a) arrange for another person to manage the trust funds; and
(b) transfer the funds to the other person for the purposes of the arrangement.
However, making an arrangement or transferring funds does not relieve the trustee of any duties or liabilities as trustee.
(6) The Commonwealth:
(a) may charge fees (whether by way of commission or otherwise) for the services of a trustee in respect of payments of compensation in accordance with the regulations; and
(b) is entitled to reasonable expenses incurred by the trustee in rendering the services.
The fees and expenses may be paid from the trust funds.
435 Powers of investment for non‑Commonwealth trustee
(1) This section applies if a trustee appointed under section 432 in respect of payments of compensation is not the Commonwealth or an employee of the Australian Public Service.
(2) The trustee may invest any trust funds not applied under paragraph 433(3)(a) in any investments authorised for the investment of trust funds by the law of the State or Territory where the person who is entitled to the compensation resides.
436 Provisions applicable on death of person
(1) A payment of an amount of compensation in respect of a deceased person forms part of the estate of the person.
(2) However, if the Commission determines that no application will be made for probate of the will or letters of administration of the estate of the deceased person, the Commonwealth is not liable to pay the compensation.
437 Amounts of compensation
An amount of compensation payable under this Act in respect of a service injury, disease or death is in addition to any other amount of compensation paid or payable under this Act in respect of that injury, disease or death.
437A Delegation by Minister
The Minister may, by writing, delegate any of his or her functions or powers under this Act, under the regulations or under any other legislative instrument made under this Act to:
(a) a Commission member; or
(b) an SES employee, or acting SES employee, in the Department.
438 Delegation by Chief of the Defence Force
The Chief of the Defence Force may, in writing, delegate any of his or her functions or powers under a provision of this Act to:
(a) a person:
(i) who is engaged under the Public Service Act 1999 and performing duties in the Department administered by the Defence Minister or the Veterans’ Affairs Minister; and
(ii) whose duties relate to matters to which the provision relates; or
(b) a member of the Defence Force whose duties relate to matters to which the provision relates.
Part 7—Regulations
439 Regulations may modify effect of Chapter 2 and Parts 3 and 4 of Chapter 4
(1) The regulations may provide for how Chapter 2 and Parts 3 and 4 of Chapter 4 apply in respect of cadets and declared members.
(2) Without limiting the generality of subsection (1), the regulations may provide that Chapter 2 and Parts 3 and 4 of Chapter 4 apply with specified modifications.
440 Regulations
The Governor‑General may make regulations prescribing matters:
(a) required or permitted by this Act to be prescribed; or
(b) necessary or convenient to be prescribed for carrying out or giving effect to this Act.

































